- Как установить заголовочные файлы ядра в Linux
- Установка заголовочных файлов ядра в Debian, Ubuntu или Linux Mint
- Установка заголовочных файлов ядра в Fedora, CentOS или RHEL
- CentOS Linux install kernel headers to build vmware / 3rd party modules
- How to Install Kernel Headers in CentOS 7
- Install Kernel Headers in CentOS 7
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
- I Need the Kernel Source
- 1. Maybe you do not need the full kernel source
- 2. If you really need the full kernel source
- Redhat enterprise Linux / CentOS installing kernel source code
- Rhel / CentOS 5 install kernel headers
- Install kernel source code
Как установить заголовочные файлы ядра в Linux
Когда вы компилируете драйвер устройства как модуль ядра, вам необходимы установленные заголовочные файлы ядра. Также они требуются, если вы собираете пользовательское приложение, которое взаимодействует напрямую с ядром. При установке заголовочных файлов ядра, необходимо убедиться, что их версия совпадает с версией ядра установленного в системе.
Если версия вашего ядра не менялась после установки дистрибутива, или вы обновляли его с использованием системного менеджера пакетов (то есть apt-get, aptitude или yum) из системных репозиториев, то заголовочные файлы вы также можете установить с помощью пакетного менеджера. Однако если вы скачивали исходный код ядра и компилировали его самостоятельно, то заголовочные файлы необходимо устанавливать с помощью команды make.
Здесь мы предполагаем, что ваше ядро установлено из основного системного репозитория вашего дистрибутива, и вы хотите установить соответствующие заголовочные файлы ядра.
Установка заголовочных файлов ядра в Debian, Ubuntu или Linux Mint
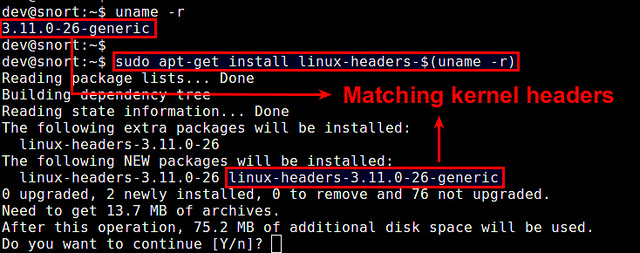
Если вы не компилировали ядро вручную, то можете установить соответствующие заголовочные файлы ядра с помощью команды apt-get.
Сначала проверьте, не установлены ли уже требуемые заголовочные файлы с помощью команды:
Теперь установите заголовочные файлы, как показано ниже.
Проверьте, что установка прошла успешно.
По умолчанию в Debian, Ubuntu или Linux Mint заголовочные файлы находятся в /usr/src.
Установка заголовочных файлов ядра в Fedora, CentOS или RHEL
Если вы не обновляли ядро вручную, то можете установить соответствующие заголовочные файлы ядра с помощью команды yum.
Сначала проверьте, не установлены ли уже требуемые заголовочные файлы. По умолчанию заголовочные файлы ядра расположены в /usr/src/kernels/.
Если подходящих заголовочных файлов не установлено, вы можете установить их с помощью команды yum. Она автоматически найдет подходящий пакет.
Если заголовочные файлы ядра, установленные с помощью вышеприведенной команды, не соответствуют установленному в системе ядре, значит оно устарело. В этом случае обновите ядро системы до последней версии с помощью приведенной ниже команды. После обновления необходимо перезагрузить систему.
Теперь проверьте, что установлены заголовочные файлы соответствующей версии с помощью команды:
Источник
CentOS Linux install kernel headers to build vmware / 3rd party modules
Q . I’ve CentOS 5 installed under vmware. When I run following command:
vmware-config-tools.pl
or
vmware-config.pl
It asks about Linux kernel headers to build custom headers.
How do I fix this problem?
A . You don’t have development package for building kernel modules to match the kernel. It is required to build 3rd party modules such as vmware or graphics card drivers.
There is a package called kernel-devel. This package provides kernel headers and makefiles sufficient to build modules against the kernel package.
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
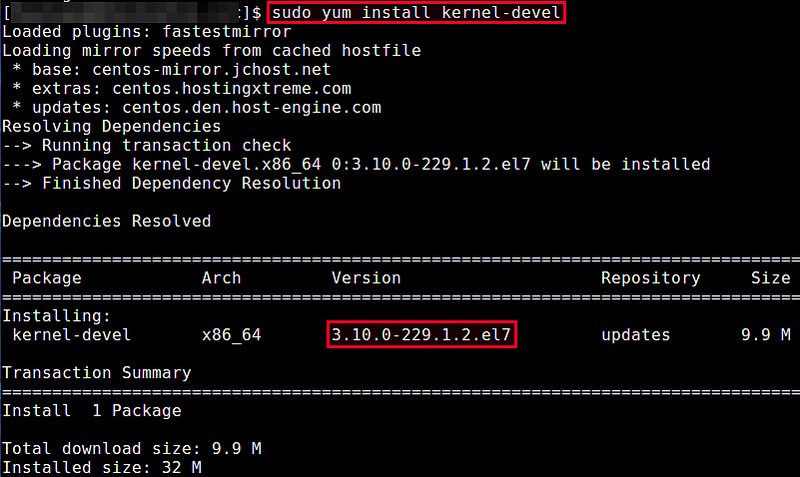
Login as the root, and use yum command to install the same:
# yum install kernel-devel
Now you should able to build kernel modules.
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
How to Install Kernel Headers in CentOS 7
When you compile a custom kernel module such as a device driver on a CentOS system, you need to have kernel header files installed on the system, which include the C header files for the Linux kernel. Kernel header files provide different kinds of function and structure definitions required when installing or compiling any code that interfaces with the kernel.
When you install Kernel Headers, make sure it matches with the currently installed kernel version on the system. If your Kernel version comes with the default distribution installation or you have upgraded your Kernel using yum package manager from system base repositories, then you must install matching kernel headers using package manager only. If you’ve compiled Kernel from sources, you can install kernel headers from sources only.
In this article, we will explain how to install Kernel Headers in CentOS/RHEL 7 and Fedora distributions using default package manager.
Install Kernel Headers in CentOS 7
First confirm that the matching kernel headers are already installed under /usr/src/kernels/ location on your system using following commands.

If no matching kernel headers are located in the /usr/src/kernels/ directory, go ahead and install kernel headers, which is provided by the kernel-devel package that can be installed using default package manager as shown.

After installing the kernel-devel package, you can find all the kernel headers files in /usr/src/kernels directory using following command.
Note on a VPS (for instance a Linode VPS), a kernel may have a customized version name, in such scenario, you have to identify the kernel version manually and check the installed kernel header files using following commands.

Sample Output
In addition, if you need header files for the Linux kernel for use by glibc, install the kernel-header package using following command.
Now you are good to go with compiling your own or existing kernel modules for software such as VirtualBox and many more.
That’s it! In this article, we have explained how to install kernel-devel and kernel-header packages in CentOS/RHEL 7 and Fedora systems. Remember that before you can compile kernel modules such as device driver on a Linux system, you should have necessary kernel header files installed. If you have queries, please use the comment form below to reach us.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник
I Need the Kernel Source
Created by JohnnyHughes. Currently maintained by AlanBartlett and AkemiYagi.
1. Maybe you do not need the full kernel source
If you need to compile a kernel driver (module), the chances are you do not really need to install the full kernel source tree. You might just need to install the kernel-devel package. (If, however, you are certain that the full source tree is required, please follow the instructions in Section 2.)
In CentOS-7, there is just one kernel-devel package available:
- kernel-devel (64-bit architecture)
(Note that CentOS-7 32-bit is available through the AltArch i386 SIG.)
You can install the kernel-devel package by:
If your kernel is not listed by yum because it is in an older tree, you can download it manually from the CentOS Vault.
Look in either the 7.N.YYMM/os/x86_64/Packages/ or the 7.N.YYMM/updates/x86_64/Packages/ directories for the kernel-devel- version.x86_64.rpm
Once you have the proper kernel[-type]-devel- version.arch.rpm package installed, try to compile your module. It should work that way. If it does not, please provide feedback to the module’s developer as this is the way all new kernel modules should be designed to be built.
2. If you really need the full kernel source
If you really must have the kernel source tree, for whatever reason, it is obtainable.
As an ordinary user, not root, create a build tree based on a
» height=»16″ src=»https://wiki.centos.org/moin_static1911/memodump/img/attention.png» title=» » width=»16″/> You are strongly advised against package building as root. (See: Building Source RPM as non-root under CentOS)
To install the source package and tools for CentOS-7:
As root install the asciidoc, audit-libs-devel, bash, bc, binutils, binutils-devel, bison, diffutils, elfutils, elfutils-devel, elfutils-libelf-devel, findutils, flex, gawk, gcc, gettext, gzip, hmaccalc, hostname, java-devel, m4, make, module-init-tools, ncurses-devel, net-tools, newt-devel, numactl-devel, openssl, patch, pciutils-devel, perl, perl-ExtUtils-Embed, pesign, python-devel, python-docutils, redhat-rpm-config, rpm-build, sh-utils, tar, xmlto, xz and zlib-devel packages:
Find the kernel source rpm package in:
(Replace the «N.YYMM» with the relevant sub-version, year and month numbers.)
As an ordinary user, not root, install the source package by executing:
Now that the source package and tools are installed, unpack and prepare the source files:
The value of $(uname -m) sets the target to the architecture of your current kernel. This is generally accepted, as most people will need either i686 or x86_64 as the target.
The kernel source tree will now be found under the
HowTos/I_need_the_Kernel_Source (последним исправлял пользователь AlanBartlett 2021-09-27 15:16:02)
Источник
Redhat enterprise Linux / CentOS installing kernel source code
Q . How do I install Linux kernel source code and headers under RHEL 5 or CentOS 5 Linux operating system?
A . Both CentOS and RHEL 5 includes following packages:
a) Kernel-headers : It includes the C header files that specify the interface between the Linux kernel and userspace libraries and programs. The header files define structures and constants that are needed for building most standard programs and are also needed for rebuilding the glibc package.
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
b) kernel-devel : This package provides kernel headers and makefiles sufficient to build modules against the kernel package.
c) Actual kernel source code : You can always download actual source code here. Look for kernel*.rpm file.
Rhel / CentOS 5 install kernel headers
Use yum command as follows:
# yum install kernel-devel Kernel-headers
Install kernel source code
Type the command as follows:
# cd /tmp
# wget ftp://ftp.redhat.com/pub/redhat/linux/enterprise/5Server/en/os/SRPMS/kernel-2.6.18-8.1.8.el5.src.rpm
# rpm -ivh kernel-2.6.18-8.1.8.el5.src.rpm
Note change version number as per your current kernel.
For recompiling or adding a new module or device driver you just need kernel-devel and Kernel-headers packages. To rebuilt kernel rpm goto /usr/src/redhat/SPECS directory, modify kernel spec file and use rpmbuild command to rebuild rhel/centos kernel rpm.
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник