- Mac OS X Start / Stop / Restart Apache Web Server
- To stop Apache web server, enter:
- To start Apache web server again, enter:
- To restart apache web server, enter:
- To run a configuration file syntax test
- To reload apache web server after editing the config file
- Sample session from above commands
- Mac OS x Restart Apache Web Server
- Task: Stop Apache Web server
- Task: Start Apache Web server
- How to stop apache permanently on mac Mavericks?
- 4 Answers 4
- Stopping and Restarting Apache HTTP Server
- See also
- Introduction
- Stop Now
- Graceful Restart
- Restart Now
- Graceful Stop
- Comments
Mac OS X Start / Stop / Restart Apache Web Server
To stop Apache web server, enter:
sudo apachectl stop
OR
sudo apachectl -k stop
To start Apache web server again, enter:
sudo apachectl start
OR
sudo apachectl -k start
To restart apache web server, enter:
sudo apachectl restart
OR
sudo apachectl -k restart
To run a configuration file syntax test
sudo apachectl configtest
To reload apache web server after editing the config file
First edit the config file, run:
$ sudo vi /etc/apache2/httpd.conf
Make changes as per your needs. Close and save the file. To reload new changes, run:
sudo apachectl graceful
OR
sudo apachectl -k graceful
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
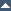
Sample session from above commands
Fig.01: apachectl in action on macOS
You can displays a brief status report by visiting the url http://localhost:80/server-status in the web browser of your choice.
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
| Category | List of Unix and Linux commands |
|---|---|
| Documentation | help • mandb • man • pinfo |
| Disk space analyzers | df • duf • ncdu • pydf |
| File Management | cat • cp • less • mkdir • more • tree |
| Firewall | Alpine Awall • CentOS 8 • OpenSUSE • RHEL 8 • Ubuntu 16.04 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Linux Desktop Apps | Skype • Spotify • VLC 3 |
| Modern utilities | bat • exa |
| Network Utilities | NetHogs • dig • host • ip • nmap |
| OpenVPN | CentOS 7 • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Debian 8/9 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Package Manager | apk • apt |
| Processes Management | bg • chroot • cron • disown • fg • glances • gtop • jobs • killall • kill • pidof • pstree • pwdx • time • vtop |
| Searching | ag • grep • whereis • which |
| Shell builtins | compgen • echo • printf |
| Text processing | cut • rev |
| User Information | groups • id • lastcomm • last • lid/libuser-lid • logname • members • users • whoami • who • w |
| WireGuard VPN | Alpine • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Firewall • Ubuntu 20.04 |
Comments on this entry are closed.
For some interesting reason, apache keeps spawning off new process however I kill it. I tried apachectl and kill -SIGTERM but apache would be killed and another process will be spawned right away.
Can you tell me why?
I have the same problem as you Antony.
I’ve used MAMP and then switched to Mac’s default Apache and problem still exists.
I think it is somehow related to xdebug. I’ll try zend_debugger. If that doesn’t work, I’m switching to another operating system.
in /Applications/XAMPP/xamppfiles/xampp include inicial line sudo apachectl stop
404-not found
could not be satisfied
Use this to stop the apache server
sudo /usr/sbin/apachectl stop
Thank you! I was tinkering around with the built-in Apache web server because I’ll be messing around with learning some HTML and CSS on my own. I found a page explaining how to start and use it, but it didn’t say how to end the process. I didn’t notice any performance change but I also didn’t want wayward processes running on my machine. Many thanks!
Источник
Mac OS x Restart Apache Web Server
H ow do I restart Apache web server under Mac OS X operating systems?
The apachectl command act as Apache HTTP Server control interface. It can be used to start, stop, and restart the Apache web server from command line.
Open a terminal and type any one of the following command:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Fig.01: Restarting Apache under Mac OS X
Task: Stop Apache Web server
Task: Start Apache Web server
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
| Category | List of Unix and Linux commands |
|---|---|
| Documentation | help • mandb • man • pinfo |
| Disk space analyzers | df • duf • ncdu • pydf |
| File Management | cat • cp • less • mkdir • more • tree |
| Firewall | Alpine Awall • CentOS 8 • OpenSUSE • RHEL 8 • Ubuntu 16.04 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Linux Desktop Apps | Skype • Spotify • VLC 3 |
| Modern utilities | bat • exa |
| Network Utilities | NetHogs • dig • host • ip • nmap |
| OpenVPN | CentOS 7 • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Debian 8/9 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Package Manager | apk • apt |
| Processes Management | bg • chroot • cron • disown • fg • glances • gtop • jobs • killall • kill • pidof • pstree • pwdx • time • vtop |
| Searching | ag • grep • whereis • which |
| Shell builtins | compgen • echo • printf |
| Text processing | cut • rev |
| User Information | groups • id • lastcomm • last • lid/libuser-lid • logname • members • users • whoami • who • w |
| WireGuard VPN | Alpine • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Firewall • Ubuntu 20.04 |
Comments on this entry are closed.
Thanks, but it might be easier this way: Open the “Sharing” preference, (de-)select “Web Sharing”.
I was just wondering if OS X got some sort of service manager. I need to dig it a little more…
thanks for the comment!
The software to start/stop (load/unload) services is called “launchctl”. From the man page:
launchctl interfaces with launchd to load, unload daemons/agents and generally control launchd. launchctl supports taking subcommands on the command line, interactively or even redirected from standard input.
These commands can be stored in $HOME/.launchd.conf or /etc/launchd.conf to be read at the time launchd starts.
Vivek, what does the -k switch do? I couldn’t find it in the man page for apachectl on a Mac OS X system.
@Robert, I will look into it.
@Leaman, the apachectl command works in two modes:
a) Sys v style mode – One line command mode which take args like start, restart, and stop, and translating them into appropriate UNIX signals to httpd.
b) Traditional UNIX mode with lots of options for testing and debugging. In this mode it can act as a simple front-end to the httpd command that simply sets necessary environment variables and then invokes httpd, passing through any command line arguments.
it does’mt work for me 🙁
sumitgupta$ apachectl -k graceful
httpd: Syntax error on line 488 of /private/etc/apache2/httpd.conf: Syntax error on line 8 of /private/etc/apache2/other/+entropy-php.conf: Cannot load /usr/local/php5/libphp5.so into server: dlopen(/usr/local/php5/libphp5.so, 10): Symbol not found: _libiconv\n Referenced from: /usr/local/php5/lib/libintl.8.dylib\n Expected in: /usr/lib/libiconv.2.dylib\n
SUM-IT:
this is the problem i am facing please help…..
i receive an error when I try to restart apache with: sudo apachectl restart
the error reads: /urs/sbin/apachectL: line 73: unlimit: open files: cannot modify limit: invalid argument
can anyone help! please.
changes are to be made in “/usr/sbin/apachectl”
comment out the these lines.
i did this through the command line using ‘vi’ commands
@Javier, I’d say there is an error in your httpd.conf file. Open it up in the plain-text editor of your choice–one that shows line numbers–and look at line 73. There is either a syntax error or an invalid argument for the option contained on that line.
lemanc,
i went to httpd.conf file and line 73 is ‘LoadModule include_module libexec/apache2/mod_include.so ‘ do you know anything about this kind of issue?
thanks in advanced!
This is not the correct solution. Please see my other reply for the solution.
Источник
How to stop apache permanently on mac Mavericks?
I’m trying to install zend server on mac and need to uninstall the apache server that is auto included with Mavericks so that the Apache server included with Zend is used instead. Can it be prevented from running on startup or permanently removed?
4 Answers 4
This will stop a running instance of Apache, and record that it should not be restarted. It records your preference in /private/var/db/launchd.db/com.apple.launchd/overrides.plist .
it will stop all
I ran into this same problem, and the culprit was pretty obtuse. It wound up that OSX was attempting to include a nonexistent php version, however the OSX httpd was also not directly accessible due to the homebrew httpd taking priority. Here’s what I did that fixed it:
First: brew unlink httpd Then which httpd revealed the following: /usr/sbin/httpd
At this point I ran sudo /usr/sbin/httpd -k stop , and the real culprit revealed itself:
I then fixed this with sudo vi /private/etc/apache2/httpd.conf , and commented out all of the lines in that file, and ran the following for good measure:
The underlying problem was that the native OSX instance was still running, but had become detached from launchctl due to the PHP not found issue. So basically launchctl thought it had properly shut the process down, but the apachectl agent refused to stop due to the PHP error, resulting in a decoupled process, which was only accessible for direct control when the homebrew version was also unlinked.
Commenting out the native PHP include allowed me to run sudo apachectl -k stop without issue.
Источник
Stopping and Restarting Apache HTTP Server
This document covers stopping and restarting Apache HTTP Server on Unix-like systems. Windows NT, 2000 and XP users should see Running httpd as a Service and Windows 9x and ME users should see Running httpd as a Console Application for information on how to control httpd on those platforms.
See also
Introduction
In order to stop or restart the Apache HTTP Server, you must send a signal to the running httpd processes. There are two ways to send the signals. First, you can use the unix kill command to directly send signals to the processes. You will notice many httpd executables running on your system, but you should not send signals to any of them except the parent, whose pid is in the PidFile . That is to say you shouldn’t ever need to send signals to any process except the parent. There are four signals that you can send the parent: TERM , USR1 , HUP , and WINCH , which will be described in a moment.
To send a signal to the parent you should issue a command such as:
kill -TERM `cat /usr/local/apache2/logs/httpd.pid`
The second method of signaling the httpd processes is to use the -k command line options: stop , restart , graceful and graceful-stop , as described below. These are arguments to the httpd binary, but we recommend that you send them using the apachectl control script, which will pass them through to httpd .
After you have signaled httpd , you can read about its progress by issuing:
tail -f /usr/local/apache2/logs/error_log
Modify those examples to match your ServerRoot and PidFile settings.
Stop Now
Sending the TERM or stop signal to the parent causes it to immediately attempt to kill off all of its children. It may take it several seconds to complete killing off its children. Then the parent itself exits. Any requests in progress are terminated, and no further requests are served.
Graceful Restart
The USR1 or graceful signal causes the parent process to advise the children to exit after their current request (or to exit immediately if they’re not serving anything). The parent re-reads its configuration files and re-opens its log files. As each child dies off the parent replaces it with a child from the new generation of the configuration, which begins serving new requests immediately.
This code is designed to always respect the process control directive of the MPMs, so the number of processes and threads available to serve clients will be maintained at the appropriate values throughout the restart process. Furthermore, it respects StartServers in the following manner: if after one second at least StartServers new children have not been created, then create enough to pick up the slack. Hence the code tries to maintain both the number of children appropriate for the current load on the server, and respect your wishes with the StartServers parameter.
Users of mod_status will notice that the server statistics are not set to zero when a USR1 is sent. The code was written to both minimize the time in which the server is unable to serve new requests (they will be queued up by the operating system, so they’re not lost in any event) and to respect your tuning parameters. In order to do this it has to keep the scoreboard used to keep track of all children across generations.
The status module will also use a G to indicate those children which are still serving requests started before the graceful restart was given.
At present there is no way for a log rotation script using USR1 to know for certain that all children writing the pre-restart log have finished. We suggest that you use a suitable delay after sending the USR1 signal before you do anything with the old log. For example if most of your hits take less than 10 minutes to complete for users on low bandwidth links then you could wait 15 minutes before doing anything with the old log.
When you issue a restart, a syntax check is first run, to ensure that there are no errors in the configuration files. If your configuration file has errors in it, you will get an error message about that syntax error, and the server will refuse to restart. This avoids the situation where the server halts and then cannot restart, leaving you with a non-functioning server.
This still will not guarantee that the server will restart correctly. To check the semantics of the configuration files as well as the syntax, you can try starting httpd as a non-root user. If there are no errors it will attempt to open its sockets and logs and fail because it’s not root (or because the currently running httpd already has those ports bound). If it fails for any other reason then it’s probably a config file error and the error should be fixed before issuing the graceful restart.
Restart Now
Sending the HUP or restart signal to the parent causes it to kill off its children like in TERM , but the parent doesn’t exit. It re-reads its configuration files, and re-opens any log files. Then it spawns a new set of children and continues serving hits.
Users of mod_status will notice that the server statistics are set to zero when a HUP is sent.
Graceful Stop
The WINCH or graceful-stop signal causes the parent process to advise the children to exit after their current request (or to exit immediately if they’re not serving anything). The parent will then remove its PidFile and cease listening on all ports. The parent will continue to run, and monitor children which are handling requests. Once all children have finalised and exited or the timeout specified by the GracefulShutdownTimeout has been reached, the parent will also exit. If the timeout is reached, any remaining children will be sent the TERM signal to force them to exit.
A TERM signal will immediately terminate the parent process and all children when in the «graceful» state. However as the PidFile will have been removed, you will not be able to use apachectl or httpd to send this signal.
The graceful-stop signal allows you to run multiple identically configured instances of httpd at the same time. This is a powerful feature when performing graceful upgrades of httpd, however it can also cause deadlocks and race conditions with some configurations.
Care has been taken to ensure that on-disk files such as lock files ( Mutex ) and Unix socket files ( ScriptSock ) contain the server PID, and should coexist without problem. However, if a configuration directive, third-party module or persistent CGI utilises any other on-disk lock or state files, care should be taken to ensure that multiple running instances of httpd do not clobber each other’s files.
You should also be wary of other potential race conditions, such as using rotatelogs style piped logging. Multiple running instances of rotatelogs attempting to rotate the same logfiles at the same time may destroy each other’s logfiles.
Comments
Copyright 2021 The Apache Software Foundation.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0.
Источник