- How To Linux Set or Change User Password
- Linux Set User Password
- Linux change password for other user account
- Linux Change Group Password
- Changing user passwords on Linux
- Forcing Linux user to change password at their next login
- Locking and Unlocking user password of the named account
- A note about setting up a secure Linux password
- Conclusion
- How do I change a user password in Ubuntu Linux?
- How to change a user password in Ubuntu
- How to change a root (superuser) password in Ubuntu
- How do I change the user account password on Ubuntu?
- Deleting a user password
- Linux locking an account
- Linux unlocking an account
- Conclusion
- How to Change a User’s Password in Linux
- Changing Password Through the UI
- Changing Password Through the Command Line
- Changing Your Own Password
- Changing Password for Another User
- Changing the Password for sudo
- About the author
- Karim Buzdar
How To Linux Set or Change User Password
Linux Set User Password
Type following passwd command to change your own password:
$ passwd
Sample Outputs:
The user is first prompted for his/her old password if one is present. This password is then encrypted and compared against the stored password. The user has only one chance to enter the correct password. The super user is permitted to bypass this step so that forgotten passwords may be changed. A new password is tested for complexity. As a general guideline, passwords should consist of 10 to 20 characters including one or more from each of following sets:
- Lower case alphabetics
- Upper case alphabetics
- Digits 0 thru 9
- Punctuation marks/spacial characters
Linux change password for other user account
You need to login as the root user, type the following command to change password for user vivek:
# passwd vivek
OR
$ sudo passwd vivek
Sample putput:
- vivek – is username or account name.
Passwords do not display to the screen when you enter them. For example:
Linux changing user password using passwd
Linux Change Group Password
When the -g option is used, the password for the named group is changed. In this example, change password for group sales:
# passwd -g sales
The current group password is not prompted for. The -r option is used with the -g option to remove the current password from the named group. This allows group access to all members. The -R option is used with the -g option to restrict the named group for all users.
Changing user passwords on Linux
As a Linux system administrator (sysadmin) you can change password for any users on your server. To change a password on behalf of a user:
- First sign on or “su” or “sudo” to the “root” account on Linux, run: sudo -i
- Then type, passwd tom to change a password for tom user
- The system will prompt you to enter a password twice
To change or set a new root (superuser) password type:
$ sudo passwd
Forcing Linux user to change password at their next login
By default, Linux passwords never expire for users. However, we can force users to change their password the next time they log in via GUI or CLI methods. The syntax is straightforward:
$ sudo passwd -e
$ sudo passwd —expire
Let us immediately expire an account’s password:
$ sudo passwd -e marlena
The system will confirm it:
When user try to login via ssh command, they will see the following on screen:
Locking and Unlocking user password of the named account
Note that the following local command does not disable the account. The user may still be able to login using another authentication token, such as an SSH key. To disable the account, administrators should use either usermod —expiredate 1
We can lock the password as follows:
$ sudo passwd -l
This option disables a password by changing it to a value which matches no possible encrypted value (it adds a ! at the beginning of the password in the /etc/shadow file. Want to unlock the password, try:
$ sudo passwd -u
The above command option re-enables a password by changing the password back to its previous value. In other words, to the value before using the -l option.
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
A note about setting up a secure Linux password
Compromises in password security typically result from careless password selection. Avoid common password such as:
- Words which appears in a dictionary
- Your first and last name
- Pet names
- Kids or spouses names
- License number
- Date of birth (DoB)
- Home or office address
I strongly recommend that you generate a unique password for all user accounts using your chosen password manager.
Conclusion
The passwd command line utility is used to update or change user’s password. The encrypted password is stored in /etc/shadow file and account information is in /etc/passwd file. To see all user account try grep command or cat command as follows:
$ cat /etc/passwd
$ grep ‘^userNameHere’ /etc/passwd
$ grep ‘^tom’ /etc/passwd
The guidance given in this quick tutorial should work with any Linux distribution, including Alpine, Arch, Ubuntu, Debian, RHEL, Fedora, Oracle CentOS, SUSE/OpenSUSE and other popular Linux distros.
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
How do I change a user password in Ubuntu Linux?
W e recently switched from Windows server operating system to Ubuntu Linux operating system at work. I am a developer by profession and do not know much about Linux. I need to change the sftp/ssh user account password on Ubuntu. How do I change a user password in Ubuntu Linux?
Introduction – Your Ubuntu Linux account information stored in a file named /etc/passwd and encrypted password in /etc/shadow . This page explains to you how to change the Ubuntu Linux root and user account password using the passwd command line.
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | Ubuntu Linux |
| Est. reading time | 2 minutes |
How to change a user password in Ubuntu
- Open the terminal application by pressing Ctrl + Alt + T
- To change a password for user named tom in Ubuntu, type:
sudo passwd tom - To change a password for root user on Ubuntu Linux, run:
sudo passwd root - And to change your own password for Ubuntu, execute:
passwd
How to change a root (superuser) password in Ubuntu
Firstly, open a terminal window. If you want to change the password for remote Ubuntu server, log in using the ssh command:
ssh user@ubuntu-server-ip
ssh vivek@ubuntu-webserver-1
Type ‘sudo -i’ at the command prompt, and Enter key:
sudo -i
Type the current user password and press Enter key. Finally type NA command and press Enter to change password for root user:
passwd
Change password for root user on Ubuntu
How do I change the user account password on Ubuntu?
Again open a terminal window. Type the following command to change the password for regular Ubuntu user account named jerry:
sudo passwd < userNameHere >
sudo passwd jerry ## ##
sudo passwd vivek ## ##
How to change the user Password in Ubuntu Linux
Deleting a user password
Users will not be able to log in when the password is deleted or expired on Ubuntu Linux.
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
The syntax is as follow to remove the password for the account called tom:
sudo passwd -d tom
## OR ##
sudo passwd —delete jerry
You will see confirmation on screen as follows:
To set up a new password when deleted, run:
sudo passwd -d tom
We can also force expire the password for the named account jerry. Open the terminal and then type the following command:
sudo passwd -e jerry
sudo passwd —expire jerry
When user login they will be forced to reset their credentials when you use the -e / —expire option:
Linux locking an account
sudo passwd -l
sudo passwd -l tom
Linux unlocking an account
sudo passwd -u
sudo passwd -u tom
Conclusion
This quick tutorial taught you how to change the Ubuntu Linux root user and other user account password using the passwd command. You must root user to change the password for all other users, however users can change their password without sudo access. For more info see the passwd command help page using the man command man passwd
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
| Category | List of Unix and Linux commands |
|---|---|
| Documentation | help • mandb • man • pinfo |
| Disk space analyzers | df • duf • ncdu • pydf |
| File Management | cat • cp • less • mkdir • more • tree |
| Firewall | Alpine Awall • CentOS 8 • OpenSUSE • RHEL 8 • Ubuntu 16.04 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Linux Desktop Apps | Skype • Spotify • VLC 3 |
| Modern utilities | bat • exa |
| Network Utilities | NetHogs • dig • host • ip • nmap |
| OpenVPN | CentOS 7 • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Debian 8/9 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Package Manager | apk • apt |
| Processes Management | bg • chroot • cron • disown • fg • glances • gtop • jobs • killall • kill • pidof • pstree • pwdx • time • vtop |
| Searching | ag • grep • whereis • which |
| Shell builtins | compgen • echo • printf |
| Text processing | cut • rev |
| User Information | groups • id • lastcomm • last • lid/libuser-lid • logname • members • users • whoami • who • w |
| WireGuard VPN | Alpine • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Firewall • Ubuntu 20.04 |
Comments on this entry are closed.
For your own password:
passwd
For root password:
sudo passwd root
FYI, we don’t set root password on Ubuntu for security reasons. One user will be added to the ‘sudo’ group and that will act as admin user. This ensures safety as root account without password is locked and cannot be used for ssh.
Источник
How to Change a User’s Password in Linux
- It includes both upper and lower case letters
- It includes digits from 0 to 9
- It has special characters and punctuation marks
- It is a lot different than your previous passwords
- It does not include information such as your full name, address, phone number, birth date, or license numbers. This information can easily be used to guess your password.
Always note down your password in a secure location from where it can not be fetched. It would help you in remembering the password in case you forgot it.
In this article, we will tell you how you can manage user passwords in Linux through the command line and GUI. We have run the commands and processes mentioned in this article on a Debian 10 Buster system but you can replicate them on most Linux distros.
Changing Password Through the UI
If you are a Linux user who prefers the graphical user interface to perform most administrative operations, you can use the Settings utility on your system.
There are two ways in which you can access the system Settings.
- Access the Application Launcher through the Super/Windows key and then enter the keywords ‘settings’ in the search bar as follows:
- Click the downward arrow in the top panel of the Debian/Ubuntu desktop and then click on the ‘settings’ icon from the following drop-down menu:
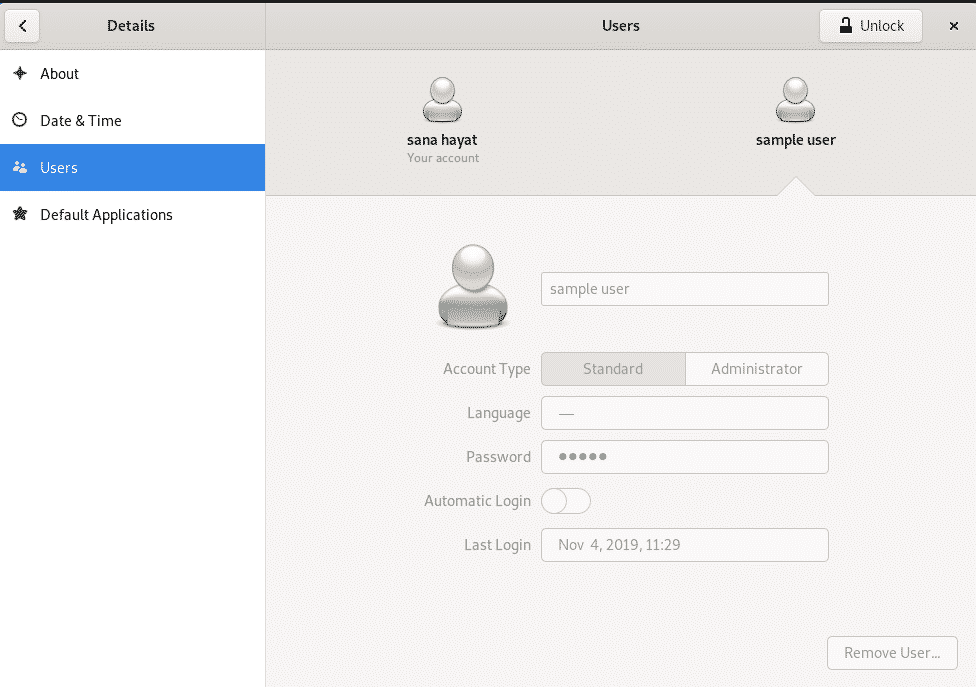
In the Settings utility, select the Details tab from the left panel and then select the Users tab on it to open the Users settings view. This is how the Users view looks like:
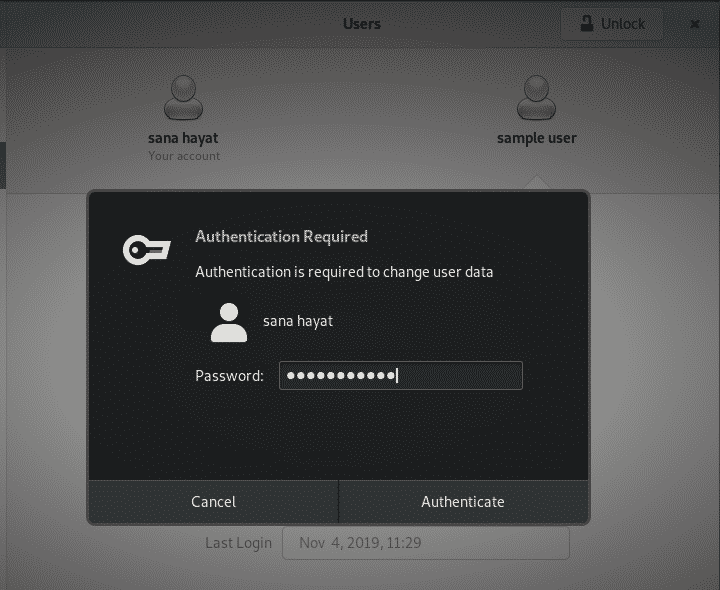
All the users on your system will be listed here. Click on the user whose details you want to change. You need to first unlock the Users view so that you can make changes to its settings. Please remember that only an authorized user/administrator can unlock the view. Click the Unlock button and enter your credentials as follows:
As you click the Authenticate button, the fields on the Users view will become active and you can make changes to them.
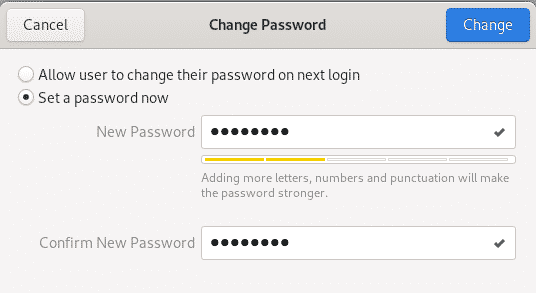
Click on the Password field and the following Change Password view will open. Enter the New Password, and then enter the same password again in the Confirm New Password field. You will now be able to see the Change button active.
Click on the Change button and the password for the selected user will be changed.
Tip: One easy and quick way to access the Users settings is to enter the keyword ‘Users’ in the Application Launcher as follows:
Changing Password Through the Command Line
The Linux command line gives an administrator much more power than the UI, to make user and system settings. In order to launch the default command line application on Linux Debian and Ubuntu, open the Application Launcher and enter the ‘Terminal’ keywords as follows:
As the Terminal opens, you can do the following with user passwords:
- Change your own password
- Change password for another user
- Change the password for sudo
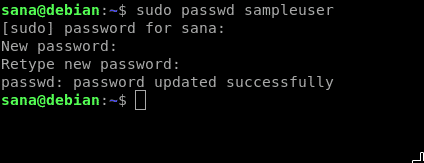
Changing Your Own Password
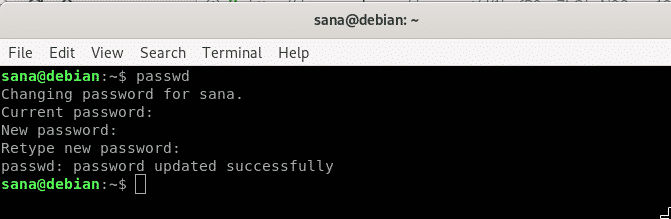
A non-administrator on Linux can only change their own password. The passwd command is used to change user passwords in Linux. This is how a user can use this command to change their own password:
As you enter the passwd command, the system prompts you to enter your current password. As you do so, this password is checked against the stored password. If it matches, you are proceeded to the next step i.e, to enter the new password. After you enter the new password, the system then asks again to type the new password for confirmation. After the two entries match, your password will be successfully changed.
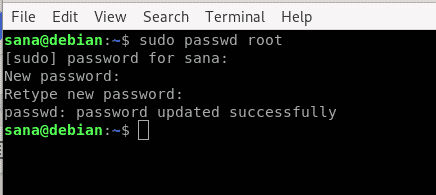
Changing Password for Another User
On Linux, only an administrator/superuser can change the password for another user. This is the command a superuser will be using:
As a user enters this command, they will be asked the password for sudo to ensure that they are indeed a super user. A super user is not required to enter the old password for a user as they might be using the command to reset a forgotten password. Anyways, the super user is also required to enter and re-enter the new password, after which, it is updated successfully.
Changing the Password for sudo
It is a good security practice to change a super user’s password on Linux from time to time. Here are two ways through which you can change a sudo password:
Method 1:
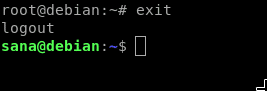
The first way is to log in as root through the following command:
When you are logged in as root after entering a valid password, use the passwd command to change the password for root.
You can then exit the root prompt through the exit command as follows:
Method 2:
The second method is to use the following command as sudo:
Enter the password for sudo and then you can change the password of root, like you do for any other user.
This was all you needed to know about changing user passwords in Linux, both through the UI and the command line. You can now maintain a much secure user account on your system.
About the author
Karim Buzdar
Karim Buzdar holds a degree in telecommunication engineering and holds several sysadmin certifications. As an IT engineer and technical author, he writes for various web sites. He blogs at LinuxWays.
Источник