- Switching Compilers
- Set compiler in the toolchain
- Set compiler in the CMake profile
- Install CLion
- System requirements
- Toolchain requirements
- Install using the Toolbox App
- Install the Toolbox App
- Install the Toolbox App
- Install the Toolbox App
- Standalone installation
- Silent installation on Windows
- Silent configuration file
- Install as a snap package on Linux
- Tutorial: Configure CLion on Windows
- MinGW
- MinGW-w64 (64- and 32-bit)
- MinGW (32-bit only)
- Cygwin
- Windows Subsystem for Linux
- Microsoft Visual C++
- MSVC compiler
- Clang-cl compiler
- MSVC debugger
- Clang compiler on Windows
- Set up the Clang compiler for MinGW
Switching Compilers
In CLion, you can use GCC and Clang compilers.
On Windows, the provided environment (Cygwin, MinGW, or Microsoft Visual C++) includes the compilers along with other tools.
There are two ways of changing the compiler for your CMake project, either in the toolchain settings or in the CMake profile settings. The difference between these two options is in their scope : toolchains are set per IDE, affecting all the projects you work with in CLion, while CMake options are configured for a particular CMake profile defined per project.
Set compiler in the toolchain
Go to Settings / Preferences | Build, Execution, Deployment | Toolchains .
In the C++ Compiler or C Compiler fields specify the path to the desired installation, for example:
Set compiler in the CMake profile
Go to Settings / Preferences | Build, Execution, Deployment | CMake .
In the CMake options field, specify the compiler by setting the CMAKE_LANG_COMPILER variable:
The LANG part specifies the language ( C for C and CXX for C++), and you need to provide the full path to the compiler, for example:
After you apply the settings, CLion will reset the CMake cache and reload your project.
When you specify the compiler in CMake settings, it overrides the selection made in the toolchain settings.
Источник
Install CLion
CLion is a cross-platform IDE that provides consistent experience on Windows, macOS, and Linux (for setup on FreeBSD, refer to this instruction).
System requirements
| Requirement | Minimum | Recommended |
|---|---|---|
| RAM | 2 GB of free RAM | 8 GB of total system RAM |
| CPU | Any modern CPU | Multi-core CPU. CLion supports multithreading for different operations and processes making it faster the more CPU cores it can use. |
| Disk space | 2.5 GB and another 1 GB for caches | SSD drive with at least 5 GB of free space |
| Monitor resolution | 1024×768 | 1920×1080 |
| Operating system | Latest 64-bit version of Windows, macOS, or Linux (for example, Debian, Ubuntu, or RHEL) |
* CLion is not available for some Linux distributions, such as RHEL6/CentOS6, which do not include glibc version 2.14 required by JBR 11.
You do not need to install Java to run CLion because JetBrains Runtime is bundled with the IDE (based on JRE 11).
Toolchain requirements
In case of using MSVC compiler: Visual Studio 2013, 2015, 2017, or 2019
In case of using WSL: Windows 10 Fall Creators Update (least version 1709, build 16299.15)
Xcode command line developer tools (to install, use the xcode-select —install command)
In case of using custom CMake: version 2.8.11 or later
In case of using custom GDB: version 7.8.x-10.2 or later
Install using the Toolbox App
The JetBrains Toolbox App is the recommended tool to install JetBrains products. Use it to install and manage different products or several versions of the same product, including Early Access Program (EAP) and Nightly releases, update and roll back when necessary, and easily remove any tool. The Toolbox App maintains a list of all your projects to quickly open any project in the right IDE and version.
Install the Toolbox App
Download the installer .exe from the Toolbox App web page.
Run the installer and follow the wizard steps.
After you run the Toolbox App, click its icon in the notification area and select which product and version you want to install.
Log in to your JetBrains Account from the Toolbox App and it will automatically activate the available licenses for any IDE that you install.
Install the Toolbox App
Download the disk image .dmg from the Toolbox App web page.
There are separate disk images for Intel and Apple Silicon processors.
Mount the image and drag the JetBrains Toolbox app to the Applications folder.
After you run the Toolbox App, click its icon in the main menu and select which product and version you want to install.
Log in to your JetBrains Account from the Toolbox App and it will automatically activate the available licenses for any IDE that you install.
Install the Toolbox App
Download the tarball .tar.gz from the Toolbox App web page.
Extract the tarball to a directory that supports file execution.
For example, if the downloaded version is 1.17.7391, you can extract it to the recommended /opt directory using the following command:
Execute the jetbrains-toolbox binary from the extracted directory to run the Toolbox App and select which product and version you want to install. After you run the Toolbox App for the first time, it will automatically add the Toolbox App icon to the main menu.
Log in to your JetBrains Account from the Toolbox App and it will automatically activate the available licenses for any IDE that you install.
You can use this shell script that automatically downloads the tarball with the latest version of the Toolbox App, extracts it to the recommended /opt directory, and creates a symbolic link in the /usr/local/bin directory.
Standalone installation
You can install CLion manually and have the option to manage the location of every instance and all the configuration files. This is useful, for example, if you have a policy that requires specific install locations.
Run the installer and follow the wizard steps.
On the Installation Options step, you can configure the following:
Create a desktop shortcut for launching CLion.
Add the directory with CLion command-line launchers to the PATH environment variable to be able to run them from any working directory in the Command Prompt.
Add the Open Folder as Project action to the system context menu (when you right-click a folder).
Associate specific file extensions with CLion to open them with a double-click.
To run CLion, find it in the Windows Start menu or use the desktop shortcut. You can also run the launcher batch script or executable in the installation directory under bin .
Extract the archive to the desired folder.
To run CLion, use the launcher batch script or executable in the extracted directory under bin .
There are separate disk images for Intel and Apple Silicon processors.
Mount the image and drag the CLion app to the Applications folder.
Run the CLion app from the Applications directory, Launchpad, or Spotlight.
Unpack the downloaded CLion-*.tar.gz archive. The recommended extract directory is /opt :
Do not extract the tarball over an existing installation to avoid conflicts. Always extract to a clean directory.
Execute the CLion.sh from bin subdirectory to run CLion:
To create a desktop entry, do one of the following:
On the Welcome screen, click Configure | Create Desktop Entry
From the main menu, click Tools | Create Desktop Entry
When you run CLion for the first time, some steps are required to complete the installation, customize your instance, and start working with the IDE.
Silent installation on Windows
Silent installation is performed without any user interface. It can be used by network administrators to install CLion on a number of machines and avoid interrupting other users.
To perform silent install, run the installer with the following switches:
/S : Enable silent install
/CONFIG : Specify the path to the silent configuration file
/D : Specify the path to the installation directory
This parameter must be the last in the command line and it should not contain any quotes even if the path contains blank spaces.
To check for issues during the installation process, add the /LOG switch with the log file path and name between the /S and /D parameters. The installer will generate the specified log file. For example:
Silent configuration file
You can download the default silent configuration file for CLion at https://download.jetbrains.com/cpp/silent.config
The silent configuration file defines the options for installing CLion. With the default options, silent installation is performed only for the current user: mode=user . If you want to install CLion for all users, change the value of the installation mode option to mode=admin and run the installer as an administrator.
The default silent configuration file is unique for each JetBrains product. You can modify it to enable or disable various installation options as necessary.
It is possible to perform silent installation without the configuration file. In this case, omit the /CONFIG switch and run the installer as an administrator. Without the silent configuration file, the installer will ignore all additional options: it will not create desktop shortcuts, add associations, or update the PATH variable. However, it will still create a shortcut in the Start menu under JetBrains .
Install as a snap package on Linux
You can install CLion as a self-contained snap package. Since snaps update automatically, your CLion installation will always be up to date.
To use snaps, install and run the snapd service as described in the installation guide.
On Ubuntu 16.04 LTS and later, this service is pre-installed.
CLion is distributed via two channels:
The stable channel includes only stable versions. To install the latest stable release of CLion, run the following command:
The —classic option is required because the CLion snap requires full access to the system, like a traditionally packaged application.
The edge channel includes EAP builds. To install the latest EAP build of CLion, run the following command:
When the snap is installed, you can launch it by running the clion.sh command.
To list all installed snaps, you can run sudo snap list . For information about other snap commands, see the Snapcraft documentation.
Источник
Tutorial: Configure CLion on Windows
On Windows, configuring CLion requires setting up the environment: Cygwin, MinGW, WSL, or Microsoft Visual C++. You can have several environments installed on your system and create separate CLion toolchains for each of them. As a determining part of a toolchain, the environment provides C and C++ compilers, the make utility, and the debugger (in case of using default tools).
For details on Remote Host toolchains, see Full Remote Mode.
MinGW
MinGW-w64 (64- and 32-bit)
Download and run the MinGW-w64 installer. It provides both 64- and 32-bit options.
In the MinGW-w64 installation wizard, make sure to select the required architecture. Note that the default suggested option is 32-bit.
Once the installation is finished, open CLion and go to File | Settings | Build, Execution, Deployment | Toolchains .
Choose the MinGW toolchain that you want to configure or create a new one using the icon.
CLion will attempt to detect the MinGW installation automatically. Check the detection result in the Environment field, and specify the path manually if required.
Wait until the tools detection finishes.
Select the Debugger : you can use either MinGW-w64 GDB or a custom GDB binary.
Click Apply when all the tools are set correctly.
MinGW (32-bit only)
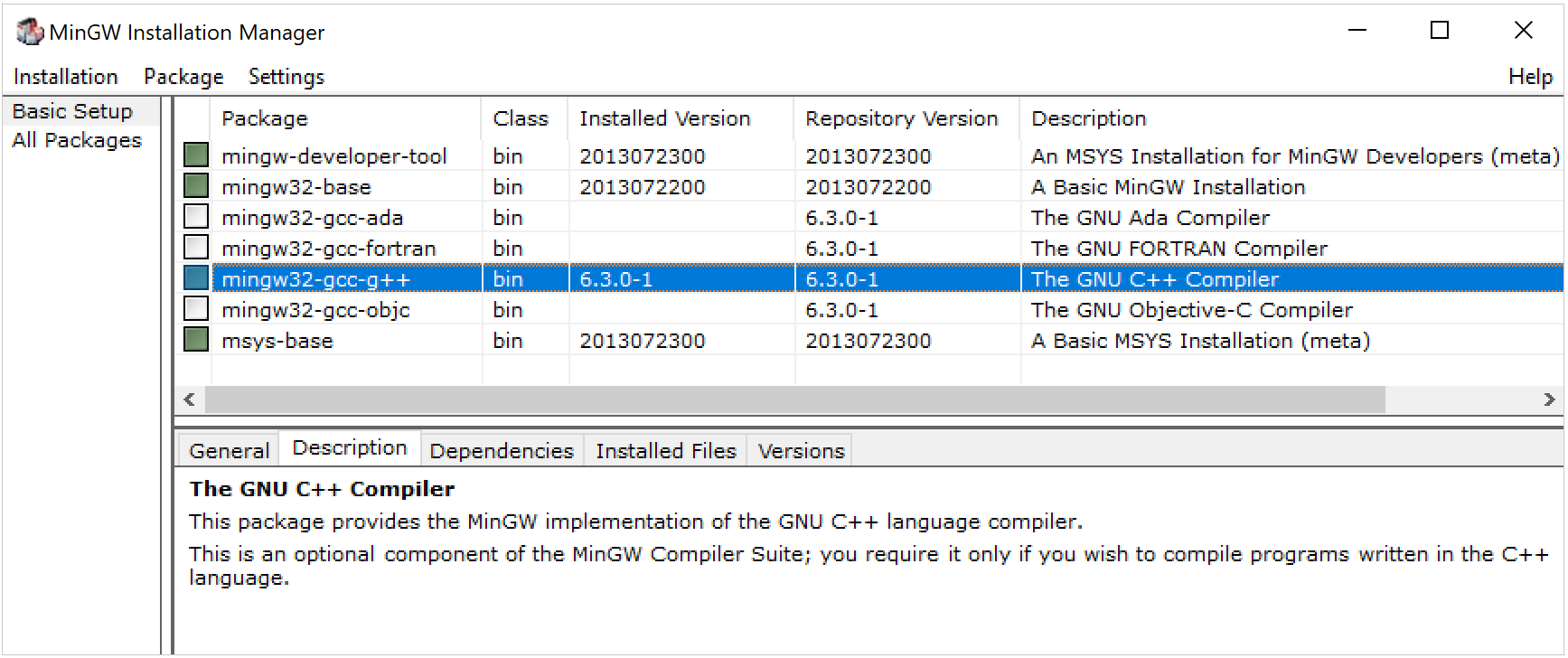
Although MinGW-w64 provides both 64- and 32-bit options, you can also install MinGW, the 32-bit-only version.
In the MinGW installation wizard, select the following packages from the Basic Setup list: mingw-developer-tool , mingw32-base , mingw32-gcc-g++ , mingw32-msys-base .
When configuring the toolchain, if CLion cannot detect compilers or make , double-check the installed packages in MinGW Installation Manager .
In the Debugger field, you can choose between the bundled GDB, MinGW GDB, or your custom GDB executable.
The recommended option is bundled GDB, since it is guaranteed to include Python support required for CLion data renderers.
Cygwin
Download the Cygwin installer, version 2.8 or later.
Run the installer and select the following packages:
- gcc-g++
- make
- gdb
To select a package, type its name in the Search field and set the version in the New column:
Once the installation is finished, open CLion and go to File | Settings | Build, Execution, Deployment | Toolchains . Choose the toolchain that you want to configure.
Select Cygwin from the Environment list. CLion will attempt to detect the Cygwin installation automatically. Check the detection result, and specify the path manually if required.
Wait until the tools detection finishes, and click Apply .
Windows Subsystem for Linux
You can use WSL, Windows Subsystem for Linux, as your working environment in CLion on Windows 10 (starting the Fall Creators Update version 1709, build 16299.15).
WSL toolchain enables you to build projects using CMake and compilers from Linux and run/debug on WSL without leaving CLion running on your Windows machine.
Refer to our WSL guide for details on setting up WSL on your system and configuring WSL toolchains in CLion.
Microsoft Visual C++
Install Visual Studio 2013, 2015, 2017, or 2019 on your system.
In CLion, go to File | Settings | Build, Execution, Deployment | Toolchains .
Click and select Visual Studio from the list of toolchain templates.
Check the Environment field. CLion will attempt to automatically detect the installed Visual Studio distribution. If the detection fails, set the path to Visual Studio manually.
If required, specify the Architecture ( x86 , amd64 , x86_arm , or another), Platform ( store , uwp , onecore , or leave it blank), and Version . To build your project for the selected architecture, CLion will call the script to configure the environment with the specified parameters.
If the version of your compiler toolset is earlier than the version of your Visual Studio installation, pass it in the Version field via the vcvars_ver flag, for example, -vcvars_ver=14.16 .
Wait until the tools detection is finished:
MSVC compiler
CLion supports the Microsoft Visual C++ compiler that ships with Visual Studio 2013, 2015, 2017, and 2019.
Note that msbuild is not supported: CLion runs CMake with the NMAKE generator instead.
For the case when your code includes MSVC extensions, CLion provides the support for:
__uuidof , __forceinline , __unaligned , and __alignof keywords;
pointer type attributes: __ptr32 , __ptr64 , __uptr , __sptr ;
MSVC built-in data types: (unsigned) __int8 , (unsigned) __int16 , (unsigned) __int32 , (unsigned) __int64 , __wchar_t ;
additional format specifiers, such as %I32 and %I64 ;
the clang ‘s -fms-extensions flag.
Clang-cl compiler
As an alternative compiler, you can use clang-cl- the MSVC-compatible compiler driver for Clang. CLion supports clang-cl version 8.0 and later.
Install clang-cl from the LLVM site or along with the Visual Studio tools.
When installed from the LLVM site, the clang-cl binary can be found at the standard location C:\Program Files\LLVM\bin\clang-cl.exe for the 64-bit version or C:\Program Files (x86)\LLVM\bin\clang-cl.exe for the 32-bit version.
In CLion, go to File | Settings | Build, Execution, Deployment | Toolchains and select the Visual Studio toolchain that you want to configure, or create a new one.
Point the C Compiler and C++ Compiler fields to clang-cl.exe . CLion will suggest the paths detected automatically.
Note that currently the -T clangcl options can’t be picked up if the bundled CMake is in use along with the Visual Studio toolchain setup (CPP-18848).
MSVC debugger
The MSVC toolchain debugger is implemented on top of LLDB, and it can work with native visualizers from the Visual Studio installation or from your project.
To enable native visualizers support and set the desired diagnostics level, select the Enable NatVis renderers for LLDB checkbox in Settings | Build, Execution, Deployment | Debugger | Data Views | C/C++ :
CLion automatically generates one-line summaries for all structures not covered by Natvis and highlights them to increase readability. Also, the built-in formatters provide visualization for wide/Unicode strings ( wchar_t , char16_t , char32_t ).
If you have custom native visualizers in your project, CLion will use them as well.
Clang compiler on Windows
With CMake 3.15, it has become possible to use the Clang compiler on Windows with the MinGW-w64/MinGW toolchain.
However, the LLVM Clang for Windows is built using Microsoft Visual Studio, and all the built-in macros and include search paths are set up for use with Visual Studio. So if you take Clang from the LLVM repository, it will not work correctly when configured with the MinGW toolchain. One of the possible workarounds is described below.
Set up the Clang compiler for MinGW
Download the following packages with the pacman tool (use the pacman -S package_name command):
Источник