- Anonymous Authentication Overview Anonymous authentication gives users access to the public areas of your Web or FTP site without prompting them for a user name or password. By default, the IUSR account, which was introduced in IIS 7.0 and replaces the IIS 6.0 IUSR_computername account, is used to allow anonymous access. An application is a grouping of files that delivers content or provides services over protocols, such as HTTP. When you create an application in IIS, the application’s path becomes part of the site’s URL. By default, IIS 7 uses Anonymous authentication. You must disable Anonymous authentication for any Web site, Web application, or Web service for which you want to enable other authentication methods such as Basic or Windows authentication. Compatibility Setup How To How to disable anonymous authentication Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager: If you are using Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2: On the taskbar, click Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager. If you are using Windows 8 or Windows 8.1: Hold down the Windows key, press the letter X, and then click Control Panel. Click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager. If you are using Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2: On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager. If you are using Windows Vista or Windows 7: On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel. Double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager. In the Connections pane, expand the server name, expand Sites, and go to the level in the hierarchy pane that you want to configure, and then click the Web site or Web application. Scroll to the Security section in the Home pane, and then double-click Authentication. In the Authentication pane, select Anonymous Authentication, and then click Disable in the Actions pane. How to change anonymous authentication credentials from the IUSR account Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager: If you are using Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2: On the taskbar, click Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager. If you are using Windows 8 or Windows 8.1: Hold down the Windows key, press the letter X, and then click Control Panel. Click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager. If you are using Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2: On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager. If you are using Windows Vista or Windows 7: On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel. Double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager. In the Connections pane, expand the server name, expand Sites, and navigate to the level in the hierarchy pane that you want to configure, and then click the Web site or Web application. Scroll to the Security section in the Home pane, and then double-click Authentication. In the Authentication pane, select Anonymous Authentication, and then click Edit. in the Actions pane. In the Edit Anonymous Authentication Credentials dialog box, do one of the following: Select Application pool identity to use the identity set for the application pool, and then click OK. Click Set. , and then in the Set Credentials dialog box, enter the user name for the account in the User name box, enter the password for the account in the Password and Confirm password boxes, click OK, and then click OK again. If you use this procedure, only grant the new account minimal privileges on the IIS server computer. Configuration Attributes Attribute Description enabled Optional Boolean attribute. Specifies whether Anonymous authentication is enabled. The default value is true . logonMethod Optional enum attribute. The logonMethod attribute can be one of the following possible values. The default is ClearText . Value Description Batch This logon type is intended for batch servers, where processes may be executing on behalf of a user without that user’s direct intervention. The numeric value is 1 . ClearText This logon type preserves the name and password in the authentication package, which allows the server to make connections to other network servers while impersonating the client. The numeric value is 3 . Interactive This logon type is intended for users who will be using the computer interactively. The numeric value is 0 . Network This logon type is intended for high performance servers to authenticate plaintext passwords. Credentials are not cached for this logon type. The numeric value is 2 . password Optional String attribute. Specifies the password for Anonymous authentication. Note: To avoid storing unencrypted password strings in configuration files, always use AppCmd.exe or IIS Manager to enter passwords. If you use these management tools, the password strings will be encrypted automatically before they are written to the XML configuration files. This provides better password security than storing unencrypted passwords. username Optional String attribute. Specifies the username for Anonymous authentication. If you leave this value blank (that is, username=»»), Anonymous authentication uses the application pool identity to authenticate anonymous users. The default value is IUSR . Child Elements Configuration Sample The following configuration example configures anonymous authentication for an IIS 7 Web site or Web application to use a local account on the Web server. (IIS 7 automatically uses AES encryption to encrypt the password.) Sample Code The following examples enable anonymous authentication and change the default username and password used for anonymous authentication to an account named IUSR and a password of P@ssw0rd. Windows Authentication Overview The element defines configuration settings for the Internet Information Services (IIS) 7 Windows authentication module. You can use Windows authentication when your IIS 7 server runs on a corporate network that is using Microsoft Active Directory service domain identities or other Windows accounts to identify users. Because of this, you can use Windows authentication whether or not your server is a member of an Active Directory domain. Windows authentication (formerly named NTLM, and also referred to as Windows NT Challenge/Response authentication) is a secure form of authentication because the user name and password are hashed before being sent across the network. When you enable Windows authentication, the client browser sends a strongly hashed version of the password in a cryptographic exchange with your Web server. Windows authentication supports two authentication protocols, Kerberos and NTLM, which are defined in the element. When you install and enable Windows authentication on IIS 7, the default protocol is Kerberos. The element can also contain a useKernelMode attribute that configures whether to use the kernel mode authentication feature that is new to Windows Server 2008. Windows authentication is best suited for an intranet environment for the following reasons: Client computers and Web servers are in the same domain. Administrators can make sure that every client browser is Internet Explorer 2.0 or later. HTTP proxy connections, which are not supported by NTLM, are not required. Kerberos version 5 requires a connection to Active Directory, which is not feasible in an Internet environment. New in IIS 7.5 The element was introduced in IIS 7.5, which allows you to configure the settings for the new extended protection features that have been integrated into Windows authentication. Compatibility Version Notes IIS 10.0 The element was not modified in IIS 10.0. IIS 8.5 The element was not modified in IIS 8.5. IIS 8.0 The element was not modified in IIS 8.0. IIS 7.5 The element was added in IIS 7.5. IIS 7.0 The element was introduced in IIS 7.0. IIS 6.0 The element replaces portions of the IIS 6.0 AuthType and AuthFlags metabase properties. Setup The default installation of IIS 7 and later does not include the Windows authentication role service. To use Windows authentication on IIS, you must install the role service, disable Anonymous authentication for your Web site or application, and then enable Windows authentication for the site or application. After you install the role service, IIS 7 commits the following configuration settings to the ApplicationHost.config file. Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2 On the taskbar, click Server Manager. In Server Manager, click the Manage menu, and then click Add Roles and Features. In the Add Roles and Features wizard, click Next. Select the installation type and click Next. Select the destination server and click Next. On the Server Roles page, expand Web Server (IIS), expand Web Server, expand Security, and then select Windows Authentication. Click Next. . On the Select features page, click Next. On the Confirm installation selections page, click Install. On the Results page, click Close. Windows 8 or Windows 8.1 On the Start screen, move the pointer all the way to the lower left corner, right-click the Start button, and then click Control Panel. In Control Panel, click Programs and Features, and then click Turn Windows features on or off. Expand Internet Information Services, expand World Wide Web Services, expand Security, and then select Windows Authentication. Click OK. Click Close. Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2 On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Server Manager. In the Server Manager hierarchy pane, expand Roles, and then click Web Server (IIS). In the Web Server (IIS) pane, scroll to the Role Services section, and then click Add Role Services. On the Select Role Services page of the Add Role Services Wizard, select Windows Authentication, and then click Next. On the Confirm Installation Selections page, click Install. On the Results page, click Close. Windows Vista or Windows 7 On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel. In Control Panel, click Programs and Features, and then click Turn Windows Features on or off. Expand Internet Information Services, then World Wide Web Services, then Security. Select Windows Authentication, and then click OK. How To How to enable Windows authentication for a Web site, Web application, or Web service Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager: If you are using Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2: On the taskbar, click Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager. If you are using Windows 8 or Windows 8.1: Hold down the Windows key, press the letter X, and then click Control Panel. Click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager. If you are using Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2: On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager. If you are using Windows Vista or Windows 7: On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel. Double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager. In the Connections pane, expand the server name, expand Sites, and then the site, application, or Web service for which you want to enable Windows authentication. Scroll to the Security section in the Home pane, and then double-click Authentication. In the Authentication pane, select Windows Authentication, and then click Enable in the Actions pane. How to enable Extended Protection for Windows authentication Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager: If you are using Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2: On the taskbar, click Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager. If you are using Windows 8 or Windows 8.1: Hold down the Windows key, press the letter X, and then click Control Panel. Click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager. If you are using Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2: On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager. If you are using Windows Vista or Windows 7: On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel. Double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager. In the Connections pane, expand the server name, expand Sites, and then the site, application, or Web service for which you want to enable Extended Protection for Windows authentication. Scroll to the Security section in the Home pane, and then double-click Authentication. In the Authentication pane, select Windows Authentication. Click Enable in the Actions pane. Click Advanced Settings in the Actions pane. When the Advanced Settings dialog box appears, select one of the following options in the Extended Protection drop-down menu: Select Accept if you want to enable extended protection while providing down-level support for clients that do not support extended protection. Select Required if you want to enable extended protection without providing down-level support. Click OK to close the Advanced Settings dialog box. Configuration The element is configurable at the site, application, or virtual directory level in the ApplicationHost.config file. Attributes Attribute Description authPersistNonNTLM Optional Boolean attribute. Specifies whether IIS automatically reauthenticates every non-NTLM (for example, Kerberos) request, even those on the same connection. False enables multiple authentications for the same connections. Note: A setting of true means that the client will be authenticated only once on the same connection. IIS will cache a token or ticket on the server for a TCP session that stays established. The default is false . authPersistSingleRequest Optional Boolean attribute. Setting this flag to true specifies that authentication persists only for a single request on a connection. IIS resets the authentication at the end of each request, and forces reauthentication on the next request of the session. The default value is false . enabled Required Boolean attribute. Specifies whether Windows authentication is enabled. The default value is false . useKernelMode Optional Boolean attribute. Specifies whether Windows authentication is done in kernel mode. True specifies that Windows authentication uses kernel mode. Kernel-mode authentication may improve authentication performance and prevent authentication problems with application pools that are configured to use a custom identity. As a best practice, do not disable this setting if you use Kerberos authentication and have a custom identity on the application pool. The default is true . Child Elements Element Description extendedProtection Optional element. Specifies extended protection options for Windows authentication. Note: This element was added in IIS 7.5. providers Optional element. Specifies security support providers used for Windows authentication. Configuration Sample The following default element is configured at the root ApplicationHost.config file in IIS 7.0, and disables Windows authentication by default. It also defines the two Windows authentication providers for IIS 7.0. The following example enables Windows authentication and disables Anonymous authentication for a Web site named Contoso. Sample Code The following examples disable Anonymous authentication for a site named Contoso, then enable Windows authentication for the site.
- Overview
- Compatibility
- Setup
- How To
- How to disable anonymous authentication
- How to change anonymous authentication credentials from the IUSR account
- Configuration
- Attributes
- Child Elements
- Configuration Sample
- Sample Code
- Windows Authentication
- Overview
- New in IIS 7.5
- Compatibility
- Setup
- Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2
- Windows 8 or Windows 8.1
- Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2
- Windows Vista or Windows 7
- How To
- How to enable Windows authentication for a Web site, Web application, or Web service
- How to enable Extended Protection for Windows authentication
- Configuration
- Attributes
- Child Elements
- Configuration Sample
- Sample Code
Anonymous Authentication Overview
Anonymous authentication gives users access to the public areas of your Web or FTP site without prompting them for a user name or password. By default, the IUSR account, which was introduced in IIS 7.0 and replaces the IIS 6.0 IUSR_computername account, is used to allow anonymous access. An application is a grouping of files that delivers content or provides services over protocols, such as HTTP. When you create an application in IIS, the application’s path becomes part of the site’s URL.
By default, IIS 7 uses Anonymous authentication. You must disable Anonymous authentication for any Web site, Web application, or Web service for which you want to enable other authentication methods such as Basic or Windows authentication.
Compatibility
Setup
How To
How to disable anonymous authentication
Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager:
If you are using Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows 8 or Windows 8.1:
- Hold down the Windows key, press the letter X, and then click Control Panel.
- Click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Vista or Windows 7:
- On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel.
- Double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
In the Connections pane, expand the server name, expand Sites, and go to the level in the hierarchy pane that you want to configure, and then click the Web site or Web application.
Scroll to the Security section in the Home pane, and then double-click Authentication.
In the Authentication pane, select Anonymous Authentication, and then click Disable in the Actions pane.
How to change anonymous authentication credentials from the IUSR account
Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager:
If you are using Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows 8 or Windows 8.1:
- Hold down the Windows key, press the letter X, and then click Control Panel.
- Click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Vista or Windows 7:
- On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel.
- Double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
In the Connections pane, expand the server name, expand Sites, and navigate to the level in the hierarchy pane that you want to configure, and then click the Web site or Web application.
Scroll to the Security section in the Home pane, and then double-click Authentication.
In the Authentication pane, select Anonymous Authentication, and then click Edit. in the Actions pane.
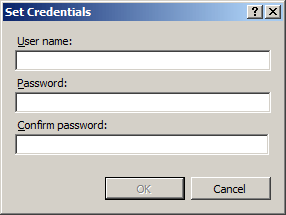
In the Edit Anonymous Authentication Credentials dialog box, do one of the following:
Select Application pool identity to use the identity set for the application pool, and then click OK.
Click Set. , and then in the Set Credentials dialog box, enter the user name for the account in the User name box, enter the password for the account in the Password and Confirm password boxes, click OK, and then click OK again.
If you use this procedure, only grant the new account minimal privileges on the IIS server computer.
Configuration
Attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| enabled | Optional Boolean attribute. |
Specifies whether Anonymous authentication is enabled.
The default value is true .
The logonMethod attribute can be one of the following possible values. The default is ClearText .
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| Batch | This logon type is intended for batch servers, where processes may be executing on behalf of a user without that user’s direct intervention. The numeric value is 1 . |
| ClearText | This logon type preserves the name and password in the authentication package, which allows the server to make connections to other network servers while impersonating the client. The numeric value is 3 . |
| Interactive | This logon type is intended for users who will be using the computer interactively. The numeric value is 0 . |
| Network | This logon type is intended for high performance servers to authenticate plaintext passwords. Credentials are not cached for this logon type. The numeric value is 2 . |
Specifies the password for Anonymous authentication.
Note: To avoid storing unencrypted password strings in configuration files, always use AppCmd.exe or IIS Manager to enter passwords. If you use these management tools, the password strings will be encrypted automatically before they are written to the XML configuration files. This provides better password security than storing unencrypted passwords.
Specifies the username for Anonymous authentication. If you leave this value blank (that is, username=»»), Anonymous authentication uses the application pool identity to authenticate anonymous users.
The default value is IUSR .
Child Elements
Configuration Sample
The following configuration example configures anonymous authentication for an IIS 7 Web site or Web application to use a local account on the Web server. (IIS 7 automatically uses AES encryption to encrypt the password.)
Sample Code
The following examples enable anonymous authentication and change the default username and password used for anonymous authentication to an account named IUSR and a password of P@ssw0rd.
Windows Authentication
Overview
The element defines configuration settings for the Internet Information Services (IIS) 7 Windows authentication module. You can use Windows authentication when your IIS 7 server runs on a corporate network that is using Microsoft Active Directory service domain identities or other Windows accounts to identify users. Because of this, you can use Windows authentication whether or not your server is a member of an Active Directory domain.
Windows authentication (formerly named NTLM, and also referred to as Windows NT Challenge/Response authentication) is a secure form of authentication because the user name and password are hashed before being sent across the network. When you enable Windows authentication, the client browser sends a strongly hashed version of the password in a cryptographic exchange with your Web server.
Windows authentication supports two authentication protocols, Kerberos and NTLM, which are defined in the
element. When you install and enable Windows authentication on IIS 7, the default protocol is Kerberos. The element can also contain a useKernelMode attribute that configures whether to use the kernel mode authentication feature that is new to Windows Server 2008.
Windows authentication is best suited for an intranet environment for the following reasons:
- Client computers and Web servers are in the same domain.
- Administrators can make sure that every client browser is Internet Explorer 2.0 or later.
- HTTP proxy connections, which are not supported by NTLM, are not required.
- Kerberos version 5 requires a connection to Active Directory, which is not feasible in an Internet environment.
New in IIS 7.5
The element was introduced in IIS 7.5, which allows you to configure the settings for the new extended protection features that have been integrated into Windows authentication.
Compatibility
| Version | Notes |
|---|---|
| IIS 10.0 | The element was not modified in IIS 10.0. |
| IIS 8.5 | The element was not modified in IIS 8.5. |
| IIS 8.0 | The element was not modified in IIS 8.0. |
| IIS 7.5 | The element was added in IIS 7.5. |
| IIS 7.0 | The element was introduced in IIS 7.0. |
| IIS 6.0 | The element replaces portions of the IIS 6.0 AuthType and AuthFlags metabase properties. |
Setup
The default installation of IIS 7 and later does not include the Windows authentication role service. To use Windows authentication on IIS, you must install the role service, disable Anonymous authentication for your Web site or application, and then enable Windows authentication for the site or application.
After you install the role service, IIS 7 commits the following configuration settings to the ApplicationHost.config file.
Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager.
- In Server Manager, click the Manage menu, and then click Add Roles and Features.
- In the Add Roles and Features wizard, click Next. Select the installation type and click Next. Select the destination server and click Next.
- On the Server Roles page, expand Web Server (IIS), expand Web Server, expand Security, and then select Windows Authentication. Click Next.
.
- On the Select features page, click Next.
- On the Confirm installation selections page, click Install.
- On the Results page, click Close.
Windows 8 or Windows 8.1
- On the Start screen, move the pointer all the way to the lower left corner, right-click the Start button, and then click Control Panel.
- In Control Panel, click Programs and Features, and then click Turn Windows features on or off.
- Expand Internet Information Services, expand World Wide Web Services, expand Security, and then select Windows Authentication.
- Click OK.
- Click Close.
Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2
- On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Server Manager.
- In the Server Manager hierarchy pane, expand Roles, and then click Web Server (IIS).
- In the Web Server (IIS) pane, scroll to the Role Services section, and then click Add Role Services.
- On the Select Role Services page of the Add Role Services Wizard, select Windows Authentication, and then click Next.
- On the Confirm Installation Selections page, click Install.
- On the Results page, click Close.
Windows Vista or Windows 7
- On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel.
- In Control Panel, click Programs and Features, and then click Turn Windows Features on or off.
- Expand Internet Information Services, then World Wide Web Services, then Security.
- Select Windows Authentication, and then click OK.
How To
How to enable Windows authentication for a Web site, Web application, or Web service
Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager:
If you are using Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows 8 or Windows 8.1:
- Hold down the Windows key, press the letter X, and then click Control Panel.
- Click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Vista or Windows 7:
- On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel.
- Double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
In the Connections pane, expand the server name, expand Sites, and then the site, application, or Web service for which you want to enable Windows authentication.
Scroll to the Security section in the Home pane, and then double-click Authentication.
In the Authentication pane, select Windows Authentication, and then click Enable in the Actions pane.
How to enable Extended Protection for Windows authentication
Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager:
If you are using Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows 8 or Windows 8.1:
- Hold down the Windows key, press the letter X, and then click Control Panel.
- Click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Vista or Windows 7:
- On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel.
- Double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
In the Connections pane, expand the server name, expand Sites, and then the site, application, or Web service for which you want to enable Extended Protection for Windows authentication.
Scroll to the Security section in the Home pane, and then double-click Authentication.
In the Authentication pane, select Windows Authentication.
Click Enable in the Actions pane.
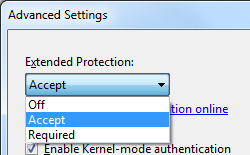
Click Advanced Settings in the Actions pane.
When the Advanced Settings dialog box appears, select one of the following options in the Extended Protection drop-down menu:
- Select Accept if you want to enable extended protection while providing down-level support for clients that do not support extended protection.
- Select Required if you want to enable extended protection without providing down-level support.
Click OK to close the Advanced Settings dialog box.
Configuration
The element is configurable at the site, application, or virtual directory level in the ApplicationHost.config file.
Attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| authPersistNonNTLM | Optional Boolean attribute. |
Specifies whether IIS automatically reauthenticates every non-NTLM (for example, Kerberos) request, even those on the same connection. False enables multiple authentications for the same connections.
Note: A setting of true means that the client will be authenticated only once on the same connection. IIS will cache a token or ticket on the server for a TCP session that stays established.
The default is false .
Setting this flag to true specifies that authentication persists only for a single request on a connection. IIS resets the authentication at the end of each request, and forces reauthentication on the next request of the session.
The default value is false .
Specifies whether Windows authentication is enabled.
The default value is false .
Specifies whether Windows authentication is done in kernel mode. True specifies that Windows authentication uses kernel mode.
Kernel-mode authentication may improve authentication performance and prevent authentication problems with application pools that are configured to use a custom identity.
As a best practice, do not disable this setting if you use Kerberos authentication and have a custom identity on the application pool.
The default is true .
Child Elements
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| extendedProtection | Optional element. |
Specifies extended protection options for Windows authentication.
Note: This element was added in IIS 7.5.
Specifies security support providers used for Windows authentication.
Configuration Sample
The following default element is configured at the root ApplicationHost.config file in IIS 7.0, and disables Windows authentication by default. It also defines the two Windows authentication providers for IIS 7.0.
The following example enables Windows authentication and disables Anonymous authentication for a Web site named Contoso.
Sample Code
The following examples disable Anonymous authentication for a site named Contoso, then enable Windows authentication for the site.


 .
.