- How to get to an MS-DOS prompt or Windows command line
- Get to a Command Prompt in Windows 10
- Get to a Command Prompt in Windows 8
- Get to a Command Prompt in Windows Vista and 7
- Get to a Command Prompt in Windows NT, 2000, and XP
- Get to a Command Prompt in Windows 95, 98, and ME
- How to restart the computer into an MS-DOS prompt
- Getting to MS-DOS
- Get to MS-DOS in Windows 3.x
- Other operating system
- Booting to dos in windows
- Загрузочная флешка с DOS
- Создание загрузочной флешки с DOS
- Booting to dos in windows
- Answered by:
- Question
- Answers
- All replies
How to get to an MS-DOS prompt or Windows command line
Below are steps on getting to an MS-DOS prompt or Windows command line in all versions of Microsoft operating systems.
Get to a Command Prompt in Windows 10
For some commands and options to work in the Windows 10 command line, you must run the command line as administrator. To do this, right-click the cmd icon and select Run as administrator.
Get to a Command Prompt in Windows 8
- Get to the Start screen
- Type cmd and press Enter .
- Move the mouse pointer to the very bottom-left corner of the screen and right-click, or press Windows key + X .
- In the power user task menu, select either Command Prompt or Command Prompt (Admin).
Get to a Command Prompt in Windows Vista and 7
For some commands and options to work in the Windows Vista and 7 command line, you must run the command line as administrator. To do this, right-click the cmd icon and select Run as administrator.
If you’re attempting to get into an MS-DOS prompt to troubleshoot the computer, boot the computer into Safe Mode.
Get to a Command Prompt in Windows NT, 2000, and XP
- Click Start.
- Click Run.
- Type cmd or command and press Enter .
- What is the difference between COMMAND.COM and CMD.EXE?
If you are attempting to get into an MS-DOS prompt to troubleshoot the computer, boot the computer into Safe Mode.
Windows 2000 and XP users who cannot boot the computer into Normal Windows mode or Safe Mode can also enter and use the Recovery Console to manage their computer from a prompt. See: How to use the Windows Recovery Console.
Finally, if you are experiencing issues getting into Windows NT, 2000, or XP, it may be necessary to run troubleshooting steps from an MS-DOS prompt. We recommend the Network Administrator gain access either using a standard MS-DOS boot diskette or the ERD diskettes created after the installation of Windows NT. Also, they may access MS-DOS by booting from a Windows XP CD.
Get to a Command Prompt in Windows 95, 98, and ME
If you can get into Windows 95, 98 or ME, you can get to an MS-DOS prompt by following the steps below.
Following the steps above opens an MS-DOS shell. However, if you are attempting to troubleshoot an issue with the computer and are using Microsoft Windows 95 or Windows 98, we suggest you restart the computer into MS-DOS. To do this, follow the steps below.
How to restart the computer into an MS-DOS prompt
- Click Start.
- Click Shutdown.
- Choose the option to restart the computer to an MS-DOS prompt.
If you cannot get into Windows 95 or Windows 98 to get to an MS-DOS prompt, follow the instructions below (Windows ME does not have this option).
- Reboot the computer
- As the computer is booting, press the F8 key when you hear a beep or when you see «Starting Windows 95» or «Starting Windows 98.» Windows 98 users sometimes may find it easier to press and hold the left Ctrl key as the computer is booting.
- If done properly, the user should get to a screen similar to the below screen.
- Select the option for Safe mode command prompt only.
Getting to MS-DOS
If you are running MS-DOS with no other operating systems, the computer should be booting into an MS-DOS prompt automatically, unless you have a shell or other program loading automatically.
If the computer cannot load MS-DOS, reboot the computer and as the computer is booting, press the F5 key when you see the message «Starting MS-DOS» or the MS-DOS version. Pressing this key should load the default settings for MS-DOS.
If this opens an MS-DOS prompt and you want to prevent further occurrences, edit the autoexec.bat or the config.sys files and remark any bad lines.
Get to MS-DOS in Windows 3.x
If you are running Windows 3.x, it is likely that the computer is booting into Windows automatically and bypassing the MS-DOS prompt. If the computer loads successfully into Windows, to exit to an MS-DOS prompt, from the Program Manager, click the file menu and select Exit.
If the computer cannot load MS-DOS, reboot the computer and as the computer is booting, press the F5 key when you see the message «Starting MS-DOS» or the MS-DOS version. Pressing this key should load the default settings for MS-DOS.
If you do not want Windows 3.x to load automatically into Windows 3.x, edit the autoexec.bat file and remove the «win» line.
Other operating system
If you want a command line, you more than likely want to access the Shell or Terminal for your operating system, not MS-DOS.
Booting to dos in windows
The MS-DOS Boot Process
If you have arrived here through a search engine, and there’s no menu to the left click here!
The System Boot Sequence consists of a series of events that the system performs when it is turned on (or rebooted with the reset switch). This always starts with the special boot program software that is in the system BIOS ROM on the motherboard. The BIOS performs several steps to test the system and make it ready before an operating system can be loaded. These steps are explained in detail here: The Master Boot Record and the System Boot Sequence.
Once the BIOS has completed its testing and system configuration, it begins the process of loading the operating system. The BIOS accomplishes this by searching the installed drives for a Master Boot Record in which is contained a boot code. Once found, the boot code is executed and the system is boot into the operating system. When looking for this Master Boot Record, the BIOS will search for boot devices (drives) in the order specified in the BIOS configuration settings controlling this aspect of the boot sequence. If it cannot find a boot device it will terminate with an error.
If the operating system is MS-DOS В® , or any variant of Windows В® other than Windows В® NT or Windows В® 2000, that starts out by booting the equivalent of DOS, then a specific operating system load sequence commences, which is referred to as the DOS Boot Process. If you are booting into Windows, additional steps are performed after the underlying MS-DOS В® operating system has loaded.
The steps below takes you through the boot process from the hard disk. If you were to boot from a floppy disk, the steps would only differ slightly in the first few steps, as the floppy disk structures are slightly different. Floppies cannot be partitioned, and hence have no master boot record or partitions. This means that the master boot record issues are skipped.
MS-DOS boot process:
- The BIOS, having completed its test and setup functions, loads the boot code found in the master boot record and then transfers control of the system to it. At that point, the master boot record code is executed. If the boot device is a floppy disk, the process skips to step 7 below.
The next step in the process is the master boot code examining the master partition table. It first must determine if there is an extended DOS partition, then it must determine if there is a bootable partition specified in the partition table.
If the master boot code locates an extended partition on the disk, it loads the extended partition table that describes the first logical volume in the extended partition. This extended partition table is examined to see if it points to another extended partition table. If it does, this second table is examined for information about the second logical volume in the extended partition. Logical volumes in the extended partition have their extended partition table chained together one to the next. This process continues until all of the extended partitions have been loaded and recognized by the system.
Once the extended partition information (if any) has been loaded, the boot code attempts to start the primary partition that is marked active, referred to as the boot partition. If no boot partitions are marked active, then the boot process will terminate with an error. The error message is often the same as that which occurs if the BIOS could not locate a boot device, generally shown on screen as «No boot device», but also can show up as «NO ROM BASIC — SYSTEM HALTED». If there is a primary partition marked active and there is an installed operating system, the boot code will boot it. The rest of the steps presume this example is of an MS- DOS primary partition.
At this stage, the master or volume boot sector is loaded into memory and tested, and the boot code that it contains is given control of the remainder of the boot process.
The boot code examines the disk structures to ensure that everything is correct. If not, the boot process will end in an error here.
During the next step, the boot code searches the root directory of the device being booted for the operating system files that contain the operating system. For MS-DOS, these are the files «IO.SYS», «MSDOS.SYS» and «COMMAND.COM».
If no operating system files are found, the boot program will display an error message similar to «Non-system disk or disk error — Replace and press any key when ready». Keep in mind that his message does not means that the system was never booted. It means that the BIOS examined the floppy disk for example and just rejected it because it couldn’t boot an operating system. The volume boot code was indeed loaded and executed, as that is what posts the message when it can’t find the operating system files.
If any of the Windows 95/98/ME versions were being started, the above would only be the beginning of the startup process. When MS-DOS starts in anticipation of loading these Windows versions, there are many more routines that are loaded and executed as part of the boot process, which includes such tasks such as reading the system registry, initializing hardware devices and starting the graphical user interface or operating system shell. We hope this has given you a better understanding of what occurs during the boot or startup process of your computer.

Notice: WindowsВ® 95, WindowsВ® 98, WindowsВ® NT, WindowsВ® 2000 and
MicrosoftВ® Office are registered trademarks or trademarks of the Microsoft Corporation.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Copyright В©1995-2001 DEW Associates Corporation. All rights reserved.
Загрузочная флешка с DOS

На работе возникла необходимость в использовании древней консольной программы для программирования оборудования. Под Windows она работала некорректно, поэтому пришлось вспомнить молодость и создать загрузочный носитель с DOS.
Так как дискеты благополучно ушли в небытие, необходимо было создать загрузочную флешку с DOS.
Ну раз надо — значит сделаем. Тем более это не сложно.
Все необходимое, для создания загрузочной флешки с DOS, находится в архиве.
usb_dos_boot_flashka.rar (586,4 KiB, 35 640 hits)
Создание загрузочной флешки с DOS
Далее опишу все пошагово
- Скачиваем архив и распаковываем
- Подключаем USB флешку к компьютеру
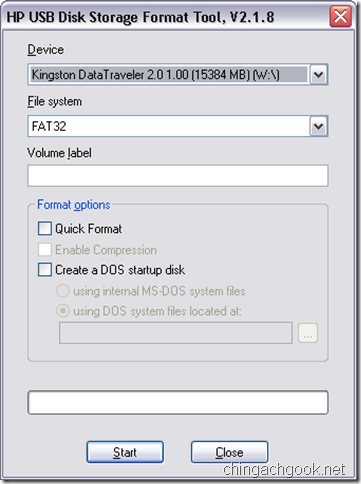
- Запускаем файл HPUSBFW.EXE
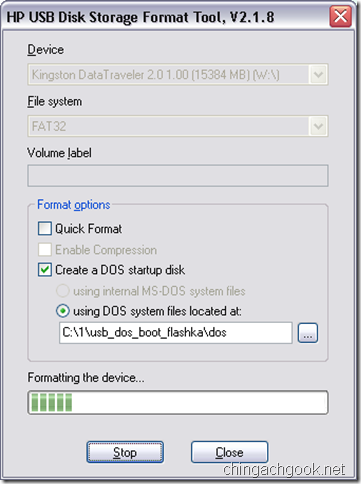
- Проверяем, что в поле Device выбрана нужная флешка
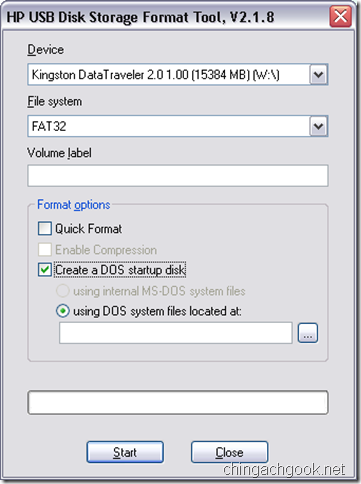
- Ставим галочку на Create a DOS startup disk
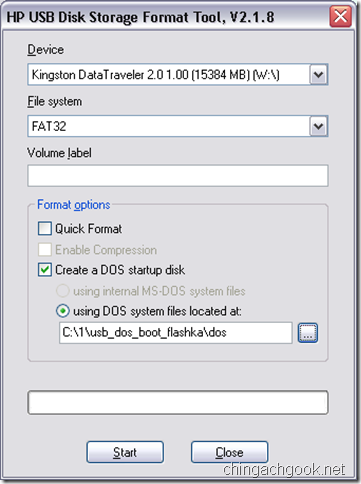
- В поле using DOS system files located at: выбираем путь к папке \dos\, которая была в архиве
- Жмем на кнопку Start
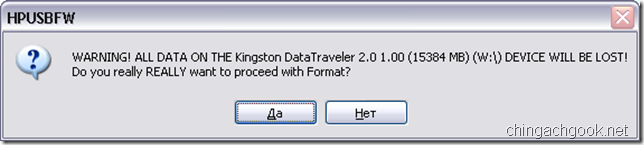
- Соглашаемся с предупреждением
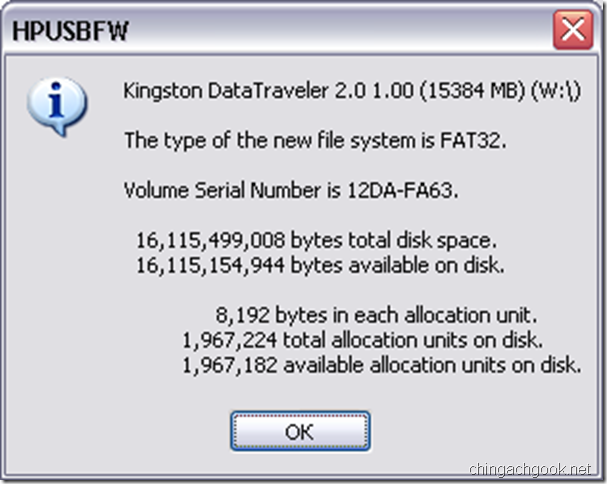
- Начнется процесс форматирования и копирования необходимых файлов
- После завершения выскочит информационное окно
- Закрываем программу
- Перезагружаем компьютер
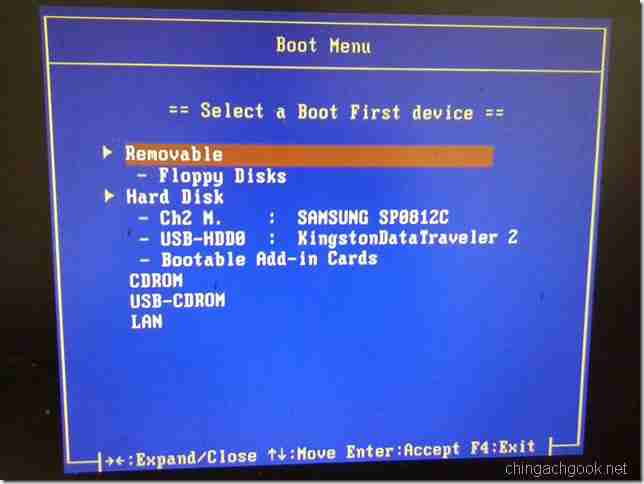
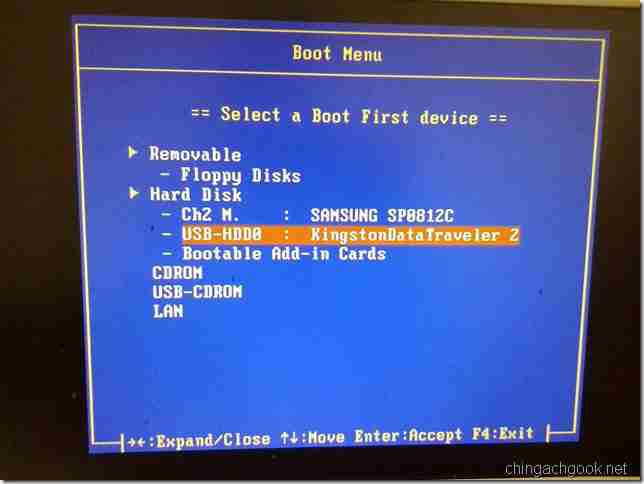
- При начале загрузки жмем на клавишу Esc или F12 (зависит от вашего BIOS-а), пока не появится окно выбора загрузочного устройства
- Выбираем нашу флешку и жмем Enter
- Все, DOS запущен
Booting to dos in windows
This forum has migrated to Microsoft Q&A. Visit Microsoft Q&A to post new questions.
Answered by:
Question
I need to update the BIOS on my machine and I have no idea how to boot to DOS.
Anyone know the trick?
Answers
If your computer can boot a usb flash drive, you could set it up to boot dos.
The MSI forum has a tool that will set up a usb flash drive this way.
You have to be a member of the MSI forum to download it.
I don’t remember is you have to use it on an MSI motherboard.
Once you have made the bootable flash drive, you can use it on non-MSI motherboards, however.
All replies
Maybe something like — google for «DOS boot» — find one that you can put on a CD, copy it, burn it, then boot from it.
Hope that helps
Kris
That’s mainly because Windows NT flavors — including XP, Vista and Windows 7 — don’t have a means to boot to DOS. The closest thing to DOS in recent flavors of Windows would be the recovery console — but that isn’t DOS, nor are you allowed to run wild with what you CAN do. It’s designed to help someone repair a hosed copy of Windows.
DOS, as they say, is dead.
There are, however, options. Depending on the motherboard and the motherboard manufacturer, they do make Windows based BIOS updaters. Some manufacturers also have DOS based updaters. Some have ones you can burn to a CD that come with their own boot loader. Check your motherboard’s site for options.
As KrisM suggested, you can google for and download a DOS boot diskette image and extract it to a floppy. Of course, you need a working floppy drive, and a working floppy diskette.
I need to update the BIOS on my machine and I have no idea how to boot to DOS.
Anyone know the trick?
Most modern BIOS updates are distributed as an executable file that will run from inside windows or as a boot disk, on a floppy or CD.
Check with the manufacturer of that BIOS for the installation instructions.
Hope this helps.
Thank You for testing Windows 7 Beta
Ronnie Vernon MVP
With Windows NT3.5/NT3.51/NT4.0/2K/XP/Vista/7, there was never a DOS. Although the command prompt appears as a DOS window similar to the DOS underpinnings of Win9x/ME, the NT family’s command prompt is a full 32bit environment that has practically no architectural similarities to DOS. Although the commands seem similar, the bits behind them differ.
Booting into SAFE MODE Command Prompt is about as close as you are going to get, visually, to booting in a DOS environment. To boot into SAFE MODE Command Prompt, hit during boot.
To update your BIOS, you will need to follow your motherboard’s instructions. Most current motherboard manufactures offer some sort of Windows executable. The executable will usually update the BIOS directly, or it will invoke a program to make a bootable floppy or CD that can then be used to update your BIOS.
Like Wolfie said: DOS is dead!
If your computer can boot a usb flash drive, you could set it up to boot dos.
The MSI forum has a tool that will set up a usb flash drive this way.
You have to be a member of the MSI forum to download it.
I don’t remember is you have to use it on an MSI motherboard.
Once you have made the bootable flash drive, you can use it on non-MSI motherboards, however.
CW, it would help if you could say what make/model of PC (if a prebuilt, OEM machine) or motherboard (if it’s you-built or local-built) you have — with that information, we could help you in your BIOS flashing effort.
As others said here, it’s very rare these days (actually, it’s been quite some time) for a motherboard to actually require a true DOS enviroment to flash the BIOS. Even of the boards that require that, the manufacturers usually also provide a floppy-disk image file (.img) with which to create the boot disc.
Most any recent board uses either a Winflash utility (is run from within Windows), and/or a native (on-chip) BIOS flashing utility (Gigabyte is a good example of the latter.)
-Chris [If this post helps to resolve your issue, please click the «Mark as Answer» or «Helpful» button at the top of this message. By marking a post as Answered, or Helpful you help others find the answer faster.]
Well, unfortunately, this is a computer built by a local system builder with an ASUSTek board on it. The only BIOS update option is from DOS, so I’ll have to give one of the above theories (like booting from a USB flash drive) a try.
Thanks for the suggestions folks.
Got a model # (and revision#) for that motherboard? If you don’t know what they are, they’ll be sinkscreened onto the board.
I have a really, really hard time believing that the only way to flash any board made in the last 5 years requires a bootable DOS disc (that you, the end user, must provide, no less) to do it. 😕
-Chris [If this post helps to resolve your issue, please click the «Mark as Answer» or «Helpful» button at the top of this message. By marking a post as Answered, or Helpful you help others find the answer faster.]
It claims to fix resume from S1, S3, and S4.
It does appear that they only have a dos utility for bios update.
You CAN get the Windows utility directly from AMI. http://www.ami.com/support/bios.cfm, has instructions and download linkd for amiflash.zip, which has both the dos and Windows utilities.
So I guess the lesson here is that if I don’t tell people I do know what I’m doing, the assumption is that I don’t. I’ll speak more clearly in the future. :’)
And thus I’m back to how to boot a Vista/Win7 machine to DOS. I’ll look in to building a bootable USB stick and go from there.
Sadly, that’s correct. And, it’s because, frankly, we have a lot of people posting question here that really don’t.
Better might heve been: «I need to flash my BIOS. The motherboard requires this be done from DOS; the mfr. suppies a floppy DOS image to do it. However, I have no floppy drive. Suggestions on how to do this by other means?»
(Note that no mention of the running OS is listed, as this doesn’t matter. You could be running *nix, and you’d still be in the same hard spot.)
Answer would have been:
HP has a utility to make a USB key bootable; it can be found here.
It does work with most non-HP keys, too. Unfortunately, it isn’t listed as compatible with NT6 (Vista/Server2k8/Win7), so it may or may not work (unless you have a 2k/XP machine to run it on.)
Alternately, there are multiple methods listed over at bootdisk.com. Method 5 looks promising for you, as it doensn’t require that you have a floppy drive to copy the files from.
HTH,
Chris [If this post helps to resolve your issue, please click the «Mark as Answer» or «Helpful» button at the top of this message. By marking a post as Answered, or Helpful you help others find the answer faster.]
So I guess the lesson here is that if I don’t tell people I do know what I’m doing, the assumption is that I don’t. I’ll speak more clearly in the future. :’)
And thus I’m back to how to boot a Vista/Win7 machine to DOS. I’ll look in to building a bootable USB stick and go from there.
When you ask how to boot into DOS on a Windows NT based machine, that question will lead others to believe that you really don’t know what you are doing when it comes to some of the inner workings of Windows NT based releases.
Like Chris said, there is a good majority of people who post here that really don’t have a good clue as to how Windows works. A lot of information is based on ingrained dogma that was applicable back in the Win9x days. Some is because people have so shunned Vista, they are now clueless as to the “new” methods that Microsoft has adopted to accomplish certain tasks or implement certain features.
When looking for an answer to a particular question, it is incumbent on the poster to make the question as clear as possible so to avoid any ambiguity.
Back to your question: If you must get into a DOS environment, you must boot from a floppy or a CD emulating a bootable floppy. This is the procedure regardless of your operating system. Windows, Linux, UNIX, etc.
A follow up question would be how to make a DOS bootable floppy from within Windows Vista/7? With a blank disk a 3.5” floppy, right-click the A drive and select format. In the format dialog box, check the Create an MS-DOS startup disk check box.