- How to create a bootable installer for macOS
- What you need to create a bootable installer
- Download macOS
- Use the ‘createinstallmedia’ command in Terminal
- Bootable usb drive creator tool mac os
- Apple hardware considerations
- 2. Requirements
- 3. Prepare the USB stick
- 4. Install and run Etcher
- 5. Etcher configuration
- 6. Write to device
- 7. Boot your Mac
- Finding help
- How to create a bootable Windows 10 USB on Mac
- Format USB to ExFAT (Under your own risk)
- Format USB with the terminal
- Copy Windows files to USB — Method 1
- Open Windows ISO
- Copy files
- UNetbootin — Method 2
- Check the path name of your USB Disk.
- Download UNetbootin:
- Makes the USB booteable
How to create a bootable installer for macOS
You can use an external drive or secondary volume as a startup disk from which to install the Mac operating system.
These advanced steps are primarily for system administrators and others who are familiar with the command line. You don’t need a bootable installer to upgrade macOS or reinstall macOS, but it can be useful when you want to install on multiple computers without downloading the installer each time.
What you need to create a bootable installer
- A USB flash drive or other secondary volume formatted as Mac OS Extended, with at least 14GB of available storage
- A downloaded installer for macOS Big Sur, Catalina, Mojave, High Sierra, or El Capitan
Download macOS
- Download: macOS Big Sur, macOS Catalina, macOS Mojave, or macOS High Sierra
These download to your Applications folder as an app named Install macOS [ version name ]. If the installer opens after downloading, quit it without continuing installation. To get the correct installer, download from a Mac that is using macOS Sierra 10.12.5 or later, or El Capitan 10.11.6. Enterprise administrators, please download from Apple, not a locally hosted software-update server. - Download: OS X El Capitan
This downloads as a disk image named InstallMacOSX.dmg. On a Mac that is compatible with El Capitan, open the disk image and run the installer within, named InstallMacOSX.pkg. It installs an app named Install OS X El Capitan into your Applications folder. You will create the bootable installer from this app, not from the disk image or .pkg installer.
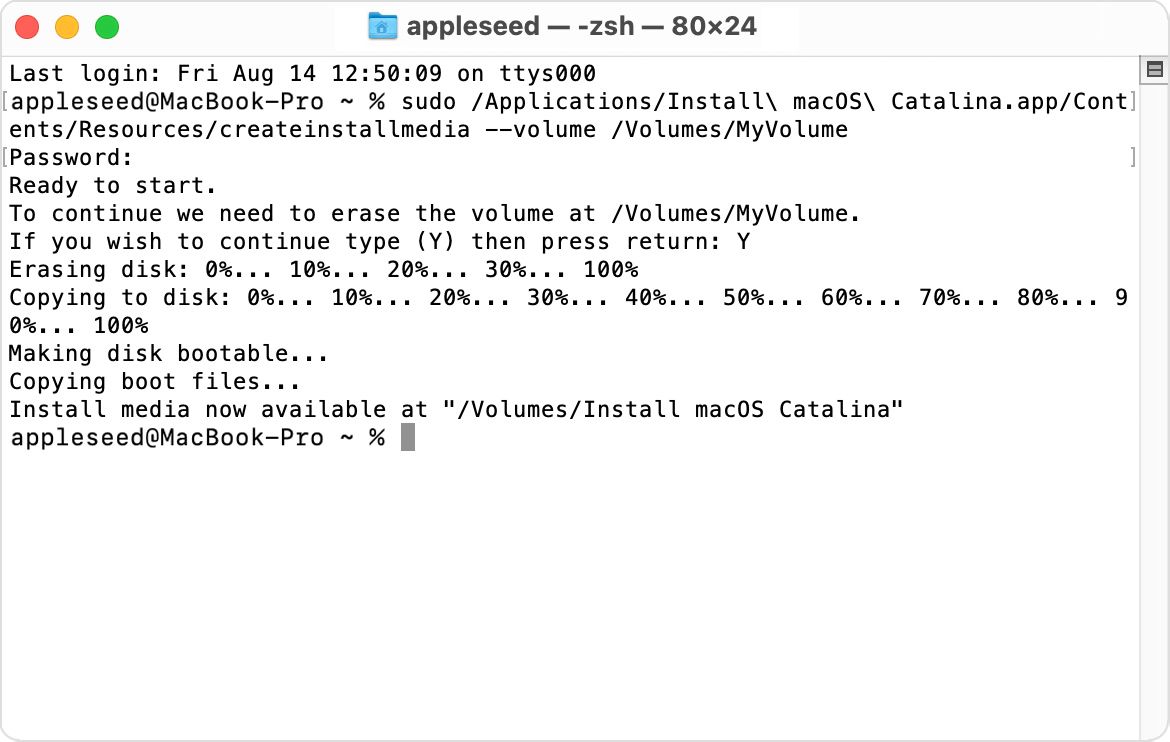
Use the ‘createinstallmedia’ command in Terminal
- Connect the USB flash drive or other volume that you’re using for the bootable installer.
- Open Terminal, which is in the Utilities folder of your Applications folder.
- Type or paste one of the following commands in Terminal. These assume that the installer is in your Applications folder, and MyVolume is the name of the USB flash drive or other volume you’re using. If it has a different name, replace MyVolume in these commands with the name of your volume.
Big Sur:*
Catalina:*
Mojave:*
High Sierra:*
El Capitan:
* If your Mac is using macOS Sierra or earlier, include the —applicationpath argument and installer path, similar to the way this is done in the command for El Capitan.
After typing the command:
- Press Return to enter the command.
- When prompted, type your administrator password and press Return again. Terminal doesn’t show any characters as you type your password.
- When prompted, type Y to confirm that you want to erase the volume, then press Return. Terminal shows the progress as the volume is erased.
- After the volume is erased, you may see an alert that Terminal would like to access files on a removable volume. Click OK to allow the copy to proceed.
- When Terminal says that it’s done, the volume will have the same name as the installer you downloaded, such as Install macOS Big Sur. You can now quit Terminal and eject the volume.
Источник
Bootable usb drive creator tool mac os
With a bootable Ubuntu USB stick, you can:
- Install or upgrade Ubuntu, even on a Mac
- Test out the Ubuntu desktop experience without touching your PC configuration
- Boot into Ubuntu on a borrowed machine or from an internet cafe
- Use tools installed by default on the USB stick to repair or fix a broken configuration
Creating a bootable USB stick is very simple, especially if you’re going to use the USB stick with a generic Windows or Linux PC. We’re going to cover the process in the next few steps.
Apple hardware considerations
There are a few additional considerations when booting the USB stick on Apple hardware. This is because Apple’s ‘Startup Manager’, summoned by holding the Option/alt (⌥) key when booting, won’t detect the USB stick without a specific partition table and layout. We’ll cover this in a later step.
2. Requirements
- A 2GB or larger USB stick/flash drive
- An Apple computer or laptop running macOS
- An Ubuntu ISO file. See Get Ubuntu for download links
3. Prepare the USB stick
To ensure maximum compatibility with Apple hardware, we’re going to first blank and reformat the USB stick using Apple’s ‘Disk Utility’. But this step can be skipped if you intend to use the USB stick with only generic PC hardware.
- Launch Disk Utility from Applications>Utilities or Spotlight search
- Insert your USB stick and observe the new device added to Disk Utility
- Select the USB stick device (you may need to enable the option View>Show All Devices) and select Erase from the tool bar (or right-click menu)
- Set the format to MS-DOS (FAT) and the scheme to GUID Partition Map
- Check you’ve chosen the correct device and click Erase
Warning: Disk Utility needs to be used with caution as selecting the wrong device or partition can result in data loss.
4. Install and run Etcher
To write the ISO file to the USB stick, we’re going to use a free and open source application called Etcher. After downloading this and clicking to mount the package, Etcher can either be run in-place or dragged into your Applications folder.
By default, recent versions of macOS block the running of applications from unidentified developers. To side-step this issue, enable ‘App Store and identified developers’ in the ‘Security & Privacy’ pane of System Preferences. If you are still warned against running the application, click ‘Open Anyway’ in the same pane.
5. Etcher configuration
Etcher will configure and write to your USB device in three stages, each of which needs to be selected in turn:
Select image will open a file requester from which should navigate to and select the ISO file downloaded previously. By default, the ISO file will be in your Downloads folder.
Select drive, replaced by the name of your USB device if one is already attached, lets you select your target device. You will be warned if the storage space is too small for your selected ISO.
Flash! will activate when both the image and the drive have been selected. As with Disk Utility, Etcher needs low-level access to your storage hardware and will ask for your password after selection.
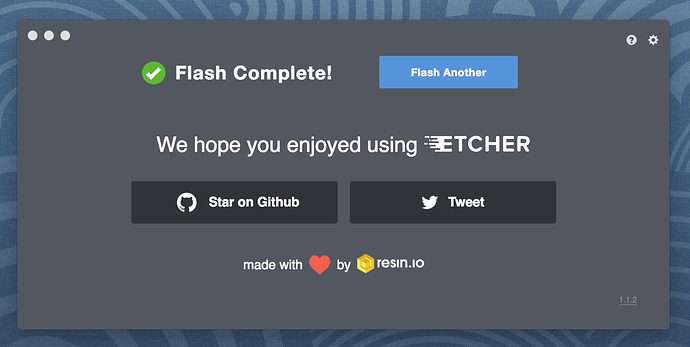
6. Write to device
After entering your password, Etcher will start writing the ISO file to your USB device.
The Flash stage of the process will show progress, writing speed and an estimated duration until completion. This will be followed by a validation stage that will ensure the contents of the USB device are identical to the source image.
When everything has finished, Etcher will declare the process a success.
Congratulations! You now have Ubuntu on a USB stick, bootable and ready to go.
Warning: After the write process has completed, macOS may inform you that ‘The disk you inserted was not readable by this computer’. Don’t select Initialise. Instead, select Eject and remove the USB device.
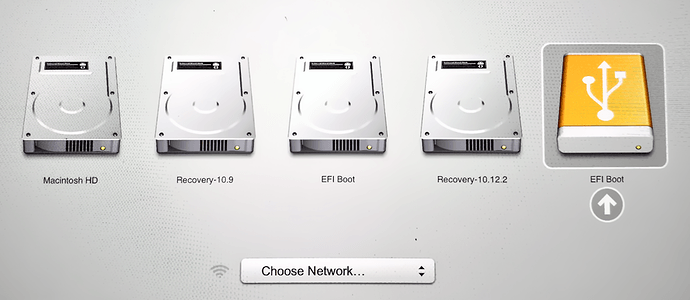
7. Boot your Mac
If you want to use your USB stick with an Apple Mac, you will need to restart or power-on the Mac with the USB stick inserted while the Option/alt (⌥) key is pressed.
This will launch Apple’s ‘Startup Manager’ which shows bootable devices connected to the machine. Your USB stick should appear as gold/yellow and labelled ‘EFI Boot’. Selecting this will lead you to the standard Ubuntu boot menu.
Finding help
If your Mac still refuses to boot off your USB stick you may find it easier to boot and install off an Ubuntu DVD instead. See our How to burn a DVD on macOS for further details.
Alternatively, if you feel confident using the macOS command line, see the community documentation on How to install Ubuntu on MacBook using USB Stick for a more manual approach.
If you want to install Ubuntu, follow our install Ubuntu desktop tutorial.
Finally, if you get stuck, help is always at hand:
Источник
How to create a bootable Windows 10 USB on Mac
The last release of Mac OS doesn’t have the option to create a bootable USB from Bootcamp like previous versions, and it is a problem because that require uses other tools.
I am updating this post today Dec 12, 2018. The reason is that I was only using UNetbootin to create the bootable USB, I will leave guide as a second method since it still working, and I will explain to you how you can create the bootable Windows USB without extra software.
The first step for both methods requires to format your USB device to NTFS, this is the default filesystem, alternative you can use ExFAT but the installation could fail.
Format USB to ExFAT (Under your own risk)
In order to boot from the USB, you need to format the USB to ExFAT, you can do it using Disk Utility (it comes with MacOS).
This step is the same for both methods. You need to show all the devices in Disk Utility» before to start the process.
Select your USB device in the list (not the partition), right click and then click on the Erase option:
In the next screen make sure you select these two options:
- Format: ExFAT
- Scheme: Master Boot Record
Click the Erase button.
If for some reason it fails, probably is because MacOS still using the USB, just repeat the steps, but if you see a screen similar to above screen is because the operation is successful.
Format USB with the terminal
You also can format the USB from the terminal, but you have to take care to use the correct device because, if you use the wrong name you will lose everything.
With this command you can list the device on MacOS:
This is an example, my USB is the disk2:
This command is to format the USB, the last parameter is the the USB:
Copy Windows files to USB — Method 1
This process is very easy doesn’t require to install other software, and they are just a few steps:
Open Windows ISO
Just double click on the ISO image, MacOS mount the image automatically.
Copy files
Now you only need to copy the files and paste them to the USB.
- Command + A Select all files.
- Command + C Copy files.
- Go to your USB Command + V paste the files.
This process could fail if you are using a USB with FAT32 because the file install.win is over 4GB, if this is the case try to open the terminal and copy paste the files from there (no always works. Try to follow the instructions to format the USB in ExFAT, NTFS works for some BIOS).
This is the command to copy the files from the ISO to the USB:
And that is all, now you can try boot from the USB.
UNetbootin — Method 2
I will show you how you can use UNetbootin to create a bootable USB, it can be used no only for Mac but for Windows and Linux distributions too.
UNetbootin is free software and it is also available for Windows and Linux.
Check the path name of your USB Disk.
Always in Disk Utility, select the new partition that we created in the previous step, and click on the information button, it will give you the information about the new partition.
You also can use the terminal and the command diskutil to see the list of drives:
Download UNetbootin:
Download the dmg directly from the Website.
And copy the app to the /Application folder.
I prefer to use homebrew to install applications, you can check this article for more information: Installing Applications on Mac with Homebrew:
Makes the USB booteable
Open UNetbootin and you only need select 3 options:
- Diskimage and ISO
- Now we need open the ISO Windows image that is on our computer.
- Select your USB device on UNetbootin.
- Click on the OK, button and wait to the process end it will take a time.
NOTES:
- I tested other tools like dd and Etcher but they are not working because Windows requires extra steps, for the moment this is the only easy tool that I know that works if you are on Windows try Rufus.
- Some users reported that UNetbootin is not working, if after to format the USB drive and change the block size is not working for you try another Drive with enough space.
Источник