- Ошибка bash permission denied
- Ошибка bash permission denied
- Выводы
- Bash permission denied Explanation and Solution
- Bash permission denied
- An Example Scenario
- The Solution
- Conclusion
- bash: permission denied error
- What do you mean by bash: ./program_name: permission denied error?
- Solution to fix the bash: ./program_name: permission denied error
- Solution Code
- How to resolve permission denied Linux error
- What is permission denied Linux error?
- Example of Permission denied Linux error
- How to resolve Permission denied Error
- Resolving Permission denied error related to script execution:
- Resolving permission denied Linux error while listing or writing to a file
- Resolving permission denied Linux error for specific user
- Download Free book
- Linux / Unix Find Command Avoid Permission Denied Messages
- Find command basic syntax
- How to hide or fix find command permission denied messages
- How does it works?
- Exclude all “permission denied” messages from “find” command on Linux
- Conclusion
Ошибка bash permission denied
Многие новички пытаются выполнить запись определенных значений в системные файлы с помощью операторов перенаправления ввода и вывода и получают ошибку bash permission denied. Эта ошибка выводится, даже если вы использовали sudo.
Казалось бы, sudo есть, значит права суперпользователя получены и все должно работать но тут все не так просто. В этой статье мы рассмотрим почему возникает ошибка bash permission denied и как ее обойти.
Ошибка bash permission denied
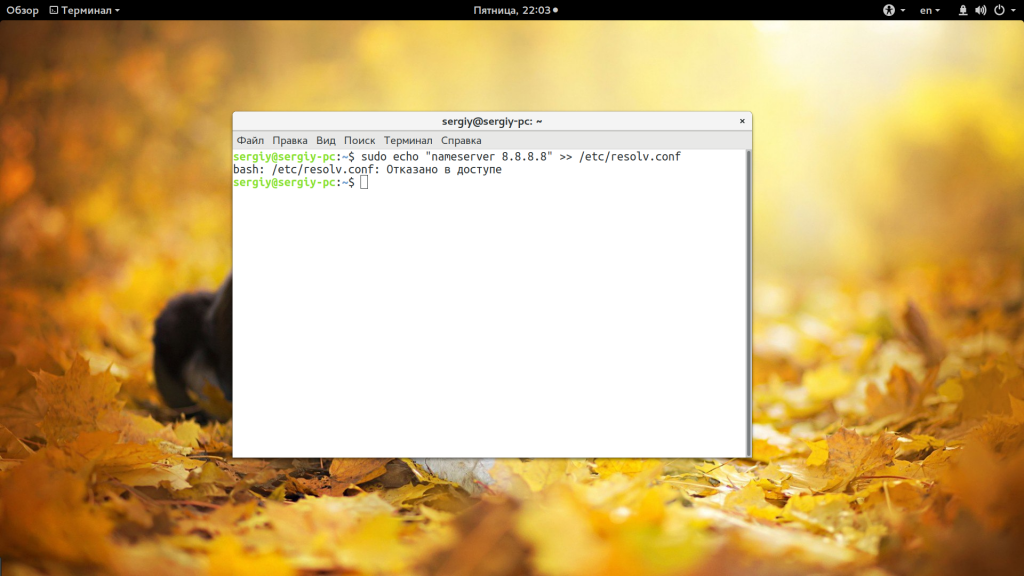
Допустим, вы выполняете команду:
sudo echo «nameserver 8.8.8.8» >> /etc/resolv.conf
А в результате вместо записи строчки в /etc/resolv.conf получаете ошибку:
bash: /etc/resolv.conf permission denied
В русской локализации это будет отказано в доступе bash linux. Так происходит потому что вы запускаете с правами суперпользователя утилиту echo и она честно выводит вашу строку в стандартный вывод bash с правами суперпользователя. Но bash запущен от обычного пользователя, и когда интерпретатор bash пытается записать полученную строчку в системный файл, естественно, что вы получите ошибку.
Но существует несколько способов обойти это ограничение, вы можете, например, использовать команду tee, которая записывает стандартный вывод в файл или запустить саму оболочку от имени суперпользователя. Рассмотрим сначала вариант с tee:
echo ‘текст’ | sudo tee -a /путь/к/файлу
echo ‘nameserver 8.8.8.8’ | sudo tee -a /etc/resolv.conf
Это очень простое решение, но, кроме того, вы можете запустить оболочку bash с правами суперпользователя, чтобы дать ей доступ на запись:
sudo sh -c ‘echo текст >> /путь/к/файлу’
sudo bash -c ‘echo текст >> /путь/к/файлу’
sudo bash -c ‘echo nameserver 8.8.8.8 >> /etc/resolv.conf
Еще одно решение, призванное, упростить эту команду, добавить такой код в
sudoe() <
[[ «$#» -ne 2 ]] && echo «Usage: sudoe
» && return 1
echo «$1» | sudo tee —append «$2» > /dev/null
>
Дальше для вывода строки в файл выполняйте:
sudoe ‘текст’ >> /путь/к/файлу
sudoe «nameserver 8.8.8.8» > /etc/resolv.conf
Теперь все будет работать, как и ожидалось, и ошибка bash отказано в доступе не появится. Еще можно поменять права на файл, а потом уже выводить в него строку. Но это очень неправильное решение. И даже не потому, что это небезопасно, а больше потому что там намного больше действий.
Выводы
В этой небольшой статье мы разобрали почему возникает ошибка bash permission denied при использовании команды echo для системных файлов, а также несколько путей ее решения. Как видите, все достаточно просто. Надеюсь, эта информация была полезной для вас.
Источник
Bash permission denied Explanation and Solution
Files on an operating system usually have permissions, making the file accessible to a limited range of people. For instance, some files on a computer are accessible only to administrators; other files are only accessible to a particular user.
- Career Karma matches you with top tech bootcamps Get exclusive scholarships and prep courses
If you try to run a file to which you have no access on a Linux computer, you will see a permission denied error. In this guide, we’re going to talk about the cause of this error and how you can solve the error. Let’s begin.
Bash permission denied
The Bash permission denied error happens when you try to run a file which you do not have permission to run. This may happen if a file can only be executed by a particular user or a group of which you are not a member.
- Career Karma matches you with top tech bootcamps Get exclusive scholarships and prep courses
Do you want to learn more about how a coding bootcamp can help you learn to code? Get started by finding the right bootcamp for you along with unlocking additional information about bootcamp cost and reviews.
On a Linux operating system, there are three types of permissions:
You can have permission to read and write a file without having execution privileges. Thus, if you encounter a Bash permission denied be sure to check whether you are allowed to run the file. You can check if you have permissions over a file by using the following command:
This command will give you information about file permissions. We discuss the output of this command in our The Solution section later in the article. Let’s look at an example scenario featuring the permission denied error, with a corresponding solution.
An Example Scenario
We have a file called example.sh. We can see this file by running the ls command. The ls command returns the following:
Career Karma entered my life when I needed it most and quickly helped me match with a bootcamp. Two months after graduating, I found my dream job that aligned with my values and goals in life!
Venus, Software Engineer at Rockbot
Find Your Bootcamp Match
We want to run our example.sh file. To do so, we can use the ./ notation:
This command lets us run the example.sh file which is present in our ./ directory (the directory we are presently viewing). Let’s see what happens when we try to run the file:
Our command returns an error.
The Solution
Our Bash shell is telling us that we do not have permissions to run our file. We can check what permissions we have by running the ls -la command:
We do not have execution privileges over any of our files. If there were an x after the rw in the first entry of the output above, we would know we can execute our file. The three characters after the first one represent read, write, and execute privileges for a user. Our group also does not have write or execute permissions.
To solve this issue, we need to give ourselves execution privileges:
This command gives our user execution (“x”) privileges over the example.sh file.
We can only run this command if we are allowed to change the privileges of the file. If this file was protected (owned by root, for example), then we would not be able to change this file.
The file is owned by the james system user so I can alter the file permissions on my james account. I could also use sudo to alter the file privileges, although this is not necessary because my user account has the necessary access.
Conclusion
The Bash permission denied error indicates you are trying to execute a file which you do not have permission to run. To fix this issue, use the chmod u+x command to give yourself permissions. If you cannot use this command, you may need to contact your system administrator to get access to a file.
Do you want to learn more about Bash? Check out our How to Learn the Command Line guide. This guide comes with top tips on how to learn Bash. You will also find a list of resources to help you accelerate your learning journey.
About us: Career Karma is a platform designed to help job seekers find, research, and connect with job training programs to advance their careers. Learn about the CK publication.
Источник
bash: permission denied error
While executing programs in Unix, a common problem which is encountered is the bash: ./program_name: permission denied error. The error usually occurs when the script you are trying to execute does not have the necessary permissions. Modifying the permissions of the script or assigning the correct ones will fix the error.
Let us look into the details of the error and also its solution.
What do you mean by bash: ./program_name: permission denied error?
The permission denied error is encountered when the script you are running does not have the execute permission. Unix and similar operating systems usually not execute a shell script if it does not have the permission to execute.
Look at the following example —
In this program, the error is raised as the script “myscript.sh” does not have execute permission.
To check the permissions assigned to a file, type in the following command in the command line –l
In the above result, you can see that the script only has read and write permissions, but no execute permissions (denoted by x). Hence, the file cannot be executed.
Solution to fix the bash: ./program_name: permission denied error
The only way to fix the error is to change the file permission settings of the script. You can do this using the chmod command, which stands for change mode. Look at the two commands –
- chmod u+x program_name– In this line, the chmod command will change the access mode to execute, denoted by x. only the file’s owner will have the permission to execute the file.
- sudo chmod +x program_name– Here, the chmod command will provide the execute permission to everyone as no reference is specified.
Chmod references include:
- u – The file owner
- g – Users who belong to the file’s group
- o – Users who are neither owners nor members of the file’s group
- a – Every user
Solution Code
Here, the chmod command assigns execute permission to every user, as no specific reference is mentioned. After running the script you can see that execute permission was assigned to the file.
You can check this by running the getfacl command. The getfacl command is used for displaying the file name, owner’s name, file group and the Access Control List (ACL). The default ACL will also be displayed.
After running this script, this is the final result –
Источник
How to resolve permission denied Linux error
This article will teach you quickly what is permission denied Linux error. And also what ways you can avoid permission denied error in Linux.
What is permission denied Linux error?
This error comes when you try to list files or try execute the file inside the directory where you don’t have sufficient permission. Since Linux operating system is very particular about its security aspect.
Example of Permission denied Linux error
Let’s say you are a normal user who is trying to list or trying change the directory inside the /root file-system. Since you do not have sufficient permissions system will respond with permission denied error message as below:
One way to avoid such error is to switch to root user using su – command. However this solution is not recommended since it will gain unnecessary access to all the root file system.
How to resolve Permission denied Error
Resolving Permission denied error related to script execution:
Let’s say you have created a shell script for performing any task. but when you try to execute the script you may end with below error due absence of permission denied error.
Now to avoid such case you need to add execute permission “x” to the file myshell.sh using chmod command as below:
In the last output you can see that there is “x” (execution) permission added after chmod command. So next time when you try to execute the shell script , it will execute without any error.
Resolving permission denied Linux error while listing or writing to a file
In this type of permission denied error you try to list or write the file in which you do not have sufficient permission to do so as below:
If you look at the permissions of the “myfolder” directory using ls -l command you will come to know about the permissions.
As per the permission given in above output only owner of the directory who is root can have all permission that is read, write and execute. So in such case you need to change the permission of the directory to read using below chmod command:
Now this time when normal user manmohan try to list directory he will not get the permission denied error.
In case you want to have write permission on this directory you need to specify w flag as well in chmod command as below:
Same is applicable to file level permission as well.
One more way is to changing the ownership of the directory using chown command. Since in our example we are getting error for user manmohan we will change ownership of the directory “myfolder” using below command.
Since manmohan user is now the owner of the directory he can able to do any operation on the directory. In case you want to recursive permission do not forget to add -r while chown command as below:
Resolving permission denied Linux error for specific user
In above method of changing the permission using chmod is not suitable as per my opinion. Because when you give permission to others, it will be open for all the users within the system. Which is wrong in terms of security perspective. To resolve this error specific to user you can implement it using access control list or ACL. Follow my article on Access control list ACL for the same.
Download Free book
Get your free copy of Linux command line Cheat Sheet.
Источник
Linux / Unix Find Command Avoid Permission Denied Messages
W hen I type find . -type d -name «foo» command I get Permission denied error messages. How do I exclude all “permission denied: messages from the find command under Linux or Unix like operating systems?
The find command is used to locate files on a Linux or Unix like operating system. The find command will search directory to match the supplied search criteria. You can search for files by
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | No |
| Requirements | find command+ Unix like os |
| Est. reading time | 2m |
type, name, owner, group, date, permissions and more. By default the find will search all subdirectories for you. Let us see how to hide and fix permission denied message when using the find on Linux or Unix-like system.
Find command basic syntax
The syntax is as follows:
find where-to-look criteria action
find /dir/to/search -name filetosearch
find /dir/to/search -name «*.c»
find /home/nixcraft/project/ -name «*.py» -print
In this example, find will search the /tmp directory for any files named “data*.txt” and display their pathnames:
Fig. 01: Find will show an error message for each directory on which you don’t have read permission.
How to hide or fix find command permission denied messages
In this above example, I do not have read permission for vmware-root and orbit-Debian-gdm directories. To to avoid this problem try the following syntax:
Sample outputs without permission denied spam from find command:
How does it works?
The 2>/dev/null at the end of the find command tells your shell to redirect the error messages (FD #2) to /dev/null, so you don’t have to see them on screen. Use /dev/null to to send any unwanted output from program/command. All data written on a /dev/null special file is discarded by the system. To redirect standard error to /dev/null and store file list to output.txt, type:
Exclude all “permission denied” messages from “find” command on Linux
There is one problem with the following command. It would filter out all error messages created by find command, not just the permission denied ones:
To avoid that try the following find command along with grep command on Linux or Unix-like systems:
In short you should use following syntax to skip “permission denied” errors messages when running find in Linux or Unix-based systems:
To store output to a file run:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Conclusion
You learned how to hide and fix permission denied messages when using the find command on your Linux, Unix, or macOS-based systems. Of course, we can also run the command as sudo when possible but avoid all this mess. Unfortunately, you will not get sudo or root access at all times. Hence, we talked about various methods here. For your ready references, sudo syntax would be as follows:
sudo find /dir/to/search -name «pattern» -action
sudo find / -name «jail.conf» -print
Please see find/bash command man page online or read it by typing the following man command:
man find
man bash
man zsh
man ksh
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
| Category | List of Unix and Linux commands |
|---|---|
| Documentation | help • mandb • man • pinfo |
| Disk space analyzers | df • duf • ncdu • pydf |
| File Management | cat • cp • less • mkdir • more • tree |
| Firewall | Alpine Awall • CentOS 8 • OpenSUSE • RHEL 8 • Ubuntu 16.04 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Linux Desktop Apps | Skype • Spotify • VLC 3 |
| Modern utilities | bat • exa |
| Network Utilities | NetHogs • dig • host • ip • nmap |
| OpenVPN | CentOS 7 • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Debian 8/9 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Package Manager | apk • apt |
| Processes Management | bg • chroot • cron • disown • fg • glances • gtop • jobs • killall • kill • pidof • pstree • pwdx • time • vtop |
| Searching | ag • grep • whereis • which |
| Shell builtins | compgen • echo • printf |
| Text processing | cut • rev |
| User Information | groups • id • lastcomm • last • lid/libuser-lid • logname • members • users • whoami • who • w |
| WireGuard VPN | Alpine • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Firewall • Ubuntu 20.04 |
Comments on this entry are closed.
Both errors and warning are thrown into stderr is there any way we can identify that the command has a warning in it and not the error ??
Apart from checking the return code !!
Just use sudo (assuming you’re not running it in a script)
Источник