- Installing and using the Cisco AnyConnect client with Debian and Ubuntu for UCI VPN
- Introduction
- Summary
- Installing the Cisco AnyConnect client
- Connecting and Disconnecting
- Connecting (Graphical window)
- Connecting (via command-line)
- Connecting automatically via Command-line (w/o typing in your Username/Password)
- NOTE 1 — Connect-error
- To disconnect (gui)
- To disconnect (command-line)
- To exit (command-line)
- De-installation / Removal
- Additional Hints, Tips, and Handling of Errors and Problems Contributed by Users
- Contact / Feedback
- Acknowledgements
- Installing and Using AnyConnect on Ubuntu Desktop using the User Interface
- Available Languages
- Download Options
- Objective
- Introduction
- AnyConnect Software Version
- Table of Contents
- Installing AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client v4.9.x
- Prerequisites
- Check these other articles out!
- Applicable Devices | Software Version
- Licensing Information
- Step 1
- Step 2
- Step 3
- Step 4
- Step 5
- Step 6
- Step 7
- Step 8
- Using AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client v4.9.x
- Step 1
- Step 2
- Step 3
- Step 4
- Step 5
- Step 6
- Conclusion
Installing and using the Cisco AnyConnect client with Debian and Ubuntu for UCI VPN
(Note: There is also an alternative method of installing UCI VPN support without using the Cisco client, but using the built-in Debian/Ubuntu openconnect and openvpn drivers, should you find the below method does not work for you, or if you prefer to use open-source non-proprietary software.)
Introduction
OIT has a good general VPN-Linux page with instructions on setting up the Cisco AnyConnect VPN client software for Linux, but I got tripped up in a couple of places and thought I’d pass on some heads-ups for other Debian and Ubuntu users.
I originally wrote this «How-To» for Ubuntu v10, and have updated it through v17.04. It should work for most or all Debian-derived distributions through 9.0 («Stretch»).
Please do write me to let me know how it went for you, and/or with any suggestions. I’d love to hear that it helped someone and/or any improvements that could be added.
Thanks to several for the help getting here.
Summary
In the instructions below, I’ll walk you through installing the Cisco VPN client on a Debian or Ubuntu system. When you’re done, you’ll have two commands available at the command-prompt, which you can run to connect to the campus VPN: ‘vpn’ (text mode) and ‘vpnui’ (graphical/windowing).
I used to also include instructions for getting VPN support to show up in the NetworkManager icon/applet in the system tray, for those who used a Gnome based desktop. I no longer do this, as it is too complicated these days to keep up with documenting the various desktop environments, and the changes (and unreliability) of NetworkManager. And it’s not really necessary anyway. If you get it going for yourself, though, Kudos to You! 🙂
Installing the Cisco AnyConnect client
- First, make sure you have the necessary Debian/Ubuntu support packages installed:
- Go to the UCI OIT Cisco Anyconnect/Linux instruction page.
- Download the 32 or 64 bit client as a .gz file.
- If you are usure whether you should use the 32 or 64 bit client: Most people are on 64-bit machines now. But if you are unsure, just run the uname command like this:As you can see from the above example, my machine has a 64-bit Intel (x86_64) based processor. If you see a ‘386’ somewhere, then you are on a 32-bit machine.
- From the command prompt, go to the directory you saved the file to, and unpack it and run, just like the OIT instructions. Note you might have to put in some back-slashes because the download file apparently comes with spaces in the file name these days:
- If you get the following message at the end instead: it most likely means you did not install the two Ubuntu packages up in step 1, above.
- However, if you have installed those two packages, and are still getting this error, then user Steve Murphy wrote me (2015-12-7) with the tip that running the following did install enough dependent packages as to make it work for him:However, while this may help some users, this normally should not be necessary, and was not in my testing.
/.bash_aliases file:(where you don’t actually type the «^D»: it means you hit Ctrl-D to finish).
If you want to edit your aliases file instead directly, you can run a simple editor, ‘nano’, which is usually available on Debian and Ubuntu systems:
Connecting and Disconnecting
Connecting (Graphical window)
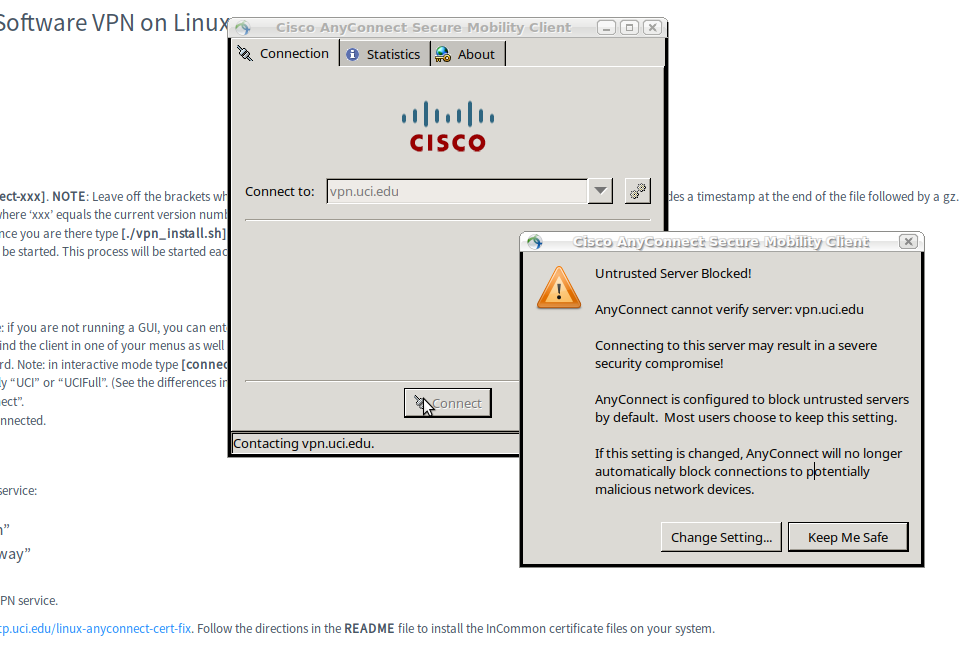
And it should show ‘vpn.uci.edu’ already. Just click Connect.
If you get an error message about an untrusted server or certificate..
..you can fix that following the instructions from Robert in the section NOTE 1 — Connect-error, below.
(By the way, depending on how the installation went, and whatever of the Linux desktop environments you are using (Gnome, Unity, KDE, Mate, Cinnamon, XFCE, etc.) you may also find that the vpnui graphical client now also appears somewhere in your Applications menu. But don’t count on it! This is Linux, after all.. 🙂 )
Connecting (via command-line)
- To start the client from a command-line prompt in a terminal window, using the alias you made above:
- At the VPN> prompt, type connect vpn.uci.edu and press Enter. (If you get an error message about an untrusted server or certificate, you can fix that following the instructions from Robert in the section NOTE 1 — Connect-error, below.) Otherwise, you should now see:If you do not see this, but get a connect error instead, please see NOTE 1 — Connect Error below.
- Ignore the message about entering your UCInetID and password, for now.
- Choose one of the choices by number and press return — usually UCI or UCIFull. (See the differences in the Tunnels below.) For instance, for UCI, press 3 and hit Enter.
- Enter your UCInetID and password in the Username and Password boxes and press return.
- At the accept? [y/n]: prompt, type y and press Enter. You may get several notices the first time about the downloader performing update checks. At the end you should see a >> state: Connected message and a new VPN> prompt. You are now connected.
- Either leave the VPN> prompt open or if you want your terminal back just type quit at the VPN> prompt (the connection will remain active).
Connecting automatically via Command-line (w/o typing in your Username/Password)
I never (not yet?) figured out how to get the Cisco anyconnect software to run via script with command-line parameters sufficient for its running without having to type in your username (UCINetID) and password. I looked into the vpn command / executable supplied by Cisco (in the anyconnect-predeploy package) and running -h on it does not give much help.
Therefore, if you need something command-line and automated, I suggest you use the alternative method using open-source openvpn/openconnect software which I mentioned at the very top of this document. I include a way to do that in an automated way, and I find it works just as well and just as fast, but without having to install proprietary Cisco software. (This is the age of Ed Snowden’s warning to us all, after all.. :-/
NOTE 1 — Connect-error
In most cases I have seen, a connection is made. I have, however, seen the below error before only once. It was when the person was installing on a netbook (running Gnome) which was on campus and usingthe campus wifi system (though I don’t know if those factors were the cause). It didn’t matter if they answered y or n, they continued to get the error and be denied connection.
Update 2015-12-6: «Robert» wrote me with a solution to this:
- ..the connect error. can be resolved by sym-linking the cisco ca directory to the system ca directory as cisco only seems to include one root certificate by default. Or you can install the certificate chain from the VPN provider — sym-linking the system certs worked fine for me. Credit goes to: https://plus.google.com/+AndreasKotowicz/posts/2afhvvNZpE6
Thank you, Robert!
To disconnect (gui)
- Just click disconnect in the window
To disconnect (command-line)
- At the VPN> prompt, type disconnect and hit Enter.
To exit (command-line)
- At the VPN> prompt, type quit and hit return.
De-installation / Removal
- Run Cisco’s provided un-install script
- Optionally, also remove the cisco directory (if you don’t need the .log files that were left behind):
Additional Hints, Tips, and Handling of Errors and Problems Contributed by Users
Several people have written in to me with some additional tips and solutions which I’ll add here:
- From pierrechauffour:
- From zviad aburjania: This turned out to be a missing library fixable by:
- From zviad aburjania (2): (If that link no longer works, it is just recommended to start /opt/cisco/anyconnect/bin/vpnagentd first.)
From pascal müller:
Pascal researched and found that the error, anyconnect was not able to establish a connection to the specified secure gateway is a known problem with Cisco clients before version 4, when these earlier clients are installed on Ubuntu 16.04+. The solution is either to downgrade your Ubuntu, or upgrade your Cisco client. At my university we have upgraded to offering version 4 (anyconnect-predeploy-linux-64-4.3.05017-k9.tar.gz), and this supposedly works with the newer Ubuntus. I did not myself test the new version 4 Anyconnect client with Ubuntus 15.x and 16.x. But I have tested it today (April 27 2017) with my Ubuntu 17.04 system, and it works great.
Contact / Feedback
Please email me to let me know how this process went for you, and/or with any suggestions for improvement on this page itself. Thanks.
Acknowledgements
- Mike Iglesias and Sylvia Bass at UCI’s OIT for for putting up the link to here from their VPN-Linux page.
- a page at Georgia Tech (now defunct), from which part of this page (the old Section 2, no longer included) was originally adapted.
- Joe Remenak for clear, concise feedback on some additional steps (1 and 11) necessary now for the newer 64-bit Ubuntus.
- Tom Distler, for the Tux/Cisco image at the top of this page, which I mooched from his page, How to connect Linux to a Cisco VPN using a PCF file.
- James Condie at UCI, who encountered multiple problems with the latest changes in the 4.3.05017 version of Cisco’s install — but patiently stuck with it — thus encouraging me to update this page once again, and clarify a few additional things for newer Linux users.
- Philippe Moisan, who caught and reported an incompatibility with the find vpnagentd command above in Installation Step 8, for some versions of Linux, and offered also a fix: to put quotes around the «*vpnagentd*» which should work with all flavors of find.
Источник
Installing and Using AnyConnect on Ubuntu Desktop using the User Interface
Available Languages
Download Options
Objective
The objective of this article is to guide you through installing and using AnyConnect VPN Client v4.9.x on Ubuntu Desktop version 20.04 using the User Interface (UI).
This article is only applicable to the RV34x series routers, not Enterprise products.
Introduction
AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client is a modular endpoint software product. It not only provides Virtual Private Network (VPN) access through Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) Internet Key Exchange version2 (IKEv2) but also offers enhanced security through various built-in modules.
AnyConnect Software Version
Table of Contents
Installing AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client v4.9.x
This toggled section provides details and tips for beginners.
Prerequisites
- You need to purchase client license(s) from a partner like CDW or through your company’s device procurement. There are options for 1 user (L-AC-PLS-3Y-S5) or packets of licenses including one year for 25 users (AC-PLS-P-25-S). Other license options available as well, including perpetual licenses. For more details on licensing, check out the links in the Licensing Information section below.
- Download the latest version of firmware available for your router.
Check these other articles out!
Applicable Devices | Software Version
- RV340 | 1.0.03.21 (Download latest)
- RV340W | 1.0.03.21 (Download latest)
- RV345 | 1.0.03.21 (Download latest)
- RV345P | 1.0.03.21 (Download latest)
Licensing Information
AnyConnect client licenses allow the use of the AnyConnect desktop clients as well as any of the AnyConnect mobile clients that are available. You will need a client license to download and use the Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client. A client license enables the VPN functionality and are sold in packs of 25 from partners like CDW or through your company’s device procurement.
Want to know more about AnyConnect licensing? Here are some resources:
Step 1
Open a web browser and navigate to the Cisco Software Downloads webpage.
Step 2
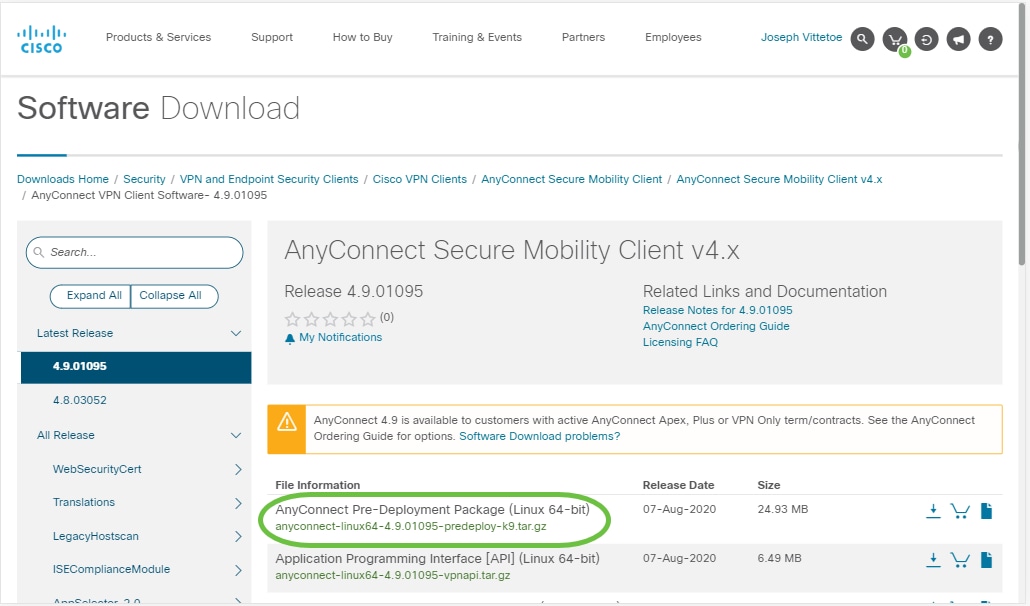
In the search bar, start typing ‘Anyconnect’ and the options will appear. Select AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client v4.x.
Step 3
Download the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client. Most users will select the AnyConnect Pre-Deployment Package (Linux 64-bit) option.
The images in this article are for AnyConnect v4.9.x, which was latest version at the time of writing this document.
If you purchased a license and you are unable to download AnyConnect, call +1 919-993-2724. Select option 2. You will need to know your Cisco ID (the one you use to log into Cisco.com) and the sales order number when you call. They will get that situation all straightened out.
Step 4
Navigate to the folder where you have downloaded the AnyConnect Client Package.
Step 5
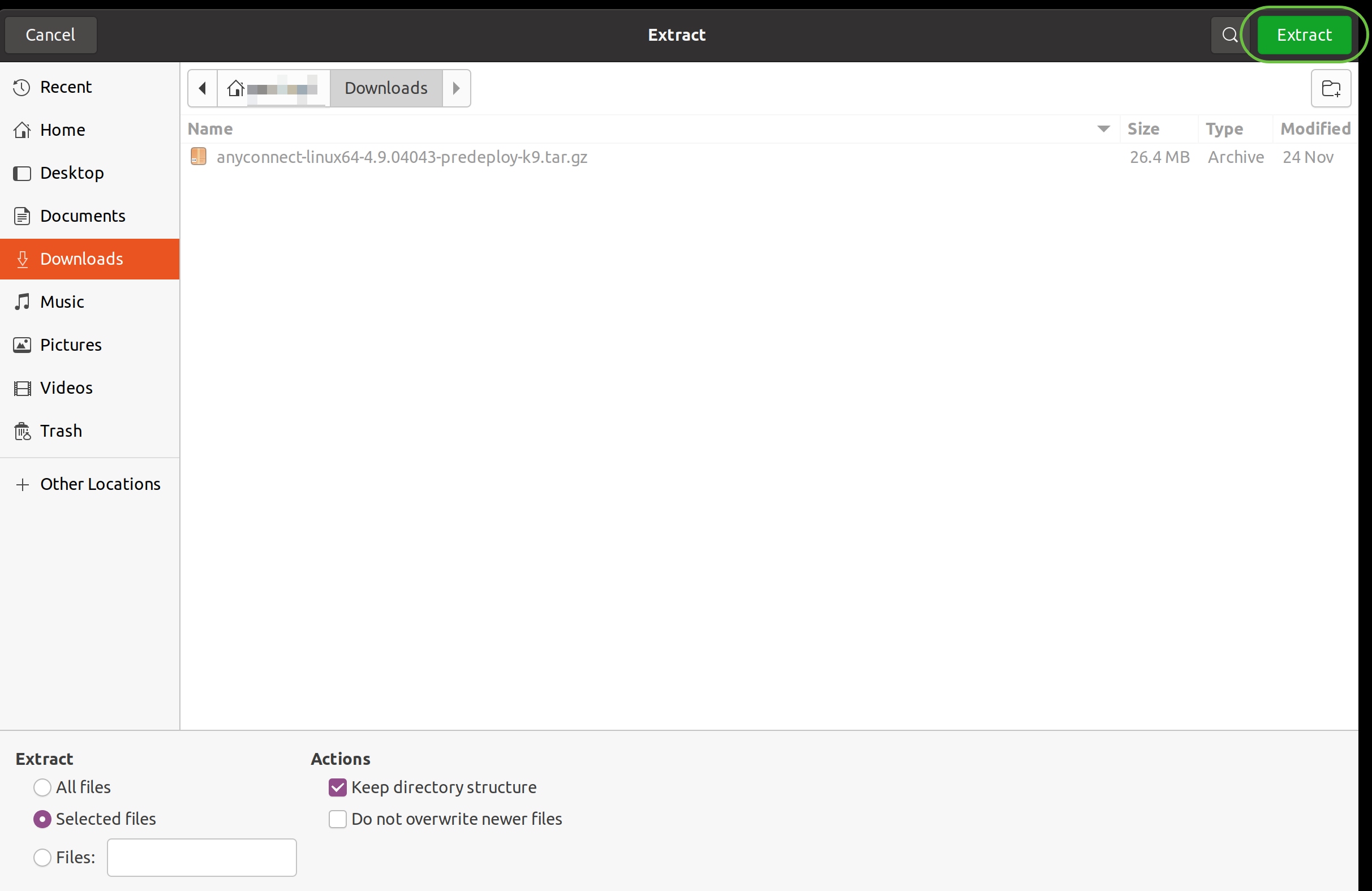
The initial download is a tarball archive (*.TAR, several files packed into one), which must be extracted. To extract the files, right- click on the AnyConnect archive and choose Open with Archive Manager. Click Extract.
Step 6
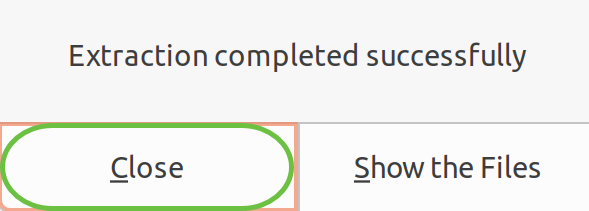
You will see a notification once the extraction is completed. Click Close.
Step 7
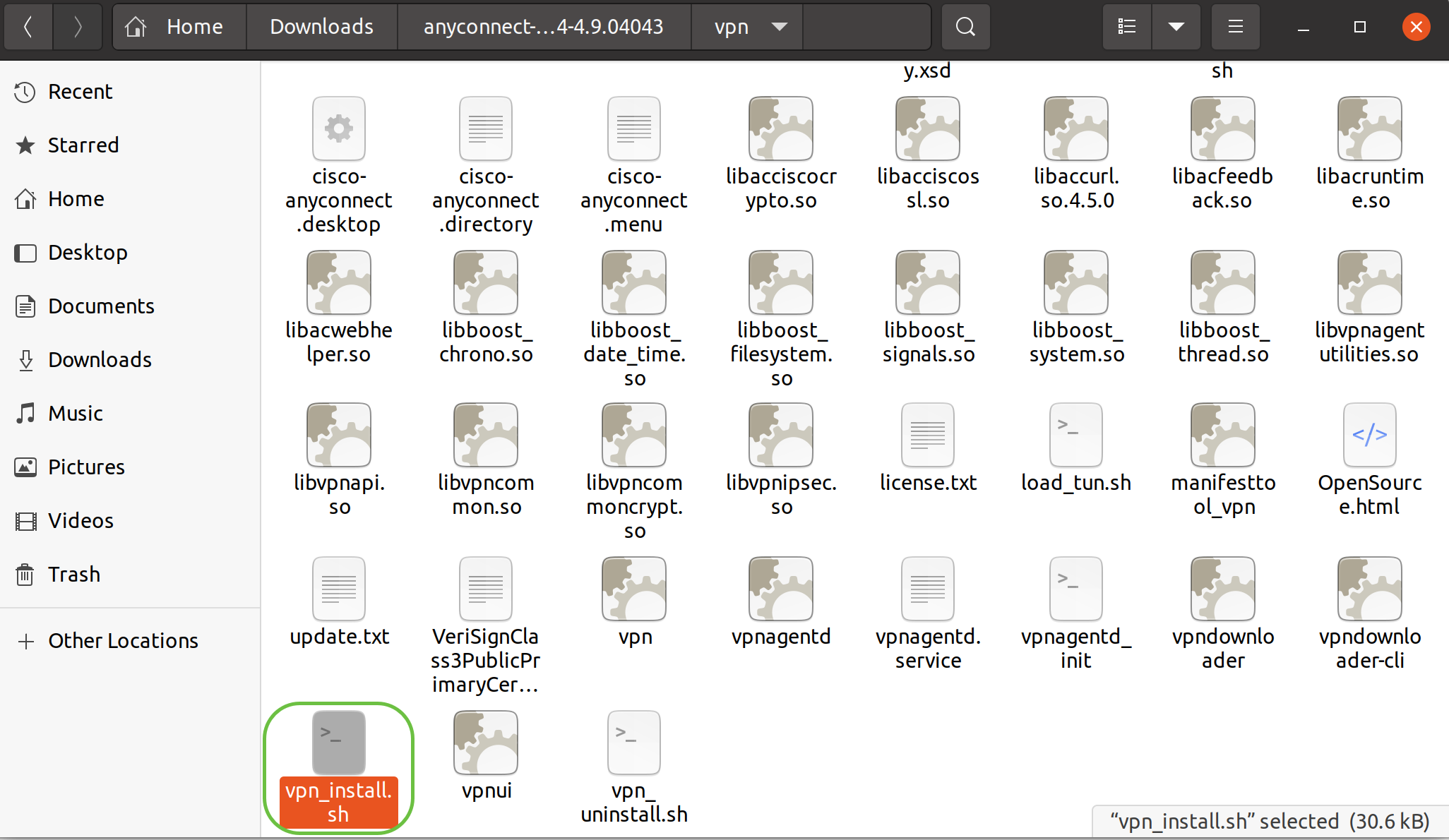
Locate the vpn_install.sh file in the extracted folder.
To run the AnyConnect install script, open a Linux Terminal by pressing Ctrl+Alt+T on your keyboard.
Type ‘sudo ./vpn_install.sh’. This will begin the installation process. For more details on the ‘sudo’ command, click here.
Step 8
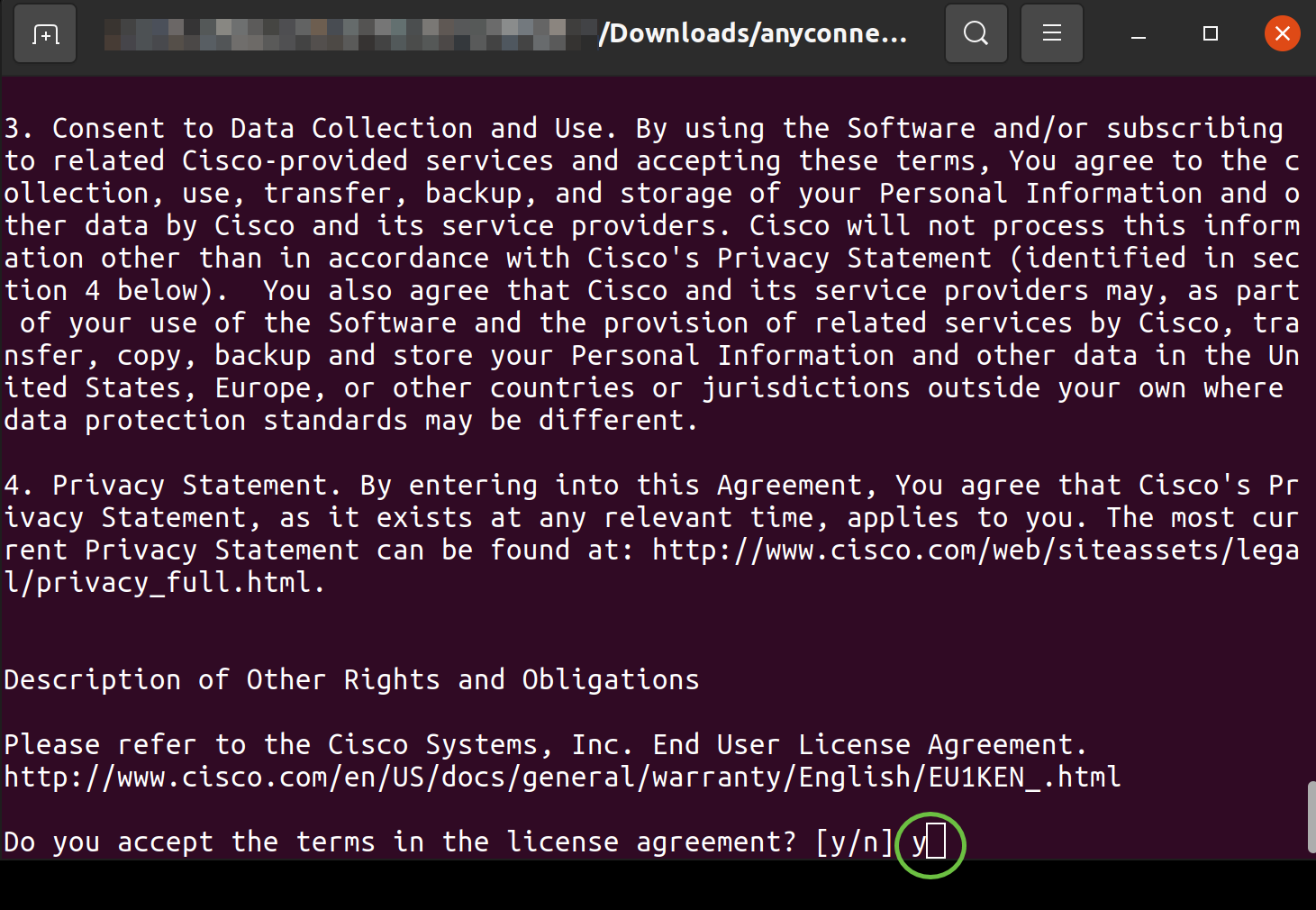
Accept the terms in the license agreement to complete the installation by typing ‘y’.
Using AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client v4.9.x
Step 1
To access the AnyConnect app, click on the start icon (appears as nine dots on the lower left corner). Choose the Cisco Anyconnect app.
Alternatively, press Super+A (Super key is the windows icon key) on your keyboard to bring up the search bar. Start typing ‘Anyconnect’ and the app will appear.
Step 2
Click on the AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client icon.
Step 3
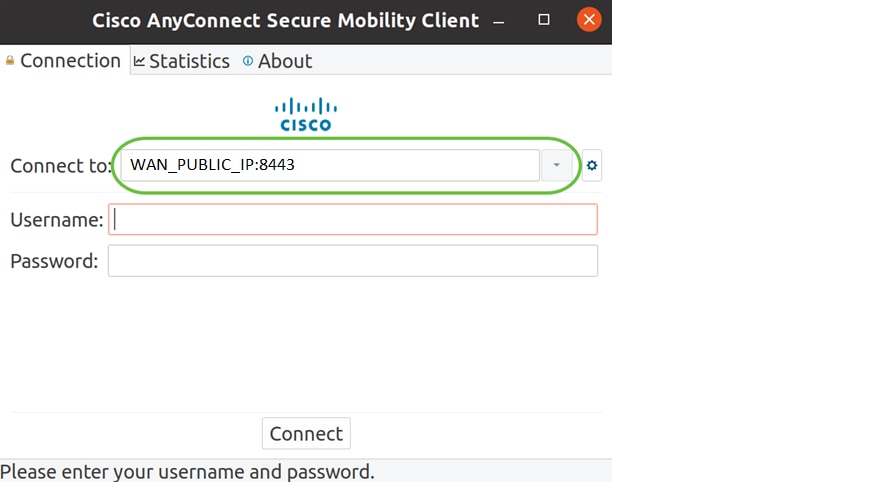
Enter the IP Address or Hostname of your desired server followed by the port number.
For RV340 family, the default port number is 8443.
Step 4
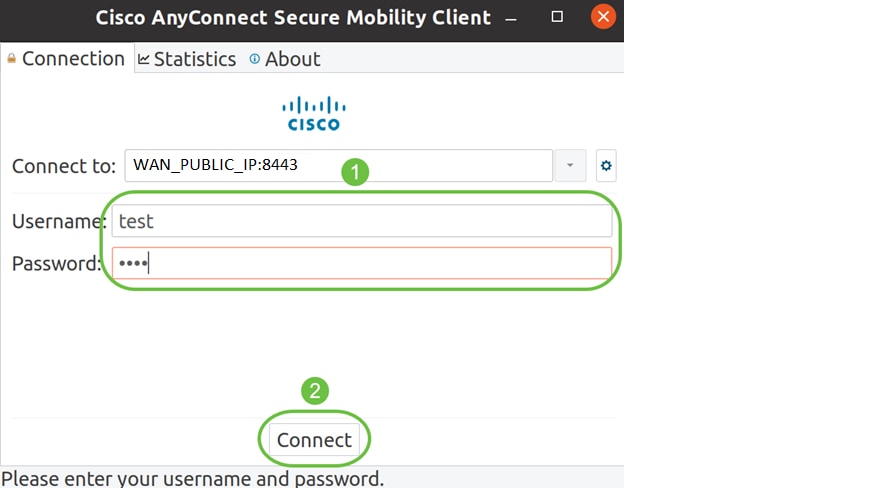
Enter your Username and Password in the fields provided. Click Connect.
Step 5
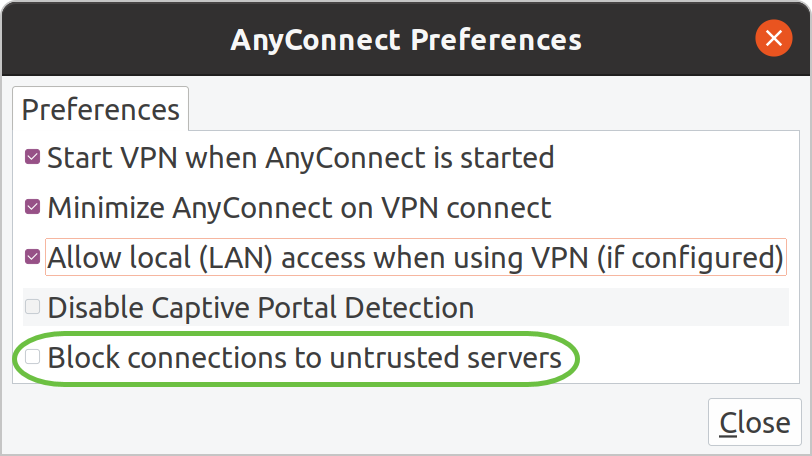
Some connections may not be secure using a trusted SSL certificate. By default, AnyConnect Client will block connection attempts to these servers.
Uncheck Block connections to untrusted servers under Preferences to connect to these servers.
Step 6
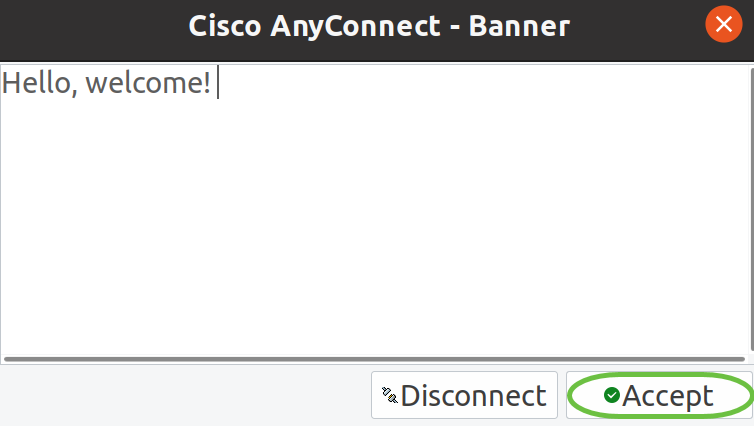
As soon as the connection is established, the login Banner will appear. Click Accept.
You will also see notification that the Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client is Connected.
Conclusion
There you have it! You have now successfully learned the steps to install and use the Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client v4.9.x on Ubuntu Desktop using the UI.
Источник