Управление правилами Windows Firewall с помощью PowerShell
Эта статья посвящена основам управления настройками и правилами встроенного Windows Firewall из командной строки PowerShell. Мы рассмотрим, как включать/отключать брандмауэр для различных профилей, создавать и удалять правила файервола, и рассмотрим небольшой скрипт, позволяющий сформировать удобную таблицу с текущим набором активных правил брандмауэра.
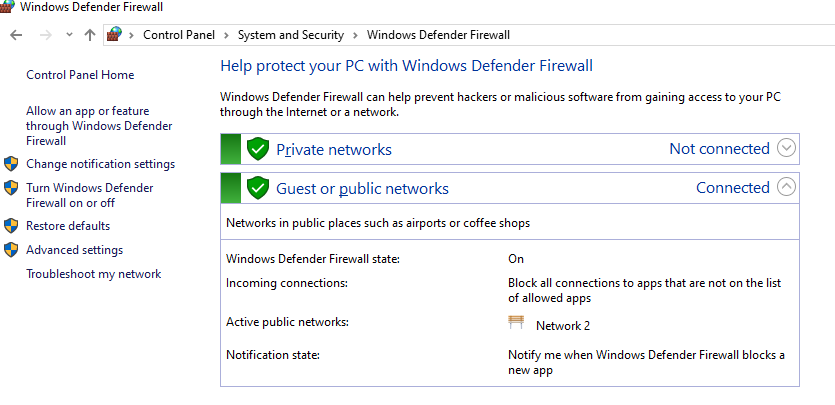
Вы можете управлять настройками Windows Firewall из графической консоли Control Panel -> System and Security -> Windows Defender Firewall. Однако начиная с Windows 8.1 (Windows Server 2012R2) для управления встроенным брандмауэром в систему был добавлен встроенный PowerShell модуль NetSecurity.
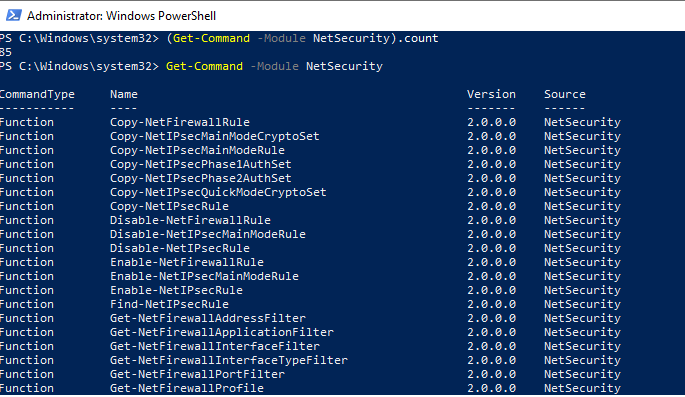
В модуле NetSecurity в Windows 10 доступно 85 команд. Вы можете вывести их список:
Get-Command -Module NetSecurity
Управление сетевыми профилями брандмауэра Windows из PowerShell
В Windows Firewall есть три типа сетевых профилей:
- Domain (Доменный) – применяется к компьютерам, включенным в домен Active Directory;
- Private (Частный) – домашние или рабочие сети;
- Public (Общий) – общедоступные сети.
Каждый профиль может отличаться используемым набором правил файервола. По умолчанию все сетевые интерфейсы компьютера защищены фаейрволом и к ним применяются все три типа профилей.
Чтобы включить все три сетевых профиля Domain, Public и Private, используйте команду:
Set-NetFirewallProfile -All -Enabled True
Либо укажите конкретный профиль вместо All:
Set-NetFirewallProfile -Profile Public -Enabled True
Чтобы отключить файервол для всех трех сетевых профилей, используется команда:
Set-NetFirewallProfile -All -Enabled False
С помощью командлета Set-NetFirewallProfile вы можете изменить параметры профиля (действие по-умолчанию, журналирование, путь и размер файла журнала, настройки оповещений и т.д.).
Как вы вероятно знаете, по умолчанию Windows Firewall включен в современных ОС для всех профилей. В настройках профилей разрешены все исходящие подключения и блокируется входящие (кроме разрешенных).
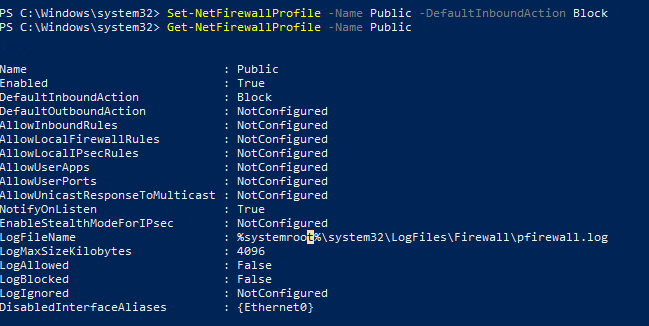
Изменим действие по-умолчнию для профиля Public – заблокировать все входящие подключения.
Set-NetFirewallProfile –Name Public –DefaultInboundAction Block
Текущие настройки профиля можно вывести так:
Get-NetFirewallProfile -Name Public
Если вы управляете настройками Windows Firewall через GPO, вы можете вывести текущие результирующие настройки профилей так:
Get-NetFirewallProfile -policystore activestore
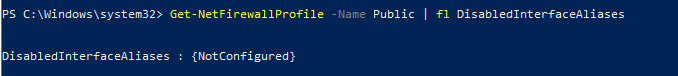
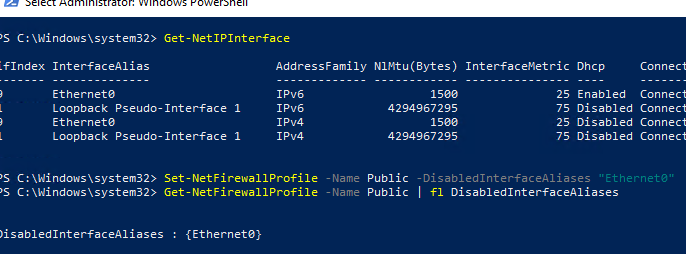
Проверим, что все параметры брандмауэра применяются ко всем сетевым интерфейса компьютера.
Get-NetFirewallProfile -Name Public | fl DisabledInterfaceAliases
Если все интерфейсы защищены, команда должна вернуть:
Можно отключить определенный профиль для интерфейса (вывести список имен интерфейсов можно с помощью командлета Get-NetIPInterface).
Set-NetFirewallProfile -Name Public -DisabledInterfaceAliases «Ethernet0»
Как вы видите, теперь профиль Public не применяется к интерфейсу Ethernet0:
Вы можете настроить параметры логирования сетевых подключений на уровне каждого профиля. По умолчанию журналы Windows Firewall хранятся в каталоге %systemroot%\system32\LogFiles\Firewall, размер файла – 4 Мб. Вы можете изменить включить журналирование подключений и увеличить максимальный размер файла:
Set-NetFireWallProfile -Profile Domain -LogBlocked True -LogMaxSize 20000 -LogFileName ‘%systemroot%\system32\LogFiles\Firewall\pfirewall.log’
Создание, редактирование и удаление правил Windows Firewall из PowerShell
Для управления правилами брандмауэра есть 9 командлетов:
- New-NetFirewallRule
- Copy-NetFirewallRule
- Disable-NetFirewallRule
- Enable-NetFirewallRule
- Get-NetFirewallRule
- Remove-NetFirewallRule
- Rename-NetFirewallRule
- Set-NetFirewallRule
- Show-NetFirewallRule
Рассмотрим несколко простых примеров открытия портов в Windows Firewall.
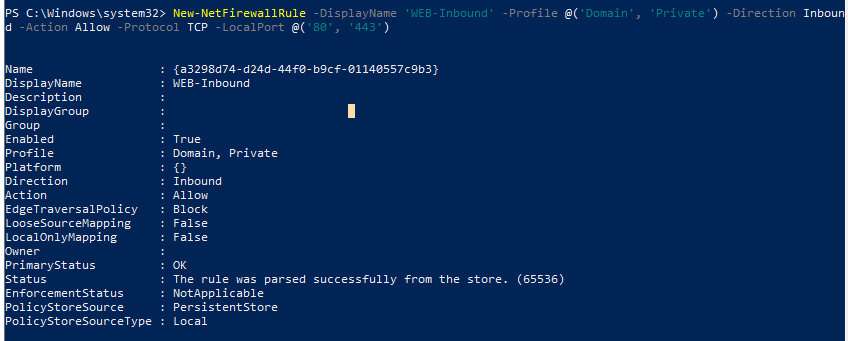
Например, вы хотите разрешить входящие TCP подключения на порты 80 и 443 для профилей Domain и Private, воспользуйтесь такой командой:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName ‘WEB-Inbound’ -Profile @(‘Domain’, ‘Private’) -Direction Inbound -Action Allow -Protocol TCP -LocalPort @(’80’, ‘443’)
Вы можете разрешить или заблокировать трафик для конкретной программы. Например, вы хотите заблокировать исходящие соединения для FireFox:
New-NetFirewallRule -Program “C:\Program Files (x86)\Mozilla Firefox\firefox.exe” -Action Block -Profile Domain, Private -DisplayName “Block Firefox” -Description “Block Firefox” -Direction Outbound
Разрешим входящее RDP подключение по порту 3389 только с IP одного адреса:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName «AllowRDP» –RemoteAddress 192.168.1.55 -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP –LocalPort 3389 -Action Allow
Чтобы разрешить ping для адресов из указанной подсети, используйте команды:
$ips = @(«192.168.1.50-192.168.1.60», «192.165.2.22-192.168.2.200», ”10.10.0.0/16”)
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName «Allow inbound ICMPv4» -Direction Inbound -Protocol ICMPv4 -IcmpType 8 -RemoteAddress $ips -Action Allow
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName «Allow inbound ICMPv6» -Direction Inbound -Protocol ICMPv6 -IcmpType 8 -RemoteAddress $ips -Action Allow
Чтобы отредактировать имеющееся правило брандмауэра, используется командлет Set-NetFirewallRule. Например, вы хотите разрешить входящие подключения с указанного IP адреса для ранее созданного правила:
Get-NetFirewallrule -DisplayName ‘WEB-Inbound’ | Get-NetFirewallAddressFilter | Set-NetFirewallAddressFilter -RemoteAddress 192.168.1.20
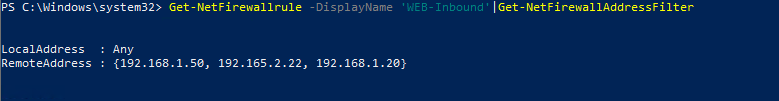
Если нужно добавить в правило файервола несколько IP адресов, используйте такой скрипт:
$ips = @(«192.168.1.50», «192.165.2.22»,”192.168.1.20”)
Get-NetFirewallrule -DisplayName ‘WEB-Inbound’|Set-NetFirewallRule -RemoteAddress $ips
Вывести все IP адреса, которые содержатся в правиле брандмауэра:
Get-NetFirewallrule -DisplayName ‘Allow inbound ICMPv4’|Get-NetFirewallAddressFilter
Вы можете включать/отключать правила файервола с помощью командлетов Disable-NetFirewallRule и Enable-NetFirewallRule.
Disable-NetFirewallRule –DisplayName ‘WEB-Inbound’
Чтобы разрешить ICMP (ping), выполните команду:
Enable-NetFirewallRule -Name FPS-ICMP4-ERQ-In
Чтобы удалить правило брандмауэре используется командлет Remove-NetFirewallRule.
Вывод правил Windows Firewall через PowerShell
Список активных правил для входящего трафика можно вывести так:
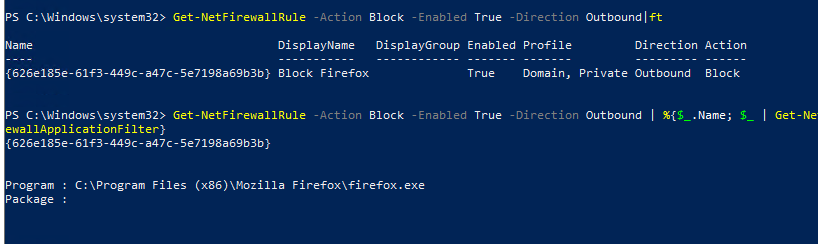
Если, например, нам нужно вывести список блокирующих исходящих правил:
Get-NetFirewallRule -Action Block -Enabled True -Direction Outbound
Если нужно отобразить имя программы в правиле:
Get-NetFirewallRule -Action Block -Enabled True -Direction Outbound | %
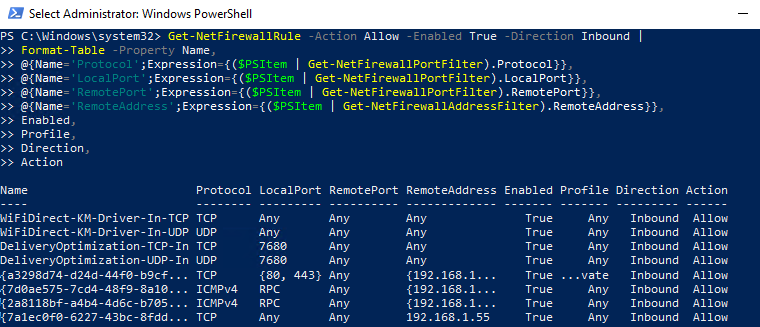
Как вы видите командлет Get-NetFirewallRule не выводит порты сетевые порты и IP адреса для правил брандмауэра. Чтобы вывести всю информацию о разрешенных входящих (исходящих) подключениях в более удобном виде с отображением номеров портов, используйте такой скрипт:
PowerShell предоставляет широкие возможности по управлению правилами Windows Firewall из командной строки. Вы можете автоматически запускать скрипты PowerShell для открытия/закрытия портов при возникновении определенных событий. В следующей статье мы рассмотрим простую систему на базе PowerShell и Windows Firewall для автоматической блокировки IP адресов, с которых выполняется удаленный перебор паролей по RDP на Windows VDS сервере.
Api для windows firewall
Windows Firewall Interface
This library provides Go with an interface for managing the Windows Firewall, using the Windows COM interface.
Normally Microsoft would expect that you would use the C++ API. Accessing it from C is not well documented, but supported.
In order to access netfw.h C interface, the CINTERFACE and COBJMACROS must be used. This will effectively allow you to access the class methods through an interface like this:
The C API wraps calls to the old Firewall API (compat_xp prefix) and the new Advanced Security COM API (ascom prefix).
Building the code on MinGW
The code is largely in C, so a C program is provided for testing the API. Besides defining the CINTERFACE and COBJMACROS , the following libraries must be included:
This last DLL is not provided by MinGW, so it is bundled with the library to allow cross-compilation. This one will provide the symbols normally provided by FirewallAPI.dll in more mothern versions of Windows.
Example minimal MinGW GCC build line:
In Go, configuration should be automatic thorugh CGO, so just providing the right C compiler backend should suffice:
As before, substitute mingw-gcc for your MinGW binary.
Files in /doc folder
This folder keeps some files that should serve for documenting the process, since this library is touching internal parts of Windows and MinGW and required some fiddling.
These files are kept for documentation purposes:
- cpp_api.c: MSDN reference file that uses de C++ API.
- netfw.h: A reference implementation of netfw.h needed because MinGW didn’t provide one. This had to be slighltly modified to compile properly.
- netfw-xp.h: A modified version of netfw.h that works with MinGW. It only supports the old API for Windows XP.
- WinXPSP2FireWall. : A reference implementation of the Firewall API for Windows XP, which has a more sparse documentation over the Internet.
About
Control the Windows Firewall from Go, supports Windows XP API and Advanced Security COM API
Api для windows firewall
Windows Firewall Helper Class Library


A class library to manage the Windows Firewall as well as adding your program to the Windows Firewall Exception list.
This project supports dotNet4.6 and NetStandard2, therefore, is compatible with NetCore2+ and any version of dotNet equal or greater than version 4.6.
Even though it is possible to reference this library under Linux or Mac; it’s obviously not going to work.
This readme file is for the version 2 of this library. Please check the V1 branch for older readme file.

This library is available as a NuGet package at nuget.org.
Help me fund my own Death Star


—OR—
You can always donate your time by contributing to the project or by introducing it to others.
The starting point of this library is the FirewallManager static class which can be used to get the instance of the class managing the firewall currently on the system.
If you are only targeting WinVista+ consider using the FirewallWAS.Instance static property to access the library’s functionality. It allows for more flexibility and is easier to work with.
This static class contains properties about the currently active Windows Firewall management class instance or the registered third party firewall products. This class also provides methods to register a third-party firewall product.
WindowsFirewallHelper.FirewallManager Static Properties
- FirewallManager.Instance : Gets an instance of the Windows Firewall management class.
- FirewallManager.Version : Gets the type of firewall that FirewallManager.Instance property returns.
- FirewallManager.IsServiceRunning : Gets a boolean value indicating if the Windows Firewall Service is currently running.
- FirewallManager.RegisteredProducts : Gets an array containing all registered third party firewall products.
WindowsFirewallHelper.FirewallManager Static Methods
- FirewallManager.RegisterProduct() : Registers a third-party firewall product returning a handle that will unregisters the product while getting disposed.
This namespace contains shared and general classes as well as the main starting point of this library, FirewallManager class.
- FirewallManager : A static class to manage the current active firewall
- FirewallProtocol : A class representing a Firewall Protocol
- FirewallLegacy : Contains properties and methods of Windows Firewall v1 — Implementing the IFirewall interface
- FirewallLegacyProfile : Contains properties of a Windows Firewall v1 profile — Implementing the IFirewallProfile interface
- FirewallWAS : Contains properties and methods of Windows Firewall with Advanced Security (Vista+) — Implementing the IFirewall interface
- FirewallWASProfile : Contains properties of a Windows Firewall with Advanced Security profile (Vista+) — Implementing the IFirewallProfile interface
- FirewallWASRuleGroup : Contains properties and methods for managing a Windows Firewall with Advanced Security rule group (Vista+)
- FirewallWASInternetControlMessage : Representing an Internet Control Message (ICM) type
- FirewallProduct : Representing a third-party firewall product
- FirewallProductRegistrationHandle : Representing a third-party firewall product registration handle that will automatically unregisters the product while getting disposed.
- IFirewall : Defines expected methods and properties of a firewall program or API
- IFirewallProfile : Defines expected properties of a firewall profile
- IFirewallRule : Defines expected properties of a firewall rule
- IAddress : Defines expected methods of a network address
This namespace contains classes that can be used for direct manipulation of a firewall rule.
- FirewallLegacyApplicationRule : Contains properties of a Windows Firewall v1 application rule — Implementing the IFirewallRule interface
- FirewallLegacyPortRule : Contains properties of a Windows Firewall v1 port rule — Implementing the IFirewallRule interface
- FirewallWASRule : Contains properties of a Windows Firewall with Advanced Security rule — Implementing the IFirewallRule interface
- FirewallWASRuleWin7 : Contains properties of a Windows Firewall with Advanced Security rule for Windows 7+ — Extending the FirewallWASRule class
- FirewallWASRuleWin8 : Contains properties of a Windows Firewall with Advanced Security rule for Windows 8+ — Extending the FirewallWASRuleWin7 class
This namespace contains exception classes that might be thrown when using this library
- FirewallLegacyNotSupportedException : The exception that is thrown when an invoked method or action is not supported with the ‘Windows Firewall API v1’ — Extending the NotSupportedException class
- FirewallWASNotSupportedException : The exception that is thrown when an invoked method or action is not supported with the ‘Windows Firewall with Advanced Security’ — Extending the NotSupportedException class
- FirewallWASInvalidProtocolException : The exception that is thrown when a passed FirewallProtocol is invalid for a ‘Windows Firewall with Advanced Security’ action or method — Extending the `InvalidOperationException« class
This namespace contains the classes needed for manipulating or understanding a network address or a network service.
- SingleIP : Represents a single network IP address — Implementing the IAddress interface
- IPRange : Represents a range of network IP addresses — Implementing the IAddress interface
- NetworkAddress : Represents a range of network IP addresses by subnet — Implementing the IAddress interface
- SpecialAddress : An abstract class represents a special network address or network service — Implementing the IAddress interface
- DefaultGateway : Represents the default network gateway — Extending the `SpecialAddress« class
- LocalSubnet : Represents thelocal network subnet — Extending the `SpecialAddress« class
- DHCPService : Represents the DHCP service — Extending the `SpecialAddress« class
- DNSService : Represents the DNS service — Extending the `SpecialAddress« class
- WINSService : Represents the WINS service — Extending the `SpecialAddress« class
This namespace contains the interface s and enum s that is used to access the underlying COM objects. Some of these types are public and can be used to directly modify a COM object. Usually firewall rules. Rest of types are internal to this library.
Check the ‘WindowsFirewallHelper.Sample’ and ‘WindowsFirewallHelper.NetCoreSample’ projects as a brief example of what can be done using this class library.
- Creating and registering a new application exception rule for outbound traffic on the currently active profile:
- Creating and registering a new port rule for inbound traffic on the currently active profile:
- Getting the list of all registered rules:
- Disabling notifications for all firewall profiles:
- Creating a heavily customized application rule (Some parts of the following code are only applicable to Windows Vista, Windows 7 and above):
- Working directly with the desired firewall management class without using the FirewallManager to add a new port rule (Following example is limited to Windows 8 and above):
The MIT License (MIT)
Copyright (c) 2016-2020 Soroush
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the «Software»), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED «AS IS», WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
About
A class library to manage the Windows Firewall as well as adding your program to the Windows Firewall Exception list.