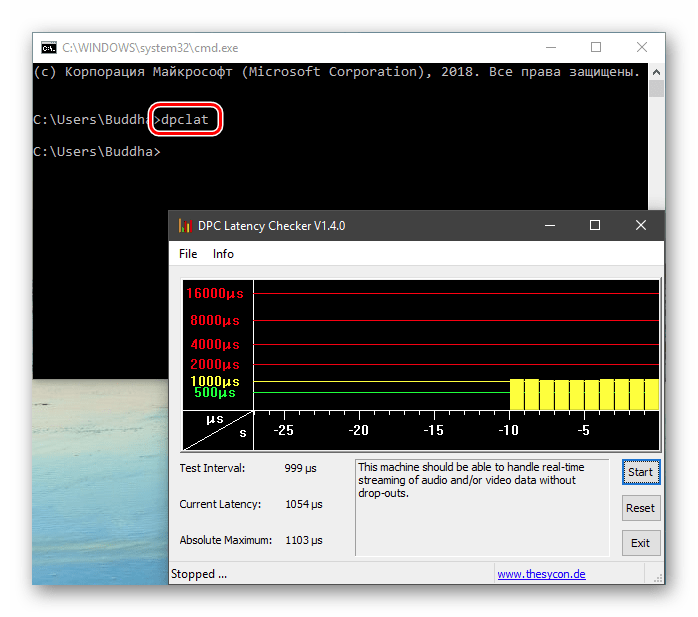
- Windows 7 — Add Path
- 6 Answers 6
- Set path from command line
- How to set path from command line?
- Add directory to system path environment variable:
- Default option is not allowed more than ‘2’ time(s)
- Изучаем переменные среды в Windows 10
- Переменные среды Windows
- Переменные PATH и PATHEXT
- Создание переменных среды
- Заключение
Windows 7 — Add Path
I need to add a new path (sumatraPDF) on my PATH variable .
I don’t know why it does not work.
I think everything is right but when I try to execute sumatrapdf.exe from CMD it cannot find the program.
This is what I did:
The path is correct, I checked it 1000 times.
The idea is use LaTeX with sublimetext and when I save a .text file sumatra has to open and show to me the result. If I want that I have to add the path of SumatraPDF. but it does not work.
6 Answers 6
I think you are editing something in the windows registry but that has no effect on the path.
the variable of interest is the PATH
also you can type on the command line:
Another method that worked for me on Windows 7 that did not require administrative privileges:
Click on the Start menu, search for «environment,» click «Edit environment variables for your account.»
In the window that opens, select «PATH» under «User variables for username» and click the «Edit. » button. Add your new path to the end of the existing Path, separated by a semi-colon ( %PATH%;C:\Python27;. ;C:\NewPath ). Click OK on all the windows, open a new CMD window, and test the new variable.
I founded the problem: Just insert the folder without the executable file.
so Instead of:
you have to write this:
In answer to the OP:
The PATH environment variable specifies which folders Windows will search in, in order to find such files as executable programs or DLLs. To make your Windows installation find your program, you specify the folder that the program resides in, NOT the program file itself!
So, if you want Windows to look for executables (or other desired files) in the folder:
because, for example, you want to install PHP manually, and choose that folder into which to install PHP, then you add the entry:
to your PATH environment variable, NOT an entry such as «C:\PHP\php.exe».
Once you’ve added the folder entry to your PATH environment variable, Windows will search that folder, and will execute ANY named executable file you specify, if that file happens to reside in that folder, just the same as with all the other existing PATH entries.
Before editing your PATH variable, though, protect yourself against foul ups in advance. Copy the existing value of the PATH variable to a Notepad file, and save it as a backup. If you make a mistake editing PATH, you can simply revert to the previous version with ease if you take this step.
Once you’ve done that, append your desired path entries to the text (again, I suggest you do this in Notepad so you can see what you’re doing — the Windows 7 text box is a pain to read if you have even slight vision impairment), then paste that text into the Windows text box, and click OK.
Your PATH environment variable is a text string, consisting of a list of folder paths, each entry separated by semicolons. An example has already been given by someone else above, such as:
Your exact version may vary depending upon your system.
So, to add «C:\PHP» to the above, you change it to read as follows:
Then you copy & paste that text into the windows dialogue box, click OK, and you should now have a new PATH variable, ready to roll. If your changes don’t take effect immediately, you can always restart the computer.
Set path from command line
Users can run an executable from windows command prompt either by giving the absolute path of the file or just by the executable file name. In the latter case, Windows searches for the executable in a list of folders which is configured in environment variables. These environment variables are as below.
1. System path
2. User path
The values of these variables can be checked in system properties( Run sysdm.cpl from Run or computer properties). Initially user specific path environment variable will be empty. Users can add paths of the directories having executables to this variable. Administrators can modify the system path environment variable also.
How to set path from command line?
In Vista, Windows 7 and Windows 8 we can set path from command line using ‘setx’ command.
For example, to add c:\dir1\dir2 to the path variable, we can run the below command.
Alternative way is to use Windows resource kit tools ‘pathman.exe‘. Using this command we can even remove a directory from path variable. See download windows resource kit tools. This works for Windows 7 also.
Add directory to system path environment variable:
Open administrator command prompt
Run the below command
Remove path from system path environment variable:
Run the below command from elevated command prompt
Setting user path environment variable
For user environment varlables, admin privileges are not required. We can run the below command to add a directory to user path environment variable.
To remove a directory from user path, you can run the below command.
Default option is not allowed more than ‘2’ time(s)
You get this error if you have not enclosed ‘path’ in double quotes. See the below example for setting the path of firefox.
Now if you move %path% to be in the double quotes
Could a context entry be created for folders, perhaps an extended one… to add to path?
what about a multi-verb option, like copy as path?
hi, when i use setx at an administrator command line, it creates a USER variable, NOT the SYSTEM variable. What am i doing wrong? How do i change the SYSTEM path at command prompt? -thx
Johny Why
Answer: Try add the parameter /M
Hi, is there a way I can add an extra variable instead on deleting the currently one and put a new Variable on the Path.
I used the command setx /M “c:\Options”, and what it does is delete the current one and then puts that one there, all I want is to add the new variable to the current one. -thx
Nuno, pathman described above does exactly that. You can download the resource tools kit and get it.
setx path “%path%;C:\yourFolder”
To set path for java & javac, can I add the paths to PATH or do I need to create the environment variable JAVA_HOME. I don’t have this defined, but windows does not seem to be able to find java binaries on my system.
You can directly add the folder to PATH. No need to define JAVA_HOME. However, adding JAVA_HOME separately avoids cluttering and helps to easily understand what is added.
hello, can someone plz explain this result? After setting path, it did not change. This was run from an Administrator command-line:
C:\Windows\system32>setx path “C:\Windows\system32;C:\Windows;C:\Windows\System32\Wbem;C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\;C:\ProgramData\chocolatey\bin;D:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft VS Code\bin”
SUCCESS: Specified value was saved.
C:\Windows\system32>path
PATH=C:\Windows\system32;C:\Windows;C:\Windows\System32\Wbem;C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\;C:\ProgramData\chocolatey\bin;D:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft VS Code\bin;D:\Program Files (x86)\metapad36;D:\Program Files (x86)\metapad36″ /M
Why won’t this work?
SET EPO = D:\Program Files (x86)\McAfee\ePolicy Orchestrator
PATH = %PATH%;%EPO%\jre\bin;%EPO%\apache2\bin
In windows 10 set path %path%; not working. it’s work like :
setx “%path%;C:\Program Files\CodeBlocks\MinGW\bin”
By unfortunately I deleted my system default path. How could I able to find my system path?
Unfortunately I deleted several files with unremembered path names. This article was useful
The following used to work for me when I am in MSDOS environment. Lately I get error messages such as INCLUDE not found. Why is this so?
Used to work
SET PLL =c:\CL5\PLL
SET PLT =c:\CL5\PLL
SET INCLUDE =c:\CL5\INCLUDE
SET PRG =c:\IMS\PRG
SET LIB =c:\CL5\LIB
SET OBJ =c:\CL5\OBJ
PATH =c:\IMS\EXE;\CL5\BIN;\CL5\NG;\CL5\PLL
pathman is one of many tools of the Windows Server 2003 Resource Kit Tools
Note: The Windows Server 2003 Resource Kit Tools are not supported on 64-bit platforms.
Huh.
When I did that on Windows 10 v1903, using setx, it replaced the USER scope paths with the SYSTEM scope paths.
Now I’m not sure what was in the old user path.
So, uh… Be careful out there.
And if anyone has a solution how to avoid that, please let me know
Thanks
Изучаем переменные среды в Windows 10
Переменные среды Windows
Получить информацию о существующих переменных можно в свойствах системы. Для этого кликаем по ярлыку Компьютера на рабочем столе правой кнопкой мыши и выбираем соответствующий пункт.
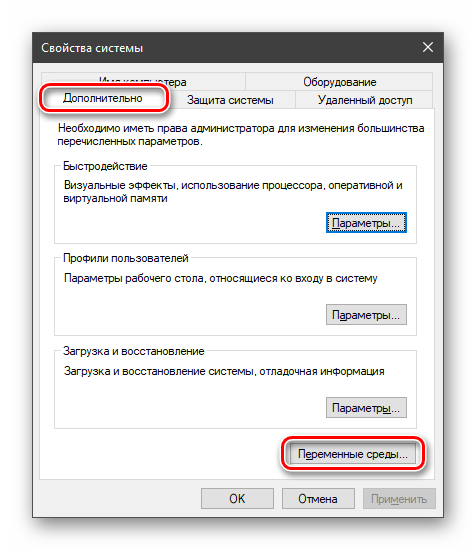
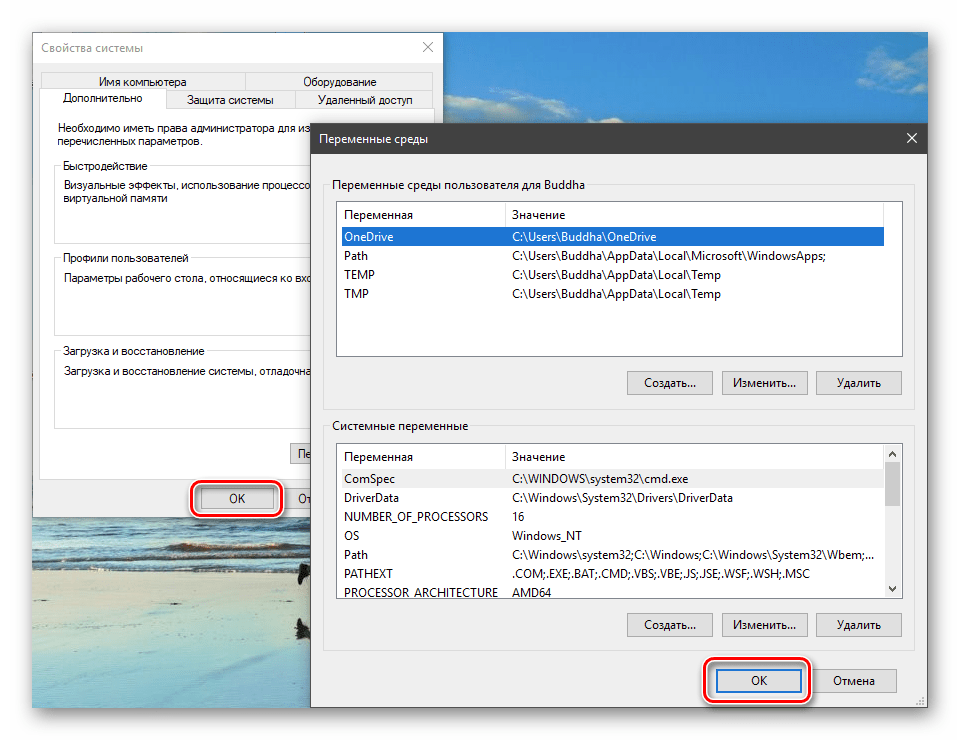
Переходим в «Дополнительные параметры».
В открывшемся окне с вкладкой «Дополнительно» нажимаем кнопку, указанную на скриншоте ниже.
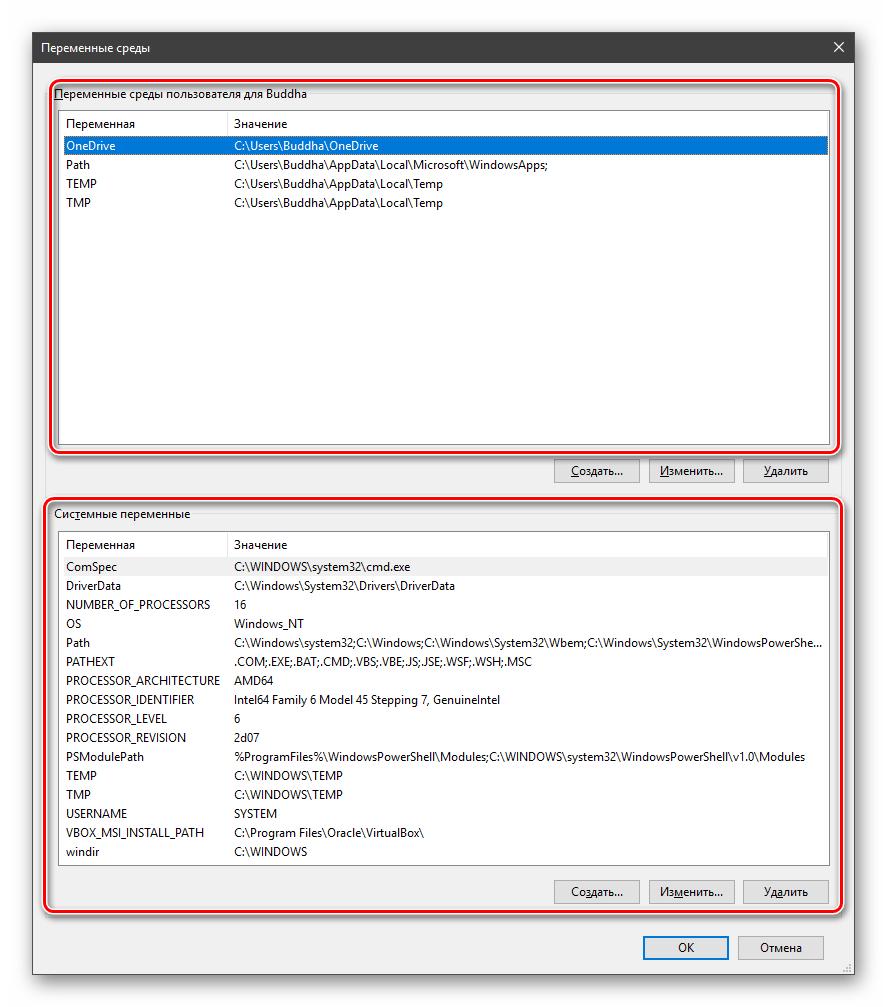
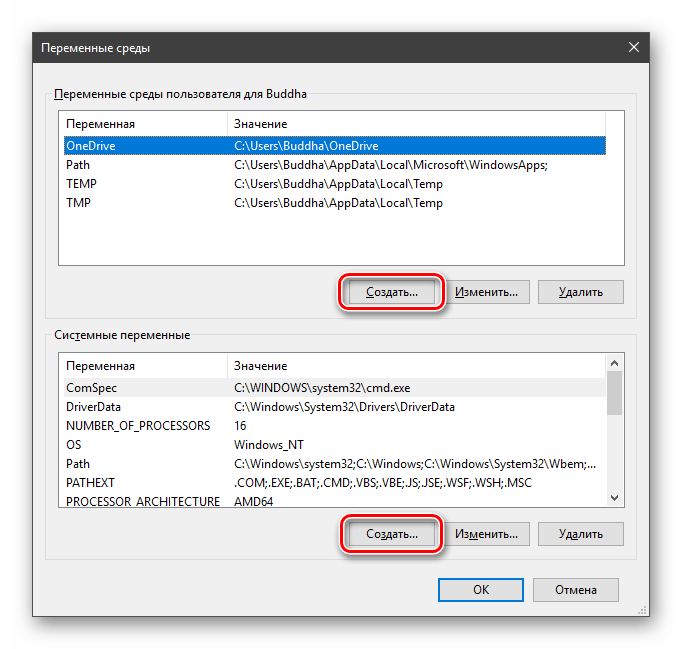
Здесь мы видим два блока. Первый содержит пользовательские переменные, а второй системные.
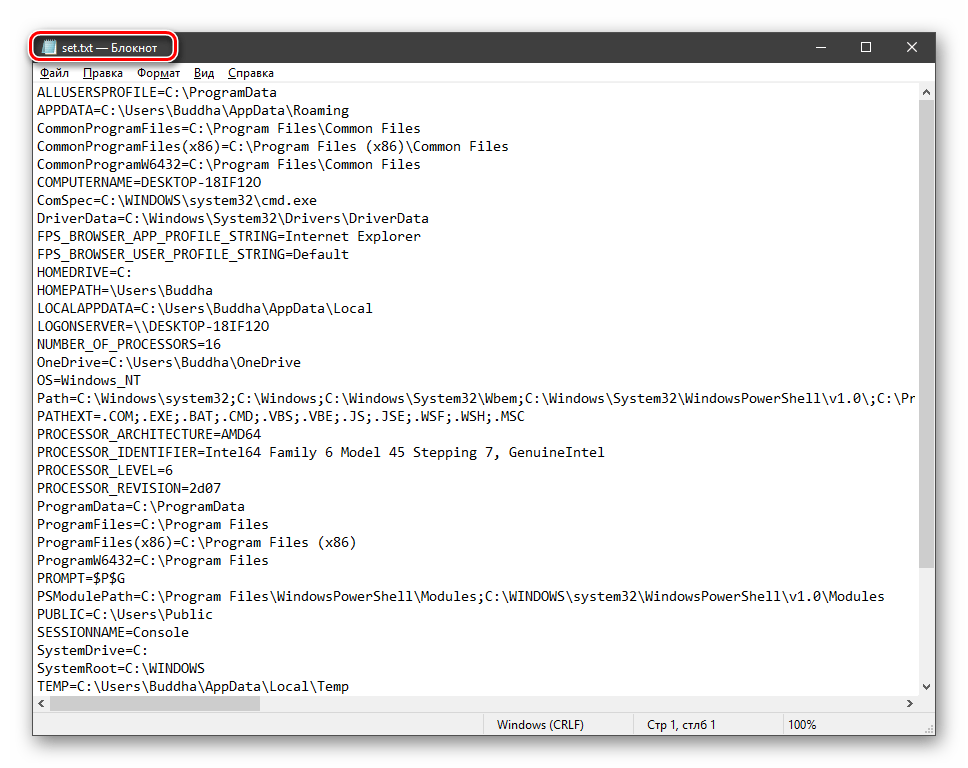
Если требуется просмотреть весь перечень, запускаем «Командную строку» от имени администратора и выполняем команду (вводим и нажимаем ENTER).
На рабочем столе появится файл с названием «set.txt», в котором будут указаны все переменные окружения, имеющиеся в системе.
Все их можно использовать в консоли или скриптах для запуска программ или поиска объектов, заключив имя в знаки процента. Например, в команде выше вместо пути
Примечание: регистр при написании переменных не важен. Path=path=PATH
Переменные PATH и PATHEXT
Если с обычными переменными все понятно (одна ссылка – одно значение), то эти две стоят особняком. При детальном рассмотрении видно, что они ссылаются сразу на несколько объектов. Давайте разберемся, как это работает.
«PATH» позволяет запускать исполняемые файлы и скрипты, «лежащие» в определенных каталогах, без указания их точного местоположения. Например, если ввести в «Командную строку»
система осуществит поиск по папкам, указанным в значении переменной, найдет и запустит соответствующую программу. Этим можно воспользоваться в своих целях двумя способами:
- Поместить необходимый файл в одну из указанных директорий. Полный список можно получить, выделив переменную и нажав «Изменить».
Создать свою папку в любом месте и прописать путь к ней. Для этого (после создания директории на диске) жмем «Создать», вводим адрес и ОК.
%SYSTEMROOT% определяет путь до папки «Windows» независимо от буквы диска.
Затем нажимаем ОК в окнах «Переменные среды» и «Свойства системы».
Для применения настроек, возможно, придется перезапустить «Проводник». Сделать это быстро можно так:
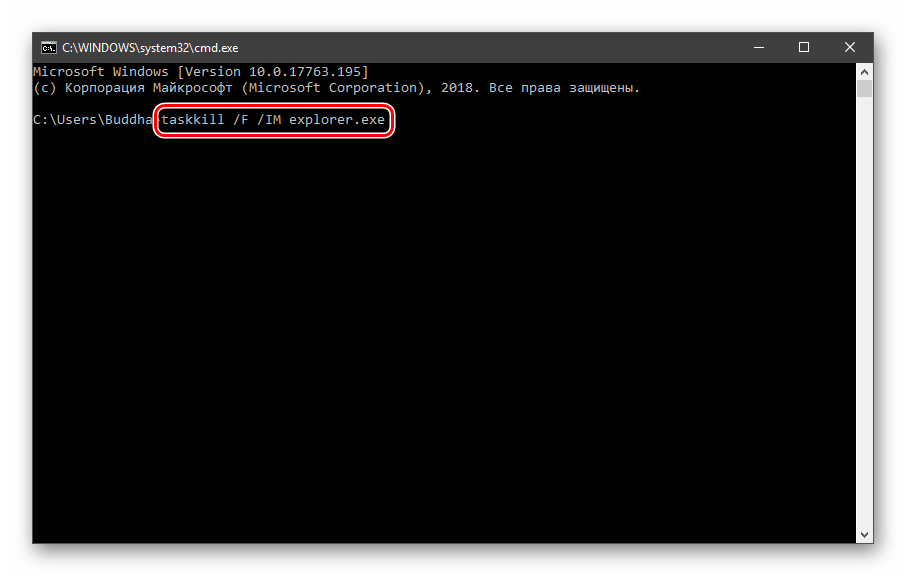
Открываем «Командную строку» и пишем команду
taskkill /F /IM explorer.exe
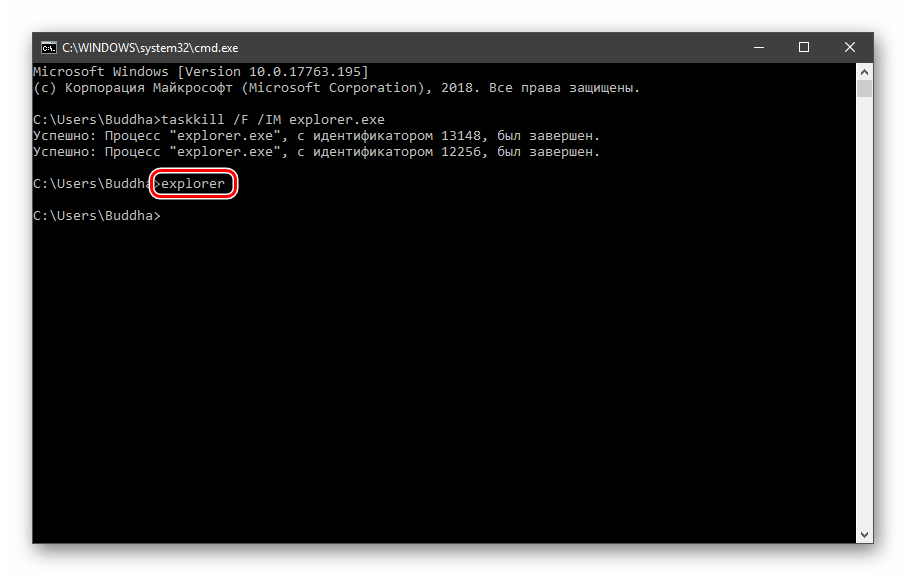
Все папки и «Панель задач» исчезнут. Далее снова запускаем «Проводник».
Еще один момент: если вы работали с «Командной строкой», ее также следует перезапустить, то есть консоль не будет «знать», что настройки изменились. Это же касается и фреймворков, в которых вы отлаживаете свой код. Также можно перезагрузить компьютер или выйти и снова зайти в систему.
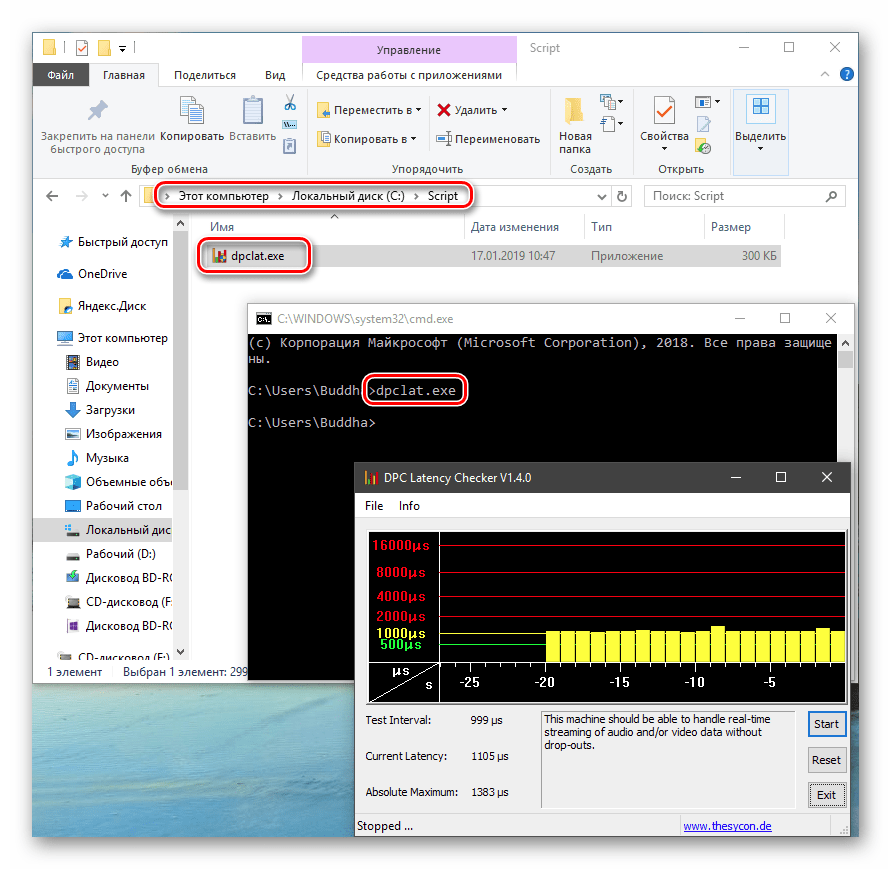
Теперь все файлы, помещенные в «C:\Script» можно будет открывать (запускать), введя только их название.
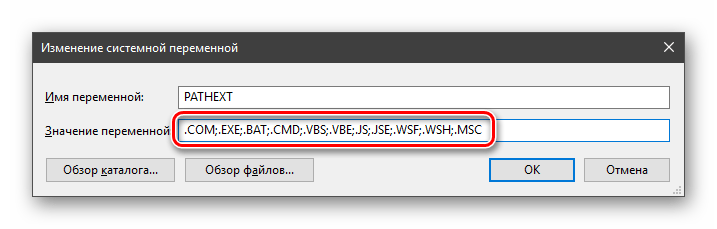
«PATHEXT», в свою очередь, дает возможность не указывать даже расширение файла, если оно прописано в ее значениях.
Принцип работы следующий: система перебирает расширения по очереди, пока не будет найден соответствующий объект, причем делает это в директориях, указанных в «PATH».
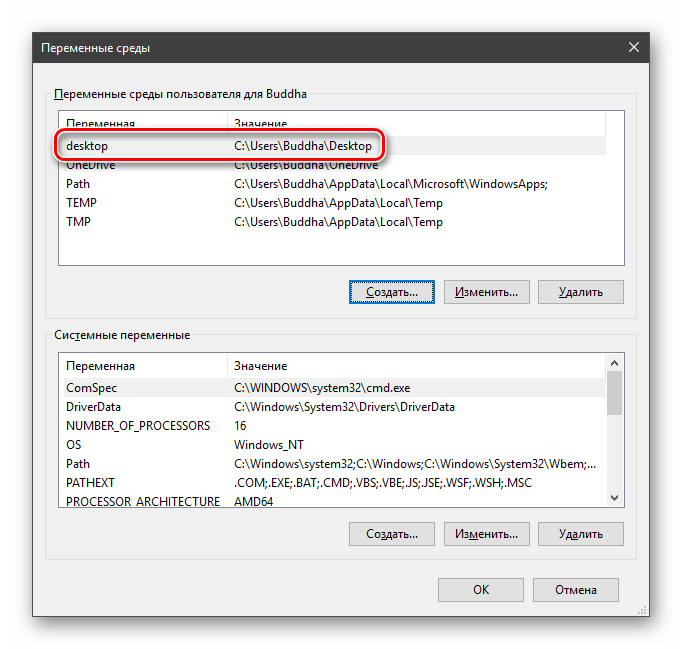
Создание переменных среды
Создаются переменные просто:
- Нажимаем кнопку «Создать». Сделать это можно как в пользовательском разделе, так и в системном.
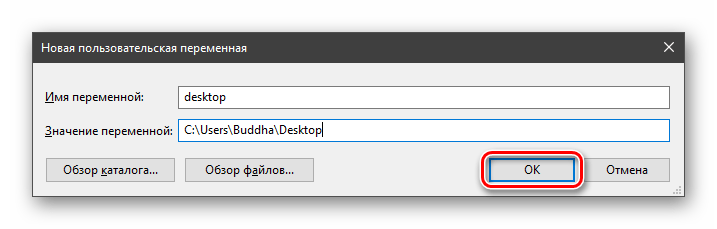
Вводим имя, например, «desktop». Обратите внимание на то, чтобы такое название еще не было использовано (просмотрите списки).
В поле «Значение» указываем путь до папки «Рабочий стол».
Нажимаем ОК. Повторяем это действие во всех открытых окнах (см. выше).
Для примера переделаем команду, которую мы использовали для получения списка (самая первая в статье). Теперь нам вместо
потребуется ввести только
Заключение
Использование переменных окружения позволяет значительно сэкономить время при написании скриптов или взаимодействии с системной консолью. Еще одним плюсом является оптимизация создаваемого кода. Имейте в виду, что созданные вами переменные отсутствуют на других компьютерах, и сценарии (скрипты, приложения) с их использованием работать не будут, поэтому перед тем, как передавать файлы другому пользователю, необходимо уведомить его об этом и предложить создать соответствующий элемент в своей системе.