- Как проверить версию Java
- Управление версиями Java
- Проверка версии Java
- Выводы
- How to Check Java Version Installed on Linux
- Method 1: Check the Java Version On Linux
- Method 2: Find Version by Checking Path Where Java is Installed
- Method 3: Search for Java in the Installed Packages List
- What is command to see all java versions installed on linux?
- 5 Answers 5
- How to check java version at linux (RedHat6)
- 3 Answers 3
- How to check Java Version on Linux Ubuntu
- Understanding the Java Version
- Checking Your Java Version
- Installing Java Using the Browser
- Some Important Commands
- Remove Java Versions
- Should You Use JRE or JDK?
- When to Use JDK
- When to Use JRE
- Some Applications of Java
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Zeeman Memon
Как проверить версию Java
Java — один из самых популярных языков программирования в мире, используемый для создания различных типов кроссплатформенных приложений.
В этой статье объясняется, как с помощью командной строки проверить, какая версия Java установлена в вашей системе Linux. Это может быть полезно при установке приложений, требующих определенной версии Java.
Управление версиями Java
Java использует семантическое управление версиями . Версии готовых к выпуску релизов представлены по следующей схеме:
Например, в Java 11.0.8 11 — это основная версия, 0 — дополнительная версия, а 8 — версия безопасности.
- MAJOR — Основные выпуски содержат новые возможности и функции.
- MINOR — второстепенные выпуски содержат различные исправления ошибок и совместимые улучшения.
- SECURITY — выпуски безопасности содержат критические исправления безопасности.
Проверка версии Java
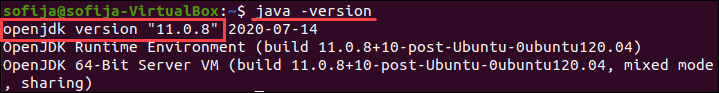
Чтобы узнать, какая версия Java установлена в вашей системе, выполните команду java -version :
Команда отобразит версию Java по умолчанию:
В этом примере в нашей системе установлена Java версии 11.0.8 . Версия, установленная в вашей системе, может отличаться.
Если вы получили сообщение «java: command not found», это означает, что Java не установлена в системе. Чтобы установить Java, воспользуйтесь одним из следующих руководств в зависимости от вашего дистрибутива Linux:
В системе также может быть установлено несколько версий Java одновременно. Чтобы проверить, есть ли на вашем компьютере несколько установок Java:
Если у вас только одна установка Java, результат будет выглядеть примерно так:
В противном случае, если у вас несколько установок Java, команда отобразит меню, в котором вы можете выбрать, какая версия будет версией Java по умолчанию:
Чтобы изменить версию Java по умолчанию, просто введите номер версии (число в столбце «Выбор») и нажмите Enter .
Выводы
Узнать, какая версия Java установлена в вашей системе Linux, очень просто, просто введите java -version .
Не стесняйтесь оставлять комментарии, если у вас есть вопросы.
Источник
How to Check Java Version Installed on Linux
Home » SysAdmin » How to Check Java Version Installed on Linux
How do I check my current Java version? There are several ways to check if Java is installed and which version is running on your system.
In this tutorial, learn how to check the Java version installed on Linux distros, including Ubuntu, CentOS, and Debian.
- A user account with sudo privileges
- Access to the command-line/terminal window
- A version of Java
Method 1: Check the Java Version On Linux
To check the Java version on Linux Ubuntu/Debian/CentOS:
1. Open a terminal window.
2. Run the following command:
3. The output should display the version of the Java package installed on your system. In the example below, OpenJDK version 11 is installed.
Note: If the output indicates there is no such package on the system, you can install it with the help of one of our guides – How to install Java on Ubuntu or How to Install Java on CentOS.
You can also check the version of the primary Java compiler – javac (pronounced “java-see”) with the command:
Method 2: Find Version by Checking Path Where Java is Installed
There are two ways to find the path of the Java directory.
The first option includes running a single command:
The system should respond with the path where Java is installed.
Note: This option may not work on CentOS systems. If you have issues finding the path of the Java directory with the command above, use the alternative outlined below.
Alternatively, you can use the whereis command and follow the symbolic links to find the Java path.
1. Run the command:
The output tells you that Java is located in /usr/bin/java.
2. List the content of the /usr/bin/java directory:
Inspecting the directory shows that /usr/bin/java is only a symbolic link for /etc/alternatives/java.
3. Just like in the previous step, list the content of the provided path by running:
Finally, the output displays /etc/alternatives/java is another symbolic link and that the real path of the Java directory is /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/java.
Method 3: Search for Java in the Installed Packages List
You can also prompt the system to list installed packages and search for Java, with its version number.
Find Java by listing all installed packages.
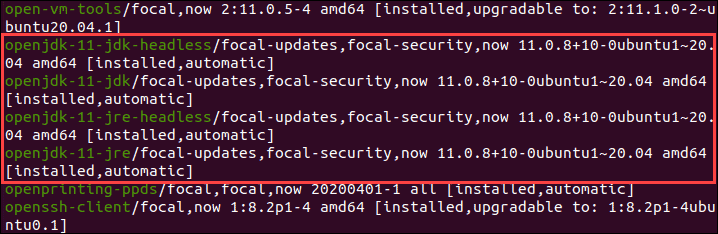
1. To generate a list of all installed packages, use the command:
2. Scroll up/down until you find the Java packages as shown in this example.
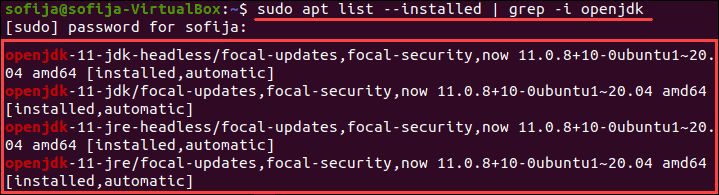
To avoid searching through all installed packages, list Java packages only. Prompt the system to list a specific software package. In this case, the package name is openjdk:
Note: CentOS users need to modify the commands for listing installed packages for their package manager. Use the commands: sudo yum list installed and sudo yum list installed | grep -i openjdk instead.
With this article, you have successfully checked the Java version installed on Linux. We also covered checking the Java path and searching for Java among the installed packages.
Once the Java version is confirmed, you can start developing anything from lightweight mobile to desktop applications.
Источник
What is command to see all java versions installed on linux?
I know about java -version. I don’t care what version I’m currently running. I care what other versions are installed on my linux box. If it’s another java -* command I didn’t see it in the java -help.
I’ve tried googling it but the answers are either for Windows or they say «use java -version.» I know I’ve done this before.
5 Answers 5
On most Linux distributions you can use update-alternatives like this:
It will list all packages that provide java command and will let you change it. If you don’t want to change it, simply Ctrl-C from it.
There is only one catch — if you installed some java not using official package manager ( dpkg / apt-get , rpm / yum ), but simply extracted it, update-alternatives will not show it.
To find all files. The package manager with your version of Linux should also be able to list them.
I use this to list the Java installs available:
I was previously using the following to determine the java 8 installation for an application that needed an environment variable set so it could use a java version that was not set as the default:
update-java-alternatives -l java-8-oracle
However, that stopped working today. The update-java-alternatives script/program is no longer installed on my Ubuntu 14.04 system. What’s installed now is alternatives .
What I use now to get a specific alternatives java path is:
alternatives —display java | grep priority | grep jdk-1.8
Then I can massage the result to get what I need for my app’s environment variable.
Источник
How to check java version at linux (RedHat6)

but when I type:
the console is returning nothing and getting stuck in a «java mode» , feels like the command called java and its waiting for my inputs, any thing I type then returns nothing. until I type crt+C it exits the mode.
3 Answers 3
If your java version more than 1.6 then it should work
if version is not installed it returns error message
Please share some snapshot so i can rectify it
To answer your question directly, you can use
For future Referenecs . You can try any of these commands.
rpm -qi «package_name_without_quotes»
It gives information of installed package. To display information about one or more packages (glob expressions are valid here as well), use the following command :
yum info «package_name_without quotes»
yum list «package_name_without_quotes»
yum —showduplicates list «package_name_without_quotes»
The yum info package_name command is similar to the rpm -q —info package_name command, but provides as additional information the ID of the Yum repository the RPM package is found in.
You can also query the Yum database for alternative and useful information about a package by using the following command :
yumdb info «package_name_without_quotes»
This command provides additional information about a package, including the check sum of the package (and algorithm used to produce it, such as SHA-256), the command given on the command line that was invoked to install the package (if any), and the reason that the package is installed on the system.
Источник
How to check Java Version on Linux Ubuntu
It is practically a Turing-complete language so anything can be done on it. Most of the things one can do in Python can also be done in Java. Jpython is a Python version that runs on Java in the JVM (Java Virtual Machine). In this guide, we will dive into the procedure of looking up the Java version on Ubuntu Linux and install it if it is not already available.
Understanding the Java Version
The Java version is an indicator of the release of Java software currently under use by your OS.
It is highly recommended that the version be updated for better performance, stability, sophisticated features, and the latest security patches. This can go a long way and help you in preventing many unwanted issues and staying up to date.
Many websites, packages, or libraries require you to update to the latest Java version. So, it is preferred to stay one step ahead and have the latest release downloaded on your system. For instance, the latest Java version enables you to view 3D images along with other exciting features.
So, without further ado, let’s delve into the procedure of Java version verification and installation.
Checking Your Java Version
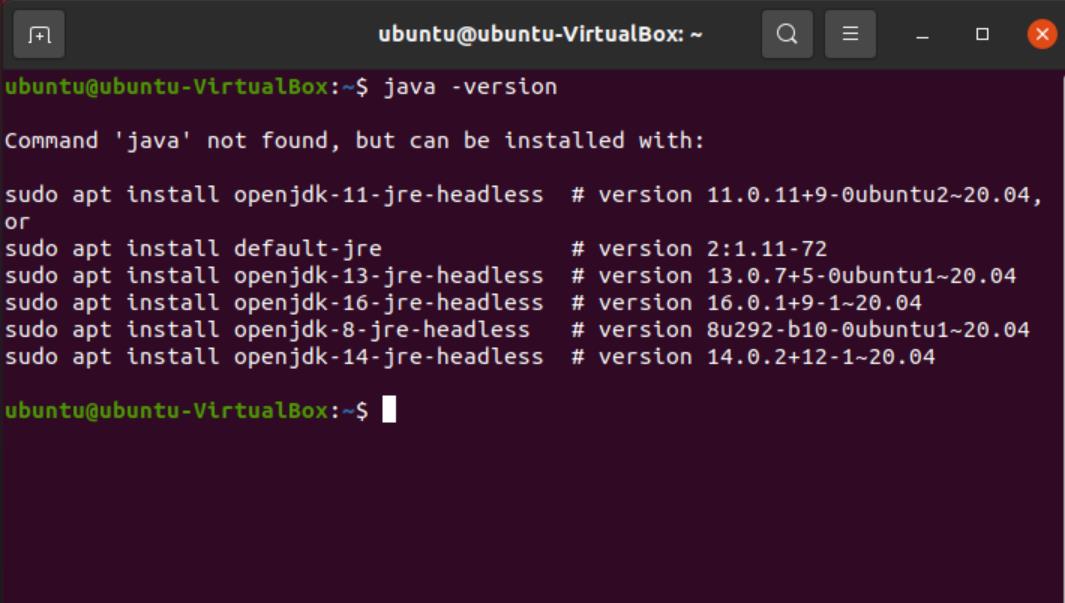
Start by checking your Java version. To do this, simply type the following in the terminal window.
This will give us the Java version that’s currently in use.
However, as evident from the picture above, Java isn’t installed on our system. But the terminal gives us options to install packages. Copying these commands and running them should get you the version installed directly via the terminal. All these versions are “headless”, meaning they don’t require a graphical user interface.
However, to download the latest release (16.02), you can use the browser method. Now, let’s go through the step-by-step process of installation.
Installing Java Using the Browser
Follow the steps to download Java.
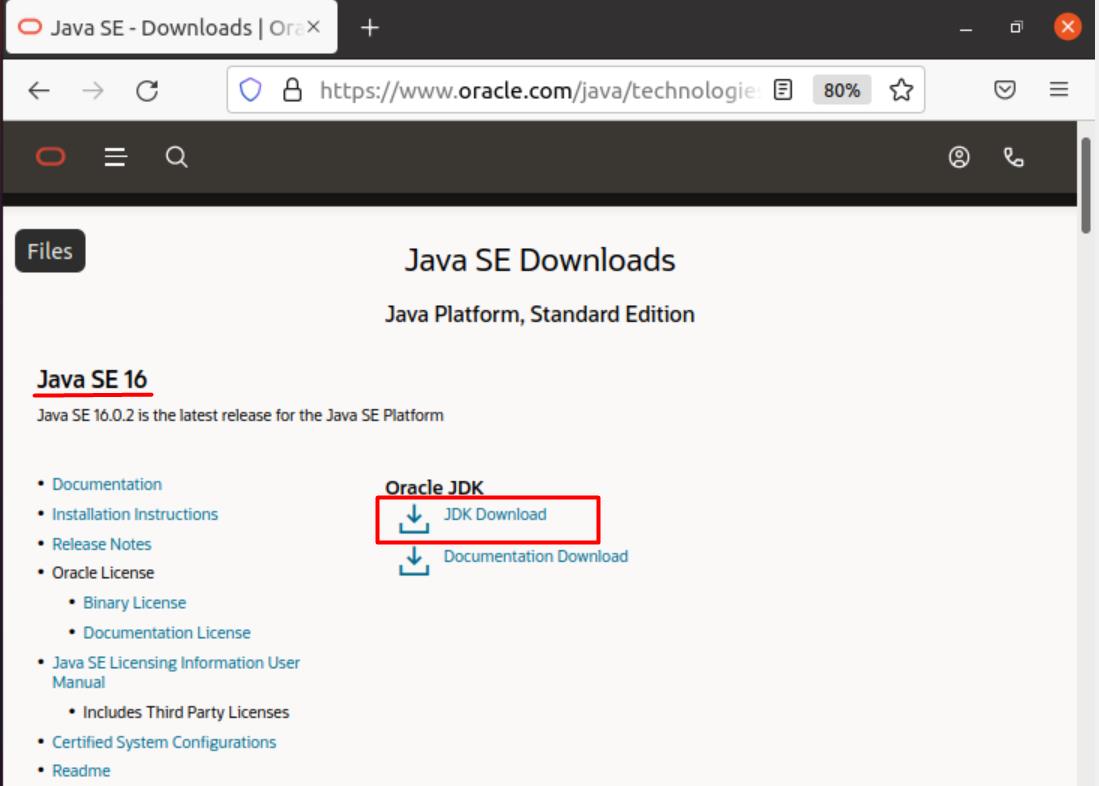
Go to Google and search “download java JDK” and open the first link from the search results.
JDK is the “Java Development Kit” used to develop programs that run on Java. Alternatively, you can click on the link here to go directly to the page.
Under the “Java SE downloads”, go to “Java SE 16” as that is the latest version. The next step is to download JDK.
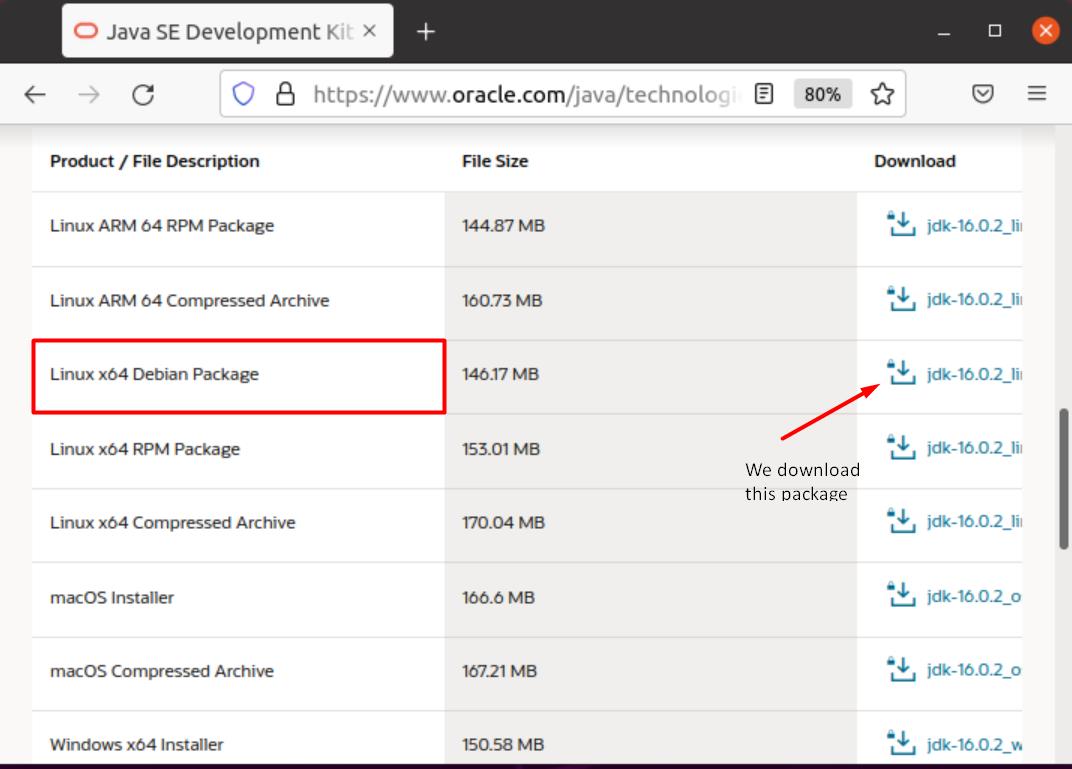
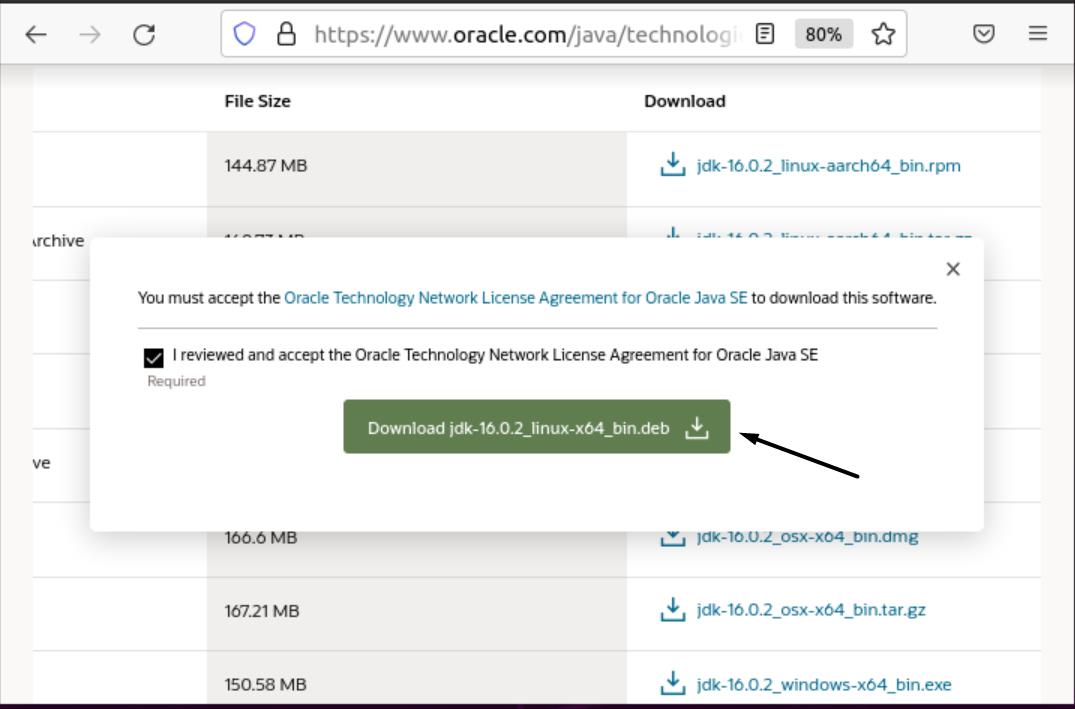
Scroll through the packages till you find the “Linux x64 Debian Package”. Download the file next to it. Ubuntu uses Debian packages to install programs, so you’ll see that the file has a .deb extension.
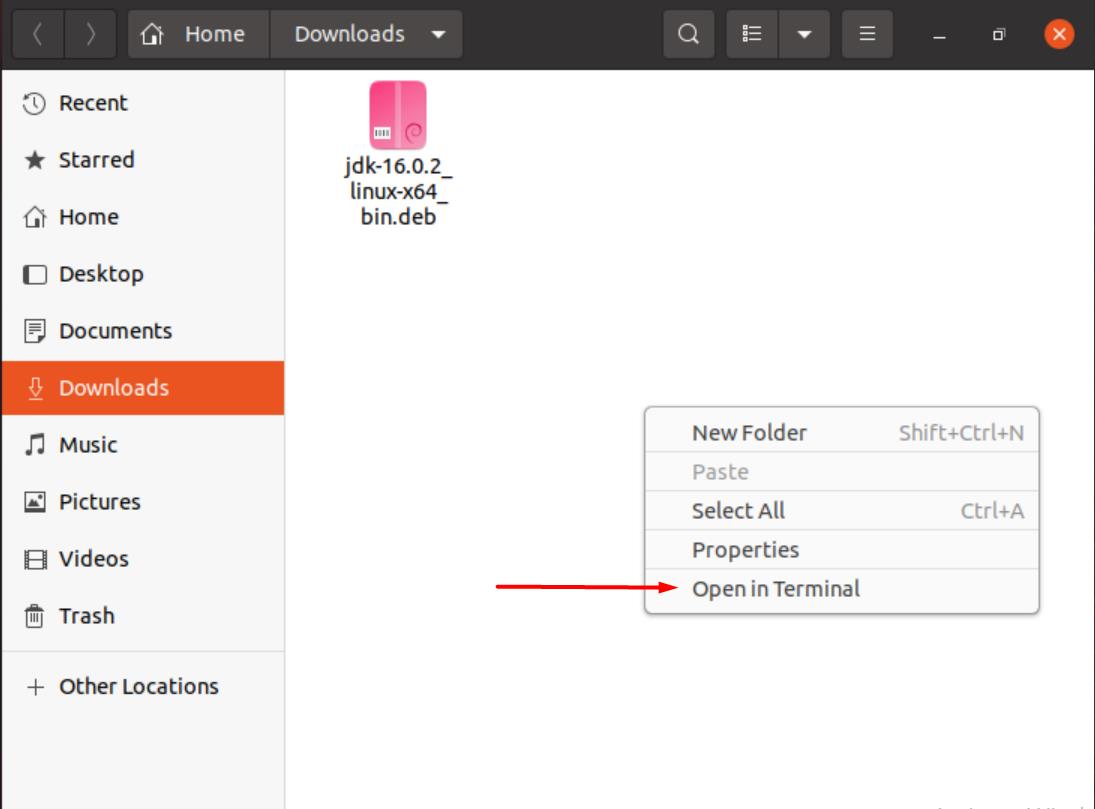
Once you are done with the download, open the folder where the downloaded package is located. Right-click anywhere in the window and select “Open in Terminal”.
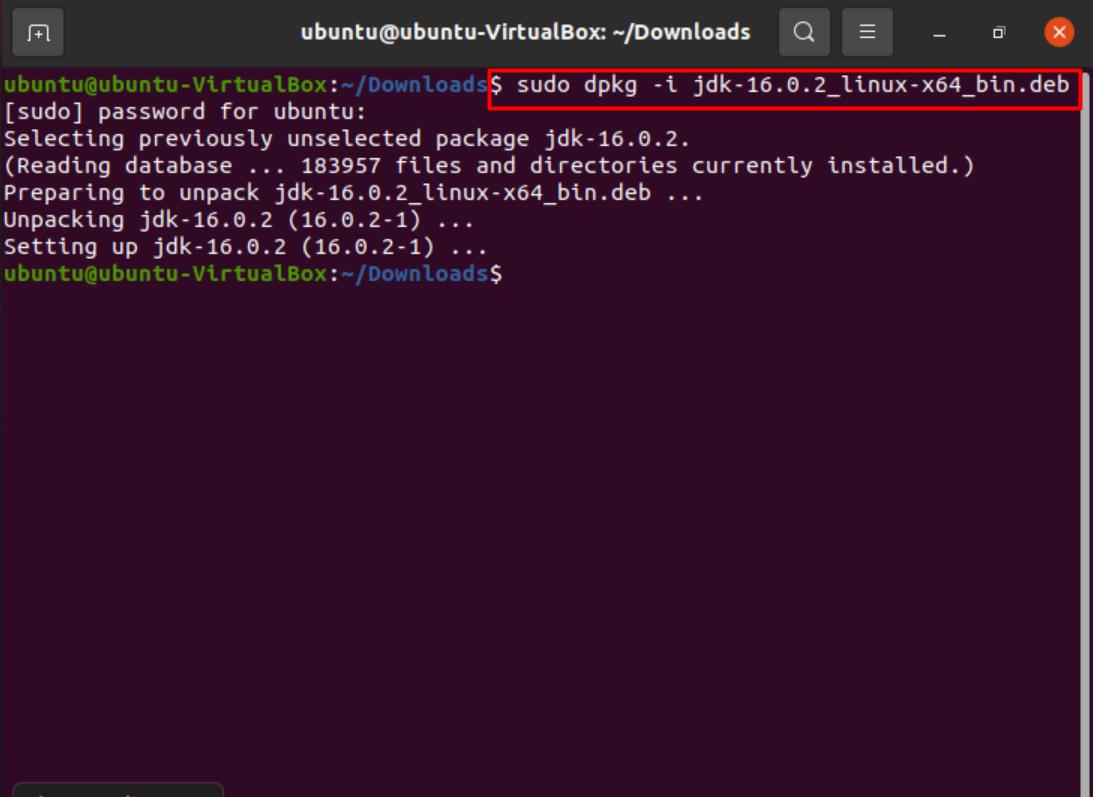
Type the following command in the terminal to start unpacking the downloaded package.
You can replace the highlighted part of the command with the name of the package corresponding to the Java version you downloaded.
Having done that, you can type in the following command to confirm that Java is installed on your system.
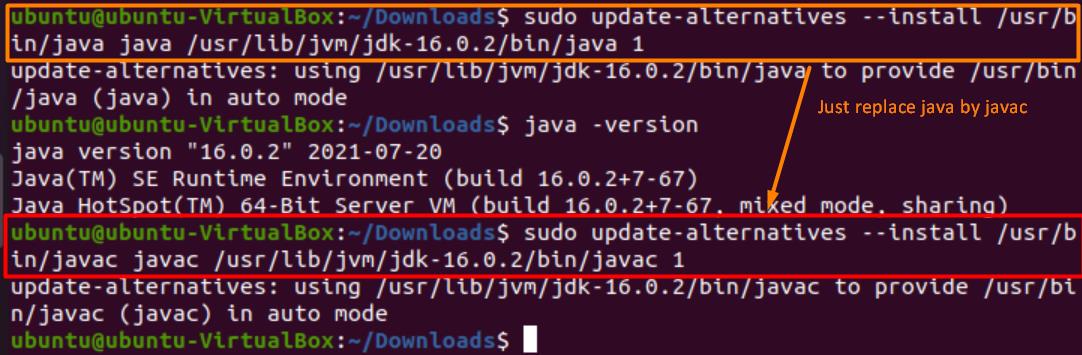
With that out of the way, set your package as the alternative. To do that, use the following command:
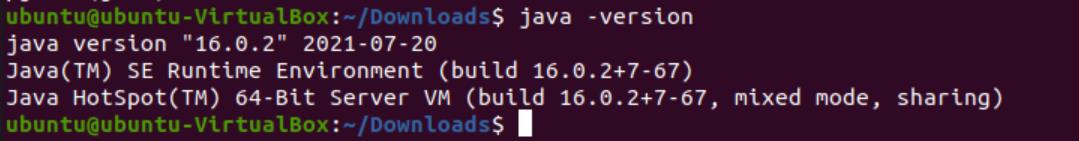
Now, we can finally check and verify our version by typing the following:
To install the compiler, just use the same command as before, only this time replace “java” with “javac”.
To check the Javac version, type the following command:
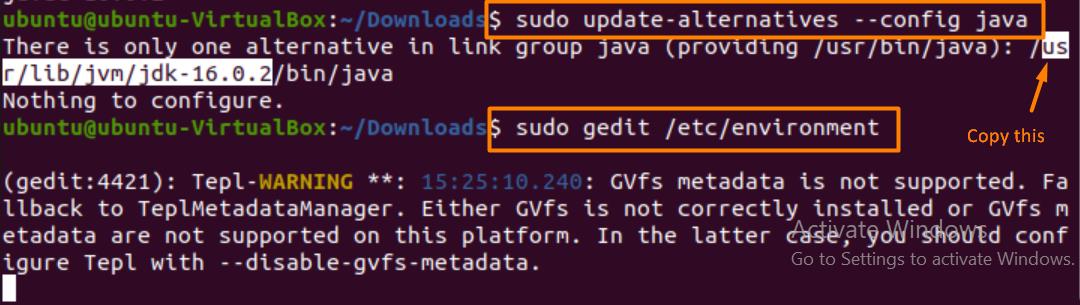
Additionally, to set the java_home path, enter the following:
$ sudo update-a;ternatives —config java
$ sudo gedit / etc / environment
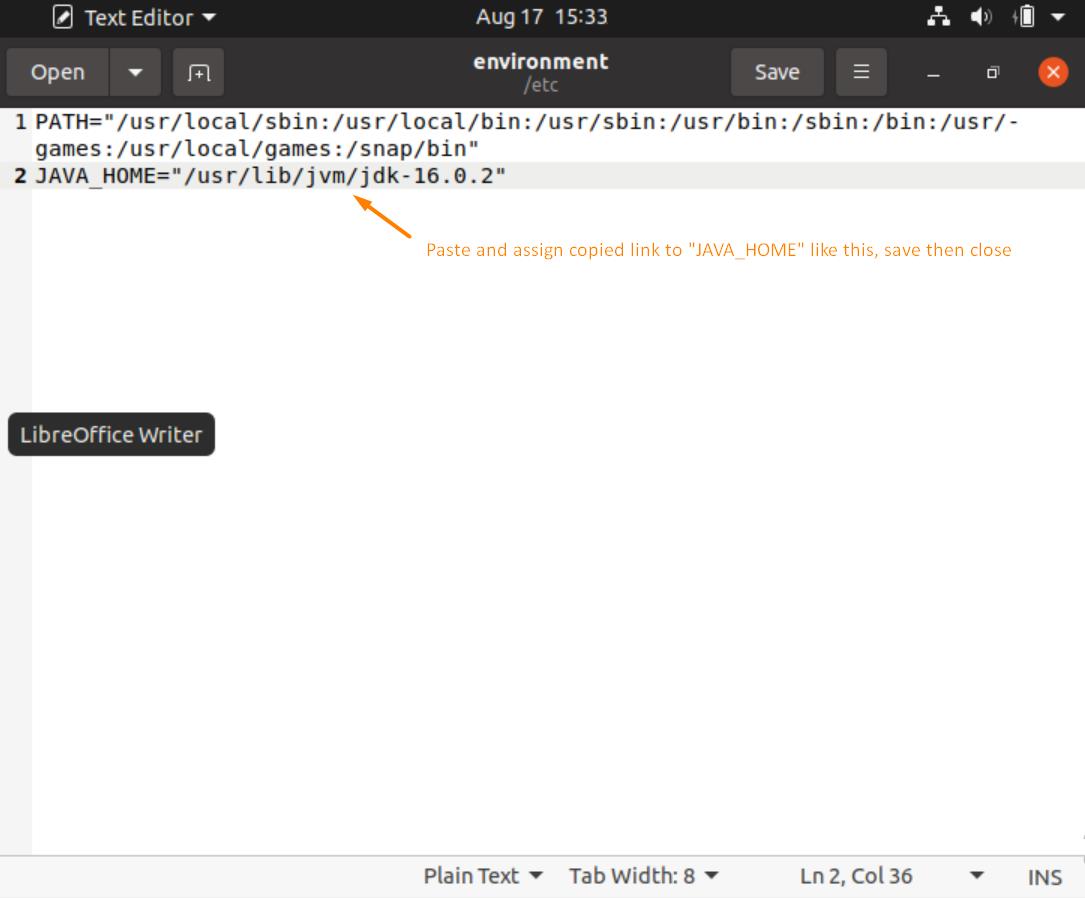
Once the text editor opens, paste the copied line and assign it to “JAVA_HOME” as demonstrated below.
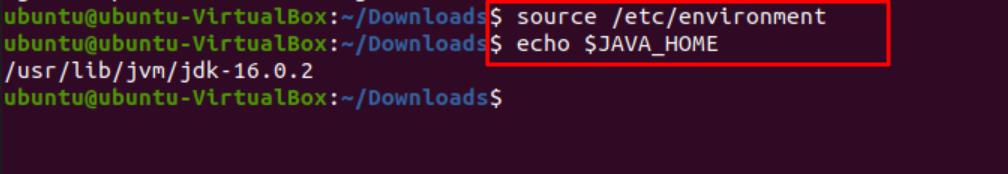
Once this is done, clear the screen and type in the following commands to complete the process of Java home path configuration.
$ source / etc / environment
Some Important Commands
Given below are certain commands you can use to check your version alongside other important things.
(This command shows all the Java versions installed on your system.)
(Shows Java version you are using.)
(Shows version of Java you are currently using.)
(Shows the version of Java compiler.)
(To find the location of Java.)
Remove Java Versions
To remove Java from your system, you can type in the following command:
To remove the package:
Press “Y” followed by “ENTER” and the package will be uninstalled.
Should You Use JRE or JDK?
To run Java programs, you’ll need JRE (Java runtime environment). It is compatible with Windows, Linux, Mac, Solaris, and many more.
JDK (Java Development Kit) is used to develop Java applications. It is usually where most programmers start from. It depends on what you want to do.
When to Use JDK
- You want to write Java programs. It comes with a compiler and Java application launcher.
- Has access to the main Java libraries for coding via Java application launcher which opens JRE.
When to Use JRE
- You have to use libraries and other files. It does not have compiler and error detection agents of its own.
- When you have to use utility packages like math or data related sets and instructions.
- To run applications running on Java.
Some Applications of Java
Java is mainly used in:
- Building Android applications.
- In developing web and cloud applications.
- Software tools like Eclipse and Netbeans.
- Chatbots.
- Games.
- Scientific and Enterprise applications
Conclusion
To stay up to date and get a hands-on experience of the latest packages and software, keeping our programs updated is a must. This check and balance can really help us a long way in keeping our system efficient, protected, and up to date.
About the author
Zeeman Memon
Hi there! I’m a Software Engineer by degree, Blogger by skills who loves to write about tech, develop websites & do SEO. You can reach out to me on LinkedIn.
Источник