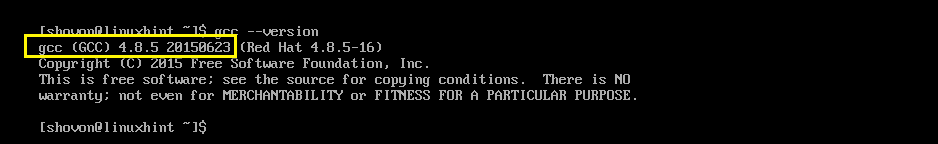- How to Write and Run a C Program in Linux
- Step 1: Install the build-essential packages
- Step 2: Write a simple C program
- Step 3: Compile the C program with gcc Compiler
- Step 4: Run the program
- Karim Buzdar
- Compile C Program in Linux Using GCC
- Installing GCC on Ubuntu and Debian GNU/Linux:
- Installing GCC on Linux Mint:
- Installing GCC on CentOS 7 and Fedora:
- Installing GCC on Arch Linux:
- Writing Your First C Program:
- Compiling and Running C Programs with GCC:
- How to Write, Compile and Run a C Program in Ubuntu and Other Linux Distributions [Beginner’s Tip]
- Method 1: How to run C programs in Linux terminal
- Method 2: How to run C programs in Linux using a code editor like Visual Studio Code
How to Write and Run a C Program in Linux
Linux is becoming programming heaven for developers, being an open-source and free operating system. Turbo C compiler is already an old approach to compile programs so let us programmers move to Linux for a new programming environment. In this article, we will explain how to write, compile, and run a simple C program. This will serve as a basis for you to move to more complicated and useful C programs that you can write and execute on Linux.
We have run the steps and commands mentioned in this article on a Ubuntu 20.04 LTS system but it will work on other versions like Ubuntu 18.04 or distributions like Debian 10 in the exact same way.
We will be using the Linux command-line tool, the Terminal, in order to compile a simple C program. To open the Terminal, you can use the Ubuntu Dash or the Ctrl+Alt+T shortcut.
Step 1: Install the build-essential packages
In order to compile and execute a C program, you need to have the essential packages installed on your system. Enter the following command as root in your Linux Terminal:
You will be asked to enter the password for root; the installation process will begin after that. Please make sure that you are connected to the internet.
Step 2: Write a simple C program
After installing the essential packages, let us write a simple C program.
Open Ubuntu’s graphical Text Editor and write or copy the following sample program into it:
Then save the file with .c extension. In this example, I am naming my C program as sampleProgram.c
Alternatively, you can write the C program through the Terminal in gedit as follows:
This will create a .c file where you can write and save a program.
Step 3: Compile the C program with gcc Compiler
In your Terminal, enter the following command in order to make an executable version of the program you have written: Advertisement
Make sure your program is located in your Home folder. Otherwise, you will need to specify appropriate paths in this command.
Step 4: Run the program
The final step is to run the compiled C program. Use the following syntax to do so:
You can see how the program is executed in the above example, displaying the text we wrote to print through it.
Through this article, you have learned how to write, compile and run a simple C program in Linux. All you need is the essential packages and the right skills to make you a programming guru in Linux!
Karim Buzdar
About the Author: Karim Buzdar holds a degree in telecommunication engineering and holds several sysadmin certifications. As an IT engineer and technical author, he writes for various web sites. You can reach Karim on LinkedIn
Источник
Compile C Program in Linux Using GCC
In this article, I will show you how to install GCC and compile C programs in Linux using GCC. I will use Debian 9 Stretch for the demonstration. But I will show you how to install GCC on wide variety of Linux distributions. Let’s get started.
Installing GCC on Ubuntu and Debian GNU/Linux:
On Ubuntu and Debian GNU/Linux distributions, GCC is really easy to install as all the required packages are available in the official package repository of Ubuntu and Debian. There is a meta package called build-essential, which installs everything you need in order to compile C and C++ programs on Ubuntu and Debian GNU/Linux distribution.
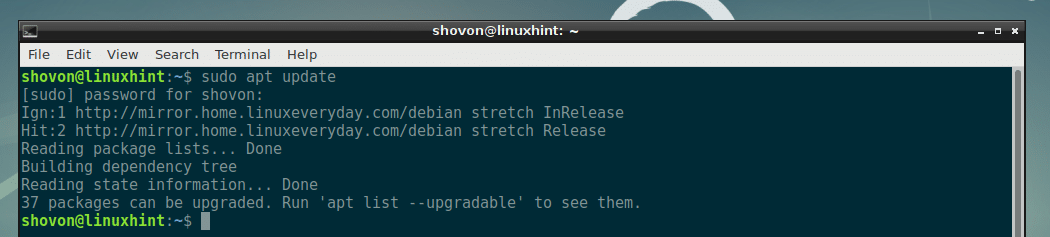
First, update the APT package repository cache with the following command:
The APT package repository cache should be updated.
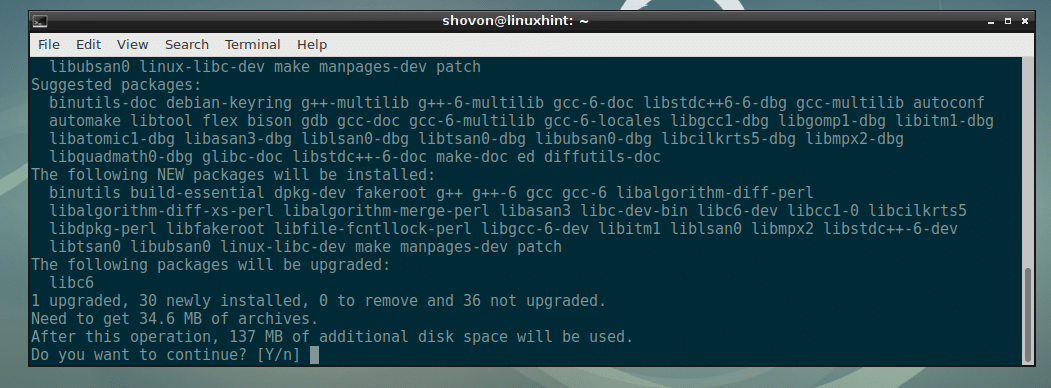
Now install build-essential with the following command:
Now press y and then press to continue.
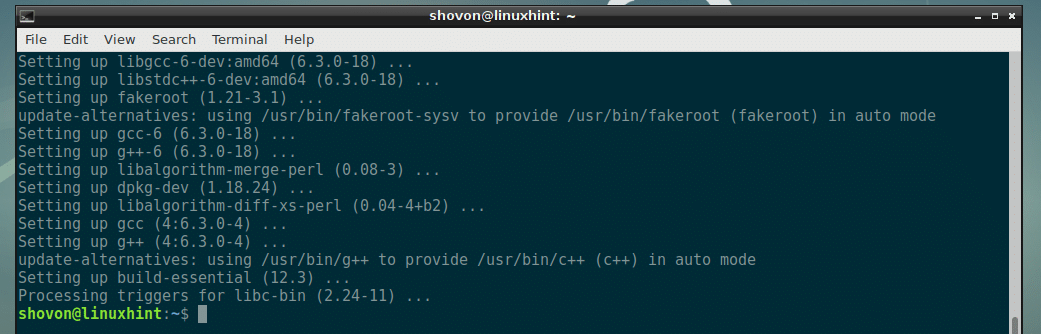
GCC should be installed.
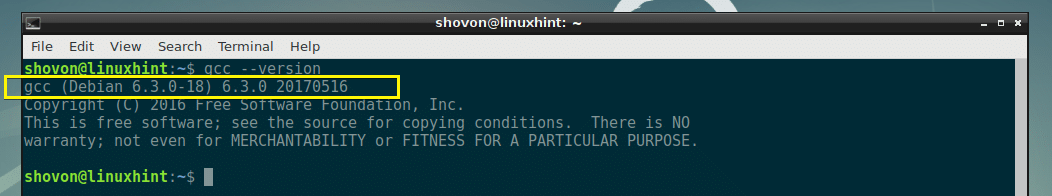
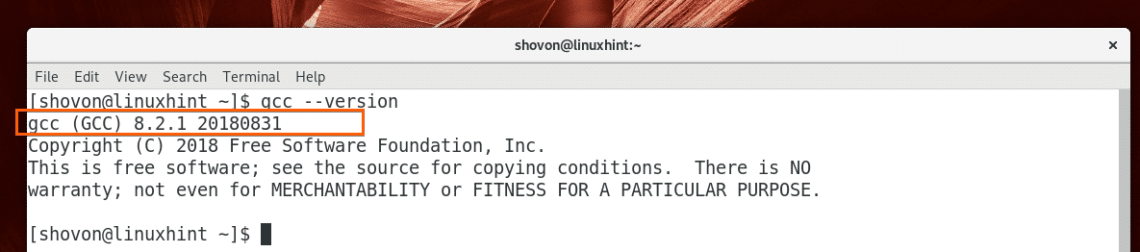
Now you can check whether GCC is working with the following command:
Installing GCC on Linux Mint:
You can install GCC on Linux Mint the same way as in Ubuntu/Debian as shown in the earlier section of this article.
Installing GCC on CentOS 7 and Fedora:
On CentOS 7 and Fedora, GCC is easier to install as well. The required packages are available in the official package repository of CentOS 7 and Fedora. You can install the Development Tools group to install all the required packages to compile C and C++ programs on CentOS 7 and Fedora.
First, update the YUM database with the following command:
YUM database should be updated.
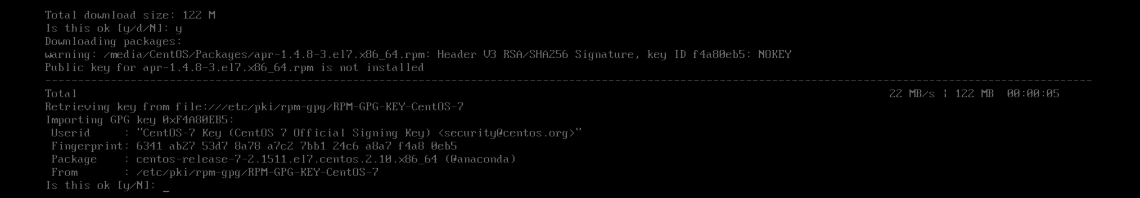
Now install Development Tools group packages with the following command:
Now press y and then press to continue.
If you see this message, just press y and then press .
GCC should be installed.
Now you can check whether GCC is working with the following command:
Installing GCC on Arch Linux:
You can install GCC on Arch Linux too. All the required packages are available in the Arch package repository. Arch also has a meta package base-devel, which you can install to get all the required tools needed to compile C and C++ programs on Arch Linux.
First, update the Pacman database with the following command:
Pacman database should be updated. In my case, it was already up to date.
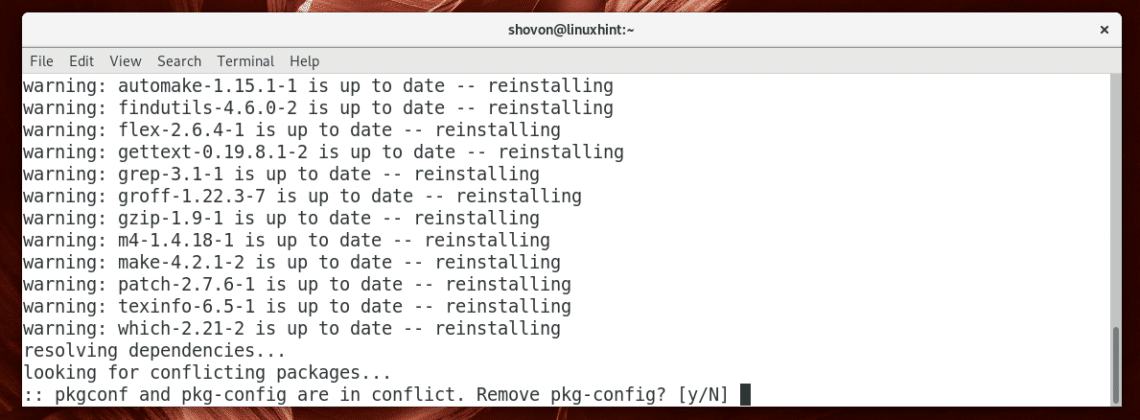
Now install base-devel package with the following command:
Now press to select all unless you want to install very specific set of packages.
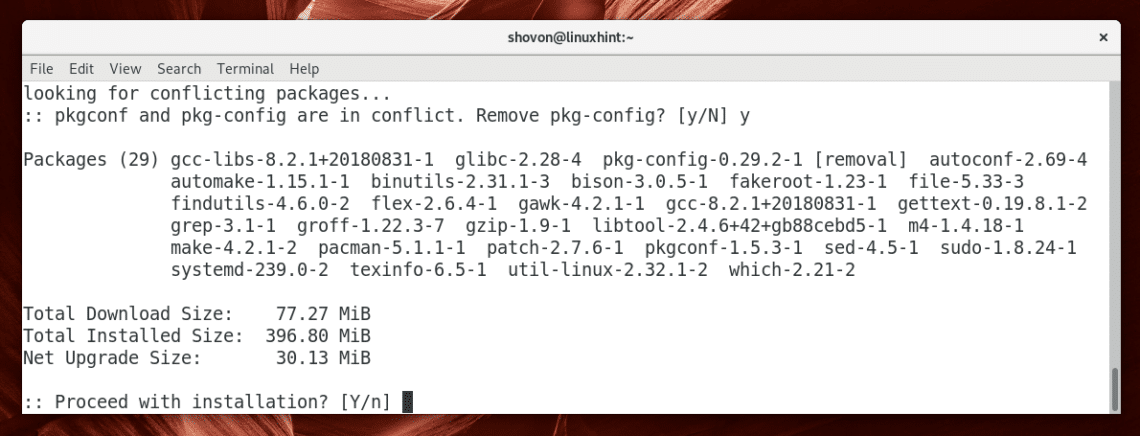
You may see something like this. It’s nothing serious as far as I know. It’s just a package was renamed from pkg-config to pkgconf. So Pacman is asking you whether you want to use the new package and remove the old one. Just press y and then press .
Now press y and then press .
GCC should be installed.
Now check whether GCC is working with the following command:
Writing Your First C Program:
Now let’s write a very simple C program, which we will compile in the next section of this article below using GCC C compiler.
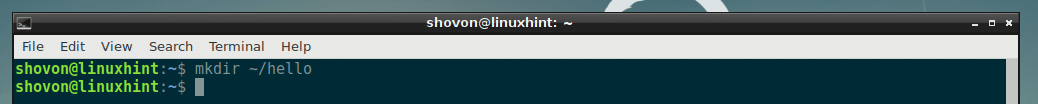
First, create a project directory (I am going to call it hello) with the following command:
Now navigate to the newly created directory with the following command:
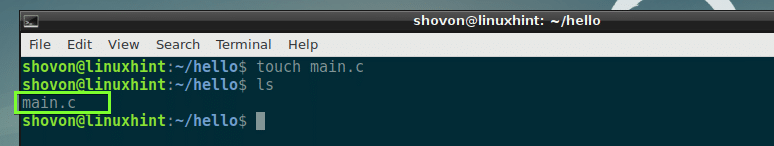
Now create a new C source file (I am going to call it main.c) here with the following command:
Now open the file with any text editor (such as vim, nano, gedit, kate etc) of your choice.
To open the file with nano, run the following command:
To open the file with vim, run the following command:
To open the file with Gedit, run the following command:
To open the file with Kate, run the following command:
I am going to use Gedit text editor in this article.
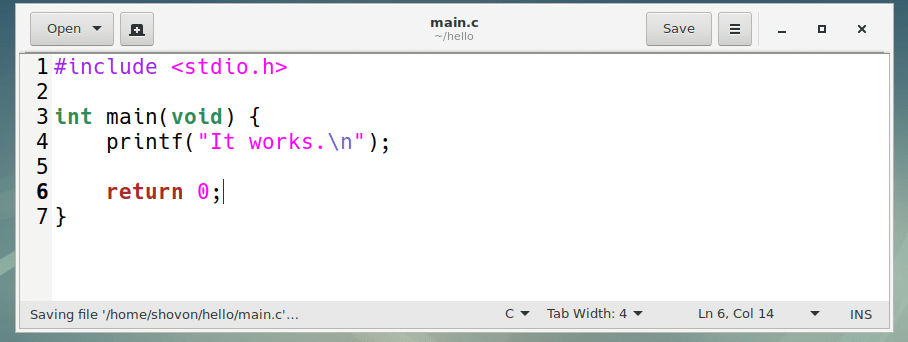
Now type in the following lines and save the file.
Here, line 1 includes the stdio.h header file. It has function definition for the printf() function I used on line 4.
Every C program must have a main() function. It is the function that will get called when you run a C program. If you don’t write a main() function, you can’t run the C program. So I wrote a main() function in line 3 – line 7.
Inside the main() function, I called printf() library function in line 4 to print some text to the screen.
Finally, in line 6, I returned 0 from the program. On Linux world, when a program returns 0, it means the program ran successfully. You can return any integer you like but there are some Linux specific rules on what return value means what.
In the next section, I will show you how to compile the C program with GCC and run it.
Compiling and Running C Programs with GCC:
The command to compile a C source file with GCC is:
NOTE: Here, SOURCE_FILES is a whitespace separated list of C source files. The compiled executable file will be saved as OUTPUT_BINARY in your current working directory.
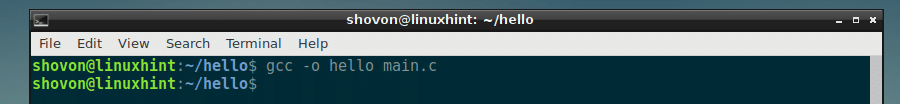
In our case, the main.c source file doesn’t depend on other C source file, so we can compile it with the following command:
The source file main.c should be compiled and hello executable file should be created as you can see in the screenshot below.
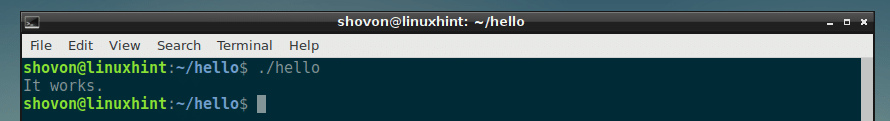
Now, you can run the hello executable binary file as follows:
As you can see, the correct output is printed on the screen.
So that’s basically how you use GCC to compile C programs on Linux. Thanks for reading this article.
Источник
How to Write, Compile and Run a C Program in Ubuntu and Other Linux Distributions [Beginner’s Tip]
Last updated October 7, 2021 By Abhishek Prakash 21 Comments
How do you program in C on Linux? It is indeed very easy and consists of three simple steps.
Step 1: You write your program and save the file with a .c extension. For example, my_program.c.
Step 2: You compile the program and generate the object file using gcc compiler in a terminal like this:
Step 3: You run the generated object file to run your C program in Linux:
This was just the quick summary on how to compile and run C program in Linux. If you are new to either C or Linux, I’ll show these steps in detail so that you feel comfortable coding C program in Linux environment.
In fact, I’ll discuss how to run C programs in Linux terminal as well as in code editor.
Method 1: How to run C programs in Linux terminal
In order to run a C program in Linux, you need to have a C compiler present on your systems. The most popular compiler is gcc (GNU Compiler Collection).
You can install gcc using your distribution’s package manager. In Debian and Ubuntu-based Linux distributions, use the apt command:
Switch to directory where you have kept your C program (or provide the path) and then generate the object file by compiling the program:
Keep in mind that it is optional to provide the output object file (-o my_program). If you won’t do that, an object file named a.out will be automatically generated. But this is not good because it will be overwritten for each C program and you won’t be able to know which program the a.out object file belongs to.
Once you have your object file generated, run it to run the C program. It is already executable. Simple use it like this:
And it will display the desired output, if your program is correct. As you can see, this is not very different from running C++ programs in Linux.
Every time you make a change in your program, you have to compile it first and then run the generated object file to run the C program.
Method 2: How to run C programs in Linux using a code editor like Visual Studio Code
Not everyone is comfortable with command line and terminal and I totally understand that.
You can use a proper C/C++ IDE like Eclipse or Code Blocks but they are often too heavy programs and more suitable for large projects.
I recommend using an open source code editor like Visual Studio Code or Atom. These are basically text editors and you can install add-ons to compile and run programs directly from the graphical code editor.
I am using Visual Studio Code editor in this example. It’s a hugely popular open source code editor from Microsoft.
First thing first, install Visual Studio Code in Ubuntu from the software center. For other distributions, please check your Linux distribution’s package manager or software center. You may also check the official website for more information.
Start Visual Studio Code and open/create a project and create your C program here. I am using a sample Hello World program.
You must ensure that you have gcc compiler installed on your Linux system.
Next thing you would want is to use an extension that allows you to run the C code. Microsoft may prompt you for installing its own extension for C/C++ program but it is complicated to setup and hence I won’t recommend it.
Instead, I suggest using the Code Runner extension. It’s a no-nonsense extension and you can run C and C++ code easily without additional configuration.
Go to the Extensions tab and search for ‘Code Runner’ and install it.
Restart Visual Studio Code. Now, you should be able to run the C code by using one of the following way:
- Using the shortcut Ctrl+Alt+N.
- Press F1 and then select or type Run Code.
- Right click the text editor and the click Run code from context menu.
When you run the program, it is compiled automatically and then run. You can see the output in terminal that is opened at the bottom of the editor. What could be better than this?
Which method do you prefer?
Running a few C programs in Linux command line is okay but using a code editor is much easier and saves time. Won’t you agree?
I let you decide whichever method you want to use.
Like what you read? Please share it with others.
Источник