- How to create a user account on Ubuntu Linux
- Steps to create a user account on Ubuntu Linux
- Ubuntu create user account commands
- Verification
- How do I log in using ssh?
- Creating a user account using useradd command on Ubuntu
- How to delete a user account
- How to change Linux user password
- Conclusion
- How To Linux Set or Change User Password
- Linux Set User Password
- Linux change password for other user account
- Linux Change Group Password
- Changing user passwords on Linux
- Forcing Linux user to change password at their next login
- Locking and Unlocking user password of the named account
- A note about setting up a secure Linux password
- Conclusion
- Создание пользователя в Linux. Команды adduser и useradd
- В чем отличия adduser и useradd?
- Команда adduser
- Создание пользователя командой adduser
- Команда useradd
- Синтаксис команды useradd
- Создание нового пользователя
- Создание нового пользователя с домашней директорией в /home
- Создание нового пользователя с произвольной домашней директорией
- Создание нового пользователя с произвольными UID, GID
- Создание пользователя с указанием оболочки (shell)
- Создать пользователя и добавить его в группы
- Заключение
- Linux Shell script to add a user with a password to the system
- Linux shell script to add a user with a password
- Step 1 – Create an encrypted password
- Step 2 – Shell script to add a user and password on Linux
- Step 3 – Change existing Linux user’s password in one CLI
- Step 4 – Create Users and change passwords with passwd on a CentOS/RHEL
- Conclusion
How to create a user account on Ubuntu Linux
Steps to create a user account on Ubuntu Linux
- Open the terminal application
- Log in to remote box by running the ssh user@your-ubuntu-box-ip
- To add a new user in Ubuntu run sudo adduser userNameHere
- Enter password and other needed info to create a user account on Ubuntu server
- New username would be added to /etc/passwd file, and encrypted password stored in the /etc/shadow file
Let us see all commands in details and
Ubuntu create user account commands
Let us say you need to add a new user in Ubuntu called vivek, type the following command in your shell:
$ sudo adduser vivek
Type your own password and other info:
Verification
Use the grep command or cat command as follows:
$ cat /etc/passwd
$ grep ‘^vivek’ /etc/passwd
Sample outputs:
How do I log in using ssh?
From your Windows (WSL) or macOS or Linux desktop, run:
$ ssh vivek@your-aws-ubuntu-server-ip
OR
$ ssh -i
/.ssh/aws.pub.key vivek@your-aws-ubuntu-server-ip
Enter the password when prompted.
Creating a user account using useradd command on Ubuntu
Alternatively, you can use the useradd command is a low level utility for adding users on Ubuntu. The syntax is:
$ sudo useradd -s /path/to/shell -d /home/
$ sudo passwd
Let us create a new user named vivek using the useradd command on Ubuntu:
$ sudo useradd -s /bin/bash -d /home/vivek/ -m -G sudo vivek
$ sudo passwd vivek
Where,
- -s /bin/bash – Set /bin/bash as login shell of the new account
- -d /home/vivek/ – Set /home/vivek/ as home directory of the new Ubuntu account
- -m – Create the user’s home directory
- -G sudo – Make sure vivek user can sudo i.e. give admin access to the new account
I strongly recommend installing ssh keys while creating the new user account. You must have RSA/ed25519 key pair on your local desktop/laptop . Use the cat command to view your current RSA/ed25519 public key on the desktop:
$ cat
View public ssh key on your macos/unix/linux desktop
How to delete a user account
Use the userdel command as follows:
sudo userdel
sudo userdel vivek
To remove home directory and mail spool too, enter:
sudo userdel -r
sudo userdel -r jerry
How to change Linux user password
Run the following passwd command:
sudo passwd
sudo passwd tom
To change your own password, enter:
passwd
First, the user is prompted for their current password. If the current password is correctly typed, a new password is requested. The new password must be entered twice to avoid password mismatch errors.
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Conclusion
In this quick tutorial, you learned how to add users in Ubuntu Linux using the CLI. The same commands works for any Debian/Ubuntu based distribution too. See useradd man page using the man command or read it online here:
man 8 useradd
man 8 passwd
man 8 adduser
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
How To Linux Set or Change User Password
Linux Set User Password
Type following passwd command to change your own password:
$ passwd
Sample Outputs:
The user is first prompted for his/her old password if one is present. This password is then encrypted and compared against the stored password. The user has only one chance to enter the correct password. The super user is permitted to bypass this step so that forgotten passwords may be changed. A new password is tested for complexity. As a general guideline, passwords should consist of 10 to 20 characters including one or more from each of following sets:
- Lower case alphabetics
- Upper case alphabetics
- Digits 0 thru 9
- Punctuation marks/spacial characters
Linux change password for other user account
You need to login as the root user, type the following command to change password for user vivek:
# passwd vivek
OR
$ sudo passwd vivek
Sample putput:
- vivek – is username or account name.
Passwords do not display to the screen when you enter them. For example:
Linux changing user password using passwd
Linux Change Group Password
When the -g option is used, the password for the named group is changed. In this example, change password for group sales:
# passwd -g sales
The current group password is not prompted for. The -r option is used with the -g option to remove the current password from the named group. This allows group access to all members. The -R option is used with the -g option to restrict the named group for all users.
Changing user passwords on Linux
As a Linux system administrator (sysadmin) you can change password for any users on your server. To change a password on behalf of a user:
- First sign on or “su” or “sudo” to the “root” account on Linux, run: sudo -i
- Then type, passwd tom to change a password for tom user
- The system will prompt you to enter a password twice
To change or set a new root (superuser) password type:
$ sudo passwd
Forcing Linux user to change password at their next login
By default, Linux passwords never expire for users. However, we can force users to change their password the next time they log in via GUI or CLI methods. The syntax is straightforward:
$ sudo passwd -e
$ sudo passwd —expire
Let us immediately expire an account’s password:
$ sudo passwd -e marlena
The system will confirm it:
When user try to login via ssh command, they will see the following on screen:
Locking and Unlocking user password of the named account
Note that the following local command does not disable the account. The user may still be able to login using another authentication token, such as an SSH key. To disable the account, administrators should use either usermod —expiredate 1
We can lock the password as follows:
$ sudo passwd -l
This option disables a password by changing it to a value which matches no possible encrypted value (it adds a ! at the beginning of the password in the /etc/shadow file. Want to unlock the password, try:
$ sudo passwd -u
The above command option re-enables a password by changing the password back to its previous value. In other words, to the value before using the -l option.
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
A note about setting up a secure Linux password
Compromises in password security typically result from careless password selection. Avoid common password such as:
- Words which appears in a dictionary
- Your first and last name
- Pet names
- Kids or spouses names
- License number
- Date of birth (DoB)
- Home or office address
I strongly recommend that you generate a unique password for all user accounts using your chosen password manager.
Conclusion
The passwd command line utility is used to update or change user’s password. The encrypted password is stored in /etc/shadow file and account information is in /etc/passwd file. To see all user account try grep command or cat command as follows:
$ cat /etc/passwd
$ grep ‘^userNameHere’ /etc/passwd
$ grep ‘^tom’ /etc/passwd
The guidance given in this quick tutorial should work with any Linux distribution, including Alpine, Arch, Ubuntu, Debian, RHEL, Fedora, Oracle CentOS, SUSE/OpenSUSE and other popular Linux distros.
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
Создание пользователя в Linux. Команды adduser и useradd
Для создания пользователей в Linux можно использовать графические утилиты, предоставляемые дистрибутивом, или воспользоваться командной строкой.
Для создания пользователей из командной строки обычно используют утилиты adduser или useradd. Рассмотрим, использование данных утилит.
В чем отличия adduser и useradd?
useradd — это низкоуровневая утилита для создания пользователей в Linux.
adduser — представляет собой более простое решение для создания пользователей и по факту является надстройкой над useradd, groupadd и usermod.
Утилита adduser доступна не во всех дистрибутивах Linux. Реализация adduser также может отличаться. Если в дистрибутиве присутствует утилита adduser, то для создания пользователей рекомендуется использовать именно ее.
Команда adduser
Создание пользователя командой adduser
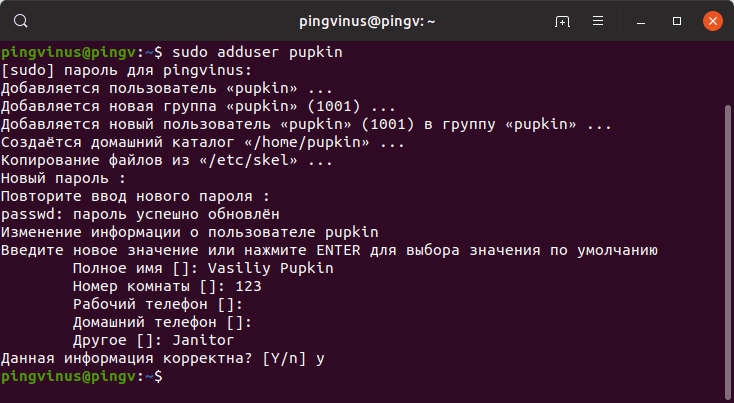
Рассмотрим, как создать обычного пользователя командой adduser
Чтобы создать нового пользователя, выполняем команду adduser и указываем имя пользователя (вместо pupkin укажите имя пользователя, которого вы создаете):
После запуска данной команды, вы должны ввести пароль для нового пользователя. Затем будет предложено ввести дополнительную информацию о пользователе: имя, номер комнаты (кабинета), телефоны и комментарий. Вводить эту информацию необязательно. Просто нажимайте Enter , чтобы пропустить ввод данных.
В результате выполнения команды adduser будут выполнены следующие действия:
- Создается новый пользователь с именем, которое вы указали при выполнении команды.
- Создается группа с тем же именем.
- Создается домашний каталог пользователя в директории /home/имяпользователя
- В домашний каталог копируются файлы из директории /etc/skel
В данной директории хранятся файлы, которые копируются в домашний каталог всех новых пользователей.
Команда useradd
Синтаксис команды useradd
Команда useradd принимает в качестве аргумента имя пользователя, а также различные опции.
Синтаксис команды следующий:
Создание нового пользователя
Чтобы просто создать пользователя используется команда useradd без каких-либо опций. Указывается только имя пользователя.
Данная команда создает нового пользователя с системными параметрами по умолчанию, которые прописаны в файле /etc/default/useradd
Чтобы пользователь мог войти в систему, необходимо задать для него пароль. Для этого используем команду:
Создание нового пользователя с домашней директорией в /home
Создадим пользователя и его домашнюю директорию.
Домашняя директория создается по умолчанию в каталоге /home . Имя директории совпадает с именем пользователя.
Создание нового пользователя с произвольной домашней директорией
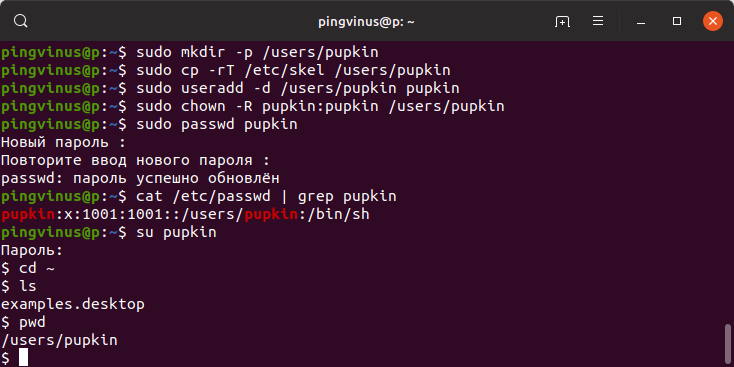
Чтобы создать пользователя с домашней директорией, расположенной в произвольном месте, используется опция -d , после которой указывается путь до директории. Директорию необходимо создать заранее.
Создаем домашнюю директорию для будущего пользователя:
Копируем файлы и директории, которые по умолчанию создаются в домашней директории пользователя в данной системе. Данные файлы находятся в директории /etc/skel
Создаем пользователя и указываем домашнюю директорию:
Меняем права доступа у домашней директории:
Задаем пароль для пользователя:
Можно просмотреть информацию о пользователе, которая сохранена в файле /etc/passwd
Создание нового пользователя с произвольными UID, GID
Каждый пользователь в Linux имеет свой числовой идентификатор — UID, а также идентификатор основной группы пользователя — GID.
При создании пользователя можно задать произвольные номера UID и/или GID. При указании номера группы, группа с этим номером должна быть создана заранее.
Создание пользователя с указанием оболочки (shell)
По умолчанию новые пользователи создаются с оболочкой /bin/sh Чтобы задать другую оболочку, используется опция -s /путь/до/оболочки
Создать пользователя и добавить его в группы
Обычно пользователи в Linux принадлежат нескольким группам. Чтобы при создании нового пользователя задать группы, к которым он будет принадлежать, используется опция -G список,групп
Заключение
Мы рассмотрели примеры создания нового пользователя в Linux с использованием команд adduser и useradd . Команда adduser более простая и в большинстве случаев рекомендуется использовать именно ее.
Источник
Linux Shell script to add a user with a password to the system
A re you wondering how to add a user with a password using a shell script under Linux? Let us see how to add a new user and set/change a password including chaning the existing Linux user’s password in a Linux shell script.
You can quickly write a shell script that reads username, password from the keyboard, and add a username to the /etc/passwd and store encrypted password in /etc/shadow file using useradd command. The useradd command/adduser command used to create a new user on Linux and passwd command to set or change password for users. This page shows how to add a user account AND password with a bash shell script running on Linux operating systems.
Linux shell script to add a user with a password
The syntax is as follows:
useradd -m -p EncryptedPasswordHere username
Where,
- -m : The user’s home directory will be created if it does not exist.
- -p EncryptedPasswordHere : The encrypted password, as returned by crypt().
- username : Add this user to the Linux system,
Step 1 – Create an encrypted password
You need to create an encrypted password using Perl crypt() as follows:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Please note that crypt() is a one-way hash function. The PLAINTEXT ($plain) and SALT are turned into a short string, called a digest, which is returned. The same PLAINTEXT and SALT will always return the same string, but there is no (known) way to get the original PLAINTEXT from the hash. Small changes in the PLAINTEXT or SALT will result in large changes in the digest. Let us try out perl example:
perl -e ‘print crypt(«2IL@ove19Pizza4_», «salt»),»\n»‘
Sample outputs:
The Perl command will display the encrypted password (sa.KT9zrGYeg2) on screen. The Perl crypt() function is a one way encryption method meaning, once a password has been encrypted, it cannot be decrypted. The password string is taken from the user and encrypted with the salt and displayed back on computer screen. We can store an encrypted password using the following syntax:
Warning : You must understand other users and system processes can view passwords processed using the CLI tools, and it is a security risk when you store passwords in a plain text format. Linux can hide processes from other users and ps command using this guide to limit some damage. I would recommend using Ansible Vault to storing passwords as well as changing them in bulk.
Step 2 – Shell script to add a user and password on Linux
Based upon above discussion here is a sample shell script (Download link):
Close and save the script file. Next set permissions using the chmod command:
chmod +x add-user-script.sh
Run it as following
$ ./add-user-script.sh
Only root may add a user to the system.
$ sudo ./add-user-script.sh
Or run it as root user:
# ./adduser
Sample outputs:
Now user roja can login with a password called HIDDEN. Here is sample session outputs:
Step 3 – Change existing Linux user’s password in one CLI
We are going use the chpasswd command that reads a list of user names and password pairs from the keyboard and uses this information to update a group of existing users. The syntax is as follows:
echo «user_name:password» | chpasswd
However, the passwords must be provided in clear-text format, and are encrypted by the chpasswd command. For example, set or change user password, run:
# echo ‘vivek:@iLovePizzaEvery1day’ | chpasswd
Verify that password has been changed using the chage command:
# chage -l vivek
We can use the grep command/egrep command to search for usernames:
grep «^username» /etc/passwd
grep «^tom» /etc/passwd
If the chpasswd command not installed, use your systems package manager tool such as apt command/apt-get command/dnf command/yum command to install the same.
Step 4 – Create Users and change passwords with passwd on a CentOS/RHEL
The passwd command on CentOS/RHEL/Fedora and co comes with a special command-line option to change the password using a shell pipe as follows:
# echo «YourPassword» | passwd —stdin UserName
# echo «I4Love2Ubu@ntuLinux_» | passwd —stdin vivek
Outputs from sample session:
So the —stdin option is used to indicate that passwd command should read the new password from standard input such as keyboard, which can be a pipe and must be run by root user.
Conclusion
You learned various methods to add a new user and set a password using a shell script. See the following for more info:
| Category | List of Unix and Linux commands |
|---|---|
| Documentation | help • mandb • man • pinfo |
| Disk space analyzers | df • duf • ncdu • pydf |
| File Management | cat • cp • less • mkdir • more • tree |
| Firewall | Alpine Awall • CentOS 8 • OpenSUSE • RHEL 8 • Ubuntu 16.04 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Linux Desktop Apps | Skype • Spotify • VLC 3 |
| Modern utilities | bat • exa |
| Network Utilities | NetHogs • dig • host • ip • nmap |
| OpenVPN | CentOS 7 • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Debian 8/9 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Package Manager | apk • apt |
| Processes Management | bg • chroot • cron • disown • fg • glances • gtop • jobs • killall • kill • pidof • pstree • pwdx • time • vtop |
| Searching | ag • grep • whereis • which |
| Shell builtins | compgen • echo • printf |
| Text processing | cut • rev |
| User Information | groups • id • lastcomm • last • lid/libuser-lid • logname • members • users • whoami • who • w |
| WireGuard VPN | Alpine • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Firewall • Ubuntu 20.04 |
Comments on this entry are closed.
I just want to send one script which I have made for changing password of any user from remote machine.
Here I have created one file called “host” which contents host ips.
Shell script code
python code – file [for crypt()]
Hope this will help somebody. 🙂
Cheers!
Appreciate your post.
Hey forgot one thing….there is one more file called “file”, and contents of these files are –
import crypt; import sys; print crypt.crypt(sys.argv[1],”salt”);
Yes, i thought so… there is line about python… thanks
I always wondered if there was a bash /CLI command to list the users, is there?
I see here
egrep “^$username†/etc/passwd >/dev/null
so there is not?
egrep -v ^xyz /etc/passwd | cut -d”:” -f1
Add this line in a script which displays all the users in your machine
i have used ^xyz , Starting with that. genarally user names will never start with that , so we get the desired result as output becouse of the option -v .
OR
As a root
vim usershow
1 #!/bin/bash
2 #this script displays the users in machine.
3 egrep -v ^xyz /etc/passwd | cut -d”:” -f1 |less
esc:wq
cp usershow /usr/local/sbin/
chmod -R +x /usr/local/sbin
Thats it…Enjoymaadi
usershow
Remove ‘>/dev/null‘ and you should see username if exists in /etc/passwd. To display list just type:
cut -d: -f1 /etc/passwd
its great but it is more powerful if you include the functionality to add lage number of users at once
like in my uni more then 15000 stuent it is almoste inpossible to create their acccounts one by one
How I need edit the script to add the user in particular group and disable them by accessing telnet.
useradd -d /home/example1 -s /bin/false -g popusers example1
># Allotment Says:
>March 23rd, 2007 (4 weeks ago) at 1:00 pm
>I always wondered if there was a bash /CLI command >to list the users, is there?
>I see here
>egrep “^$username†/etc/passwd >/dev/null
>so there is not?
You can use gawk to list users
gawk -F: ‘< if ( $3>500 ) print $1 >’/etc/passwd
Could you kindly help me to integrate in this first script to add a user in /etc/shadow from a comma separeted file?
I would like to export a list from a company application, create a .csv , and lunch it from a shell script or a php page in a website to import users in 1 step.
The important is that the password used to access sistem by users is the one I can read in clear characters in the csv file.
Let me know please, and put my address in copy fabio@conecta.it
egrep “^$username†/etc/passwd
don’t u people think that this will not match string
perfectly means if there is user like bhushan and i want to create user bhush…then it will give msg that user already exists…
Sure you can use word based matching:
hi vivek,
how to add user without using useradd command?
With all information such as uid(by incrementing existing highest one), gid,…….etc.
I need a shell script that will create a password for users already on the system. How can I do that?
Another way to get encrypted password is command:
openssl passwd yourpass
PASSWORD checking is limited to 8 characters long.
I tried the Script above (adduser.sh), and the password checking is some how up-to 8 characters only. Meaning as long as you have the first 8 characters correct you can login to the system (I tested using su command)
The part I changed on the script is to set username and password as a variable:
it will allow secr3t12333333333 or secr3t12
I found the same thing. 8 characters and it ignores the rest.
How do you make it store more than 8 characters?
How can you also get this script to add a samba password at the same time it creates a unix password?
Useful article, I was was looking to add users with a one liner so this helped .. since Debian lacks the crypt command, I didn’t even think to use perl ..
Since I maintain the web server we use, exclusively .. I know all of my accounts have home directories, so I simply do my test to see if a user exists in perl .. but the same could be done in a shell script
hi,
i compile this program but when i move to the second part I cant execute it in root . I got a error.
No such file or directory
why is that .
pls reply me….
how about this one liner script
# useradd -m -p `perl -e ‘print crypt(«your_password», «salt»),»n»‘` your_username
hi
how to create new user to assign perssion to particular shell and set userid and groupid make this one line command
I like to add bulk of user using bash scripting taking the user name from a text file from a given location and also want to set a sample passwd for the all user who have been created. and also the script has to mail to the corresponding user regarding the username and passwd . Can anyone help me out
Thanks in advance
Sample shell script to add a user
How do I change this to add the users full name ans login shell
Hi Vivek(nixcraft)
Your mentioned shell script giving me an error message while executing it
“line 19: syntex error: unexpected end of the file”
Please check and where it is get stuck..
Thanks
Charanjit Singh
Can someone let me know, How to write script for password expiry notification in solaries.
Hello Everyone,
My self Ravi and I am trying to make one PHP page, from which i can able to create
new user in linux. where in php code will show three boxes
1.) New User Name:
2.) Password:
3.) Botton: Add now
with this php code i want to add new user in linux through web interface.
Kindly please help me out to do that so.
i need to help me. i want to good 100% user email, password and forget password.
frisrt sign user email then get get password number in then open in base.
if forget password then send email get password
Can anyone help me thank harold
simple: echo PASSWORD | passwd USER –stdin
It was very useful your sample,
Hey I need a scrip to add 100 users to UNIX server using an Input file which has two input one full name the other username . But i need to generate password in the script which gets incremented with each added user ….
Thanks a lot in advance ….
Very good script.
hi guys
can any one tell me how to write a script such that the script reads the password and enters to tat user
i just want to know the script
Write a shell script that can be used to:
Detailed requirements
1. The script can only be executed by the root user, administrator or users with administrative rights.
2. If the root user starts the program as specified, it should read the input file and check the new users’ information one by one. If a new user’s information is valid, it should create the account for the user and write the account information to a report file. The report file should have the following format:
account_name;user_id;group_name;group_id;created_date;user_fullname
3. If a new user’s information is not valid, it should not create the account for the user. The error should be written to an error report file. You need to specify the file format.
4. If the root user executes the script incorrectly, e.g., without the necessary parameters or with incorrect parameters, it should provide an appropriate help message to the user. For example, it could show the correct usage of the command.
5. If the root user executes the command with the –h switch, the program should give detailed information about the program and the file structure of the input file.
6. The input file should have the following structure:
• Each line is a user record.
• Each record has four fields separated by commas (,) as follows:
Username,password,groupname,fullname
Note: The password field must be between 9 and 12 characters long. The field for the user’s full name may contain blank spaces. You must specify the features of the other fields. If a group does not exist, the program should create a default group automatically.
pass=$(perl -e ‘print crypt($ARGV[0], «password»)’ $password)
in this block what does $ARGV[0] stores and how it will work
we really appreciate your useful code
The student should write a bash program named myuseradd that accepts a list of users as argument
Script syntax: myuseradd [ [ ..]]
At least one argument must be provided and must not exceed 10 alphanumeric characters.
The script must not use the usedadd or similar commands. It must:
1- Check if user is root. If not the script cannot be run and it exits.
2- Check the number of arguments. If none the script exits.
3- Check if is already used, if yes the script exits.
4- Ask the user to provide the following data:
a. Home directory:
Default is /home/
The script accepts either /home/ or /. must
not exceed 10 alphanumeric characters and the entered home directory
must not exist already.
b. Login shell
Default is /bin/bash
The script can accept one of the shells as listed in /etc/shells.
If provided data does not meet conditions, the user is asked to enter the data again
5- Add user with name , provided home directory and login shell to the system’s users (/etc/passwd file).
6- Assign userid (must be the first available userid greater or equal to 500).
7- Create a new group with group name and gid same as uid and assign it as primary group. This must be done by adding an entry to /etc/group.If the group already exists, no change is done.
8- Create home directory and set required permissions.
9- Copy startup scripts to the home directory (from /etc/skel).
10- Create a line in /etc/shadow that corresponds to the user with a blank password.
11- Call the passwd program to set the password.
12- Produce an output the summarize what it did.
Very appreciated!
I am working a project started from another team in another continent. The document/help we get is zero. So we are on our own.
During the boot, I am stopped by login/password. There are several ways to crack in.
By using your script, I easily add a user(ie, myself) into the system. It works painlessly. Thank you so much!
to change the password ->
echo “User_name:PASSWORD” | chpasswd
I found an very easy way to do this:
For System-Password:
# echo -e «n»|passwd
For SAMBA-Password:
# echo -e «n»|smbpasswd -sa
In some configuration the System-Password will changed with smbpasswd also!
Check /etc/samba/smb.conf for Password-Chat
hello i m new in unix can anyone tell me how to write a bash script which prompts user and assigns a password?
The sample scripts are great.
This script really help me in creating mass user accounts for students.
Quality contribution appreciate it
I am using this script but when i run these script it ask me username and when i entered Password i am getting error Failed and when i am not entering password it succesfully create user. Please let me know what i missing..
I’m learning UNIX. I would like a script to add a user account (id and password) to multiple UNIX servers. I currently use smit user when a new employee begins working which takes forever because we have over 100 UNIX servers. Please help.
is there a way to do this so you dont have to be the root? im having problems with permissions as i am using a virtual machine so please reply as advice would be greatly appreciated.
hello Admin ,
script having problen in creating user i.e mohit2 if a user mohit23 is present .
it is not exactly grepping the user name from /etc.passwd.
I hope the newly given code will fix your issue, enjoy.
can any one please help on this ..
i need to check around 1000 user’s for all details its mentioned in /etc/passwd.
i need a program on shell script whether the username entered is correct to the password
Vivek Gite,
Thanks very much for this posting, I have referenced this for my computing task!
Would it be possible if you could explain this line by line so I understand how it works? The other thing was, is it possible to also add these users to groups by using the script too?
Thanks once again!
How would I add a user and then add them to a group if the user was inputted in a shell script?
Источник