- Настройка WiFi в Arch Linux из командной строки
- Сканирование сети
- Настройка Wi-Fi с помощью netctl
- Простой способ – Wifi-menu
- Сложный способ
- Запуск netctl
- Другие утилиты
- Заключение
- Arch linux wifi 2021
- Contents
- Installation
- Usage
- iwctl
- Connect to a network
- Connect to a network using WPS/WSC
- Disconnect from a network
- Show device and connection information
- Manage known networks
- Network configuration
- WPA-PSK
- WPA Enterprise
- EAP-PWD
- EAP-PEAP
- TTLS-PAP
- Eduroam
- Other cases
- Optional configuration
- Disable auto-connect for a particular network
- Disable periodic scan for available networks
- Enable built-in network configuration
- IPv6 support
- Setting static IP address in network configuration
- Select DNS manager
- Deny console (local) user from modifying the settings
- Troubleshooting
- Verbose TLS debugging
- Restarting iwd.service after boot
- Connect issues after reboot
- Wireless device is not renamed by udev
- No DHCP in AP mode
Настройка WiFi в Arch Linux из командной строки
Оригинал: How To Setup A WiFi Network In Arch Linux Using Terminal
Автор: Mohd Sohail
Дата публикации: 26 октября 2016 года
Перевод: А. Кривошей
Дата перевода: октябрь 2017 г.
Если вы ранее не работали с дистрибутивом Arch CLI, то одной из самых сложных задач для вас может стать настройка WiFi в терминале. В этой статье проведу вас через пошаговое руководство по настройке подключения Arch Linux к вашей сети WiFi.
Существует множество программ по настройке беспроводного соединения в Linux, для настройки подключения к интернету мы могли бы использовать ip и iw , но это было бы немного сложно для новичков. Поэтому мы будем использовать netctl, это инструмент командной строки, применяемый для настройки и управления сетевыми подключениями с помощью профилей.
Примечание: для всех настроек вам будут нужны права root.
Сканирование сети
Определите имя своего сетевого интерфейса с помощью команды:
Выполните следующую команду:
Запустите поиск доступных сетей WiFi:
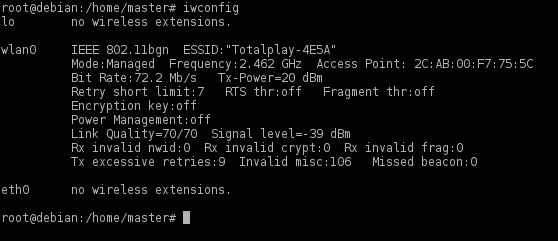
Примечание: здесь interface — это ваш сетевой интерфейс, который вы ранее нашли с помощью команды iwconfig.
Настройка Wi-Fi с помощью netctl
Перед настройкой соединения с помощью netctl необходимо проверить совместимость вашей сетевой карты с Linux.
Эта команда проверит, загружен ли модуль ядра — драйвер беспроводной карты. Ее вывод должен быть примерно таким:
Если ядро не загрузило дравер, вам необходимо установить его, подключившись к интернету по Ethernet (или с помощью мобильной сети). Официальный Linux Wireless Wiki: https://wireless.wiki.kernel.org/
Если ваша беспроводная карта совместима с Linux, можно приступать к настройке netctl.
netctl работает с профилями — то есть файлами, в которых содержится информация о соединении. Профиль можно создать двумя способами.
Простой способ – Wifi-menu
Если вы хотите использовать wifi-menu, у вас должен быть установлен dialog.
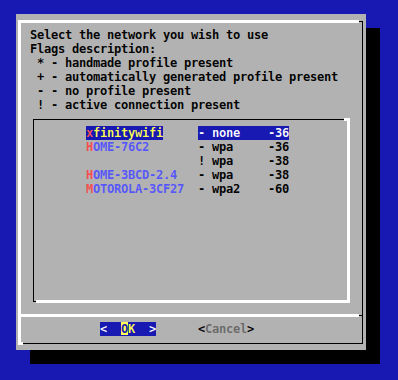
1. Выполните команду: wifi-menu
2. Выберите вашу сеть для настройки wifi в arch.
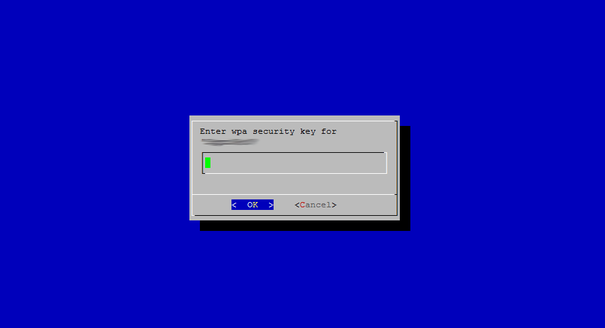
3. Введите правильный пароль и ждите.
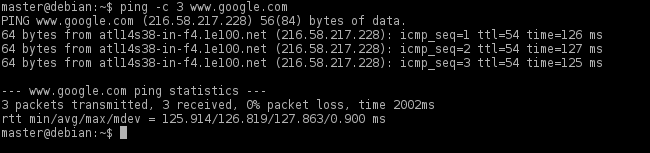
Если вы не получили сообщения о неудачном подключении, вы можете проверить его работу командой:
Если он пингуется, то сеть настроена успешно. Теперь вы подключены к сети Wi-Fi в Arch Linux. Если у вас возникли какие-либо ошибки, повторите описанные выше шаги. Возможно, вы что-то пропустили.
Сложный способ
По сравнению с вышеописанным, этот метод немного сложнее. В приведенной выше команде сетевой профиль был настроен автоматически. Сейчас мы настроим профиль вручную. Но не беспокойтесь, это будет ненамного сложнее. Давайте начнем!
1. Первое, что вы должны сделать, это узнать имя вашего интерфейса, как правило, это wlan0/wlp2s0, но может быть много исключений. Чтобы узнать имя вашего интерфейса, необходимо использовать команду iwconfig.
2. Выполните команду:
В этой поддиректории вы увидите различные примеры профилей.
3. Скопируйте пример своего профиля в /etc/netctl/your_profile
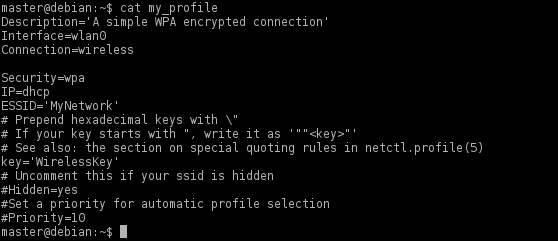
4. Вы можете просмотреть содержимое профиля с помощью команды:
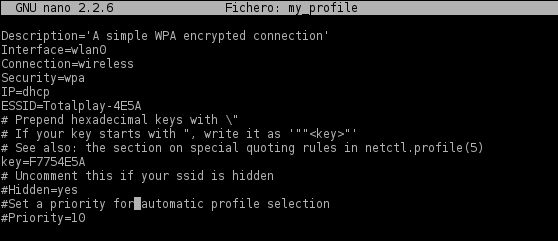
5. Отредактируйте следующие поля в профиле с помощью vi или nano:
1. Interface: это должен быть wlan0
2. ESSID: имя вашей сети
3. key: пароль вашей сети
Запуск netctl
1. Выполните команды:
Вы должны увидеть профиль, созданный с помощью wifi-menu, например wlan0-SSID; или, если вы использовали сложный способ, то вы должны увидеть профиль, созданный вами.
2. Запустите свой профиль с помощью команды:
3. Протестируйте подключение:
4. В конце вы должны выполнить следующую команду:
При этом будет создана и активирована служба systemd, которая будет запускаться при загрузке компьютера. Теперь вы настроили wifi в своем Arch Linux.
Другие утилиты
Вы также можете использовать для настройки беспроводного соединения и другие программы, например iw:
iw dev wlan0 link – статус
iw dev wlan0 scan – сканирование сетей
iw dev wlan0 connect your_essid – подключение к открытой сети
iw dev wlan0 connect your_essid key your_key — подключение к сети с защитой WEP, используя шестнадцатеричный ключ.
Заключение
Итак, на этом все! Я упомянул 3 способа подключения к сети WiFi в Arch Linux. Одна вещь, на которую я хочу обратить внимание: когда вы выполняете первую команду, обратите внимание на интерфейс. В следующей команде, где мы сканируем сети, используйте не interface, а имя вашего интерфейса, например wlan0 или wlp2s0 (которое вы узнали из вывода предыдущей команды). Не забудьте поделиться этой статьей со своими друзьями в социальных сетях. Спасибо!
Источник
Arch linux wifi 2021
iwd (iNet wireless daemon) is a wireless daemon for Linux written by Intel. The core goal of the project is to optimize resource utilization by not depending on any external libraries and instead utilizing features provided by the Linux Kernel to the maximum extent possible.
iwd can work in standalone mode or in combination with comprehensive network managers like ConnMan, systemd-networkd and NetworkManager.
Contents
Installation
Usage
The iwd package provides the client program iwctl , the daemon iwd and the Wi-Fi monitoring tool iwmon .
Start/enable iwd.service so it can be controlled using the iwctl command.
iwctl
To get an interactive prompt do:
The interactive prompt is then displayed with a prefix of [iwd]# .
To list all available commands:
Connect to a network
First, if you do not know your wireless device name, list all Wi-Fi devices:
Then, to scan for networks:
You can then list all available networks:
Finally, to connect to a network:
If a passphrase is required, you will be prompted to enter it. Alternatively, you can supply it as a command line argument:
Connect to a network using WPS/WSC
If your network is configured such that you can connect to it by pressing a button (Wikipedia:Wi-Fi Protected Setup), check first that your network device is also capable of using this setup procedure.
Then, provided that your device appeared in the above list,
and push the button on your router. The procedure works also if the button was pushed beforehand, less than 2 minutes earlier.
If your network requires to validate a PIN number to connect that way, check the help command output to see how to provide the right options to the wsc command.
Disconnect from a network
To disconnect from a network:
Show device and connection information
To display the details of a WiFi device, like MAC address:
To display the connection state, including the connected network of a Wi-Fi device:
Manage known networks
To list networks you have connected to previously:
To forget a known network:
Network configuration
By default, iwd stores the network configuration in the directory /var/lib/iwd . The configuration file is named as network.type , where network is the network SSID and .type is the network type, either .open, .wep, .psk or .8021x. The file is used to store the encrypted PreSharedKey and optionally the cleartext Passphrase and can also be created by the user without invoking iwctl . The file can be used for other configuration pertaining to that network SSID as well. For more settings, see iwd.network(5) .
WPA-PSK
A minimal example file to connect to a WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK secured network with SSID «spaceship» and passphrase «test1234»:
To calculate the pre-shared key from the passphrase, one of these two methods can be used:
- Enter the passphrase in cleartext in the configuration file:
The pre-shared key will be appended to the file at the first connect:
- Or the pre-shared key can be calculated from the SSID and the passphrase using wpa_passphrase (from wpa_supplicant ) or wpa-pskAUR . See wpa_supplicant#Connecting with wpa_passphrase for more details.
WPA Enterprise
EAP-PWD
For connecting to a EAP-PWD protected enterprise access point you need to create a file called: essid.8021x in the /var/lib/iwd directory with the following content:
If you do not want autoconnect to the AP you can set the option to False and connect manually to the access point via iwctl . The same applies to the password, if you do not want to store it plaintext leave the option out of the file and just connect to the enterprise AP.
EAP-PEAP
Like EAP-PWD, you also need to create a essid.8021x file in the directory. Before you proceed to write the configuration file, this is also a good time to find out which CA certificate your organization uses. This is an example configuration file that uses MSCHAPv2 password authentication:
TTLS-PAP
Like EAP-PWD, you also need to create a essid.8021x file in the directory. Before you proceed to write the configuration file, this is also a good time to find out which CA certificate your organization uses. This is an example configuration file that uses PAP password authentication:
Eduroam
Eduroam offers a configuration assistant tool (CAT), which unfortunately does not support iwd. However, the installer, which you can download by clicking on the download button then selecting your university, is just a Python script. It is easy to extract the necessary configuration options, including the certificate and server domain mask.
The following table contains a mapping of iwd configuration options to eduroam CAT install script variables.
| Iwd Configuration Option | CAT Script Variable |
|---|---|
| file name | one of Config.ssids |
| EAP-Method | Config.eap_outer |
| EAP-Identity | Config.anonymous_identity |
| EAP-PEAP-CACert | Config.CA |
| EAP-PEAP-ServerDomainMask | one of Config.servers |
| EAP-PEAP-Phase2-Method | Config.eap_inner |
| EAP-PEAP-Phase2-Identity | username@ Config.user_realm |
Other cases
More example tests can be found in the test cases of the upstream repository.
Optional configuration
File /etc/iwd/main.conf can be used for main configuration. See iwd.config(5) .
Disable auto-connect for a particular network
Create / edit file /var/lib/iwd/network.type . Add the following section to it:
Disable periodic scan for available networks
By default when iwd is in disconnected state, it periodically scans for available networks. To disable periodic scan (so as to always scan manually), create / edit file /etc/iwd/main.conf and add the following section to it:
Enable built-in network configuration
Since version 0.19, iwd can assign IP address(es) and set up routes using a built-in DHCP client or with static configuration. It is a good alternative to standalone DHCP clients.
To activate iwd’s network configuration feature, create/edit /etc/iwd/main.conf and add the following section to it:
There is also ability to set route metric with RoutePriorityOffset :
IPv6 support
Since version 1.10, iwd supports IPv6, but it is disabled by default. To enable it, add the following to the configuration file:
This setting is required whether you want to use DHCPv6 or static IPv6 configuration. It can also be set on a per-network basis.
Setting static IP address in network configuration
Add the following section to /var/lib/iwd/network.type file. For example:
Select DNS manager
At the moment, iwd supports two DNS managers—systemd-resolved and resolvconf.
Add the following section to /etc/iwd/main.conf for systemd-resolved :
Deny console (local) user from modifying the settings
By default iwd D-Bus interface allows any console user to connect to iwd daemon and modify the settings, even if that user is not a root user.
If you do not want to allow console user to modify the settings but allow reading the status information, then create a D-Bus configuration file as follows.
Troubleshooting
Verbose TLS debugging
This can be useful, if you have trouble setting up MSCHAPv2 or TTLS. You can set the following environment variable via a drop-in snippet:
Check the iwd logs afterwards by running journalctl -u iwd.service as root.
Restarting iwd.service after boot
On some machines, it is reported that iwd.service has to be restarted to work after boot. See FS#63912 and thread 251432. This probably occurs because the Linux kernel and services start too early and iwd starts before wireless network card powers on. As a workaround, extend the unit to add a delay:
Then reload the systemd manager configuration.
Connect issues after reboot
A low entropy pool can cause connection problems in particular noticeable after reboot. See Random number generation for suggestions to increase the entropy pool.
Wireless device is not renamed by udev
Since version 1.0, iwd disables predictable renaming of wireless device. It installs the following systemd network link configuration file which prevents udev from renaming the interface to wlp#s# :
As a result the wireless link name wlan# is kept after boot. This resolved a race condition between iwd and udev on interface renaming as explained in iwd udev interface renaming.
If this results in issues try masking it with:
No DHCP in AP mode
Clients may not receive an IP address via DHCP when connecting to iwd in AP mode. It is therefore necessary to enable network configuration by iwd on managed interfaces:
The mentioned file has to be created if it does not already exist.
Источник