- Linux – Determine / Find Ethernet Connection Speed
- How do I determine ethernet connection speed?
- How to Test Network Speed in Linux via CLI
- Test Network Speed on Linux Via Command Line
- Using speedtest-cli to Test Internet Speed
- Using fast-cli to Test Internet Speed
- Using CMB to Show Network Speed
- Using iperf to Measure Network Speed Between Two Devices
- Using nload to View Incoming and Outgoing Network Traffic
- Using tcptrack to Test Network Activity
- Using iftop to Test Speed on a Network Interface
- Using wget to Test Download Speed
- Using youtube-dl to Test Internet Speed
Linux – Determine / Find Ethernet Connection Speed
Most intelligent network devices use an autonegotiation protocol to communicate what media technologies they support, and then select the fastest mutually supported media technology.
How do I determine ethernet connection speed?
Type the following command to get speed for eth0:
$ ethtool eth0 | less
OR
$ ethtool eth0 | grep -i speed
Sample outputs:
Fig.01: Ubuntu Linux verify the speed of my NIC (network card)
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
| Category | List of Unix and Linux commands |
|---|---|
| Documentation | help • mandb • man • pinfo |
| Disk space analyzers | df • duf • ncdu • pydf |
| File Management | cat • cp • less • mkdir • more • tree |
| Firewall | Alpine Awall • CentOS 8 • OpenSUSE • RHEL 8 • Ubuntu 16.04 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Linux Desktop Apps | Skype • Spotify • VLC 3 |
| Modern utilities | bat • exa |
| Network Utilities | NetHogs • dig • host • ip • nmap |
| OpenVPN | CentOS 7 • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Debian 8/9 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Package Manager | apk • apt |
| Processes Management | bg • chroot • cron • disown • fg • glances • gtop • jobs • killall • kill • pidof • pstree • pwdx • time • vtop |
| Searching | ag • grep • whereis • which |
| Shell builtins | compgen • echo • printf |
| Text processing | cut • rev |
| User Information | groups • id • lastcomm • last • lid/libuser-lid • logname • members • users • whoami • who • w |
| WireGuard VPN | Alpine • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Firewall • Ubuntu 20.04 |
Comments on this entry are closed.
Is there any similar functionality on Windows?
I want to see the Duplex and Speed on Windows as well.
yes you have to go to your Ethernet card properties which can me done through device manger and there select advance option and change the LAN link speed either to 10 or 100 Mbps full or half duplex
I’m using Ubuntu 8.10 alpha 3 32bits.
I tried “ethtool eth0 | grep -i speed ” but needed to add sudo to execute it.
Without sudo:
Cannot get device settings: Operation not permitted
Cannot get wake-on-lan settings: Operation not permitted
Cannot get link status: Operation not permitted
jp@jp-desktop810:
$ sudo ethtool eth0 | grep -i speed
Speed: 100Mb/s
Talk about difficult to find out what my nic link speed is with linux (fedora 8) …
I would have expected “settings/network or network status” to show me.
On windows just look at the properties/status of the network card object and it shows link speed, duplex and real time packet count.
On Windows, you type in a fairly long command to get it, instead of just “ethtool “, which is shorter. You’re comparing the graphical tools available on Windows to the command line of Linux. Apples and oranges.
Tried this on ubuntu, uhm, 8 or something (was some old usb livestick i often use to revive data from dead computers and laptops).
I had to install the ethtool first, but a permission denied. This command worked though:
sudo apt-get install ethtool
Then I tried the first command in this article, which gave me no info and I didn´t know howto get out of the program. Closed the terminal and opened it up again, then ran the second command. Permission denied. But a sudo !! did the trick. In short, this would work after doing the apt-get-install:
sudo ethtool eth0 | grep -i speed
Hope this helps others out who are just as newb as me 🙂
apt-get and ethtool are administrator tools hence the need to use sudo before the actual commands. Users are normally not able to use them as they can affect the system and possibly cause major failures in connectivty or software.
On amazon Linux on EC2, ethtool only says whether a link is detected or not.
ifconfig -a
cat /proc/net/bonding/bond0
cat /proc/net/bonding/bond1
If you don’t have ethtool installed, you may have mii-tool:
# mii-tool
eth0: negotiated 1000baseT-FD flow-control, link ok
eth1: negotiated 100baseTx-FD flow-control, link ok
Can any one tell me ,How to get Ethernet Link Speed(through command prompt i e Terminal ) in MAC OS X ?
Thank you
If your interface name is en6, enter:
ifconfig en6 | grep media
media: autoselect (100baseTX )
If your interface name is en0, enter:
ifconfig en0 | grep media
Источник
How to Test Network Speed in Linux via CLI
Home » SysAdmin » How to Test Network Speed in Linux via CLI
With the increase in people staying at home and spending more time on the Internet, ISPs have seen traffic loads higher than ever. If you noticed your network speed was slower at times, this global overload is the reason.
There are many online tools to test internet speed. However, Linux users can do this from the command prompt window. Some of the utilities for testing both local and internet speed we will cover are:
- Speedtest
- Fast
- Color Bandwidth Meter (CBM)
- iPerf
- nload
- Tcptrack
- Iftop
- Wget
- youtube-dl
Follow the instructions in this article to learn how to test network connection speed on Linux using the terminal. The steps work in both normal and headless mode.
- A machine running Linux
- sudo / root permissions
- Access to a terminal / command-prompt window
Test Network Speed on Linux Via Command Line
The tools in this guide help you check the Internet and LAN speed on a Linux machine. The article uses Ubuntu 20.04 for instructions, but the utilities work for any Linux distribution.
Note: Use the appropriate package manager for your Linux distribution, for example, yum for RHEL / CentOS, to install the apps.
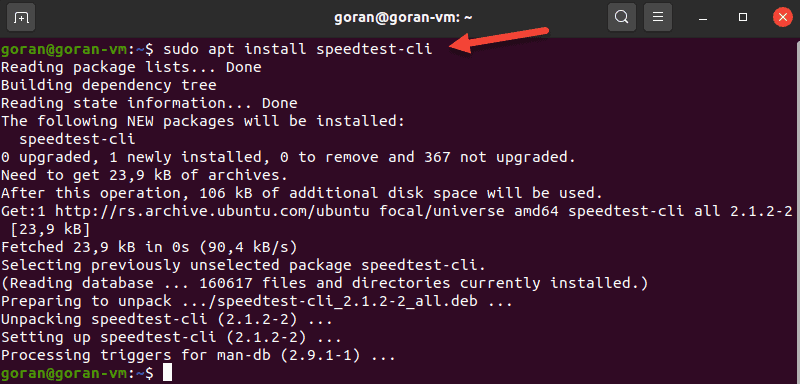
Using speedtest-cli to Test Internet Speed
One of the most famous online internet connection test apps is speedtest.net. To install Speedtest on Linux via the terminal, use a package manager for your distro.
On Ubuntu, enter:
Optionally, use pip to install speedtest-cli in Python:
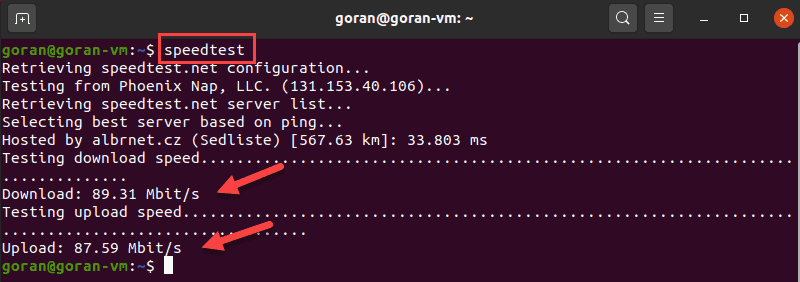
To run the test, type:
The standard speedtest-cli output shows all steps, including selecting a server. To display a shorter output, enter:
The test is simple to use and provides multiple options. To view all of them, pass the -h flag to display the speedtest-cli help file.
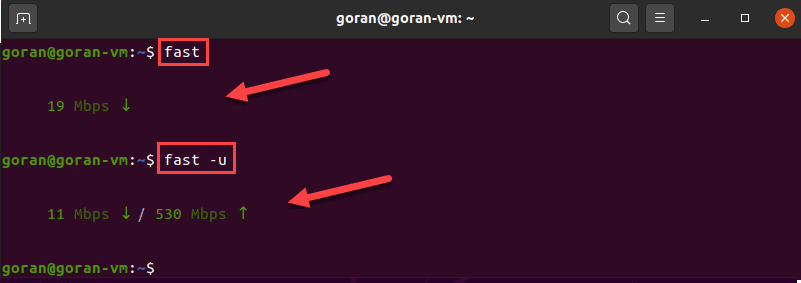
Using fast-cli to Test Internet Speed
Fast is a lightweight CLI utility based on the web speed test fast.com. The test uses Netflix servers to provide results.
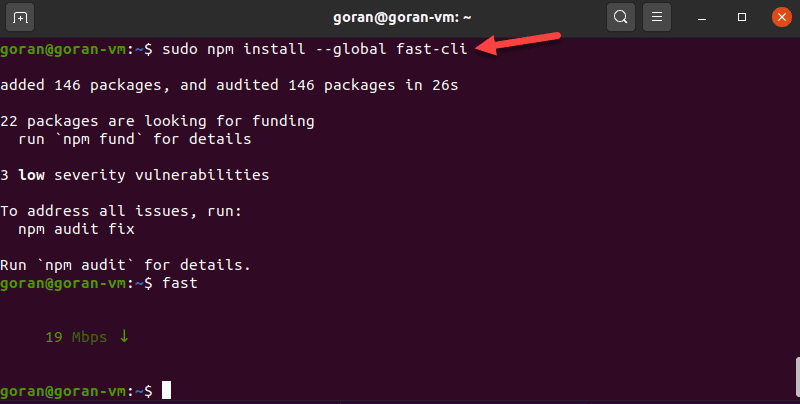
Fast-cli is simple to use, but you need the node package manager (NPM) on your machine. The package comes with Nodejs.
For example, to install Node.js version 15, enter these commands:
Then, run the install command:
If needed, run the npm init command and then install Fast:
To test the download speed, enter:
To show both the download and upload speed, add the -u option:
This internet speed test aims to provide only the information about your connection speed, without any bells and whistles.
Note: Since NPM is a requirement, it can be a hassle to install fast-cli. If you need more help with NPM installation, see our guides How To Install Node.Js And NPM On CentOS or How To Install Node.Js & NPM On Ubuntu.
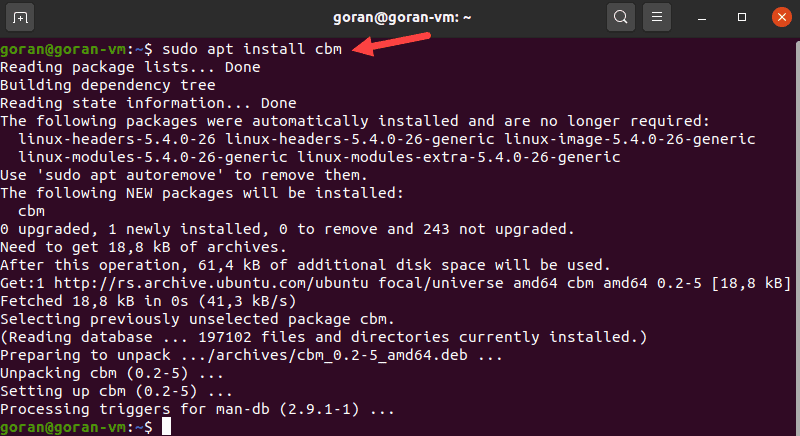
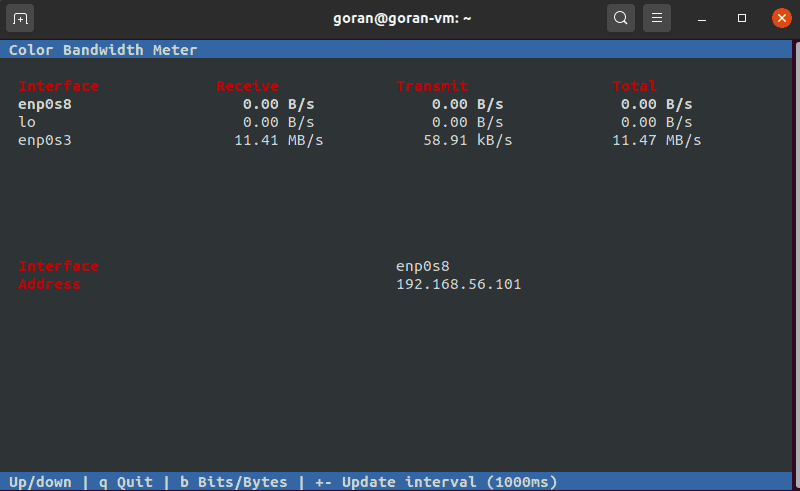
Using CMB to Show Network Speed
The Color Bandwidth Meter (CMB) is a Linux tool that displays activity on all network interfaces. After the installation, run the tool to see network speeds in color-coded columns.
To install CBM, run this command:
When the process finishes, run the tool:
The output displays the transmit, receive, and total speed. Use the arrows to switch between the interfaces.
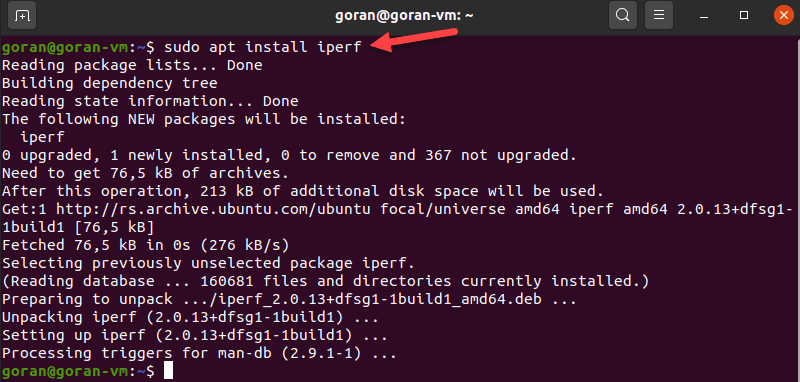
Using iperf to Measure Network Speed Between Two Devices
The iPerf tool provides many options for testing connection speed between a server and a client. Hence, to perform a test, you need to install the utility on both machines:
Make sure the client can reach the server. For quick confirmation, run a ping test.
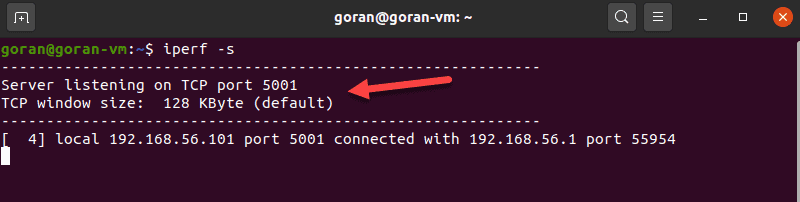
If port 5001 is open, the connection works. So, on the server machine, enter:
The device starts listening for a connection request.
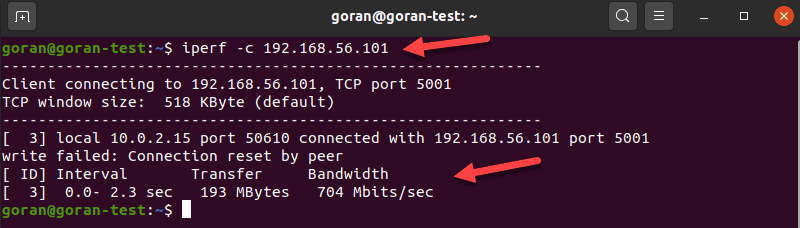
On the other machine, enter:
The output shows the transfer and bandwidth information:
Using nload to View Incoming and Outgoing Network Traffic
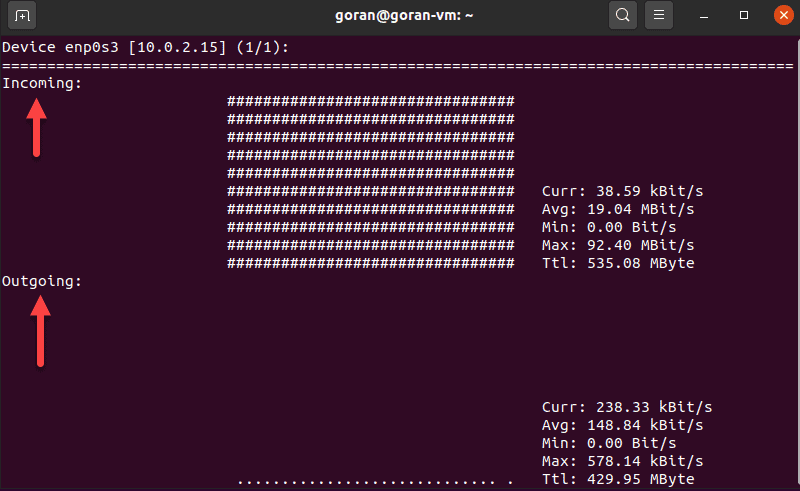
Nload is a tool that monitors incoming and outgoing activity on a network interface you specify. The application splits the traffic into two sections for easier data analysis.
To install the tool, enter:
To run the application, specify the network interface:
If there is activity on the selected interface, nload displays network speed details.
Using tcptrack to Test Network Activity
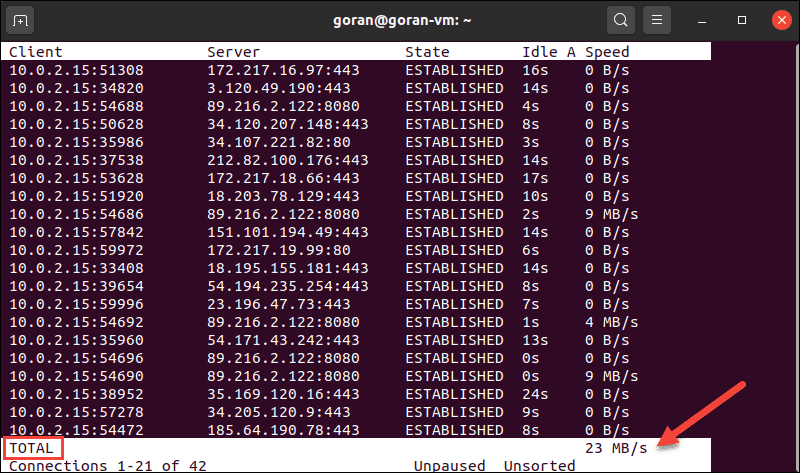
TCPtrack shows the connection status for a network interface. When your machine’s network is active, run this tool to view and monitor bandwidth speed and usage.
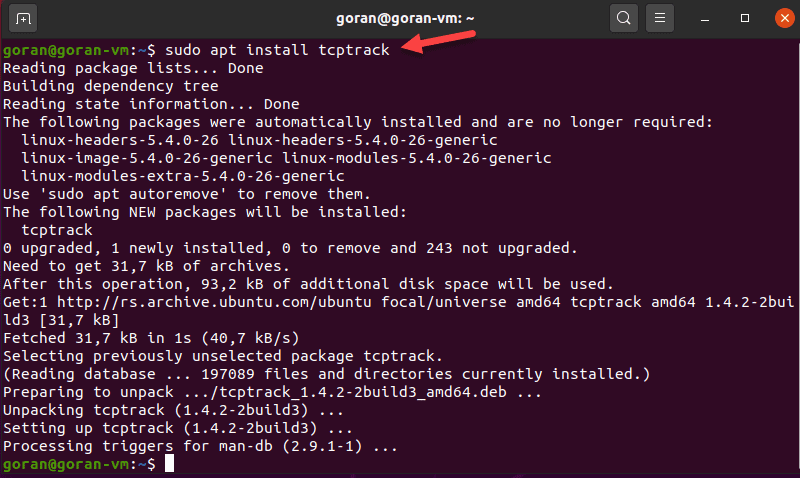
To install tcptrack on Linux Ubuntu, enter:
To view network activity with TCPtrack, specify the network interface. To find the device name, use the ifconfig tool.
In our case, it is enp0s3
The terminal displays the network activity on the selected interface. The total network speed is at the bottom of the terminal:
Note: Make sure you run tcptrack with sudo . Otherwise, this error pops up: pcap_open_live: enp0s3: You don’t have permission to capture on that device (socket: Operation not permitted)
TCPtrack is customizable and offers options to narrow down the test to specific ports, for example.
To do so, pass the port option and the port number:
If there is no activity on the port, the output is blank.
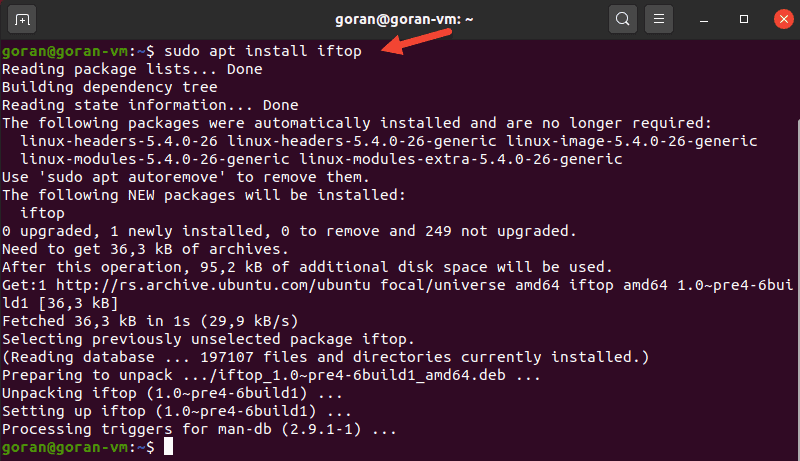
Using iftop to Test Speed on a Network Interface
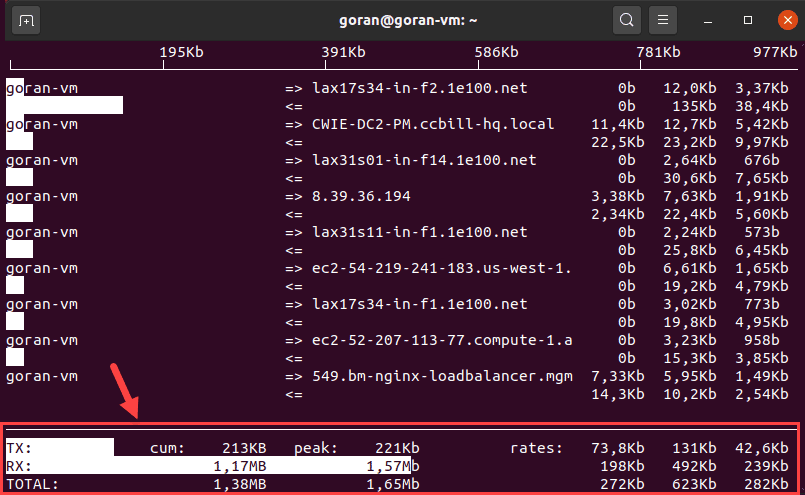
Iftop lets you view network speed for a defined interface. The tool shows a similar output to what tcptrack provides.
To install iftop, run this command:
To launch the utility, use the -i flag and specify your network interface.
In our case:
The output shows the activity for the device. The bottom of the screen provides a traffic summary.
If you do not specify a network interface, iftop selects the first available. Make sure you run the command with sudo to avoid any errors.
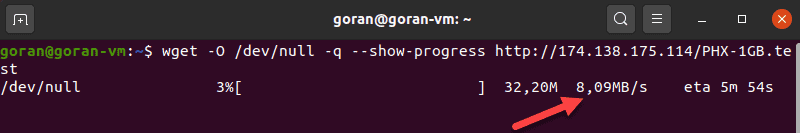
Using wget to Test Download Speed
Wget is a CLI tool for downloading content from web servers. Since the tool does not upload files, you can only test the download speed.
If you do not have wget on your Ubuntu machine, enter this command to install it:
Now, choose a reliable server to download a file and test your internet speed. For example, use phoenixNAP’s 1GB test file from the list.
This example uses a server located in Phoenix:
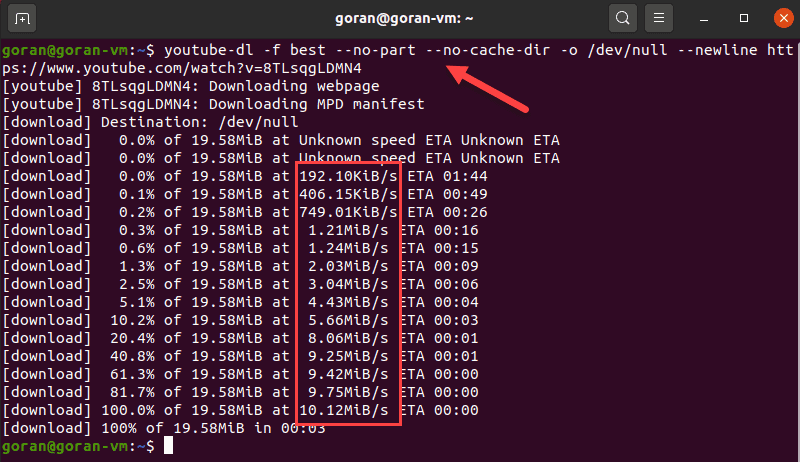
Using youtube-dl to Test Internet Speed
An unconventional way to test your download speed is to use the youtube-dl CLI utility. The tool allows you to download YouTube videos and view the download speed.
To install youtube-dl, enter:
The application takes around 268MB of space. While the installation is in progress, choose a video you want to download and save the URL.
When the process finishes, use this command but replace the URL with the one you selected:
The terminal shows the download progress, file size, download speed, and ETA.
The command above does not save the file to any filesystem, hence the /dev/null part.
This example used a short phoenixNAP BMC demo video of around 19MB. Choose a longer video for more precise results.
The article showed you nine ways to test network speed in Linux via CLI. Choose the tool depending on whether you want to test local network speed, internet speed, etc.
The tools work for all Linux distributions, so make sure you use the right package manager.
Источник