- How to Add to Windows PATH Environment Variable
- Add Directories to PATH Variable
- How to set the path and environment variables in Windows
- Setting the path and variables in Windows 10
- Setting the path and variables in Windows 8
- Setting the path and variables in Windows Vista and Windows 7
- Setting the path and variables in Windows 2000 and Windows XP
- What is the default Windows %PATH%?
- Setting path in the MS-DOS and Windows command line
- Windows CMD: PATH Variable – Add To PATH – Echo PATH
- Echo Windows PATH Variable
- Add To Windows PATH
- Set Windows PATH For The Current Session
- Set Windows PATH Permanently
- How can I display the contents of an environment variable from the command prompt in Windows 7?
- 8 Answers 8
- Can I set an environment variable for an application using a shortcut in Windows?
- 4 Answers 4
How to Add to Windows PATH Environment Variable
Works for Windows 10 or 7
If you’re a coder or programmer, you probably spend a decent amount of time using the command prompt to execute programs or compile code. In order to complete those tasks, you most likely have to use a command from a library or software package installed (like Python) on your system.
By default, most of these programs will add their own custom shortcuts to the Windows environment variables. The most used environment variable in Windows is probably the PATH variable. It basically allows you to run any executables that are located inside the paths specified in the variable at the command prompt without having to give the full path to the executable.
In this article, I’ll show you how you can add more paths to the Windows PATH variable in case you want to run executables from your own custom directories. It’s worth noting that the procedure below is for Windows 10, but it’s almost exactly the same for Windows 7 also.
Add Directories to PATH Variable
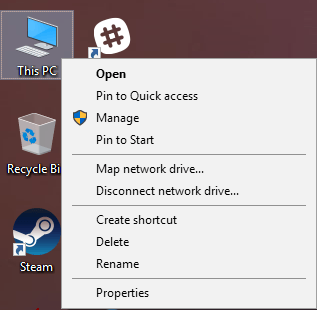
To get started, right-click on the Computer or This PC icon on the desktop and select Properties. If you don’t have that icon on your desktop already, you can add any missing desktop icons easily.
On the System dialog page, you’ll see an Advanced system settings link on the left-hand side.
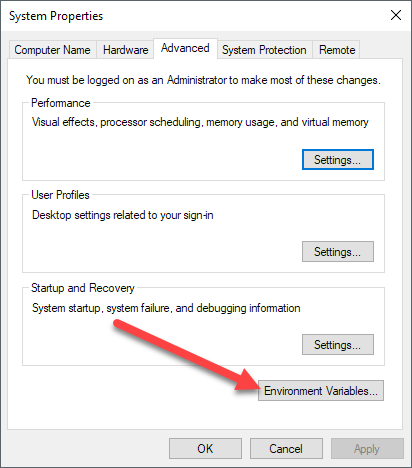
This will bring up the System Properties dialog, which should already be open to the Advanced tab. Go ahead and click on the Environment Variables button at the very bottom.
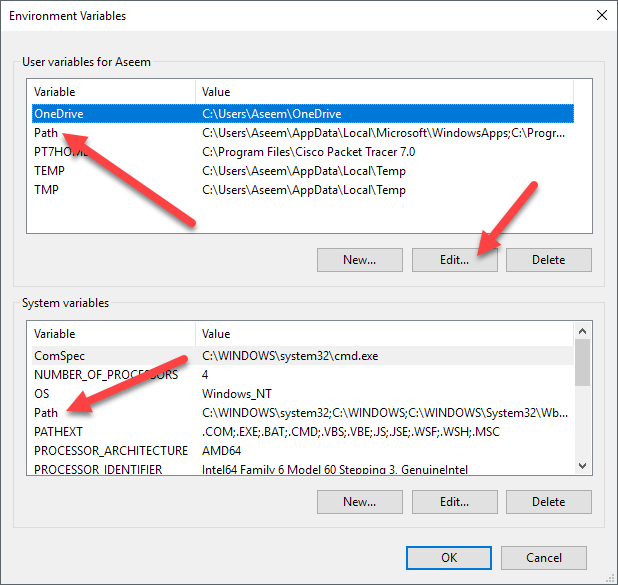
On the Environment Variables dialog, you’ll see two sets of variables: one for user variables and the other for system variables. Both lists have the PATH variable, so you have to decide which one to edit.
If you only need the commands for your own user account, then edit the user variable. If you need it to work across the computer system regardless of which user is logged in, then edit the system variable. Click on Path and then click on Edit.
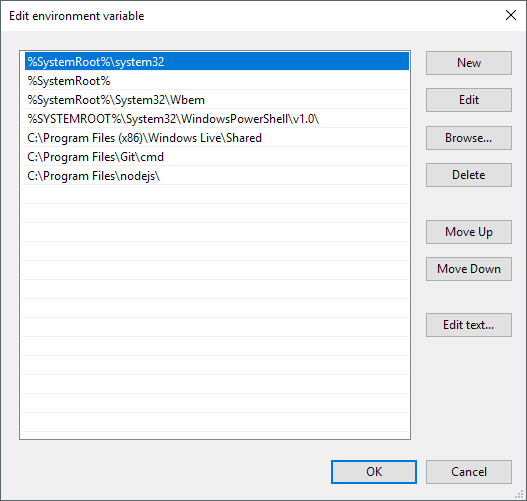
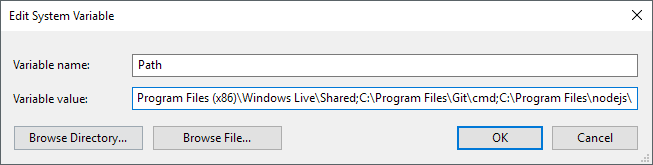
On the Edit environment variable dialog, you’ll see a list of all the paths that are currently in the PATH variable. As you can see, Node.js and Git already added their paths so that I can run Git commands and Node.js commands from anywhere while in the command prompt.
To add a new path, simply click on New and it’ll add a new line to the bottom of the list. If you know the path, simply type it in or copy and paste it. If you prefer, you can also click Browse and then navigate to the desired path.
To edit any path, simply select it and then click on the Edit button. You can also delete paths using the Delete button. Note that you can also move items up and down on the list. When you type a command at the command prompt, Windows has to search through each directory stored in the PATH variable to see if that executable exists or not. If you want your executable to be found faster, just move that path up to the top of the list.
This can also come in handy if you have multiple versions of the same command in different paths and need to have one run instead of the other. The one that shows up higher in the list will be run when you type in the command.
Lastly, if you click on Edit text, it will load a dialog where you can edit the Path variable using the old interface where all the paths are listed in one text box.
That’s all there is to it! If you want to learn more about environment variables, make sure to check out my post on how to create your own custom environment variables. Enjoy!
Founder of Help Desk Geek and managing editor. He began blogging in 2007 and quit his job in 2010 to blog full-time. He has over 15 years of industry experience in IT and holds several technical certifications. Read Aseem’s Full Bio
How to set the path and environment variables in Windows
Setting the path and environment variables will differ depending on the version of Windows you have on your computer. Choose a link below for your version of Windows.
Administrator privileges are usually required to modify the path and environment variables.
Setting the path and variables in Windows 10
- From the desktop, right-click the very bottom-left corner of the screen to get the Power User Task Menu.
- From the Power User Task Menu, click System.
- In the Settings window, scroll down to the Related settings section and click the System info link.
- In the System window, click the Advanced system settings link in the left navigation pane.
- In the System Properties window, click the Advanced tab, then click the Environment Variablesbutton near the bottom of that tab.
- In the Environment Variables window (pictured below), highlight the Path variable in the System variables section and click the Edit button. Add or modify the path lines with the paths you want the computer to access. Each different directory is separated with a semicolon, as shown below.
You can edit other environment variables by highlighting the variable in the System variables section and clicking Edit. If you need to create a new environment variable, click New and enter the variable name and variable value.
To view and set the path in the Windows command line, use the path command.
Setting the path and variables in Windows 8
- From the desktop, right-click the very bottom-left corner of the screen to get the Power User Task Menu.
- From the Power User Task Menu, click System.
- Click the Advanced System Settings link in the left column.
- In the System Properties window, click the Advanced tab, then click the Environment Variablesbutton near the bottom of that tab.
- In the Environment Variables window (pictured below), highlight the Path variable in the System variables section and click the Edit button. Add or modify the path lines with the paths you want the computer to access. Each different directory is separated with a semicolon, as shown below.
You can edit other environment variables by highlighting the variable in the System variables section and clicking Edit. If you need to create a new environment variable, click New and enter the variable name and variable value.
To view and set the path in the Windows command line, use the path command.
Setting the path and variables in Windows Vista and Windows 7
- From the desktop, right-click the Computer icon and select Properties. If you don’t have a Computer icon on your desktop, click Start, right-click the Computer option in the Start menu, and select Properties.
- Click the Advanced System Settings link in the left column.
- In the System Properties window, click the Advanced tab, then click the Environment Variablesbutton near the bottom of that tab.
- In the Environment Variables window (pictured below), highlight the Path variable in the System variables section and click the Edit button. Add or modify the path lines with the paths you want the computer to access. Each different directory is separated with a semicolon, as shown below.
You can edit other environment variables by highlighting the variable in the System variables section and clicking Edit. If you need to create a new environment variable, click New and enter the Variable name and Variable value.
To view and set the path in the Windows command line, use the path command.
Setting the path and variables in Windows 2000 and Windows XP
The path is now managed by Windows 2000 and Windows XP and not the autoexec.bat or autoexec.nt files, as was done with earlier versions of Windows. To change the system environment variables, follow the steps below.
- From the desktop, right-click My Computer and click Properties. If you don’t have a My Computer icon on your desktop, click Start, right-click the My Computer option in the Start menu, and select Properties.
- In the System Propertieswindow, click the Advancedtab.
- In the Advanced section, click the Environment Variablesbutton.
- In the Environment Variables window (as shown below), highlight the Path variable in the System Variable section and click the Edit button. Add or modify the path lines with the paths you want the computer to access. Each different directory is separated with a semicolon, as shown below.
You can edit other environment variables by highlighting the variable in the System variables section and clicking Edit. If you need to create a new environment variable, click New and enter the Variable name and Variable value.
To view and set the path in the Windows command line, use the path command.
What is the default Windows %PATH%?
The path is based on programs installed on the computer, so there is no «default path.» However, the Windows minimum path is often the path below.
Keep in mind that as you install programs, the path is updated with the paths for the newly installed programs. So, if you have erased your path after installing other programs, those programs may be affected.
Setting path in the MS-DOS and Windows command line
To view and set the path in MS-DOS and in the Windows command line, use the path command.
Windows CMD: PATH Variable – Add To PATH – Echo PATH
PATH is an environment variable that specifies a set of directories, separated with semicolons ( ; ), where executable programs are located.
In this note i am showing how to print the contents of Windows PATH environment variable from the Windows command prompt.
I am also showing how to add a directory to Windows PATH permanently or for the current session only.
Cool Tip: List environment variables in Windows! Read More →
Echo Windows PATH Variable
Print the contents of the Windows PATH variable from cmd :
The above commands return all directories in Windows PATH environment variable on a single line separated with semicolons ( ; ) that is not very readable.
To print each entry of Windows PATH variable on a new line, execute:
Cool Tip: Set environment variables in Windows! Read More →
Add To Windows PATH
Warning! This solution may be destructive as Windows truncates PATH to 1024 characters. Make a backup of PATH before any modifications.
Save the contents of the Windows PATH environment variable to C:\path-backup.txt file:
Set Windows PATH For The Current Session
Set Windows PATH variable for the current session:
Set Windows PATH Permanently
Run as Administrator: The setx command is only available starting from Windows 7 and requires elevated command prompt.
Permanently add a directory to the user PATH variable:
Permanently add a directory to the system PATH variable (for all users):
Info: To see the changes after running setx – open a new command prompt.
How can I display the contents of an environment variable from the command prompt in Windows 7?
In Windows 7, when I start the Command prompt, is there any command to display the contents of an environment variable (such as the JAVA_HOME or PATH variables)?
I have tried with echo $PATH , echo PATH and $PATH but none of these work.
8 Answers 8
In Windows Command-Prompt the syntax is echo %PATH%
To get a list of all environment variables enter the command set
To send those variables to a text file enter the command set > filename.txt
To complement the previous answer, if you’re using Powershell echo %PATH% would not work. You need to use the following command instead: echo $Env:PATH
As an additional bit of information: While SET works with global or system variables, sometimes you want to write and read User variables, and this is done with the SETX command. SETX is included in the base installs of Windows beginning with Vista, but was also available in Windows XP by installing the Resource Pack.
One difference about SETX though is that you cannot read the variable out in the same command window you wrote it in. You have to write the SETX command in one Command or Powershell window, and then open a new window to read it using ECHO.
SETX can also write global or system variables.
To Set a user variable using SETX:
To set a global or system variable using SETX:
To read a user or global variable:
Remember, you must open a new Command or Powershell window to read this variable.
Can I set an environment variable for an application using a shortcut in Windows?
I have a feeling I should be able add a directory to the PATH environment variable on an application-lifetime basis, but I can’t find out how to do this. Is it possible to add a parameter to a Windows shortcut that appends a directory to the current value of PATH for use by the application being linked?
4 Answers 4
Let the shortcut execute a batch file (.cmd), that
- Sets the environment variable
- execute the app
- You use «START» to execute the app, this will start the app in another process, but it will copy the environment. You do not wait for the app to finish.
- Now you can exit the batch file.
Should look like this:
Set Target to e.g.:
To avoid see the command prompt for a split second before it close again, you should set
on the Shortcut tab
(Tested on Windows 7, Windows 10)
Linking directly to a batch file spawns an annoying console that you probably want to avoid. Here’s a work-around. The simpler solution is to use the «Start Minimized» option in your link, but on Windows 7 you’ll see a momentary console light up your task bar.
You can do this with PowerShell easily. PowerShell exposes environment variables using the $env: prefix. For example, I wanted to launch TeamSQL with custom JAVA_HOME and PATH environment variables, so I could connect to a PostgreSQL database. TeamSQL depends on JDK / OpenJDK for this purpose.
First, I downloaded pre-built OpenJDK and extracted the ZIP archive with 7-Zip.
Next, in PowerShell, I ran the following:
Store that PowerShell code in a .ps1 file, and you can run it with PowerShell. Because child processes inherit the environment variables from the PowerShell session, your program is good to go.