- How to check network adapter status in Linux
- Command to check network adapter names in Linux
- Getting IP address and other information
- How to query or control network driver and hardware settings in Linux
- Display the physical status of an Ethernet port in Linux
- See network device driver information
- Is eno1 Ethernet device is up or down?
- A note abou Find Wireless Wifi Driver Chipset Informationt checking Wireless network adapter status in Linux
- 4 Useful Way to Know Plugged USB Device Name in Linux
- Find Out Plugged USB Device Name Using df Command
- Use lsblk Command to Find USB Device Name
- Identify USB Device Name with fdisk Utility
- Determine USB Device Name with dmesg Command
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
- How to Find What Devices are Connected to Network in Linux
- A. Using Linux command to find devices on the network
- Step 1: Install nmap
- Step 2: Get IP range of the network
- Step 3: Scan to find devices connected to your network
- B. Using GUI tool to find devices connected to network
- List USB Devices Linux
- Listing USB Devices using lsusb Command
- Listing USB devices with usb-devices Command
- Listing Block USB Devices
How to check network adapter status in Linux
Command to check network adapter names in Linux
Open the Terminal application and type the following command to see all network device names and other info:
sudo lshw -class network -short
Sample outputs:
So wlp1s0 is my Wireless and eno1 is my Ethernet Connection.
Getting IP address and other information
Simply use the ip command as follows:
How to query or control network driver and hardware settings in Linux
For wired Ethernet devices, you need to use a command called ethtool. It provides the following information from the Linux CLI
- Display info about network adapter status
- Find identification and diagnostic information
- Get extended device statistics
- Set or get speed, duplex, autonegotiation and flow control for Ethernet devices
- Control checksum offload and other hardware offload features
- Update or set DMA ring sizes and interrupt moderation
- Control receive queue selection for multiqueue devices
- Upgrade firmware in flash memory
Display the physical status of an Ethernet port in Linux
The syntax is:
sudo ethtool
sudo ethtool [option]
For example, get info about eno1 Ethernet device:
sudo ethtool eno1
Sample outputs:
See network device driver information
Run:
sudo ethtool -i eno1
Is eno1 Ethernet device is up or down?
Run the following cat command:
cat /sys/class/net/eno1/carrier
cat /sys/class/net/eno1/operstate
Another option is use the ip command along with grep command/egrep command:
ip a s eno1 | grep state
OR
sudo ethtool eno1 | grep -i ‘Link det’
OR
nmcli device status
Various command to check your network connections on Linux
A note abou Find Wireless Wifi Driver Chipset Informationt checking Wireless network adapter status in Linux
To find Wireless (Wifi) driver chipset information on Linux, run:
lspci | less
lspci | grep -i intel
lspci | grep -i broadcom
lspci | grep -i wireless
lshw -C network | grep -B 1 -A 12 ‘Wireless interface’
Sample outputs:
Источник
4 Useful Way to Know Plugged USB Device Name in Linux
As a newbie, one of the many things you should master in Linux is identification of devices attached to your system. It may be your computer’s hard disk, an external hard drive or removable media such USB drive or SD Memory card.
Using USB drives for file transfer is so common today, and for those (new Linux users) who prefer to use the command line, learning the different ways to identify a USB device name is very important, when you need to format it.
Once you attach a device to your system such as a USB, especially on a desktop, it is automatically mounted to a given directory, normally under /media/username/device-label and you can then access the files in it from that directory. However, this is not the case with a server where you have to manually mount a device and specify its mount point.
Linux identifies devices using special device files stored in /dev directory. Some of the files you will find in this directory include /dev/sda or /dev/hda which represents your first master drive, each partition will be represented by a number such as /dev/sda1 or /dev/hda1 for the first partition and so on.

Now let’s find out device names using some different command-line tools as shown:
Find Out Plugged USB Device Name Using df Command
To view each device attached to your system as well as its mount point, you can use the df command (checks Linux disk space utilization) as shown in the image below:

Use lsblk Command to Find USB Device Name
You can also use the lsblk command (list block devices) which lists all block devices attached to your system like so:

Identify USB Device Name with fdisk Utility
fdisk is a powerful utility which prints out the partition table on all your block devices, a USB drive inclusive, you can run it will root privileges as follows:

Determine USB Device Name with dmesg Command
dmesg is an important command that prints or controls the kernel ring buffer, a data structure which stores information about the kernel’s operations.
Run the command below to view kernel operation messages which will as well print information about your USB device:

That is all for now, in this article, we have covered different approaches of how to find out a USB device name from the command line. You can also share with us any other methods for the same purpose or perhaps offer us your thoughts about the article via the response section below.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник
How to Find What Devices are Connected to Network in Linux
Last updated September 30, 2019 By Abhishek Prakash 60 Comments
Brief: This quick trick shows you how to find devices connected to your local network in Linux.
Wireless networks have always been a desirable target for wannabe hackers. Wireless networks are also more vulnerable to hacking than the wired ones.
Forget hacking, do you ever wonder that someone might be leeching off your hard paid wifi network? Maybe a neighbor who once connected to your network and now uses it as his/her own?
It would be nice to check what devices are on your network. This way you can also see if there are some unwanted devices on your network.
So you might end up thinking, “how do I find what devices are connected to my network”?
I’ll show you how to do that in this quick tutorial. Not only it’s a good idea from security point of view, it is also a good little exercise if you have interest in networking.
We will use both, command line and GUI, way for finding out what devices are connected to your local network in Linux. The process is very simple and easy to use even for beginners.
A. Using Linux command to find devices on the network
Step 1: Install nmap
nmap is one of the most popular network scanning tool in Linux. Use the following command to install nmap in Ubuntu based Linux distributions:
You can easily install it in other Linux distributions as well. It should be in the official software repository.
Step 2: Get IP range of the network
Now we need to know the IP address range of the network. Use the ifconfig command to find the IP address in Linux. Look for wlan0 if you are using wifi or eth0 if you are using Ethernet.
$ ifconfig
wlan0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 70:f1:a1:c2:f2:e9
inet addr:192.168.1.91 Bcast:192.168.1.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::73f1:a1ef:fec2:f2e8/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:2135051 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:2013773 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:1434994913 (1.4 GB) TX bytes:636207445 (636.2 MB)
The important things are highlighted in bold. As you see my IP is 192.168.1.91 and the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0 which means that the ip address range on my network varies from 192.168.1.0 to 192.168.1.255.
You may also use ip a command to know your IP address in Ubuntu and other Linux distributions.
At the same time, I’ll recommend you to read about basic Linux networking commands for more information.
Step 3: Scan to find devices connected to your network
It is advisable to use root privileges while scanning the network for more accurate information. Use the nmap command in the following way:
$ sudo nmap -sn 192.168.1.0/24
Starting Nmap 5.21 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2012-09-01 21:59 CEST
Nmap scan report for neufbox (192.168.1.1)
Host is up (0.012s latency).
MAC Address: E0:A1:D5:72:5A:5C (Unknown)
Nmap scan report for takshak-bambi (192.168.1.91)
Host is up.
Nmap scan report for android-95b23f67te05e1c8 (192.168.1.93)
Host is up (0.36s latency).
As you can see that there are three devices connected to my network. The router itself, my laptop and my Galaxy S2.
If you are wondering about why I used 24 in the above command, you should know a little about CIDR notation. It basically means that the scanning will be from 192.168.1.0 to 192.168.1.255.
B. Using GUI tool to find devices connected to network
When I first wrote this article, there was no GUI tool for this task. Then I saw a Google+ discussion about a new network monitoring tool being developed for elementary OS. I suggested including a periodic device scan feature in this tool and the developer readily agreed.
So, now we have a GUI tool that does this task. It’s called Nutty. Just run install this app and run it. It will periodically scan for new devices on the network and will notify you if there is a new device.
This application is only available for elementary OS, Ubuntu and hopefully, other Ubuntu based Linux distributions. You can find installation instructions on this detailed article on Nutty.
Oh, you can also log in to your router and see the devices connected to your devices. I let you figure the best way to find devices connected to your network.
Like what you read? Please share it with others.
Источник
List USB Devices Linux
In the world of USB computer peripherals, almost everyone uses some sort of USB devices in their computer. These days there are USB webcams, USB hard drives, USB stick also known as PenDrive etc. Almost every device has a USB version of it. So if you’re using Linux, listing what USB device is connected to your system might be necessary at some point.
There are many programs and many ways to list USB devices on Linux.
In this article, I will show you how to list USB devices on Linux. I am using Ubuntu 18.04 Bionic Beaver for the demonstration, but these commands are available on every Linux distribution. So let’s get started.
Listing USB Devices using lsusb Command
The widely used lsusb command can be used to list all the connected USB devices in Linux.
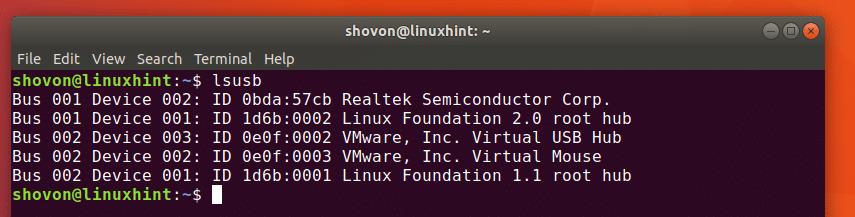
As you can see from the output of the lsusb command in the screenshot below, all the connected USB device is listed. The Bus ID, Device ID, USB ID, and a title is displayed in the output of lsusb command.
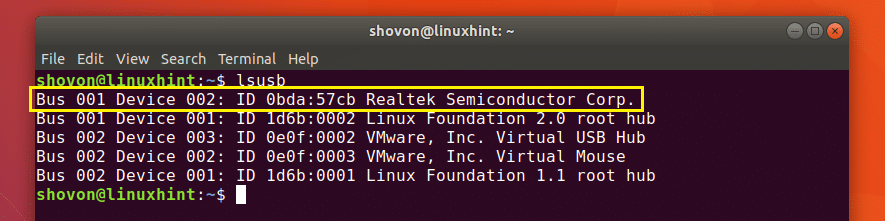
As you can see in the marked section of the screenshot below, Realtek Semiconductor Corp. with ID 0bda:57cb, this is my USB Webcam.
You can’t tell that it’s a Webcam by looking at the output of lsusb command, Can you? Nope! So how do I know this? It’s because I checked the output of the lsusb command before and after connecting the USB Webcam and once I compared the outputs, the newly added row is the USB device I connected. Plain! But there are ways to find out what the USB device is.
You can use the dmesg command to find out more information about the connected USB devices. The last connected USB device is the easiest to find with dmesg command. It is more widely used for debugging purpose. You will shortly see why.
You run dmesg command as follows:
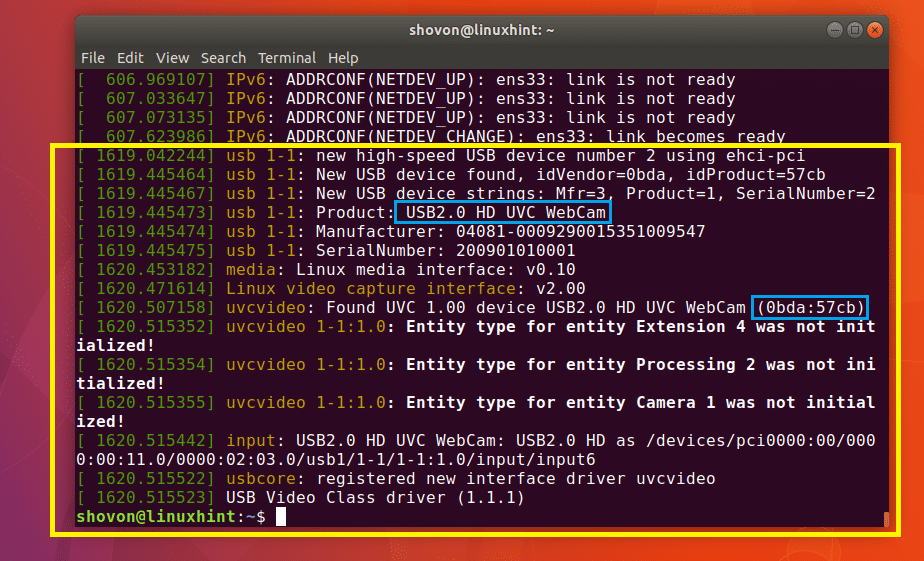
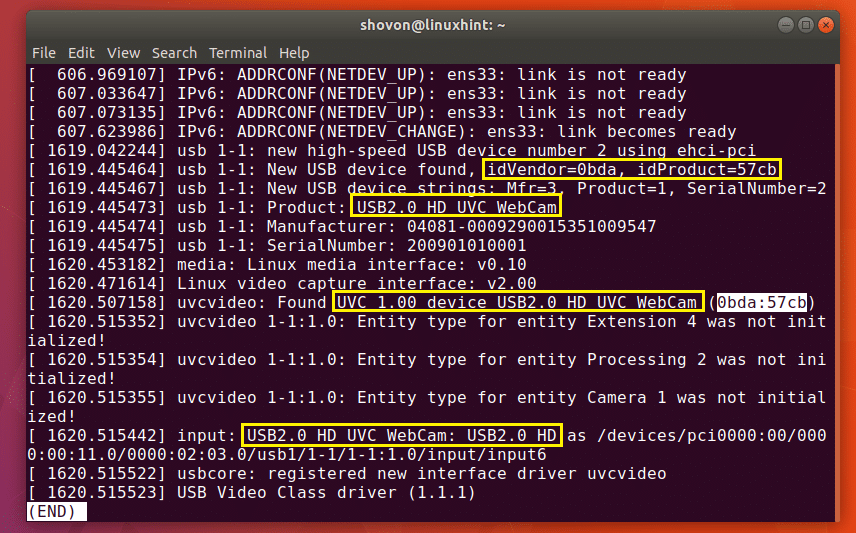
As you can see in the yellow marked box in the screenshot below, these are information about the USB device I connected last, which was my USB Webcam. You can see in one of the blue marked box, the USB device I connected is a HD UVC WebCam and its ID is 0bda:57cb.
By now you may have found out that the output of dmesg command is system log messages. Well yes, it is.
You can also search for a specific USB device by its ID in the dmesg system log.
Run the following command to open the output of dmesg command with less text pager:
You should see the following window:
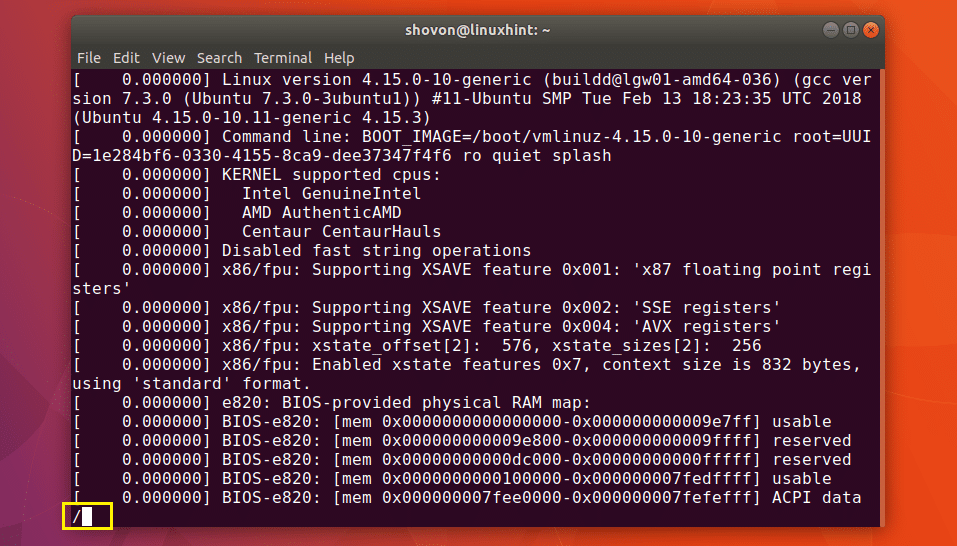
Now to search for a string, press / key on your keyboard. And you should the a / appear on the bottom of terminal window as marked in the screenshot below.
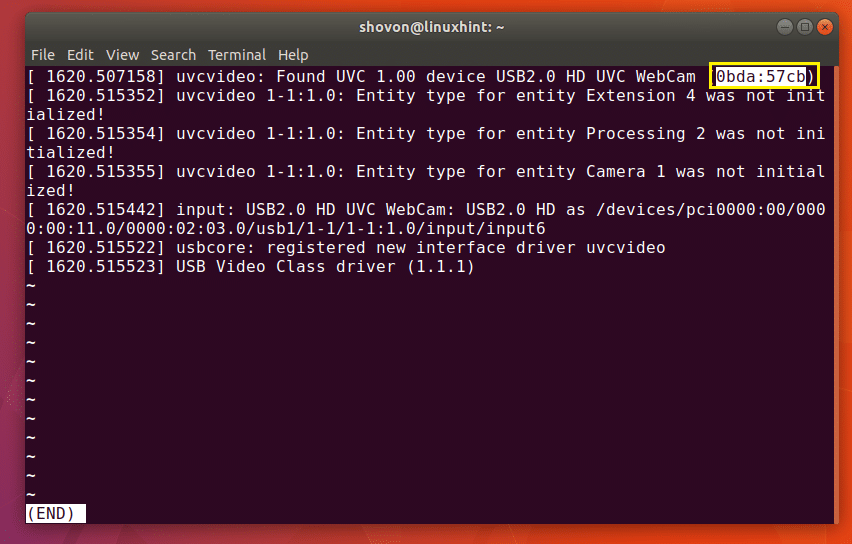
Now type in the USB device ID. For example, earlier when I listed the connected USB devices with lsusb command, one of the USB device had ID 0bda:57cb
Type in the USB Device ID and press . As you can see in the marked section of the screenshot below, the search string is marked white.
You may press and arrow keys to navigate up and down and read through it. You should find a lot of information about that USB device as you can see in the marked section of the screenshot below.
Listing USB devices with usb-devices Command
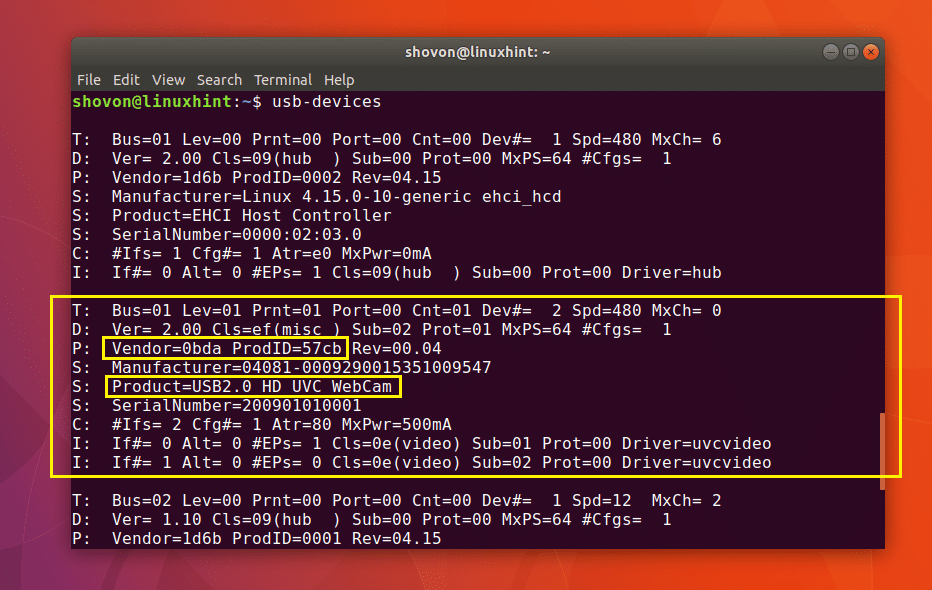
You can run the following command to list all the connected USB devices of your system:
As you can see in the screenshot below, all the connected USB devices are listed. we can find out pretty much the same information as before with usb-devices command.
Listing Block USB Devices
If you want to list all the USB block storage devices, that is all the USB storage devices, then you can use the lsblk or fdisk command to do so.
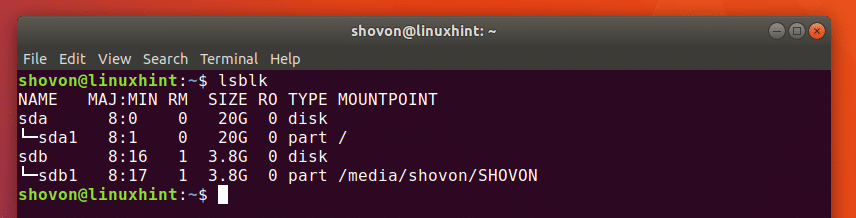
Listing USB block storage devices with lsblk:
As you can see in the screenshot below, all the available block storage devices (including the USB block storage devices) are listed.
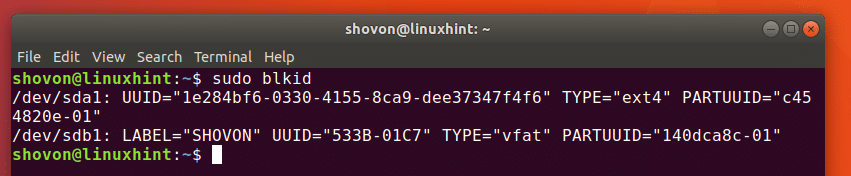
You can get almost the same information as lsblk command with blkid command. But you have to run it as root as follows:
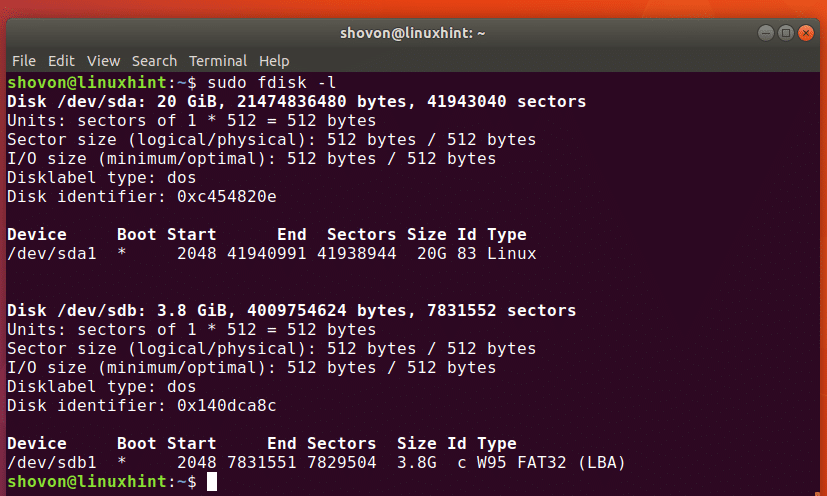
You can also use fdisk command to list all the USB block storage devices as follows:
As you can see in the screenshot below, the connected block storage devices (including the USB devices) are listed.
That’s how you list all the USB devices on Linux. Thanks for reading this article.
Источник