- Fix Windows Update errors
- Windows Update troubleshooting
- Why am I offered an older update?
- My device is frozen at scan. Why?
- Feature updates are not being offered while other updates are
- Issues related to HTTP/Proxy
- The update is not applicable to your computer
- Issues related to firewall configuration
- Issues arising from configuration of conflicting policies
- Device cannot access update files
- Updates aren’t downloading from the intranet endpoint (WSUS or Configuration Manager)
- You have a bad setup in the environment
- High bandwidth usage on Windows 10 by Windows Update
- How can I tell if Windows Update is stuck?
- What can I do if Windows 10 Update is stuck?
- 1. Check if the process is really stuck
- 2. Verify if your PC’s CPU and RAM are being used
Fix Windows Update errors
What does this guided walk-through do?
This guided walk-through provides steps to fix problems with Windows Updates for Windows 8.1 and 7, such as taking a long time to scan, or error codes while installing updates.
For help with Windows Update issues in Windows 10, see Troubleshoot problems updating Windows 10 instead.
A common cause of errors is inadequate drive space. If you need help freeing up drive space, see Tips to free up drive space on your PC.
Common error codes
The steps in this guided walk-through should help with all Windows Update errors and other issues— you don’t need to search for the specific error to solve it. As an example, here are some commonly seen error codes: 0x0xc1900223223; 0x80240034; 0x8007000E, 0x80242006, 0x80244018, 0x80D02002, 0x80246017, 0x80240438, 0x80070070, 0x8007000D, 0x80246008, 0x80096004, 0x80070020.
The steps provided here should help fix any errors that come up during the Windows Update process.
How does it work?
We’ll begin by asking you questions about the Windows version you’re using and the issue you’re experiencing. Next, we’ll take you through a series of troubleshooting steps that are specific to your situation. At the end of each step, you’ll be asked “Did this resolve the issue?” If it’s resolved, select Yes, and you’re done! If it isn’t resolved, select No and continue with the guided walk-through.
Windows Update troubleshooting
If you run into problems when using Windows Update, start with the following steps:
Run the built-in Windows Update troubleshooter to fix common issues. Navigate to Settings > Update & Security > Troubleshoot > Windows Update.
Install the most recent Servicing Stack Update (SSU) that matches your version of Windows from the Microsoft Update Catalog. See Servicing stack updates for more details on servicing stack updates.
Make sure that you install the latest Windows updates, cumulative updates, and rollup updates. To verify the update status, refer to the appropriate update history for your system:
Advanced users can also refer to the log generated by Windows Update for further investigation.
You might encounter the following scenarios when using Windows Update.
Why am I offered an older update?
The update that is offered to a device depends on several factors. The following are some of the most common attributes:
- OS Build
- OS Branch
- OS Locale
- OS Architecture
- Device update management configuration
If the update you’re offered isn’t the most current available, it might be because your device is being managed by a WSUS server, and you’re being offered the updates available on that server. It’s also possible, if your device is part of a deployment group, that your admin is intentionally slowing the rollout of updates. Since the deployment is slow and measured to begin with, all devices will not receive the update on the same day.
My device is frozen at scan. Why?
The Settings UI communicates with the Update Orchestrator service that in turn communicates with to Windows Update service. If these services stop unexpectedly, then you might see this behavior. In such cases, follow these steps:
Close the Settings app and reopen it.
Start Services.msc and check if the following services are running:
- Update State Orchestrator
- Windows Update
Feature updates are not being offered while other updates are
Devices running Windows 10, version 1709 through Windows 10, version 1803 that are configured to update from Windows Update (including Windows Update for Business) are able to install servicing and definition updates but are never offered feature updates.
Checking the WindowsUpdate.log reveals the following error:
The 0x80070426 error code translates to:
Microsoft Account Sign In Assistant (MSA or wlidsvc) is the service in question. The DCAT Flighting service (ServiceId: 855E8A7C-ECB4-4CA3-B045-1DFA50104289) relies on MSA to get the global device ID for the device. Without the MSA service running, the global device ID won’t be generated and sent by the client and the search for feature updates never completes successfully.
To resolve this issue, reset the MSA service to the default StartType of «manual.»
Issues related to HTTP/Proxy
Windows Update uses WinHttp with Partial Range requests (RFC 7233) to download updates and applications from Windows Update servers or on-premises WSUS servers. Therefore proxy servers on the network must support HTTP RANGE requests. If a proxy was configured in Internet Explorer (User level) but not in WinHTTP (System level), connections to Windows Update will fail.
To fix this issue, configure a proxy in WinHTTP by using the following netsh command:
You can also import the proxy settings from Internet Explorer by using the following command: netsh winhttp import proxy source=ie
If downloads through a proxy server fail with a 0x80d05001 DO_E_HTTP_BLOCKSIZE_MISMATCH error, or if you notice high CPU usage while updates are downloading, check the proxy configuration to permit HTTP RANGE requests to run.
You might choose to apply a rule to permit HTTP RANGE requests for the following URLs:
*.download.windowsupdate.com
*.dl.delivery.mp.microsoft.com *.delivery.mp.microsoft.com
If you can’t allow RANGE requests, you’ll be downloading more content than needed in updates (as delta patching will not work).
The update is not applicable to your computer
The most common reasons for this error are described in the following table:
| Cause | Explanation | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| Update is superseded | As updates for a component are released, the updated component will supersede an older component that is already on the system. When this occurs, the previous update is marked as superseded. If the update that you’re trying to install already has a newer version of the payload on your system, you might receive this error message. | Check that the package that you are installing contains newer versions of the binaries. Or, check that the package is superseded by another new package. |
| Update is already installed | If the update that you’re trying to install was previously installed, for example, by another update that carried the same payload, you may encounter this error message. | Verify that the package that you are trying to install was not previously installed. |
| Wrong update for architecture | Updates are published by CPU architecture. If the update that you’re trying to install does not match the architecture for your CPU, you may encounter this error message. | Verify that the package that you’re trying to install matches the Windows version that you are using. The Windows version information can be found in the «Applies To» section of the article for each update. For example, Windows Server 2012-only updates cannot be installed on Windows Server 2012 R2-based computers. Also, verify that the package that you are installing matches the processor architecture of the Windows version that you are using. For example, an x86-based update cannot be installed on x64-based installations of Windows. |
| Missing prerequisite update | Some updates require a prerequisite update before they can be applied to a system. If you are missing a prerequisite update, you may encounter this error message. For example, KB 2919355 must be installed on Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 computers before many of the updates that were released after April 2014 can be installed. | Check the related articles about the package in the Microsoft Knowledge Base (KB) to make sure that you have the prerequisite updates installed. For example, if you encounter the error message on Windows 8.1 or Windows Server 2012 R2, you may have to install the April 2014 update 2919355 as a prerequisite and one or more pre-requisite servicing updates (KB 2919442 and KB 3173424). To determine if these prerequisite updates are installed, run the following PowerShell command: get-hotfix KB3173424,KB2919355, KB2919442 . If the updates are installed, the command will return the installed date in the InstalledOn section of the output. |
Issues related to firewall configuration
Error that you might see in Windows Update logs:
Go to Services.msc and ensure that Windows Firewall Service is enabled. Stopping the service associated with Windows Firewall with Advanced Security is not supported by Microsoft. For more information, see I need to disable Windows Firewall.
Issues arising from configuration of conflicting policies
Windows Update provides a wide range configuration policy to control the behavior of the Windows Update service in a managed environment. While these policies let you configure the settings at a granular level, misconfiguration or setting conflicting policies may lead to unexpected behaviors.
Device cannot access update files
Ensure that devices can reach necessary Windows Update endpoints through the firewall. For example, for Windows 10, version 2004, the following protocols must be able to reach these respective endpoints:
| Protocol | Endpoint URL |
|---|---|
| TLS 1.2 | *.prod.do.dsp.mp.microsoft.com |
| HTTP | emdl.ws.microsoft.com |
| HTTP | *.dl.delivery.mp.microsoft.com |
| HTTP | *.windowsupdate.com |
| HTTPS | *.delivery.mp.microsoft.com |
| TLS 1.2 | *.update.microsoft.com |
| TLS 1.2 | tsfe.trafficshaping.dsp.mp.microsoft.com |
Be sure not to use HTTPS for those endpoints that specify HTTP, and vice versa. The connection will fail.
The specific endpoints can vary between Windows 10 versions. See, for example, Windows 10 2004 Enterprise connection endpoints. Similar articles for other Windows 10 versions are available in the table of contents nearby.
Updates aren’t downloading from the intranet endpoint (WSUS or Configuration Manager)
Windows 10 devices can receive updates from a variety of sources, including Windows Update online, a Windows Server Update Services server, and others. To determine the source of Windows Updates currently being used on a device, follow these steps:
- Start Windows PowerShell as an administrator.
- Run $MUSM = New-Object -ComObject «Microsoft.Update.ServiceManager».
- Run $MUSM.Services.
Check the output for the Name and OffersWindowsUPdates parameters, which you can interpret according to this table.
| Output | Meaning |
|---|---|
| — Name: Microsoft Update -OffersWindowsUpdates: True | — The update source is Microsoft Update, which means that updates for other Microsoft products besides the operating system could also be delivered. — Indicates that the client is configured to receive updates for all Microsoft Products (Office, etc.) |
| — Name: DCat Flighting Prod — OffersWindowsUpdates: True | — Starting with Windows 10 1709, feature updates are always delivered through the DCAT service. — Indicates that the client is configured to receive feature updates from Windows Update. |
| — Name: Windows Store (DCat Prod) — OffersWindowsUpdates: False | -The update source is Insider Updates for Store Apps. — Indicates that the client will not receive or is not configured to receive these updates. |
| — Name: Windows Server Update Service — OffersWindowsUpdates: True | — The source is a Windows Server Updates Services server. — The client is configured to receive updates from WSUS. |
| — Name: Windows Update — OffersWindowsUpdates: True | — The source is Windows Update. — The client is configured to receive updates from Windows Update Online. |
You have a bad setup in the environment
In this example, per the Group Policy set through registry, the system is configured to use WSUS to download updates (note the second line):
From Windows Update logs:
In the above log snippet, we see that the Criteria = «IsHidden = 0 AND DeploymentAction=*» . «*» means there is nothing specified from the server. So, the scan happens but there is no direction to download or install to the agent. So it just scans the update and provides the results.
As shown in the following logs, automatic update runs the scan and finds no update approved for it. So it reports there are no updates to install or download. This is due to an incorrect configuration. The WSUS side should approve the updates for Windows Update so that it fetches the updates and installs them at the specified time according to the policy. Since this scenario doesn’t include Configuration Manager, there’s no way to install unapproved updates. You’re expecting the operational insight agent to do the scan and automatically trigger the download and installation but that won’t happen with this configuration.
High bandwidth usage on Windows 10 by Windows Update
Users might see that Windows 10 is consuming all the bandwidth in the different offices under the system context. This behavior is by design. Components that might consume bandwidth expand beyond Windows Update components.
The following group policies can help mitigate this situation:
Other components that connect to the internet:
How can I tell if Windows Update is stuck?
- A common problem that many users encounter is that the Windows 10 Update gets stuck.
- The occurrence of this problem can be extremely frustrating. At first glance, it seems that there are no viable options to deal with this problem.
- But there are a few solutions to fix this problem. First, you can check if the update process is really stuck.
- Another viable solution is to check the PC’s CPU and RAM to see if there is any activity.
- Download Restoro PC Repair Tool that comes with Patented Technologies (patent available here).
- Click Start Scan to find Windows issues that could be causing PC problems.
- Click Repair All to fix issues affecting your computer’s security and performance
- Restoro has been downloaded by 0 readers this month.
If you’ve ever asked yourself the question: How can I tell if Windows Update is stuck?, then you came to the right place. This issue is more common than you might think.
Because Windows 10 updates the services constantly, in some cases, it might happen that the installer got stuck at a certain percentage of the download or installation process.
This can cause a lot of anger, and some people even ended up having to reinstall their operating system again, as they stopped the process forcibly, while it was still working.
In today’s article we will explore the most common circumstances in which you might find yourself in. We will also discuss the best way to make sure that your Windows update is stuck or not, so keep reading.
What can I do if Windows 10 Update is stuck?
1. Check if the process is really stuck
In some cases, the update process inside Windows 10 will be slower than in other cases.
For this reason, drawing the conclusion that the process might be stuck will vary depending on your patience, internet speed, and CPU speed as well.
To make sure that you’re not stopping your update process while it’s still running, it is recommended that you wait 2-3 hours before reacting.
If after 2-3 hours the bar doesn’t advance at all, then you can safely assume the update process has stopped.
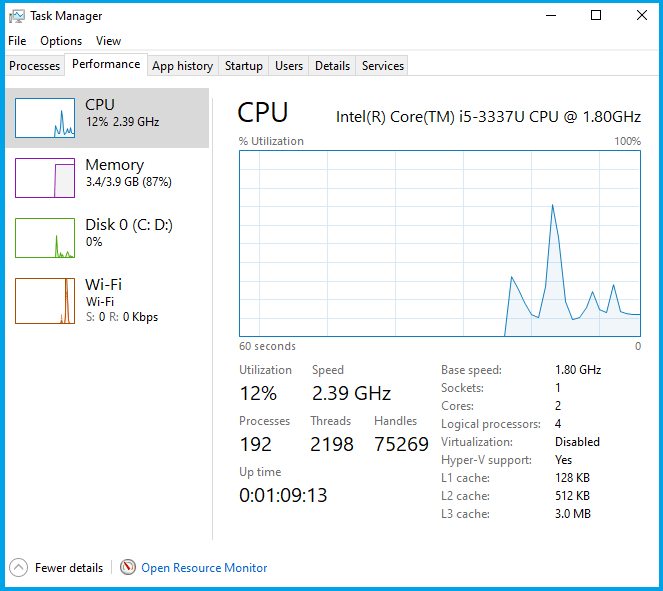
2. Verify if your PC’s CPU and RAM are being used
- Press the Ctrl+ Shift+ Esc buttons to open the Task Manager.
- Press More details inside the window.
- Select the Performance tab, and check activity of CPU, Memory, Disk, and Internet connection.
- In the case that you see a lot of activity, it means that the update process is not stuck.
- If you can see little to no activity, that means the update process could be stuck, and you need to restart your PC.
In this article we discussed how can you tell if Windows Update is stuck, or if its just taking longer than expected.
Using these methods will surely provide you with the required information to make an informed decision about your next step.
We would love to know if this guide answered your question. Please feel free to let us know by using the comment section found below.