- Block or Unblock Programs in Windows Defender Firewall
- You Might Also Like
- Reader Interactions
- Comments
- Did this help? Let us know! Cancel reply
- Primary Sidebar
- Recent Posts
- Who’s Behind Technipages?
- Steps to Block All Outgoing Connections in Windows Firewall
- Steps to Block All Outgoing Connections with Windows Firewall
- Whitelist Applications to Allow Outbound Connections
- FIXED: Some Applications can Still Connect to the Internet After Blocking Outgoing Connections
- Blocking connections with windows firewall
- Answered by:
- Question
- Answers
Block or Unblock Programs in Windows Defender Firewall
By Mitch Bartlett 15 Comments
In Microsoft Windows 10 you can set the Windows Defender Firewall to block or unblock certain applications. Here’s how.
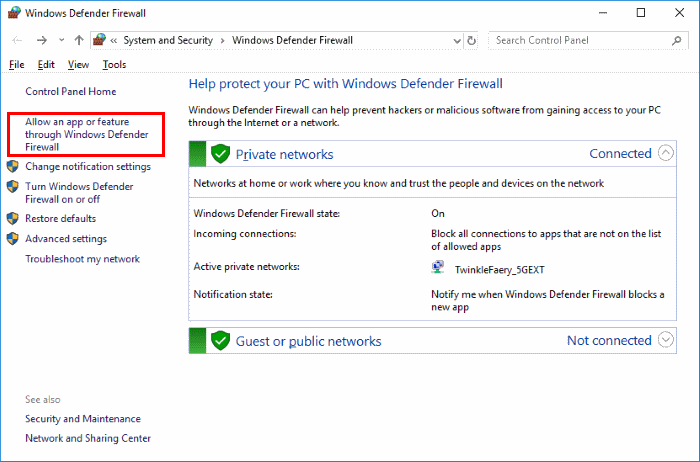
- Select the “Start” button, then type “firewall“.
- Select the “Windows Defender Firewall” option.
- Choose the “Allow an app or feature through Windows Defender Firewall” option in the left pane.
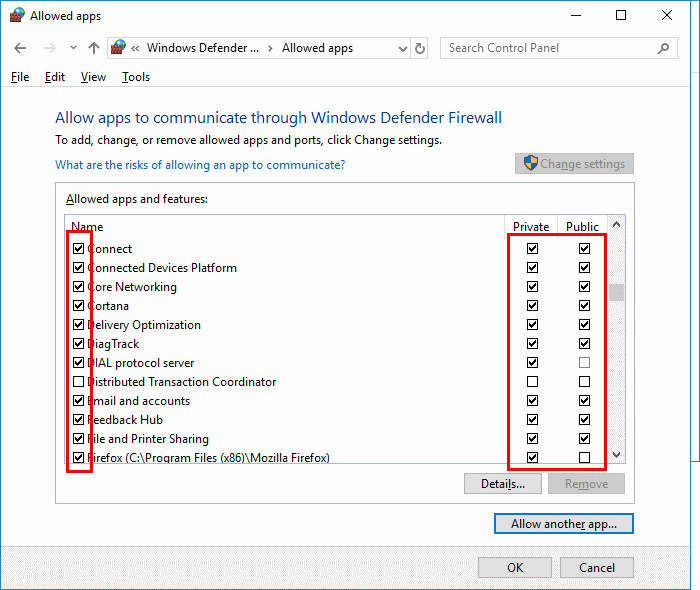
- Unchecking the box to the left of the application name disallows it from accessing network resources, while checking it allows access. You can also check the boxes to the right of the name labeled “Private” or “Public” to allow and disallow the app on private or public networks respectively.
- If the program you wish to block or unblock is not listed, you can click the “Allow another app…” button to add it. Choose the application in the list and select “Add“. If the program is not in this list, use the “Browse…” button to select the program file manually.
You Might Also Like
Filed Under: Windows Tagged With: Windows 10
Reader Interactions
Comments
Susan Olson says
No…I am definitely not a pro…so a little more explanation would be great…say, what about gallery or settings….?
Susan Olon says
Could you give me an example as to what applications should NOT cross the firewall??
Any application can block any crack microsoft office .. can you help me how to block any crack microsoft on my laptop ..
Richard Jordan says
The firewall is blocking access to open areas of the United Nations website. Even public press releases. How do I uninstall Micrsoft Edge, if that is what is blocking me.
So, what’s the meaning of a checked box and an unchecked box?
I am trying to allow zoom to have access but firewall is blocking it.
I’m trying to block Microsoft family features so it won’t send me the annoying pop-ups about signing in.
I’m on the correct thing but I can’t uncheck the box beside it. If I click the box it does nothing,
Do we have any registry settings for the same.
Thanks, it worked
What if when you click “Allow another app” and then Choose the app in the directory and it gives an error about a possible virus?
Josh Everett says
Is there any way to do this without Administrator rights?
Settings for some pro, doesn’t change!
its somehow locked, as if a registry rule is overriding this windows rules.
Richard S Nye says
I have been trying for hours to Block “Fortnite” from my PC windows 10
Edwin Wetzel says
nothing helps. i’ve been trying to hook up my wifi scanner and i’ve been doing this for hours without any success. i’ve followed all the different procedures on line including going into the defender advanced settings and allowing file and printer sharing rules and still does not work.
What if you cant click the “Allow the app or feature through windows defender firewall”?
Mike Bading says
Mitch,
First, I hope this note finds all well with you and yours.
Second, thank you for your effort here.
Third, my question(s):
What do you do when Windows Defender keeps resetting Microsoft Apps you have unchecked/deselected in Windows 10 Home or Windows 10 Pro?
Example: Let’s say I wish to block Cortana (or any other app). I then follow your instructions here and uncheck/deselect all the boxes pertaining to Cortana and then close the window.
Let’s say, that for whatever reason(s), I return to the window in your example only to find that Windows has reset/unblocked Cortana without notice and without my permission. This would happen all the time in Win10Home; and I would like to know if this would happen in Win10Pro and what to do about it if it does.
Respectfully,
Mike Bading
Did this help? Let us know! Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
Primary Sidebar
Recent Posts
Who’s Behind Technipages?

Follow me on Twitter, or visit my personal blog.
Steps to Block All Outgoing Connections in Windows Firewall
Windows Firewall allows you to block all outgoing connections to restrict applications from connecting to the internet. Here’s how.
Windows comes with a default firewall application that gives you granular control over the internet access and also allows you to configure all the incoming and outgoing connections. By default, the Windows firewall is configured to allow all outgoing connections unless they are blacklisted and block all incoming connections unless they are whitelisted.
Most Windows programs have almost unrestricted access to outgoing connections. This means that the applications can phone home and perform other activities without any restrictions.
If you don’t like this behavior then you can use the Windows Firewall options to block all outgoing connections. Blocking oubound connections is helpful when you want granular control over which applications can send data over the internet.
The method shown below is verified to work with Windows 10, 8, & 7. Before making any changes, I strongly recommend you to backup Windows Firewall settings.
Steps to Block All Outgoing Connections with Windows Firewall
These are the steps you should follow to block outgoing connections in Windows Firewall.
- Open the Start menu.
- Search for “Windows Defender Firewall” and open it.
- Click on the “Advanced Settings” link in the Firewall application.
- Here, select the “Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security on Local Computer” option on the left panel.
- Click on the “Windows Defender Firewall Properties” link in the middle panel.
- In the Firewall properties window, go to the profile tab of your choice.
- Domain profile tab: If the system is joined in a domain.
- Private profile tab: If the system is connected to a private network (like home or office network).
- Public profile tab: If the system is connected to a public network (like a coffee shop WiFi)
In my case, I’m selecting the Private profile tab because I’m connected to a private network. For a vast majority of users, this is the option to select.

The changes are instant. From now on, all outbound connections are blocked and applications cannot send any data over the network.
Whitelist Applications to Allow Outbound Connections
To allow outgoing connections for specific applications, you need to manually whitelist them. Whitelisted application takes priority over the general block rule for outbound connections. For example, maybe you want the Chrome browser to work even when you blocked the outbound connections.
Follow these steps to whitelist applications for outbound connections.
- Open Windows Firewall.
- Click on the “Advanced Settings” link.
- Select “Outbound rules” on the left panel.
- Click on the “New rule” option in the right panel.
- Select “Program” and click “Next“.
- Select “This program path” and click “Browse“.
- Find the application’s exe file, select it, and click on the “Open” button.
- Click “Next“.
- Select “Allow this connection” and click “Next“.
- Select Domain, Private, and Public checkboxes and click “Next“.
- Name the rule and click “Finish“.
As soon as you click the Finish button, the outbound rule will be created and applied to the firewall. From now, the whitelisted application should be able to send data over the network even if the outbound connections are blocked.
FIXED: Some Applications can Still Connect to the Internet After Blocking Outgoing Connections
Even after block all outbound connections, some applications can still send data over the network. For example, most built-in Windows applications and services can send data over the network. This is because those applications are whitelisted by the system.
If you don’t want those applications accessing the outgoing connections, you have to manually disable the outbound rule for those applications in the Firewall settings. Let me show you how.
- Open the Windows Firewall application.
- On the left panel, click on the “Advanced Settings” link.
- Here, select the “Outbound Rules” option on the left panel.
- In the middle panel, find the rule related to the application you want to block.
- For example, I want to block the Windows 10 Email app. So, I selected it.
- Right-click on the rule and select the “Disable Rule” option.
That is it. The changes are instant. For demonstration purposes, I also blocked the outbound rule for the legacy Edge browser. As you can see from the image below, it cannot connect to the internet due to the restriction of the outgoing rule. Do this to all the applications you don’t want connecting to the internet.
I hope that helps. If you are stuck or need some help, comment below and I will try to help as much as possible.
Blocking connections with windows firewall
This forum has migrated to Microsoft Q&A. Visit Microsoft Q&A to post new questions.
Answered by:
Question
I’ve got a problem during a Windows 7 deployment project. We want to configure the integrated Windows Firewall to block all outbound network traffic when the client is on a «public» network (public firewall profile). We only want to open the necessary ports that are needed for a VPN into the enterprise environment. These are in our situation DHCP, DNS, different rules for CRLs (for checking the client certificate) and the rules for the VPN itself. These rules are working well, but we have got a problem with the network profile identification.
We configured the firewall with a GPO, that all unknown networks are identified as public networks. The user can’t change the network profile to «Home» or «Work». So the network profiles can only be «public» or «domain».
We have a problem by opening only the ports mentioned above. When our client was on a «public» network it can’t find the way back to the domain profile. This may has something to do with the network identification by Network Location Awareness (NLA). Therefore we logged all dropped packages and found out there were many dropped packages on the following ports:
— 389 (TCP/UDP)
— 135, 137, 138 (UDP/TCP)
— 88 (Kerberos)
— 15032 .
We opened port 389 for UDP and TCP. After that we can sucessfully jump between public networks and the domain network.
But when we are on a public network and connecting to the VPN, the VPN network adapter do not find the way to the «domain» profile. It stays always on the «public» profile. Afterwards we opened the port 88 (Kerberos) and then the network profile on the VPN adapter changed to public with a yellow exclamation mark as the profile icon and the status «(Not authenticated)».
After opening the NetBios ports (135. ) and the strange port 15032, the VPN network adapter could change to the domain profile.
Can anyone tell me which ports are needed for a correct network profile identification by Network Location Awareness (NLA)? And why are these ports needed? It is very important for us to have a clear statement why we should open all these ports, because it is a high secure environment.
I hope you can help me with this problem. I can’t find any documentation from Microsoft about blocking all outbound connections in Windows Firewall.
Thanks a lot!
fox
Answers
Generally speaking, blocking all «outbound» traffic can be very problematic and is not typically recommended. You need to to know and control every port used for communications on the network. For applications that use RPC, this means restricting the ports on which communication can occur.
For more on controlling this behavior, see the following article «How to configure RPC dynamic port allocation to work with firewalls»
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/154596
Though it may not be acceptable due to being a high security environment, you might consider testing a rule allowing all, or at least a wider range of, traffic to the specific IP of the authenticating DC. AuthIP can be tested to enhance security by requiring that a security principle be authenticated before allowing the connection. This is still not without risk if the box is compromised, but then again so are any open ports.
VPN virtual adaptors can also pose a unique challenge. 3rd Party vendors can often times present unique behaviors in the face of NLA. Some, totally ignore the process and will always follow the profile of the physical adaptor. Others, implement a block on all traffic other than what you specifically allow. Still others, force interface configuration information that prevents NLA from operating. It is not stated here, and we may be using the Windows native client making this a moot point, but I offer the info merely to illustrate the added level of complexity introduced by virtual adaptors.
DNS 53, Kerb 88, and LDAP 389 are required for resolving and connecting to the Domain Controller, but you may also see traffic from various name resolution / registration providers, such as NbtNs, LLMNR, WSDiscovery, SSDP, etc. Additional traffic may be required for the VPN authentication. The 15032 is an unknown, but it may be something specific to that box, perhaps even specific to the VPN client software itself if using 3rd party, or RPC. More information from a trace taken using Network Monitor 3.4 may be helpful, for example; additional detail about the frame and the destination IP might provide a little insight. With NetMon you can also add the «Process» column which may help identify the generating process.
Ketan Thakkar | Microsoft Online Community Support