- Ubuntu Wiki
- AppleMagicMouse
- Pairing the Magic Mouse
- Problem: Pairing does not persist between reboots on Maverick (10.10)
- Multitouch status
- Finding your input device
- Installing PyMT and configuring it
- Related links
- Bluetooth mouse
- Contents
- Configuration
- Apple Magic Mouse scroll speed
- Apple Magic Mouse middle click
- Mouse pairing and dual boot
- Troubleshooting
- Mouse lag
- Problems with the USB dongle
- Mouse always disconnects
- Thinkpad Bluetooth Laser Mouse problems
- Kensington Expert Wireless Trackball problems
- Problems with the Logitech BLE mouse (M557, M590, anywhere mouse 2, etc)
- Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
- Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
- Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
- Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
- Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
- Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
- Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
- Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
- Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
- Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
- Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
- Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
- Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
- Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
- Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
- Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
- Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
- Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
- Ubuntu Documentation
- Ubuntu 10.04 and earlier
- README
- INSTALLING THE MAGICMOUSE DRIVER
Ubuntu Wiki
AppleMagicMouse

The Magic Mouse is a multi-touch mouse produced by Apple Inc.
It can be used as a single-touch or multi-touch device in Ubuntu by pairing it using the Bluetooth utilities in Ubuntu. The following setup instructions only need to be followed once, then Ubuntu will recognize the Magic Mouse without further configuration.
Note: This has been tested in Ubuntu Maverick (10.10) only.
Pairing the Magic Mouse
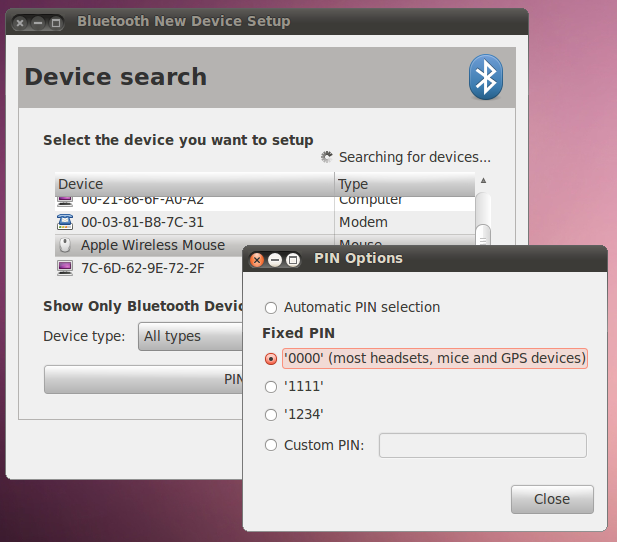
Once you have inserted batteries in your Magic Mouse, if your system is Bluetooth-capable and its radio is enabled, go to System > Preferences > Bluetooth and click on Setup new device. . Once the Bluetooth setup dialog opens, you should see you mouse listed. Click once on it, then choose «PIN options..». Make sure «0000» is selected under «Fixed PIN»:
Clicking Forward should then complete the pairing, which Ubuntu will remember.
The Magic Mouse can be forced in pairing mode by turning it off and on again (the «on» position will show green color in the switch position).
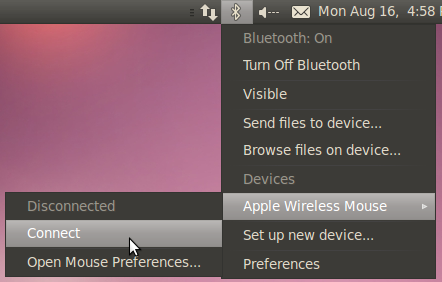
Once the device has been connected once or moved from another system, you can force pairing again by going to the Bluetooth applet and choosing Apple Wireless Mouse > Connect (if a PIN is asked, you can provide 0000 as the PIN code and press Enter to pair the mouse):
Once these steps have been completed the mouse will remain available in Ubuntu.
Problem: Pairing does not persist between reboots on Maverick (10.10)
If you find that you are not being prompted to «Always grant access» (refer to the Apple Magic Trackpad article) and that the device is not available after a reboot (i.e., you have to reconnect), try adding the pincode for the device (0000) to /var/lib/bluetooth/
/pincodes, like so:
Determine the physical (model-specific) and unique device IDs from the output of lsinput (from the «input-tools» package) as shown below.
/pincodes as the root user (or with sudo): Add this line to the new file, save, and exit:
is a backslash-escaped physical device ID, like D8\:30\:62\:38\:18\:02, and is your device’s unique ID, both from the output of lsinput.
Multitouch status
Finding your input device
Once your mouse has been paired, the hid_magicmouse module should automatically load. To verify this, issue the following command from a terminal:
Here is example output for lsinput (from the «input-tools» package) with a Magic Mouse present (other irrelevant input device removed):
In this case the input device would be /dev/input/event7. The input device number would be 7.
For more information on testing this device for multi-touch support, see Multitouch/Testing.
Installing PyMT and configuring it
To experiment multi-touch capabilities of the Apple Magic Mouse, you can try using PyMT, an open source library for developing multi-touch applications. You will need the device name as ound aboce (in this example, /dev/input/event7). See the Ubuntu PyMT documentation for this.
Related links
Multitouch — Ubuntu community documentation
Multitouch/AppleMagicTrackpad — community documentation for the Magic Trackpad, a similar device with some support in Ubuntu 10.10 and later for additional multitouch gestures.
Multitouch/AppleMagicMouse (последним исправлял пользователь cprofitt 2013-04-24 12:53:34)
The material on this wiki is available under a free license, see Copyright / License for details.
Источник
Bluetooth mouse
This article describes configuration & troubleshooting steps specific to Bluetooth mice. The information here builds on the main Bluetooth article, and assumes the user has already followed any installation, configuration, or troubleshooting from that article.
Contents
Configuration
Apple Magic Mouse scroll speed
If the scroll speed is too slow, you can try
Scroll speed can be set from 0 to 63.
If the speed suits you, you can make the change permanent in /etc/modprobe.d/
Apple Magic Mouse middle click
If you find the middle click to be too finicky, you can disable it
If this setting suits you, you can make the change permantent in /etc/modprobe.d/
Mouse pairing and dual boot
When dual booting Windows and Linux, you may find yourself having to re-pair your Bluetooth mouse again and again. This will happen every time you switch OS, because when you pair your device, your Bluetooth service generates a unique set of pairing keys. And the core reason is that the set of pairing keys cannot be shared between the two OS.
First, your computer stores the Bluetooth device’s mac address and pairing key. Second, your Bluetooth device stores your computer’s mac address and the matching key. This usually works fine, but the mac address for your Bluetooth port will be the same on both Linux and Windows (it is set on the hardware level). However, when you re-pair the device in Windows or Linux, it generates a new key. That key overwrites the previously stored key on the Bluetooth device. Windows overwrites the Linux key and vice versa.
To fix the problem, follow the instructions on [1].
if using a Bluetooth LE device use this python script, slightly edited to adapt for arch, originally discussed on [2].
Troubleshooting
Mouse lag
If you experience mouse lag you can try to increase the polling rate. See Mouse polling rate for more information.
You can try to set the minimum/maximum latency for the mouse in BlueZ [3]:
Add or modify the following section in /var/lib/bluetooth/mac-of-your-adapter/mac-of-your-mouse/info (adapt the path accordingly):
Also, you can use hcitool (in bluez-utils-compat AUR ) to change latency parameters of the device:
Note that this method is only effective for the current connection. If the mouse gets disconnected, you will need to execute again.
Alternatively, you can change the default latency settings via debugfs. See /sys/kernel/debug/bluetooth/hci0/conn_
This example will solve the lag problems, but you must un pair and pair the mouse:
Problems with the USB dongle
If you have trouble with your USB dongle, you may also want to try:
At this point, you should get an hci0 device with:
Sometimes the device is not active right away. Try starting the interface with:
and searching for devices as shown above.
Mouse always disconnects
If the mouse stops working but works again after restarting bluetooth, or the mouse seemingly keeps «falling asleep» after a couple of seconds of inactivity (which is the case for at least some models of Dell XPS 13 [4]), you may need to disable USB autosuspend for the selected device.
The issue may also lie in the device timeout and HID settings. See #Thinkpad Bluetooth Laser Mouse problems.
If you are using a Logitech device, this issue may be resolved by following the procedure in #Problems with the Logitech BLE mouse (M557, M590, anywhere mouse 2, etc).
Thinkpad Bluetooth Laser Mouse problems
If you are experiencing that your Thinkpad Bluetooth Laser Mouse rapidly connects and then (after a few milliseconds) disconnects again every few seconds (when you move the mouse or press a button), try pairing it with the code 0000 instead pairing without a code.
If the above is unhelpful, the issue may be in the device timeout settings. Edit/create the file /etc/bluetooth/input.conf and apply the following changes:
These changes will prevent device timeout in order to remain connected. The second setting enables userspace HID handling for bluetooth devices. Restart bluetooth.service to test changes. You also may need a reboot and to re-pair the device.
Kensington Expert Wireless Trackball problems
The Kensington Expert Wireless Trackball has default polling rates in the 200ms range, which make it laggy. To fix that, add or modify the [ConnectionParameters] section in /var/lib/bluetooth/mac-of-your-adapter/mac-of-your-mouse/info (adapt the path according to your mouse bluetooth address) as shown above, especially lower the latency to a small number or even 0 .
Problems with the Logitech BLE mouse (M557, M590, anywhere mouse 2, etc)
In some case, the mouse is paired but not moving when used. The device add to be trusted and unblocked. First of all open a terminal and run bluetoothctl
- Power off the bluetooth:
- Power on the bluetooth, then enable the pairing method on the mouse if needed:
- List the available bluetooth devices, you have to copy the mouse device ID XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:
- Unpair the device if already paired:
- Put device in pairing mode (typically by long pressing a button, or a key combination on some keyboards). It will be detected by scan and displayed. Mind that the device ID may have changed (slightly), so copy the device ID shown by the scan.
- Trust the device:
- Pair the mouse with the computer:
- Connect the computer with the mouse:
- Unblock the device control:
- Power the bluetooth off and on.
If the mouse does not work directly, just power off and power on the mouse.
In some cases, it may also be necessary to load the uhid kernel module.
Источник
Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
Чего там с драйверами под новую эпловскую мышку ? Если я правильно понял, то без них не будет скроллинг работать — не кошерно.
Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
а нахрена этот зонд нужен в наших уютных линуксах?
Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
А ты представь, как удобно можно путешествовать между виртуальными мониторами. Во все стороны
Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
под веществами что ли? я за компьютером не путешествую, а работаю
Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
Genius Traveler 915BT — металлический верх, резина по бокам, с полпинка в моём линуксе работает, проблем с поддержкой мыши мне ещё не хватало. Я счастлив.
Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
> а нахрена этот зонд нужен в наших уютных линуксах?
Отучаемся говорить за всех (с)
Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
> Genius Traveler 915BT
Год назад брал пару штук. Не сложилось. Обе садились за сутки. Пока логитеками пользуюсь (450, 555, 470).
Все-таки хочется новую ябломышку. Прикалывает отсутствуие кнопок и колеса.
Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
> Прикалывает отсутствуие кнопок и колеса.
+1, тоже хочется. но, как я понял, оно пока только под маком работает.
Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
По неделе живёт, ЧЯДНТ?
Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
тоже интересно, а пока жду — 15 декабря придет, тогда посмотрю
Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
> По неделе живёт, ЧЯДНТ?
ХЗ. Может мне совсем не повезло. Все равно мало. Грамотные мышки на синезубе живут пару месяцев. Ну по крайней мере, мои логитековские.
В свое время очень возбудился на эту мышку. Конструктив клевый. Только вот, не срослось 🙁
Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
Отпишитесь обязательно. Буду ждать.
По свединиям ОБС — на венде работают клики 2 кнопками, а дальше без драйверов непонятно. Мне всякие многопальцевые осьминоговые жесты не особо нужны. Только скроллинг, как колесиком.
Излазал крупные линуксовые форумы — там пока нема отзывов.
Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
Возможно, но у меня аккумуляторам — 3 года.
Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
мыши у Apple традиционно образец дизайнерского «креатива» и неудобства
Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
> В свое время очень возбудился на эту мышку
Быть гомосеком уже не модно? На периферию возбуждаемся?
Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
Ну вам виднее, что модно. Я не в курсе.
Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
Раз мышь, то это скорее зоофилия.
Apple Magic Mouse + Linux ?
А если её сырыми руками брать, то не будет работать, как и обычный тачпад?
Судя по картинке, её держать неудобно, она настолько тонкая, что ухватиться не за что.
Вообще, Openoffice Mouse (кстати, я так и не понял, фейк ли это), судя по картинке, и удобнее, и функциональнее, чем сабж, за исключением того, что те кнопки, которые находятся сзади от классических «правой» и «левой», будут мешаться (опять же, если судить по картинке). Можно было бы ими пожертвовать, а классические кнопки сделать побольше. Ну и справа тоже джойстик могли бы сделать, чтобы и левшам можно было бы пользоваться, и правши, возможно, применение бы нашли.
Источник
Ubuntu Documentation
The Magic Mouse is a wireless mouse with a multi-touch surface that serves as mouse buttons and scroll wheel. It should work with Ubuntu 11.04 out of the box. To configure the mouse
- Open Bluetooth Preferences
- Switch on the Magic Mouse
- Click Set up new Device.
- The set up wizard will appear, click Forward
- Your computer will scan for new devices. Once your mouse is found select it and click Forward
- You will be asked for a pin to pair the mouse. Enter 0000 and then click OK.
- Click Finish
Ubuntu 10.04 and earlier
For Ubuntu 10.04 and 9.10 there is a driver for this device that is still under development, you can download it from the following address:
README
This code contains a Linux kernel driver for the magic mouse. Please see the INSTALL file for directions on how to use it with your kernel.
This code also contains three standalone programs:
hid-parse reads one or more input files (specified on the command line) that contain hexadecimal-formatted HID report descriptors, and prints out human-readable text forms of the descriptors. It should be considered fairly complete and stable.
mtalk talks to an Apple Magic Mouse (using L2CAP with the HID control and interrupt Protocol and Service Multiplexors [PSMs]) and prints human-readable forms of the messages that it receives. Typically the only command-line parameters you would pass are -r . It should be considered 85% complete.
usb-bt-dump reads a text dump in the format generated by Linux’s usbmon (e.g. /sys/kernel/debug/usb/usbmon/0u) to parse Bluetooth messages at various layers (HCI, L2CAP, etc) and print annotations with the parsed form. It is woefully incomplete and buggy and will probably not be maintained.
I wrote usb-bt-dump first, followed by mtalk, followed by hid-parse. mtalk is the only one that I expect to modify going forward.
INSTALLING THE MAGICMOUSE DRIVER
The Magic Mouse driver for linux is a module named hid-magicmouse.
Older kernels do not have all the hooks that a driver needs to talk to the Magic Mouse. These are provided in this directory; you must apply them and rebuild the kernel before you can load hid-magicmouse. To apply the patch series, change to your linux-2.6 directory, and run either:
OR (in a Bourne shell, such as /bin/sh):
This series were cherry-picked from the HID and Bluetooth trees onto v2.6.32.8. They should be filtering from the HID and Bluetooth trees into the mainstream kernel between v2.6.33 and v2.6.34. This directory’s hid-magicmouse.c should match the final result of applying the patches in sequence.
You will obviously need to reboot into the new kernel before the module can be loaded, but at that point user-space should see it as a normal input device, including a(n emulated) scroll wheel and middle button.
AppleMagicMouse (последним исправлял пользователь alex-moreati 2011-07-02 13:47:36)
The material on this wiki is available under a free license, see Copyright / License for details
You can contribute to this wiki, see Wiki Guide for details
Источник