- How to Clear BASH Command Line History in Linux
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
- How to Clear Linux Command Line History
- Bash’s history feature
- 1) Remove Linux history command
- a. Delete the previous commands
- b. Delete a single command
- 2) Clear bash completely
- 3) Turn off bash history
- a. Turn off for all users
- b. Turn off for a specific user
- c. Edit .bashrc
- 4) Delete some entries lines
- How to clear all history in linux/ubuntu terminal or bash permanently? [closed]
- 2 Answers 2
- How To Clear Command Line History In Linux
- Why should we clear Command line history?
- Why shouldn’t we clear Command line history?
- Clear Command line history in Linux
- 1. Clear entire Command line history using history command
- 2. Avoid saving commands in history list by inserting a blank space before each command
- 3. Clear or delete specific commands from history
- 4. Clear Command line history automatically at logout
- 5. Delete Command line history permanently
- Conclusion
How to Clear BASH Command Line History in Linux
The bash history keeps a record of all commands executed by a user on the Linux command line. This allows you to easily run previously executed commands by using the “up arrow” or “down arrow” keys to scroll through the command history file.
In this article, we will show you two simple ways to clear your command-line history on a Linux system.
The major reason for removing command-line history from the Linux terminal is to prevent another user, who could be using the same account.
For instance if you have typed a command that contained a password in plain-text and you don’t want another system user or an attacker to see this password, you need to delete or clear the history file.
Take a look at the command below, here the user aaronkilik has typed the database server password on the command line.
If you look into th bash history file towards the end, you will see the password typed above in there.

The bash_history file is normally located in a user’s home directory /home/username/.bash_history.
To remove a single line from the history file, use the -d option. For example, if you want to clear a command where you entered clear-text password as in the scenario above, find the line number in the history file and run this command.
To delete or clear all the entries from bash history, use the history command below with the -c option.
Alternatively, you can use the command below to delete history of all last executed commands permanently in the file.
Note: A normal user can only view his/her own command history, but the root user can view the command history of all other users on the system.
You can learn more about the bash history file and useful history commands here: The Power of Linux “History Command” in Bash Shell.
Always remember that all commands you run are recorded in a history file, so do not type plain-text passwords on the command line. If you have questions or thoughts to share with us, make use of the feedback form below.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник
How to Clear Linux Command Line History
You may want to clear the history file and the screen for security reasons. Some Linux distributions may clear the screen when you logout but others do not. Many programs read input as a single line at a time.
The GNU history library is able to keep track of those lines, associate arbitrary data with each line, and utilize information from previous lines in composing new ones. Bash and other shells may use this history library. The default file is
Bash’s history feature
bash’s history function depends on a variable called HISTFILE, normally set to the current user’s .bash_history file (located in the user’s home directory). When echoed, it returns the full path and name of the user’s history file, like so:
1) Remove Linux history command
History can be reset with some command but after the operation, if you logout and login in your shell, you will see the same history
a. Delete the previous commands
You can use history -c command to clear the previous history command in the current shell. That’s enough (but overkill) if you’ve just typed your password and haven’t exited that shell or saved its history explicitly.
The example below shows our current history
Now let’s use the command.
When you exit bash, the history is saved to the history file. The history created during the current session is appended to the file, entries that are already present are unaffected. Let’s check the new history
Let us add some command to our history.
To overwrite the history file with the current shell’s history, run history -w after history -c command
After login again, let’s us check our history
You can see that our history begin at history -w entry command.
b. Delete a single command
You can delete the history’s entries which you don’t want with the -d option. This will delete the history entry at position offset. But when you close terminal and open it again histories are not deleted. So we finally use history -w to save the changes.
Now, if you want to delete the sixth entry which is mkdir command just use:
You can see that we didn’t have mkdir command entry above.
2) Clear bash completely
To clear the bash history completely on the server, an alternative solution is to link
/.bash_history to /dev/null
However, one annoying side-effect is that the history entries is linked to the memory and it will flush back to the file when you log out. To workaround this, you can use the following command:
3) Turn off bash history
You can stop logging history using one of the two ways: turn it off for all users, or turn off logging history for a single user.
a. Turn off for all users
You can turn off the bash history for all user adding unset HISTFILE line in /etc/profile file. This line deactivate the history file of each user on the system
You need to have the permission to apply the command above
b. Turn off for a specific user
The command above, it is possible to turn off the bash history of a specific user. You just need to indicate his bash_profile file.
Every the user will login, his history will be reset as below. All his history command will save until user logout
c. Edit .bashrc
You can remove the history command by editing two values of history command parameters.
- HISTSIZE which is the number of lines or commands that are stored in memory in a history list while your bash session is ongoing
- HISTFILESIZE which saves the amount of lines used for the history stack when it’s written to the history file.
To do it, edit your .bashrc and add
Now you can successfully delete the bash history and even stop logging to bash history using any of the above-listed commands.
4) Delete some entries lines
You can use history -d offset built in to delete a specific line from the current shell’s history. It’s not really practical if you want to remove a range of lines since it only takes one offset as an argument, but you could wrap it with a loop.
Just this one liner in the command prompt will help.
for i in <1..N>; do history -d START_NUM; done
Where START_NUM is starting position of entry in history N is no of entries you may want to delete.
Let’s check the last 15 entries of our history command
Now let us delete 13 entries beginning at the line 986
for i in <1..13>; do history -d 986; done
Now let’s check the result
You can see that we don’t have the same result.
When a user logs in with either a login or interactive/non-login shell, the user’s .bash_history file is opened. Now can operate on this file with some useful commands. The history is useful to retrieve commands used before but you can need to delete some entries of theses used commands. The
/.bash_history file does not record what you type in response to other programs’ prompts, just what you type at the bash prompt itself.
Источник
How to clear all history in linux/ubuntu terminal or bash permanently? [closed]
Want to improve this question? Update the question so it’s on-topic for Stack Overflow.
Closed 10 years ago .
When you use the up key in a Linux terminal, you can use previous commands again. Great feature. However, I started logging mysql into mysql with the sensitive details in the command.
How can I delete that history permanently?
2 Answers 2
You can clear your bash history like this:
/bash_history . Have to restart terminal for this though.
/.bash_profile : export SHELL_SESSION_HISTORY=0 , then do a source
/.bash_profile and to finish quit and restart your Terminal app. If you want to understand what this export command does, then you should definitely check this following link: superuser.com/questions/950403/…
If you use bash, then the terminal history is saved in a file called .bash_history. Delete it, and history will be gone.
However, for MySQL the better approach is not to enter the password in the command line. If you just specify the -p option, without a value, then you will be prompted for the password and it won’t be logged.
Another option, if you don’t want to enter your password every time, is to store it in a my.cnf file. Create a file named
/.my.cnf with something like:
Make sure to change the file permissions so that only you can read the file.
Of course, this way your password is still saved in a plaintext file in your home directory, just like it was previously saved in .bash_history.
Источник
How To Clear Command Line History In Linux
In Bash, all the commands that you run in the Terminal are stored in a text file named in .bash_history in your home directory. We can use the history command to display a list of the commands entered since you started the session. For some reason, you may want to delete all or a specific command from the Bash history. In this brief guide, let us learn how to clear command line history in Linux with examples.
Before getting to the topic, first let us see why should we clear the command line history and why shouldn’t we do it in some cases.
Why should we clear Command line history?
There are chances that you don’t want to expose the Command line history of your Linux system. Say for example, if you are a Linux trainer/tutor, you might have taught some commands to your students in the Lab computer.
Those commands might be harmful and are not supposed to use. But the students may not fully aware of the consequences of such critical commands.
A curious student might search the command line history, and wonder what does those commands will do, and start to test them one by one. The result? He/she might inadvertently break the system.
Would you allow that? Of course, we can re-install or repair the system in couple minutes. However, it is completely unnecessary if you are bit careful. So, clearing Command line history from time to time, especially in a shared computer, is a good practice.
It is just an example. There could be many other reasons to clear Linux command line history.
Why shouldn’t we clear Command line history?
Clearing Command line history is a good practice, however you must not clear history in some cases. Say for example, you want to repeat a specific command often. Would you type the same command every time? That’s not necessary.
As I said earlier, the commands that you run on the Terminal will be retained in the
/.bash_history file. You can retrieve the previously executed commands by pressing the UP arrow in the keyboard.
When you hit the UP, the list of commands that you run recently will appear. Just keep hitting the UP arrow key until you find the command that you want to run. Once you find the command that you want to run, just hit ENTER to execute. That’s it. You don’t have to type the entire command every time.
Sometimes you can’t remember some lengthy and complex commands in a previous session. In such cases, you can use history command to retrieve the previously executed commands.
So if you already cleared the Bash history, you can access the previously entered commands. This is why you should decide whether you want to clear the command line history or not.
Without further ado, let us see how to clear command line history in Linux.
Clear Command line history in Linux
There are many ways to clear Command line history. Here I have listed five ways.
1. Clear entire Command line history using history command
As stated earlier, the history command will display the last executed commands.
To view the previously executed commands in Linux, run:
To clear the history, just run any one of the following commands:
The above commands will clear the command line history.
2. Avoid saving commands in history list by inserting a blank space before each command
Using this method, you can eliminate a specific command getting saved in the history list. Just put a blank space (Hit space bar from the keyboard) before any command. The command will not be recorded in history.
To do that, you must set HISTCONTROL environment variable’s value as “ignorespace” or “ignoreboth”.
Add the following line at the end:
Save and close the file. Run the following command to take effect the changes.
Or, simply log out and log back in to apply the changes.
To verify it, run a few commands. And put a blank space in-front of any command. I put a blank space in last command.
Here indicates a blank space.
Refer the following screenshot:
Put a blank space before a command to avoid saving it in history in Linux
Now, run the history command to view the recently executed commands:
Sample output:
clear Command line history in Linux
As you see in the above output, the «sudo ping ostechnix.com» command is not displayed in the history command output.
3. Clear or delete specific commands from history
Sometimes you might want to delete some particular commands from history list, instead of clearing the entire history.
Let me show you an example. I am going to run the following commands in the Terminal.
Then, display the history command output using command:
sample output:
As you see in the above output, the history command displays the last executed commands.
To clear or delete a particular command from the history, use -d flag with the command prefix number:
Here represents the line number of each command.
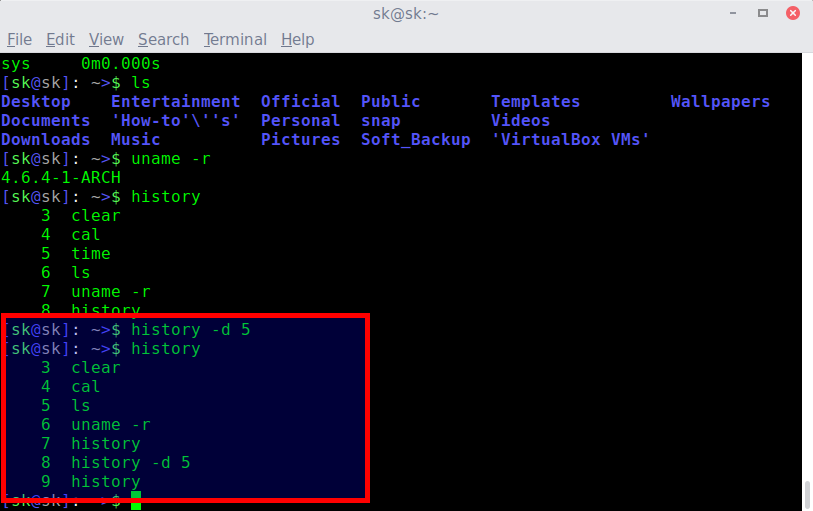
For example, to delete the «time» command with line number «5» from the history, run:
Now, display the command line history to see if the command is removed or not.
Sample output:
Clear or delete specific commands from history
As you see, the «time» command has been removed. Similarly, you can delete any command from the history list.
4. Clear Command line history automatically at logout
Instead of manually clearing history each time, you can automatically clear it at logout.
Add the following line:
Save and close the file. Now, the history will be cleared after you logout from the session.
5. Delete Command line history permanently
All of the above methods will only remove the commands from the active session i.e currently opened terminal. If you have multiple terminals running different commands, the history command will only delete the history from where you run this command. The commands from other terminals will still be available.
To remove all commands from Bash history in all sessions, you must remove the contents of .bash_history file. This file contains the list of commands that we run in the terminal. You can either clear this file manually each time or setup a cron job to clear it at regular intervals.
To manually clear the contents of this file, run:
Like I said, this will delete the entire history. The next time this file will start to record the history. You should run this command everyday to clear the contents of this file.
Alternatively, you can schedule this task at regular interval using cron jobs.
Add the following commands:
Save and exit file. The history will be automatically cleared at 8 pm everyday.
Recommended read:
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you have learned why should we clear the command line history, and why you shouldn’t do it in some cases. Also, you have learned the different ways to clear command line history in Linux. If you know any other method to do it, feel free to let us know in the comment section below.
Источник