- Переменная PATH в Linux
- Переменная PATH в Linux
- Выводы
- How to Permanently Set $PATH in Linux
- Understanding the $PATH Variable
- Using bash_profile to Set your PATH
- Using bashrc to Set your PATH
- Using a Profile File to Set your PATH
- Free eBook: Git Essentials
- Permanently Setting your PATH for Other Shells like ZSH and KSH
- Permanently Setting System-Wide PATH for all Users
- Troubleshooting PATH Problems
- What is this $PATH in Linux and how to modify it
- 3 Answers 3
- How can I edit the $PATH on linux?
- 8 Answers 8
Переменная PATH в Linux
Когда вы запускаете программу из терминала или скрипта, то обычно пишете только имя файла программы. Однако, ОС Linux спроектирована так, что исполняемые и связанные с ними файлы программ распределяются по различным специализированным каталогам. Например, библиотеки устанавливаются в /lib или /usr/lib, конфигурационные файлы в /etc, а исполняемые файлы в /sbin/, /usr/bin или /bin.
Таких местоположений несколько. Откуда операционная система знает где искать требуемую программу или её компонент? Всё просто — для этого используется переменная PATH. Эта переменная позволяет существенно сократить длину набираемых команд в терминале или в скрипте, освобождая от необходимости каждый раз указывать полные пути к требуемым файлам. В этой статье мы разберёмся зачем нужна переменная PATH Linux, а также как добавить к её значению имена своих пользовательских каталогов.
Переменная PATH в Linux
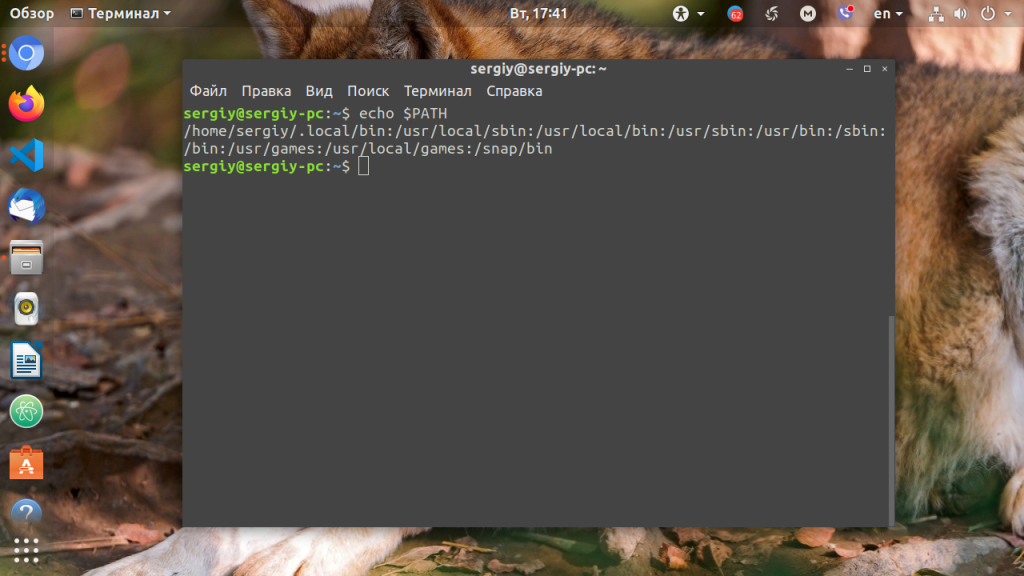
Для того, чтобы посмотреть содержимое переменной PATH в Linux, выполните в терминале команду:
На экране появится перечень папок, разделённых двоеточием. Алгоритм поиска пути к требуемой программе при её запуске довольно прост. Сначала ОС ищет исполняемый файл с заданным именем в текущей папке. Если находит, запускает на выполнение, если нет, проверяет каталоги, перечисленные в переменной PATH, в установленном там порядке. Таким образом, добавив свои папки к содержимому этой переменной, вы добавляете новые места размещения исполняемых и связанных с ними файлов.
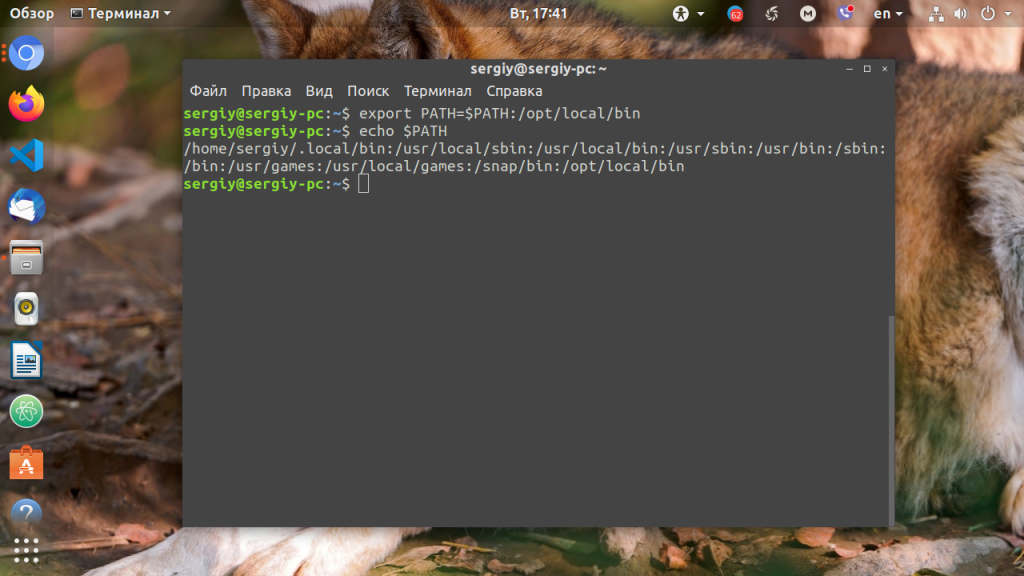
Для того, чтобы добавить новый путь к переменной PATH, можно воспользоваться командой export. Например, давайте добавим к значению переменной PATH папку/opt/local/bin. Для того, чтобы не перезаписать имеющееся значение переменной PATH новым, нужно именно добавить (дописать) это новое значение к уже имеющемуся, не забыв о разделителе-двоеточии:
Теперь мы можем убедиться, что в переменной PATH содержится также и имя этой, добавленной нами, папки:
Вы уже знаете как в Linux добавить имя требуемой папки в переменную PATH, но есть одна проблема — после перезагрузки компьютера или открытия нового сеанса терминала все изменения пропадут, ваша переменная PATH будет иметь то же значение, что и раньше. Для того, чтобы этого не произошло, нужно закрепить новое текущее значение переменной PATH в конфигурационном системном файле.
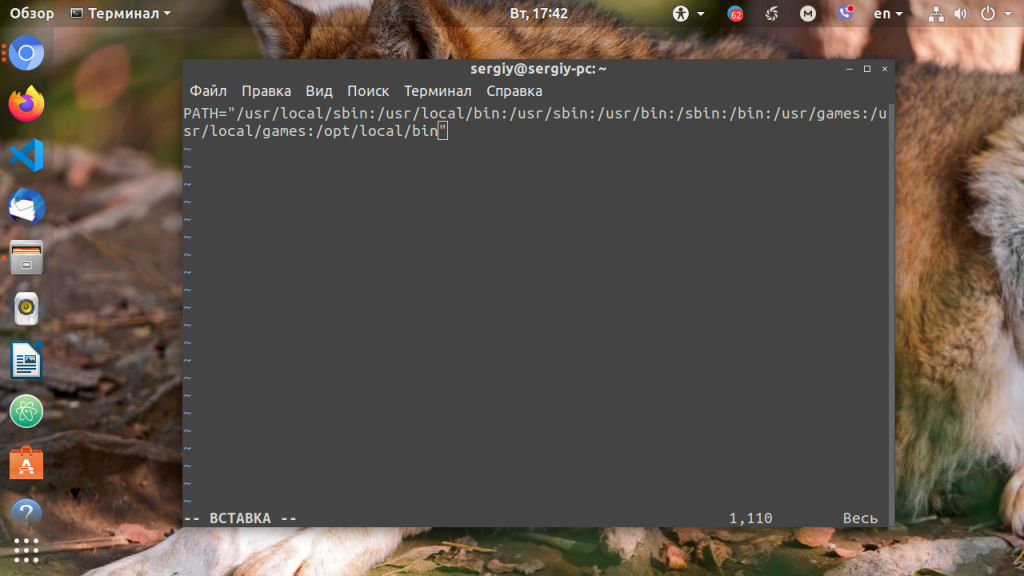
В ОС Ubuntu значение переменной PATH содержится в файле /etc/environment, в некоторых других дистрибутивах её также можно найти и в файле /etc/profile. Вы можете открыть файл /etc/environment и вручную дописать туда нужное значение:
sudo vi /etc/environment
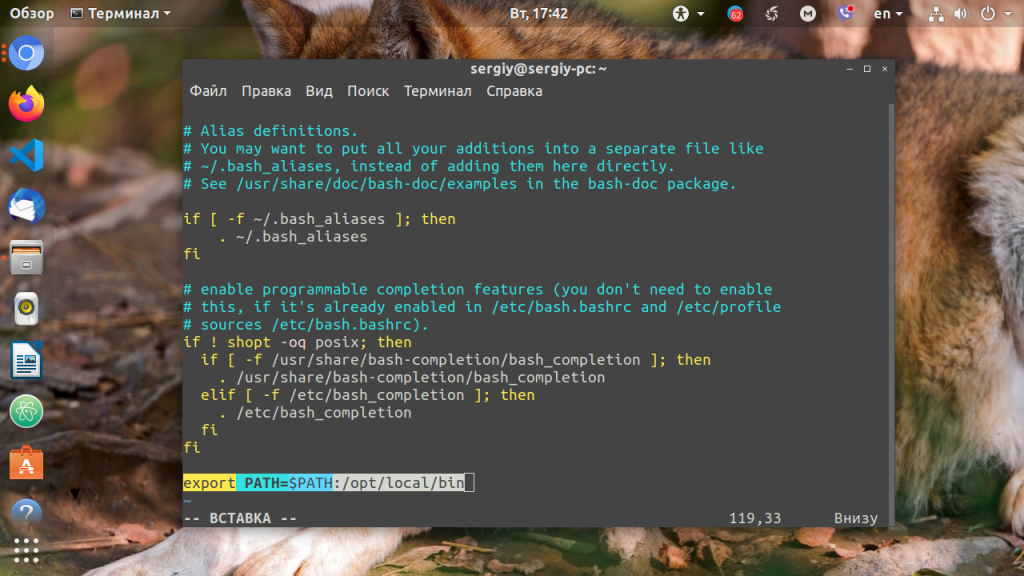
Можно поступить и иначе. Содержимое файла .bashrc выполняется при каждом запуске оболочки Bash. Если добавить в конец файла команду export, то для каждой загружаемой оболочки будет автоматически выполняться добавление имени требуемой папки в переменную PATH, но только для текущего пользователя:
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели вопрос о том, зачем нужна переменная окружения PATH в Linux и как добавлять к её значению новые пути поиска исполняемых и связанных с ними файлов. Как видите, всё делается достаточно просто. Таким образом вы можете добавить столько папок для поиска и хранения исполняемых файлов, сколько вам требуется.
Источник
How to Permanently Set $PATH in Linux
Understanding the $PATH Variable
In this tutorial, we will show you how to permanently set your PATH on Linux.
First off, why should you care?
The $PATH variable, or just PATH, without the $ indicating variables, specifies a list of directories that impacts your computing platform’s functionality in a critical way. This is because the $PATH is the list of directories in which the system searches for executable programs, scripts, or files.
Imagine trying to run the ssh command, for example, to connect to a server. What happens if the system cannot find the ssh program? You are unable to connect to servers and run computations. You have a plethora of useful programs, examples like python , javac , npm , make , chmod , apt-get and so on, that your computer needs to be able to find when you invoke them at the command line.
The $PATH variable is the key that makes it possible to find the correct program and execute it at your command without needing the executable’s full directory path. When your PATH is set incorrectly, your shell will be unable to find programs, and certain commands will fail.
Using bash_profile to Set your PATH
A common mistake with the $PATH variable is to set it in the current shell only, without persisting the change. When you open a new shell, the changes are lost, and you are once again unable to execute certain commands because those programs are not found in the PATH.
The first way of setting your $PATH permanently is to modify the $PATH variable in your Bash profile file, located at /home/ /.bash_profile .
For example, let’s say I want to add a new directory /home/tomahawk/tools/jdk1.8.0_92/bin to my PATH. You might recognize this as a Java Development Kit installation. However, that is beside the point. Whatever the directory contains, I can add it to our path and make the programs that this bin directory contains accessible from the command line by adding the following line to the end of the file
A good way to edit the file is to use nano , vi , vim or emacs . You can use the command sudo
/.bash_profile , and enter your admin password when prompted, then add that line to the end and save the file.
To activate the changes in the current shell, you have to «source» the updated bash_profile file. You do this with the command:
This simply imports the file’s settings into the current shell. Now every time you open your shell, your bash_profile will automatically be «sourced» and you won’t need to run this command every time.
Now we can invoke commands or programs in the new directory /home/tomahawk/tools/jdk1.8.0_92/bin , such as javac , located at /home/tomahawk/tools/jdk1.8.0_92/bin/javac by just typing at the command prompt the name of the program. We can do this now from any directory, because the PATH has been updated to look for executable programs in our new directory.
Now runs the correct javac program, printing out something like the following:
bash_profile is appropriate when you want to set a PATH variable customized for a single user of the system. If you wanted to set PATH for all users of a system, there are better ways to do so, which we cover further on in this guide.
Using bashrc to Set your PATH
Instead of setting the PATH in
/.bash_profile , we can also add the directories we want to the PATH in
/.bashrc instead. Setting the PATH in bashrc looks identical to how we set it in bash_profile .
For example, to include the directory /home/tomahawk/.rbenv/bin in my path, I edit or create the file /home/tomahawk/.bashrc , adding the following line:
Notice that, like last time, the first thing in our new PATH export is the inclusion of the existing $PATH variable. This ensures that we preserve the current value of PATH, and just add any additional directories on to the PATH, after the $PATH variable. If you do not do this, you will overwrite the PATH variable entirely, and miss critical directories the system needs to be on the PATH. As a result, your system can become unusable.
The difference between using bashrc and bash_profile is that bash_profile is used for login shells. These run when you login via the console, or log in using ssh . In contrast, once you are logged in, and you open a command shell or run the bash command, the bashrc file will run. Your PATH settings from bashrc will then be available.
The effect of setting the PATH is similar. In addition, we must activate any changes in the bashrc file into the current shell the first time we make this change, just as we did for the bash_profile file. This time, we run source
/.bashrc . We can now access the new PATH at the command line. It has been set permanently and will stay the same between multiple logins into the system.
Using a Profile File to Set your PATH
We can also set the PATH permanently using a user’s profile file. This is different from
/.bash_profile in that it is set not for shells only, but for all programs.
User profiles are loaded at login. The PATH variable can be set in the
To set my PATH to include everything already in $PATH, as well as a new directory /home/tomahawk/.exenv/bin , I edit the file at
/.profile and set the PATH as follows
As in all prior examples, we will need to source these changes to make them active for the current shell, but subsequent logins will persist the changes.
Free eBook: Git Essentials
Check out our hands-on, practical guide to learning Git, with best-practices, industry-accepted standards, and included cheat sheet. Stop Googling Git commands and actually learn it!
Once that’s done, I can run the exenv command, which is one of the programs available in the folder I just added to the PATH, and I get back the output of my exenv version:
You can read more about the exenv program here, but you can use this process to set PATH permanently to include any program or directory you want.
Permanently Setting your PATH for Other Shells like ZSH and KSH
If you use alternative shells such as zsh, ksh and others, you can set the PATH permanently using those shells’ configuration.
Like bash, both zsh and ksh use a zshrc and khsrc file, respectively, to set the path for non-login shells. For login shells, they use the analogous shell profile files zprofile and kprofile.
You can therefore set the PATH permanently for these shells in a similar way to what we did for Bash. For zsh, you can find these files, or create them if they do not exist, at
Similarly, you can set PATH permanently for ksh in the configuration files located at
There are plenty of other shells you can use, such as the C Shell and the tcsh shell. Setting the PATH permanently for them will generally follow the pattern we have seen here.
Permanently Setting System-Wide PATH for all Users
System-wide settings for all users can be set in /etc/profile . There is considerable flexibility and multiple options for setting the PATH permanently system-wide.
Your Linux system will execute all script files ending in .sh in /etc/profile.d whenever a bash shell is entered, as well as when the desktop session loads.
You can therefore add a new file, such as env.sh inside the directory /etc/profile.d . In this file, we can export the PATH variable, setting it permanently to our choice of path directories, for example:
Files in /etc/profile.d are sourced by /etc/profile, thus activating our system-wide PATH whenever a user logs in.
We can also set PATH for all users in /etc/environment , which takes key-value pairs of the form:
Troubleshooting PATH Problems
As we saw, setting the PATH permanently in Linux has many options. You can set the PATH for only a certain user, for all users, or for only certain types of command shells. However, it’s a good idea to not fiddle with system-wide PATH settings unless you really know what you are doing.
If you encounter problems, a good starting point is to find out the current value of $PATH, by running the command:
For more troubleshooting tips, check out this resource.
Источник
What is this $PATH in Linux and how to modify it
I have a few questions on this $PATH in Linux.
I know it tells the shell which directories to search for executable files, so:
- What does it mean an environmental variable?
- How to change its path? and is it recommended to change it?
- IF i change it what are the consequences?
3 Answers 3
To get your path current $PATH variable type in:
It tells your shell where to look for binaries.
Yes, you can change it — for example add to the $PATH folder with your custom scripts.
So: if your scripts are in /usr/local/myscripts to execute them you will have to type in a full path to the script: /usr/local/myscripts/myscript.sh After changing your $PATH variable you can just type in myscript.sh to execute script.
Here is an example of $PATH from RHEL:
To change your $PATH you have to either edit
/.bash_profile ) for user or global $PATH setting in /etc/profile .
One of the consequences of having inaccurate $PATH variables is that shell will not be able to find and execute programs without a full $PATH .
Firstly, you are correct in your statement of what $PATH does. If you were to break it somehow (as per your third point), you will have to manually type in /usr/bin/xyz if you want to run a program in /usr/bin from the terminal. Depending on how individual programs work, this might break some programs that invoke other ones, as they will expect to just be able to run ls or something.
So if you were to play around with $PATH, I would suggest saving it somewhere first. Use the command line instruction
to save it in someRandomFile.txt
You can change $PATH using the export command. So
HOWEVER, this will completely replace $PATH with someNewPath. Since items in path are separated by a «:», you can add items to it (best not to remove, see above) by executing
The fact that it is an environmental variable means that programs can find out its value, ie it is something that is set about the environment that the program is running in. Other environmental variables include things like the current directory and the address of the current proxy.
Источник
How can I edit the $PATH on linux?
I am using ubuntu 9.04 I need to add some folder to my $PATH. I know how to read the path:
I want to be able to edit it and add 2 other paths.
8 Answers 8
To permanently store your path, you have a few options.
I suggest you read the Ubuntu community wiki on Environment Variables but the short answer is the best place is
/.profile for your per-user PATH setting or /etc/profile for global settings.
Do something like export PATH=$PATH:/your/new/path/here
You can also put this in the global environment:
Append to the entries already in your path
Reload the environment
It has already been answered on how to do that, but I’d like to give you a little tip. Here is whatI do:
I have a directory called .bash.d in my $HOME and within that I keep a set of shell scripts that do stuff to my environment (for instance setup maven correctly, modify the path, set my prompt etc.). I keep this under version control by using git, which makes it easy to go back to a working version of your env, if you screw something up badly. To get all the modifications, I simply source all files in that dir at the end of my .bashrc like this:
This gives you a very flexible environment that you can easily modify and restore + you are able to export it to other machines just by using git.
Источник