- Fixed glass
- Picture Windows with Fixed Glazing
- Benefits of Fixed Picture Windows
- Where to use Fixed Glass Windows
- WINDOW Software Downloads
- Release Notes:
- NOTE: WINDOW downloads will not be available April 9 — 11 and April 23-25 due to server maintenance.
- WINDOW 8 and THERM 8 Research Version
- Release Notes:
- NOTE: WINDOW downloads will not be available April 9 — 11 and April 23-25 due to server maintenance.
- Installation Files
- IMPORTANT: Please read the Installation Notes below
- Comparisons with Previous Versions
- WINDOW 7 Release History
- IMPORTANT Installation Notes — PLEASE READ and install the 2 libraries linked below
- This version will not update WINDOW 7.6 versions — it makes a completely new version
- Redistributable Packages/Libraries that MUST BE installed before this version will run (if you have not previously installed them)
- If you do not install these you will get error messages about DLLs not being found.
- Known Bugs
- Environmental Conditions — Can’t make a new record
- Bug Fixes
- Glass Library Update
- Gap Library: New name reverts to Default on Save
- Gap Library: Up and down arrows don’t work when creating a gas mixture
- Error opening WINDOW 7.4 database in 7.7
- Improvements in Libraries when saving new records
- Program asks to save record even if nothing has changed
- If the program can’t open a WINDOW database, it gets into an infinite loop
- Window Library: Double arrow selection of Type does not update the image
- Window Library: Under some circumstances, the name was not saved
- Release Notes:
- Installation Files
- Comparisons with Previous Versions
- Installation Notes
- This version will not update WINDOW 7.6 versions — it makes a completely new version
- Redistributable Packages/Libraries that MUST BE installed before this version will run (if you have not previously installed them)
- Enhancements
- Shading Layer Library
- Matrix Library reader
- Radiance
- Compiled with updated libraries
- Better Scaling on high DPI (resolution) monitors
- Glass Library ID Limit of 65000 no longer exists
- Approval symbol now displayed for Shading Systems in the Glazing System Library
- Vertical and Horizontal blinds
- Eliminated calculation time estimate for genBSDF calculations
- Bug Fixes
- Database name and path didn’t appear in the program title bar immediately on opening the program
- Incorrect absorptance calculation in BSDF
- Glazing System Report change
- Angular calculations for some cases (PET) were not correct
- Command line did not support new PermeabilityFactor input
- Angular calculations resulted in R+T>1 in some cases
- Angular calculations were broken when using the matrix method for specular glass
- «Frame doesn’t exist» message
- When reading BSDF matrix values the program was not using the standard library
- Chromogenics calculations fixed
- D esigning Buildings Wiki Share your construction industry knowledge www.designingbuildings.co.uk
- Window
- Contents
- [edit] Introduction
- [edit] Elements of a window
- [edit] Materials
- [edit] Opening type
- [edit] Fixed light
- [edit] Vertical slider/sash
- [edit] Casement
- [edit] Tilt and turn
- [edit] Pivot
- [edit] Bi-fold
- [edit] Louvre
- [edit] Other types
- [edit] Number of panes
- [edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki:
- [edit] External references
- Comments
Fixed glass
Picture Windows with Fixed Glazing
Picture windows, also known as fixed windows, feature fixed glazing installed directly into the window frame and do not open. The name comes from the design providing a picture-like space on a wall and being unable to open. This makes them a popular choice for letting in natural light or creating good views in areas that either do not require opening windows or where it would make little sense (e.g. stairwells, interior areas).
Benefits of Fixed Picture Windows
Without a movable sash, fixed glass windows already insulate better than standard casement windows. Therefore, upgrading them with insulated glass in the form of double or triple glazing is a good idea. This allows you to enjoy the increased light and view while increasing thermal insulation, reducing heat loss and saving energy. Further energy efficiency options such as krypton or argon gas filled cavities and special coatings will further boost their u-values.
Stepping back from the idea that all windows must open, it becomes clear that there are far more options for your home design than you perhaps realize. Floor to ceiling windows, skylights, transom windows and more are all typically fixed but provide excellent views, natural light and look good despite not opening.
Where to use Fixed Glass Windows
Fixed, non-opening windows are not just an option when selecting your windows, but the best solution for many locations. Common examples include:
- Large glass facades, whether residential or commercial
- Stairwells
- Skylights
- Store windows
- Transom windows
Wherever ventilation is not required and light and a good view are the top priority, picture windows are the best solution.
WINDOW Software Downloads
Release Notes:
NOTE: WINDOW downloads will not be available April 9 — 11 and April 23-25 due to server maintenance.
WINDOW 8 and THERM 8 Research Version
WINDOW 8 and THERM 8 are the latest versions of our tools that are available for testing. The main added functionality for THERM 8 is transient moisture and thermal modeling.
It is not recommended that the THERM 8 Research Version is used for conventional thermal modeling, as it is still in the testing phase.
Click here to access a web page with both WINDOW 8 and THERM 8 installation files and documentation
Release Notes:
NOTE: WINDOW downloads will not be available April 9 — 11 and April 23-25 due to server maintenance.
Installation Files
IMPORTANT: Please read the Installation Notes below
Complete installation if you have never installed WINDOW before
Smaller installation if you have installed previous versions of WINDOW
Radiance for WINDOW (RadianceForWindowSetup.exe)
Radiance installation needed for the WINDOW Radiance Feature
Comparisons with Previous Versions
100 glazing system set comparison
Berkeley Lab WINDOW 7.4.14 vs Berkeley Lab WINDOW 7.7.10 [PDF]
WINDOW 7 Release History
The link below will access a list of the Enhancements, Bug Fixes and Known issues for the major WINDOW 7 release notes
IMPORTANT Installation Notes — PLEASE READ and install the 2 libraries linked below
This version will not update WINDOW 7.6 versions — it makes a completely new version
When you install this new version of WINDOW, a completely new set of directories is created, so that you can have other versions (WINDOW 7.4 and 7.6) installed at the same time.
Redistributable Packages/Libraries that MUST BE installed before this version will run (if you have not previously installed them)
It is necessary to download and then install the following «redistributable» software packages in order for this version of WINDOW to run.
If you do not install these you will get error messages about DLLs not being found.
- Microsoft Visual C++
Click on this link to access the Visual Studio 2017 web page, where you can download the file shown below
https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/2977003/the-latest-supported-visual-c-downloads
Under the section Visual Studio 2017, download the «x86» file called «vc_redist.x86.exe» and then run it (double click on it) once it is downloaded - Intel Fortran
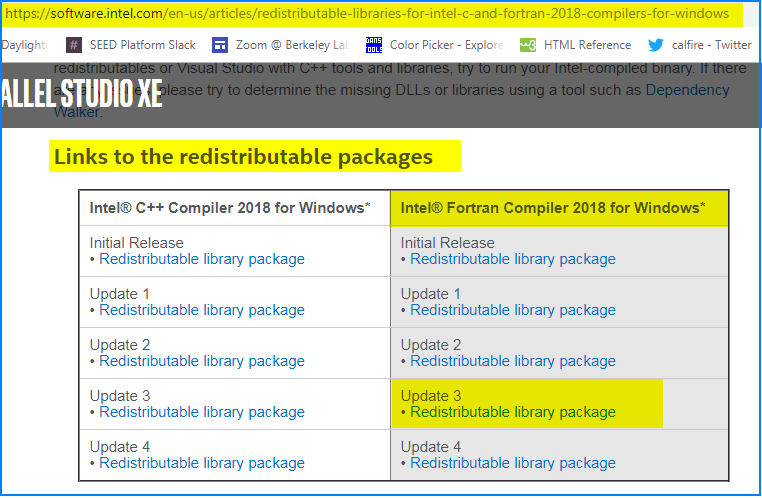
Click on this link to access the Intel web page, where you can download the file shown below
https://software.intel.com/en-us/articles/redistributable-libraries-for-intel-c-and-fortran-2018-compilers-for-windows
Under the section «Links to the redistributable packages» download the file «Update 3 Redistributable library package» (in the right hand column)
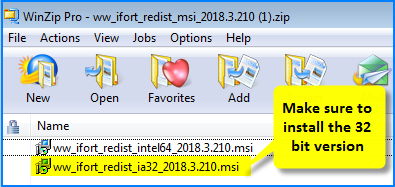
- The downloaded file (called ww_ifort_redist_msi_2018.3.210.zip) is a ZIP file and contains two installations, one for 32 bit and one for 64 bit.
- Unzip it, and install the 32 bit package (ww_ifort_redist_ia32_2018.3.210.msi)
- If you install the 64 bit version, you will probably get a
0xc000007b Error
If you have any other problems or questions about the installation, email [email protected] .
Known Bugs
Environmental Conditions — Can’t make a new record
In this version, it is not possible to make new Environmental Conditions. If you need this functionality, you should probably uninstall 7.7.10 and install 7.7.07
Bug Fixes
Glass Library Update
Fixed issue reported by user of sometimes getting an error code when updating the Glass Library to the latest version of the IGDB. This has been fixed.
Gap Library: New name reverts to Default on Save
Program now should keep the changed name on Save (rather than reverting back to Default).
Gap Library: Up and down arrows don’t work when creating a gas mixture
This has been fixed
Error opening WINDOW 7.4 database in 7.7
This has been fixed
Improvements in Libraries when saving new records
Under some circumstances, program would create a new record in a library even if the «Overwrite existing records is checked». This has been fixed in the Glazing System Library, but may still be a problem in the Glass Library.
Program asks to save record even if nothing has changed
This annoying bug has been at least partially fixed. The program should no longer ask to save the record (when going from Detail view to List view) if nothing has changed. There still may be edge cases that aren’t covered, but hopefully this is a much needed improvement for the general case.
If the program can’t open a WINDOW database, it gets into an infinite loop
When this happens, the program now allows you to select another database, rather than having to end the program through Task Manager (!)
Window Library: Double arrow selection of Type does not update the image
This has been fixed
Window Library: Under some circumstances, the name was not saved
This has been fixed
Release Notes:
Installation Files
Complete installation if you have never installed WINDOW before
Smaller installation if you have installed previous versions of WINDOW
Radiance for WINDOW (RadianceForWindowSetup.exe)
Radiance installation needed for the WINDOW Radiance Feature
Comparisons with Previous Versions
100 glazing system set comparison
Berkeley Lab WINDOW 7.4.14 vs Berkeley Lab WINDOW 7.7.07 [PDF]
Installation Notes
This version will not update WINDOW 7.6 versions — it makes a completely new version
When you install this new version of WINDOW, a completely new set of directories is created, so that you can have other versions (WINDOW 7.4 and 7.6) installed at the same time.
Redistributable Packages/Libraries that MUST BE installed before this version will run (if you have not previously installed them)
It is necessary to download and then install the following «redistributable» software packages in order for this version of THERM to run.
- Microsoft Visual C++
Click on this link to access the Visual Studio 2017 web page, where you can download the file shown below
https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/2977003/the-latest-supported-visual-c-downloads
Under the section Visual Studio 2017, download the «x86» file called «vc_redist.x86.exe» and then run it (double click on it) once it is downloaded - Intel Fortran
Click on this link to access the Intel web page, where you can download the file shown below
https://software.intel.com/en-us/articles/redistributable-libraries-for-intel-c-and-fortran-2018-compilers-for-windows
Under the section «Links to the redistributable packages» download the file «Update 3 Redistributable library package» (in the right hand column)
- The downloaded file (called ww_ifort_redist_msi_2018.3.210.zip) is a ZIP file and contains two installations, one for 32 bit and one for 64 bit.
- Unzip it, and install the 32 bit package (ww_ifort_redist_ia32_2018.3.210.msi)
- If you install the 64 bit version, you will probably get a
0xc000007b Error
If you have any other problems or questions about the installation, email [email protected] .
Enhancements
Shading Layer Library
Added Optical Openness input for shading layers in the Shading Layer Library
Matrix Library reader
Has been adapted to use the new Radiance version
Radiance
Updated to Radiance version 5.2, Oct 29, 2018
Compiled with updated libraries
WINDOW (and THERM) were compiled with Visual Studio 2017 and Intel Fortran Composed XE 2018. Hence the need to install these as redistributables when installing this new version
Better Scaling on high DPI (resolution) monitors
Using the newer Microsoft Visual C++ components allowed better scaling on high resolution monitors. Now WINDOW list views are scaled better so that they are (hopefully) readable.
Glass Library ID Limit of 65000 no longer exists
When importing a glass layer from Optics, WINDOW was restricting the ID to a value no larger than 65000. This limit no longer exists.
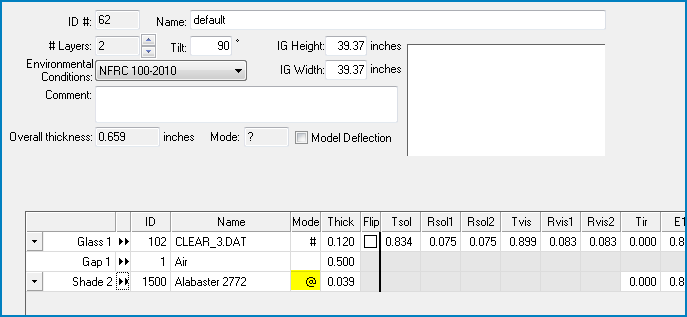
Approval symbol now displayed for Shading Systems in the Glazing System Library
The «approval» symbol (# for NFRC, @ for AERC) is now displayed for records in the Glazing System Library.
Vertical and Horizontal blinds
EnerygPlus now uses different algorithms for the thermal calculations of vertical and horizontal slatted blinds. This resulted in
- Additions to the Energy Plus BSDF IDF file from WINDOW to reflect these changes
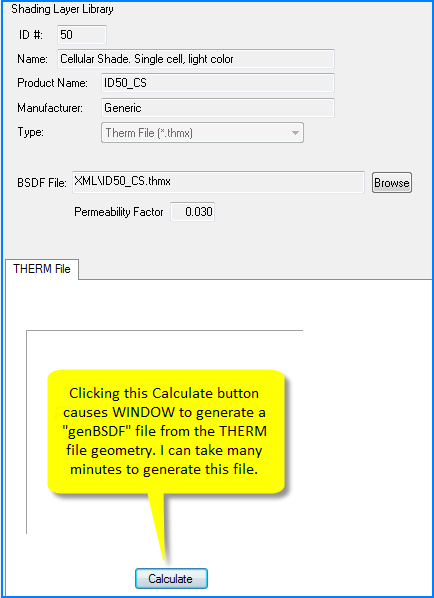
Eliminated calculation time estimate for genBSDF calculations
In the Shading Layer Library when Type = THERM, when you click the Calc button, the program generates a «genBSDF» file that can take the program a long time to generate (many minutes). The program used to try to estimate the time it would take to do this calculation; that estimation just added yet MORE time to the simulation (!), so that estimate has been eliminated from the calculation process. Just know that calculating the genBSDF files can take a long time.
Bug Fixes
Database name and path didn’t appear in the program title bar immediately on opening the program
This has been fixed
Incorrect absorptance calculation in BSDF
This has been fixed
Glazing System Report change
Vtc has been changed to Tvis under the Optical Properties section
Angular calculations for some cases (PET) were not correct
This has been fixed
Command line did not support new PermeabilityFactor input
This has been fixed
Angular calculations resulted in R+T>1 in some cases
This has been fixed
Angular calculations were broken when using the matrix method for specular glass
This has been fixed
«Frame doesn’t exist» message
In some cases, the program would display the message «Frame doesn’t exist» in a Window Library record, when the frame actually did exist in the Frame Library. This has been fixed.
When reading BSDF matrix values the program was not using the standard library
This has been fixed
Chromogenics calculations fixed
Previous versions resulted in different results for Chromogenics glazing systems in List and Detail view in the Window Library. This has been fixed.
D esigning Buildings Wiki Share your construction industry knowledge www.designingbuildings.co.uk
Search
Window
Contents
[edit] Introduction
Windows are openings fitted with glass to admit light and allow people to see out. They are often openable to allow ventilation.
Although the historic use of glass dates back to the Romans, glass windows only became common domestically in England in the early-17th century, gradually becoming more versatile and widespread as plate glass processes were perfected during the Industrial Age.
England, France, Ireland and Scotland introduced a window tax during the 18th and 19th centuries which was payable based on the number of windows in a house. It is still common to see buildings from that period with windows that were bricked-up to avoid the tax. The tax was repealed in 1851.
[edit] Elements of a window
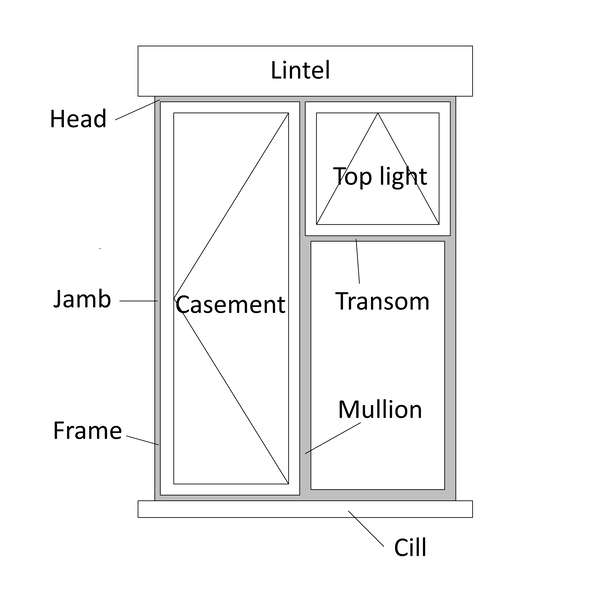
Windows are can include a number of different components:
- Light — The area between the outer parts of a window, usually filled with a glass pane.
- Frame — This holds the light in place and supports the window system.
- Lintel — A beam over the top of a window.
- Jamb — The vertical parts forming the sides of the frame.
- Sill (or cill) — The bottom piece in a window frame, often projecting beyond the line of the wall.
- Mullion — A vertical element between two windowunits or lights.
- Transom — A horizontal element between two windowunits or lights.
- Head — The uppermost member of the frame.
- Sash — The frame holding the glazing.
- Casement — A window (or sash) attached to its frame by one or more hinges.
[edit] Materials
It is important that windows be made of suitable and durable materials:
- With good thermal and sound insulation properties.
- Capable of resisting wind, and rain.
- Easy to clean.
- Providing safety and security.
Most styles of windows are available in a number of different materials. Traditionally, windows were made of timber, either hardwood or softwood, and often protected against decay using paint or a natural wood finish. This finish requires regular maintenance.
Steel and aluminium alloy windows are capable of creating larger areas of glass with a thinner frame. However, historically, these could give rise to condensation on the metal components.
PVC windows are capable of providing excellent heat and sound insulation, as well as requiring little maintenance. However, they may have a shorter life than a well-maintained timber window.
The efficiency of windows is improved by double glazing, treble glazing, low-e coatings, the construction of the frame, the type of glass, the gas used to fill the sealed unit and so on. Generally, more efficient windows are more expensive, but the capital cost may be recovered during the life of the window life through lower energy bills. In addition, the conditions within the enclosed space are likely to be more comfortable.
The BFRC Window Energy Rating (WER) scheme is based on a traffic-light style A-G ratings system for energy efficiency similar to that used for fridges, washing machines, cookers and so on. An A rating indicates a good level of energy efficiency, whilst G is the lowest possible rating.
[edit] Opening type
[edit] Fixed light
A window that is fixed in place and cannot be opened. Often used where light or vision alone is required rather than ventilation, but fixed lights are commonly used in conjunction with other openable types of window.
[edit] Vertical slider/sash
Glass is fitted in ‘sashes’ (moveable panels) that slide vertically past each other:
- Single-hung sash: One sash is moveable and the other is fixed.
- Double-hung sash: Sashes are hung on spring balances or counterweights and made up of two sashes that overlap slightly and slide up and down vertically inside the frame.
- Horizontal sliding sash: Two sashes that overlap slightly and slide horizontally on guide rails within the frame.
[edit] Casement
An opening window fixed to the frame by hinges along one of its edges:
- Side hung casement: The sash side opens outwards.
- Top hung casement: The sash top opens outwards. Also known as awning windows.
- Bottom hung casement: The sash bottom opens inwards. Also known as hopper windows.
Casement windows preceded sash windows in the UK and traditionally opened inwards, although now they more commonly open outwards so as to free space inside and better direct air inwards for ventilation.
Casement windows require a metal bar called a ‘stay’ to hold them open. Different types are available such as the peg type (the stay has holes along it which allow it to fit over pegs), telescopic (tube shaped), and friction (a bent arm allows the window to open to 180-degrees).
[edit] Tilt and turn
Tilt and turn windows Include a mechanism that allows them to tilt inwards from one edge or to open inwards from one side. The stability of the mechanism allows tilt and turn windows to be larger than casement windows. They are also easy to clean from the inside.
[edit] Pivot
Pivot windows are hung on one hinge at centre points on each of two opposite sides. This allows the window to revolve when opened. The pivots can either be vertical, with the hinges mounted top and bottom, or horizontal, with the hinges mounted at each jamb. Pivot hinges incorporate a friction device that enables the window to hold itself open against its own weight. Pivot windows tend to be more expensive than casement windows but can allow for easy cleaning access.
[edit] Bi-fold
These are made up of a number of individual sashes, usually 2, 3 or 4, hinged together. They can be opened up in a concertina style and stacked neatly against each other at the side of the window frame.
[edit] Louvre
These windows use a series of parallel pieces of glazing that are hung on centre pivots positioned at intervals down the vertical jambs that allow them to open and close using a crank or lever. They allow for good ventilation with only small projections.
[edit] Other types
- Tilt and slide window — The sash tilts inwards at the top and slides horizontally behind the fixed pane.
- Toplight — These are usually above doors.
- Sidelight — Positioned beside a door or main window.
- Skylight — These are windows positioned in the roof. The brand name ‘Velux’ has become associated with opening domesticrooflights.
- Clerestory — Bands of windows across the tops of buildings that allow natural light in without compromising privacy or security.
- Bay window — Multi-panel windows that project in front of the external wall line, being supported by a sillheight wall.
- Bow window — A curved bay window.
- Multi-lite window — Windowsglazed with small panes of glass separated by glazing bars, or muntins.They can be arranged decoratively to suit aesthetic needs or architectural styles.
- Stained glass window — Decorative windows made of coloured glass separated by glazing bars, popular in churches and Victorian houses.
- Topguided — Tracks and slides enable the top to slide downwards whist the bottom opens out.
- Sidehung — A variation on a casement window, side opening controlled by tracks and slides.
- Dormer window — A small roofed structure that projects outwards from the main pitched roof of a building. See Dormer window for more information.
- Rooflight — A domelight, lantern light, skylight, ridge light, glazedbarrel vault or other element intended to admit daylight through a roof.
- Roof window — A window that is in the same plane as the surrounding roof, and has a minimum pitch of 15-degrees. See also Velux window.
[edit] Number of panes
Thermal performance and acoustic requirements will typically determine the need for:

[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki:
[edit] External references
- https://www.sashwindowslondonltd.co.uk/bespoke-products/double-glazed-sash-windows/
- https://www.planningportal.co.uk/info/200130/common_projects/14/doors_and_windows
- http://www.build.com.au/styles-and-types-windows
- ‘BuildingConstruction Handbook’ (6th ed.), CHUDLEY, R., GREENO, R., Butterworth-Heinemann (2007)
- http://www.rationel.co.uk/windows-doors/
Comments
Great post, really interesting read!
I had my windows installed and maintained by a company called Hugo Carter. They were incredible, truly couldn’t recommend them more!