- Команда MSG – отправить сообщение пользователю.
- Create a Message in Windows Mail From the Command Line
- Create a Message in Windows Live Mail, Windows Mail or Outlook Express from the Command Line
- Using command line arguments for Windows Terminal
- Command line syntax
- Options and commands
- Command line argument examples
- Target a specific window
- Open a new profile instance
- Target a directory
- Multiple tabs
- Multiple panes
- Multiple tabs and panes
- Tab title
- Using application title (Preview)
- Tab color
- Color scheme (Preview)
- Tab focus
- Examples of multiple commands from PowerShell
- Single quoted parameters
- Escaped quotes
- Using start
Команда MSG – отправить сообщение пользователю.
Команда MSG существовала еще в Windows 2000/XP и предназначалась для обмена сообщениями между пользователями вошедшими в систему локально и пользователями терминальных сессий ( подключившихся к удаленному рабочему столу ) . В Windows Vista и более поздних операционных системах семейства Windows команда MSG стала основным стандартным средством обмена сообщениями, поскольку команда net send в данных ОС больше не поддерживается.
Формат командной строки:
Описание параметров командной строки :
пользователь — Имя пользователя.
имя сеанса — Имя сеанса.
ID сеанса — Идентификатор сеанса.
@имя файла — Файл, содержащий список имен пользователей, сеансов или идентификаторов сеансов, которым отправляется сообщение.
* — Отправить сообщение всем сеансам на указанном сервере.
/SERVER:сервер — Сервер (по умолчанию — текущий).
/TIME:секунд — Интервал ожидания подтверждения от получателя.
/V — Отображение информации о выполненных действиях.
/W — Ожидание ответа от пользователя, полезно вместе с /V.
сообщение — Отправляемое сообщение. Если не указано, выдается запрос или принимается ввод из STDIN.
Нынешняя реализация msg.exe прекрасно подходит для обмена сообщениями между сеансами локальных и терминальных пользователей в пределах одной системы, однако, в случаях обмена между разными компьютерами локальной сети, потребуется изменить некоторые настройки безопасности, принятые по умолчанию в операционных системах Windows Vista, 7 и более поздних.
При стандартных настройках, отправка сообщения пользователям удаленных компьютеров не выполняется и сопровождается сообщением:
Ошибка 1722 при получении имен сеанса
Это означает, что на компьютере, где должно приниматься посылаемое сообщение, невозможно получить информацию о вошедших в систему пользователях. Причиной может быть то, что брандмауэр блокирует входящие соединения, недостаточны права пользователя по отношению к удаленной системе, запрет удаленного вызова процедур в параметрах службы сервера терминалов. Как минимум, для обмена сообщениями с использованием команды msg между компьютерами, необходимо иметь учетную запись пользователя, действительную по отношению к удаленной системе и выполнить следующие настройки:
на каждом компьютере, которому будут отправляться сообщения, добавить в раздел реестра HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server параметр AllowRemoteRPC типа REG_DWORD и равный 1 Для изменения настроек можно использовать .reg-файл следующего содержания:
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server]
«AllowRemoteRPC»=dword:00000001
В ОС Windows Vista, Windows 7, 8, 10 ключ реестра AllowRemoteRPC существует, но имеет значение равное 0 , что необходимо исправить. Для применения изменений требуется перезагрузка.
поскольку для обмена сообщениями утилита msg.exe использует протокол SMB (Server Message Block ), на каждом компьютере, которому будут отправляться сообщения, должен быть открыт TCP порт 445
Примеры использования MSG :
msg * /server:Server «Тестовое сообщение » — отправить тестовое сообщение всем пользователям компьютера Server
msg * /server:192.168.0.1 «Тестовое сообщение » — отправить тестовое сообщение всем пользователям компьютера с IP-адресом 192.168.0.1
msg RDP-Tcp#0 /server:TSServer «Тестовое сообщение» — отправить тестовое сообщение пользователю терминальной сессии с именем RDP-Tcp#0 на компьютере TSServer
msg console /server:Windows7 «Тестовое сообщение» — отправить тестовое сообщение текущему локальному пользователю компьютера Windows7
msg console «Тестовое сообщение» — отправка тестового сообщения от пользователя сеанса RDP локальному пользователю. Если эта команда выполняется не пользователем терминальной сессии, то сообщение будет отправлено локальным пользователем самому себе.
Для выполнения команды msg от имени другого пользователя можно воспользоваться утилитой PSExec из пакета PSTools или штатным средством runas.exe
psexec -u otheruser -p otherpass msg * /server:win10 TEST message
runas /user:otheruser «msg * /server:win10 Test message»
Сообщения, отправляемые командой msg локальному пользователю компьютера с операционной системой Windows XP, который отсутствует ( еще не вошел в Windows ) отображаются в окне с приглашением к регистрации в системе и могут быть доступны посторонним.
Create a Message in Windows Mail From the Command Line
Marcus Butt / Getty Images
What could be easier than starting a new message in Windows Live Mail, Windows Mail or Outlook Express? All it takes is a click on the Create Mail button.
But what if you fancy starting a new message from a command prompt, possibly without the main window of Windows Live Mail, Windows Mail or Outlook Express showing, or if you want to create messages programmatically from other applications?
Both can be accomplished with command line arguments. You can create a simple message, but you can also specify default recipients as well as a default subject and message text.
Create a Message in Windows Live Mail, Windows Mail or Outlook Express from the Command Line
To create a new email message in Windows Live Mail, Windows Mail or Outlook Express from the Windows command line:
- For Windows Live Mail:
- Type ‘«C:\Program Files\Windows Live\Mail\wlmail» /mailurl:%‘.
- For Windows Mail:
- Type ‘«C:\Program Files\Windows Mail\WinMail» /mailurl:%‘.
- For Outlook Express:
- Type ‘«C:\Program Files\Outlook Express\msimn» /mailurl:%‘.
- Make sure you do include the inner (double) but leave out the outer (single) quotation marks.
- Hit Enter.
To create a message with default To:, Cc:, Bcc:, Subject and message body fields:
- Type ‘«C:\Program Files\Windows Live\Mail\wlmail» /mailurl:%‘ (Windows Live Mail) ‘«C:\Program Files\Windows Mail\WinMail» /mailurl:%‘ (Windows Mail) or ‘«C:\Program Files\Outlook Express\msimn» /mailurl:‘ (Outlook Express).
- Use the mailto URL encoder to construct a mailto: URL containing the desired default values.
- For a message sent To: «recipient@example.com» by default with a Subject: of «Hello» and a body of «Hi there», the URL would be «mailto:recipient@example.com?subject=Hello&body=Hi%20there«, for example.
- Copy and paste the URL to the command line, appending it immediately after «mailurl:«.
- Enter a quotation mark ‘»‘ between «mailto:» and the email address of the default recipient.
- The full command line using the above example is, using Windows Live Mail, ‘«C:\Program Files\Windows Live\Mail\wlmail» /mailurl:mailto:»recipient@example.com?subject=Hello&body=Hi%20there‘ (again including the inner but not including the outermost quotation marks).
You cannot attach files from the command line or have the message delivered automatically.
Using command line arguments for Windows Terminal
You can use wt.exe to open a new instance of Windows Terminal from the command line. You can also use the execution alias wt instead.
If you built Windows Terminal from the source code on GitHub, you can open that build using wtd.exe or wtd .
Command line syntax
The wt command line accepts two types of values: options and commands. Options are a list of flags and other parameters that can control the behavior of the wt command line as a whole. Commands provide the action, or list of actions separated by semicolons, that should be implemented. If no command is specified, then the command is assumed to be new-tab by default.
To display a help message listing the available command line arguments, enter: wt -h , wt —help , wt -? , or wt /? .
Options and commands
Below is the full list of supported commands and options for the wt command line.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| —help , -h , -? , /? | Displays the help message. |
| —maximized , -M | Launches the terminal maximized. |
| —fullscreen , -F | Launches the terminal as full screen. |
| —focus , -f | Launches the terminal in the focus mode. Can be combined with maximized . |
| —window , -w | Launches the terminal in a specific window. |
| Command | Parameters | Description |
|---|---|---|
| new-tab , nt | —profile, -p profile-name , —startingDirectory, -d starting-directory , commandline , —title , —tabColor | Creates a new tab. |
| split-pane , sp | -H, —horizontal , -V, —vertical , —profile, -p profile-name , —startingDirectory, -d starting-directory , —title , —tabColor , —size, -s size , commandline , -D, —duplicate | Splits a new pane. |
| focus-tab , ft | —target, -t tab-index | Focuses on a specific tab. |
| move-focus , mf | direction | Move focus between panes in the given direction. Accepts one of up , down , left , right . |
When opening Windows Terminal from cmd (Command Prompt), if you want to use your custom «cmd» profile settings, you will need to use the command wt -p cmd . Otherwise, to run your default profile settings, just use wt cmd .
The -D, —duplicate parameter for split-pane is only available in Windows Terminal Preview.
Command line argument examples
Commands may vary slightly depending on which command line you’re using.
Target a specific window
The ability for the —window,-w parameter to accept window names is only available in Windows Terminal Preview.
Below are examples of how to target specific windows using the —window,-w option.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running.
Open a new profile instance
To open a new terminal instance, in this case the command will open the profile named «Ubuntu-18.04», enter:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running.
The -p flag is used to specify the Windows Terminal profile that should be opened. Substitute «Ubuntu-18.04» with the name of any terminal profile that you have installed. This will always open a new window. Windows Terminal is not yet capable of opening new tabs or panes in an existing instance.
Target a directory
To specify the folder that should be used as the starting directory for the console, in this case the d:\ directory, enter:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running.
Multiple tabs
To open a new terminal instance with multiple tabs, enter:
PowerShell uses a semicolon ; to delimit statements. To interpret a semicolon ; as a command delimiter for wt command-line arguments, you need to escape semicolon characters using backticks. PowerShell also has the stop parsing operator (—%), which instructs it to stop interpreting anything after it and just pass it on verbatim.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running.
To open a new terminal instance with multiple tabs, in this case a Command Prompt profile and a PowerShell profile, enter:
PowerShell uses a semicolon ; to delimit statements. To interpret a semicolon ; as a command delimiter for wt command-line arguments, you need to escape semicolon characters using backticks. PowerShell also has the stop parsing operator (—%), which instructs it to stop interpreting anything after it and just pass it on verbatim.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; backslash + semicolon separates commands.
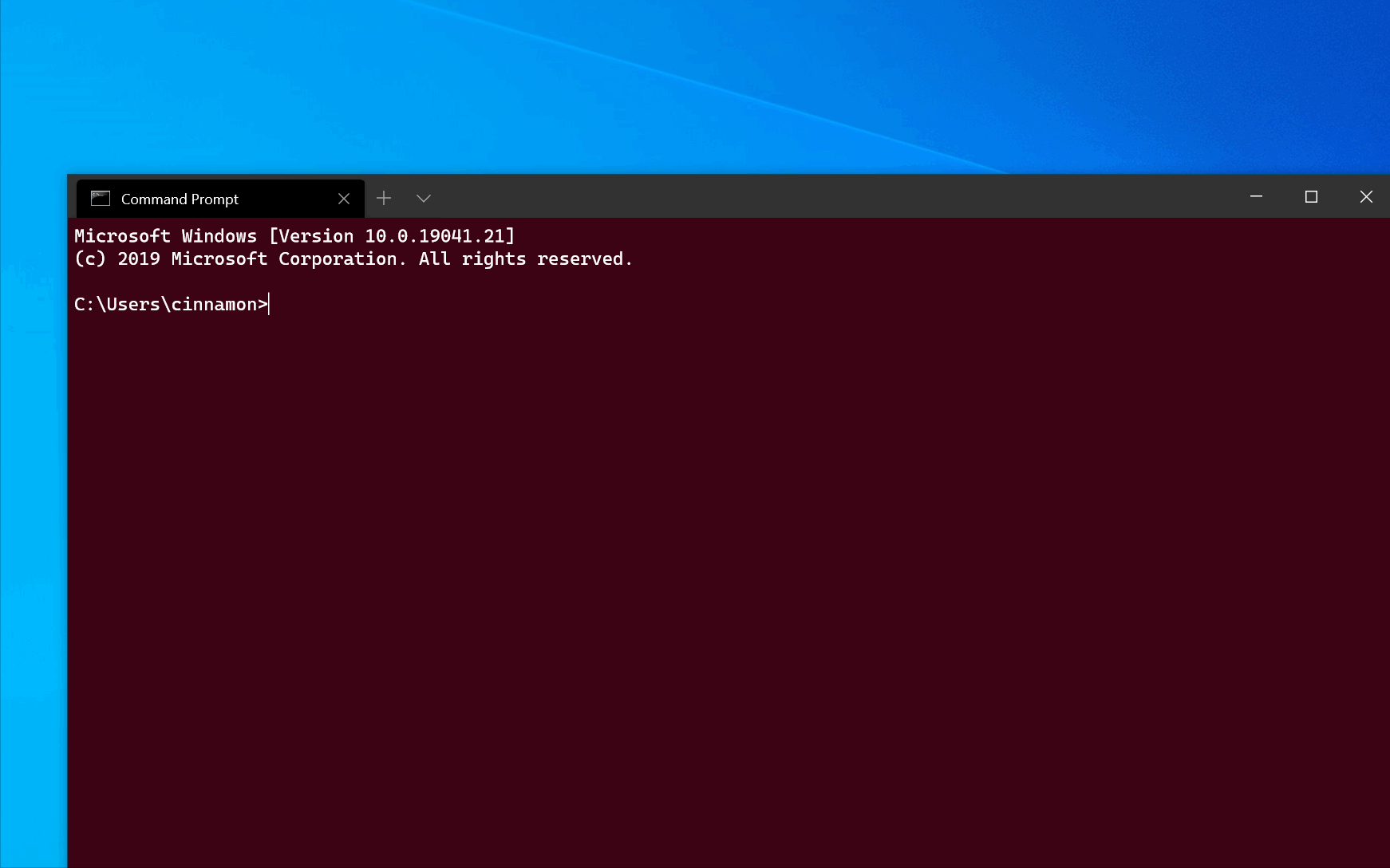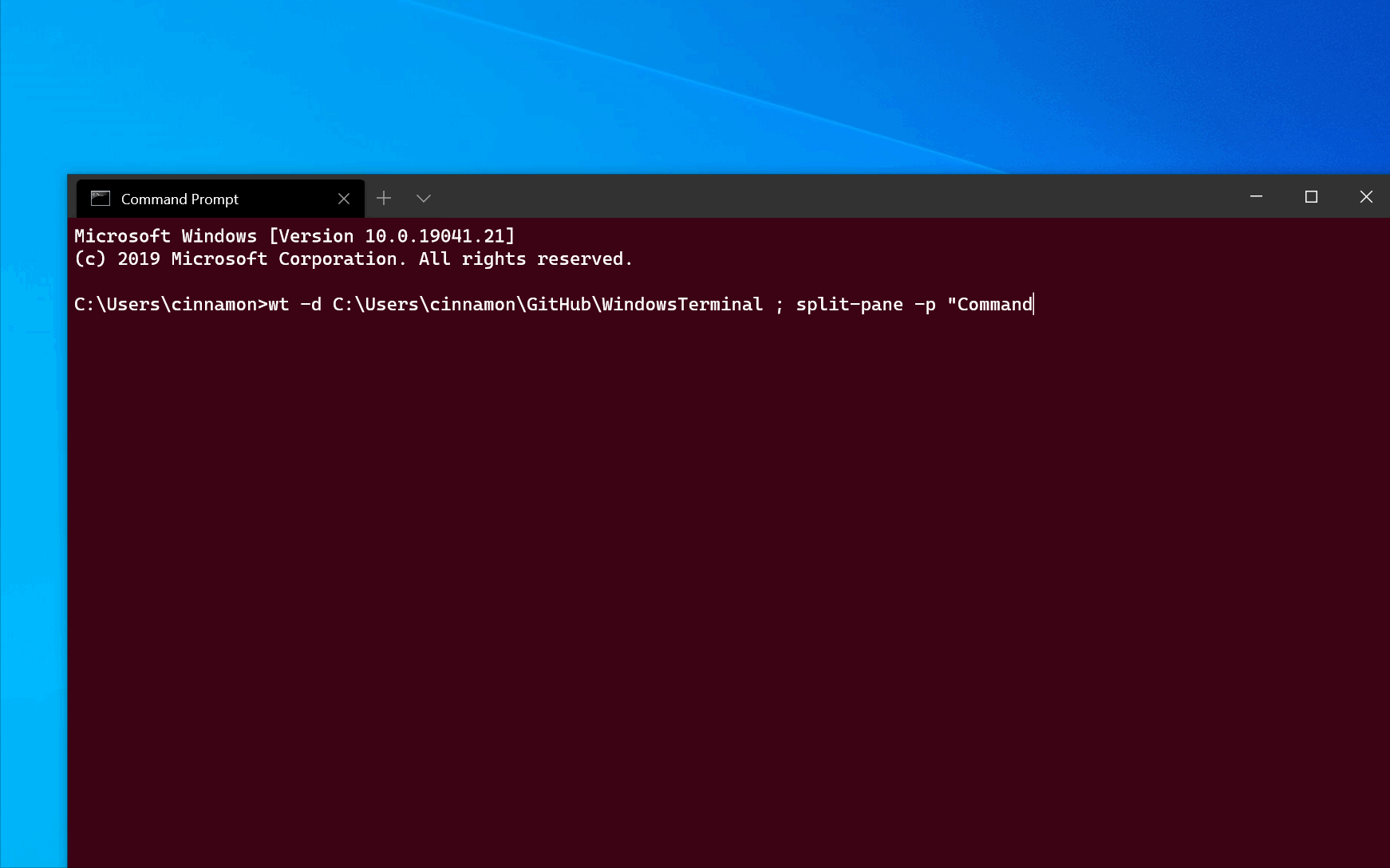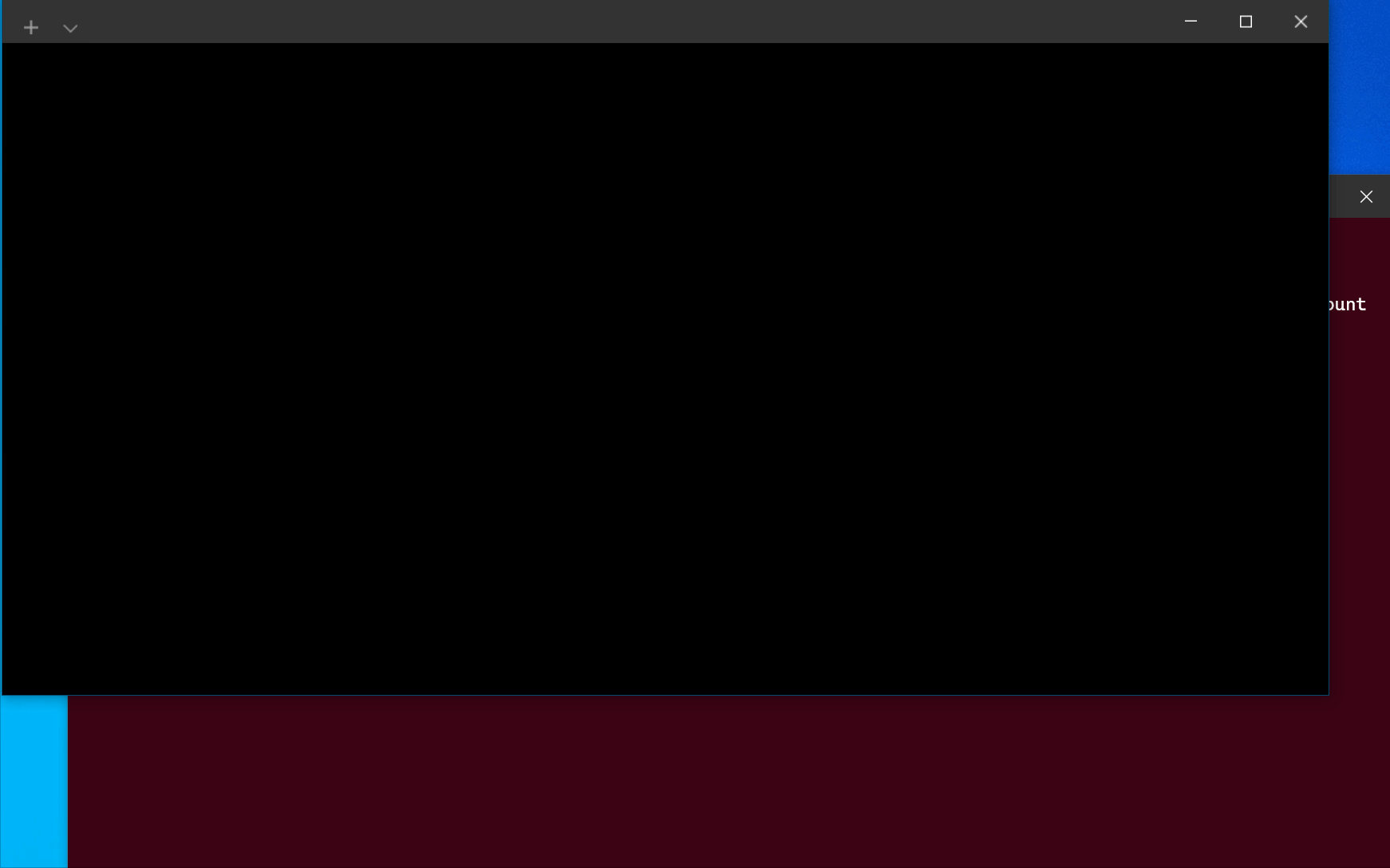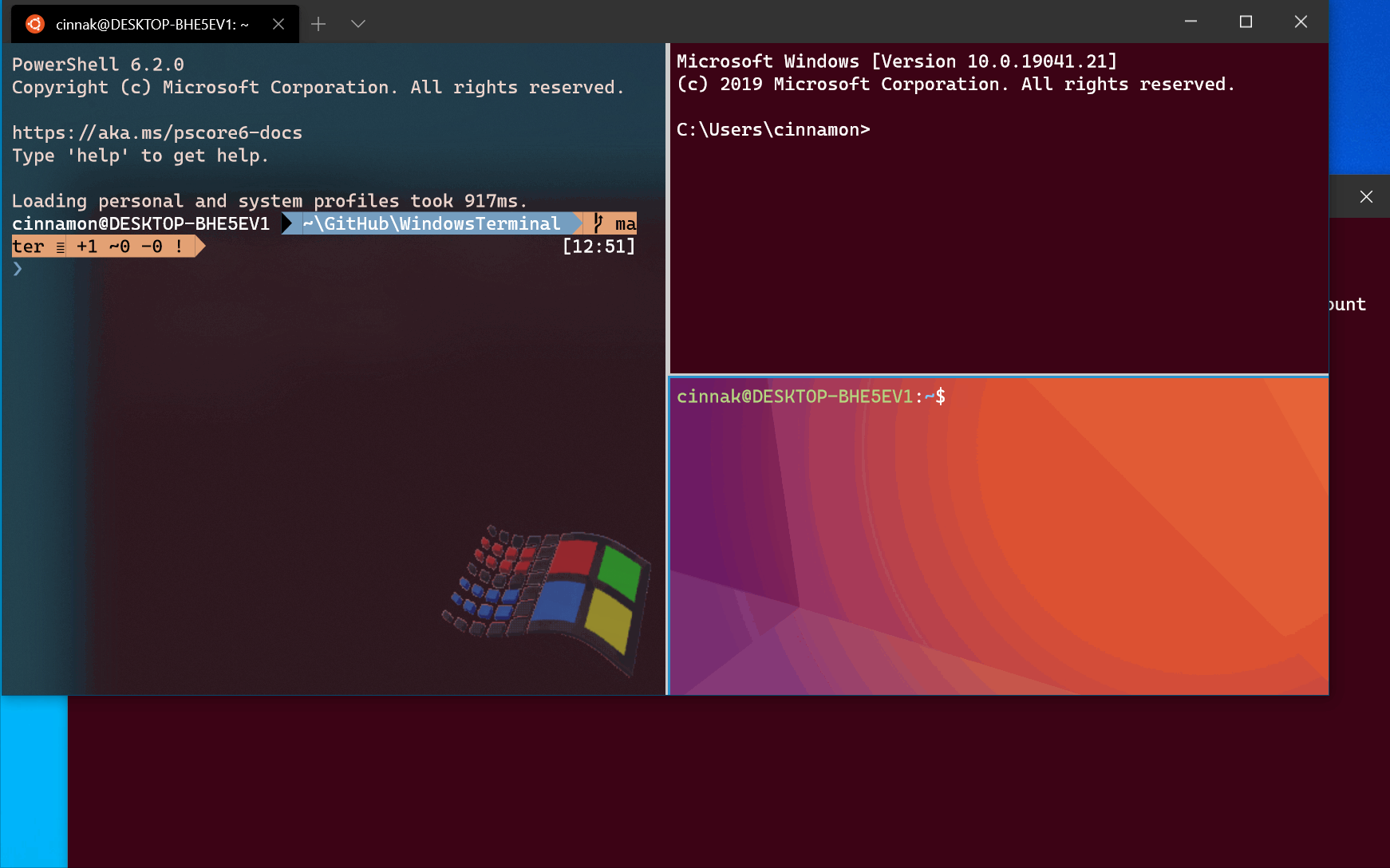
Multiple panes
To open a new terminal instance with one tab containing three panes running a Command Prompt profile, a PowerShell profile, and your default profile running a WSL command line, enter:
PowerShell uses a semicolon ; to delimit statements. To interpret a semicolon ; as a command delimiter for wt command-line arguments, you need to escape semicolon characters using backticks. PowerShell also has the stop parsing operator (—%), which instructs it to stop interpreting anything after it and just pass it on verbatim.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; backslash + semicolon separates commands.
The -H flag (or —horizontal ) indicates that you would like the panes to be split horizontally. The -V flag (or —vertical ) indicates that you would like the panes split vertically.
Multiple tabs and panes
The new-tab and split-pane commands can be sequenced to get multiple tabs, each with split panes. To open a new terminal instance with two tabs, each with two panes running a Command Prompt and a WSL command line, with each tab in a different directory, enter:
PowerShell uses a semicolon ; to delimit statements. To interpret a semicolon ; as a command delimiter for wt command-line arguments, you need to escape semicolon characters using backticks. PowerShell also has the stop parsing operator (—%), which instructs it to stop interpreting anything after it and just pass it on verbatim.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; backslash + semicolon separates commands. Note to specify a Windows directory as the starting directory for wsl.exe that two backslashes \\ are required.
Tab title
To open a new terminal instance with custom tab titles, use the —title argument. To set the title of each tab when opening two tabs, enter:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; forward-slash + semicolon separates commands.
Using application title (Preview)
To open a new terminal instance allowing applications within it to set the tab title by sending title change messages, use the —useApplicationTitle flag. To suppress these messages, use the —suppressApplicationTitle flag. If none of these flags are provided, the behavior is inherited from the profile’s settings. To open a tab with title tabname that will not be overridden by the application, enter:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; backslash + semicolon separates commands.
This feature is only available in Windows Terminal Preview.
Tab color
To open a new terminal instance with custom tab colors, use the —tabColor argument. This argument overrides the value defined in the profile, but can be overridden as well using the tab color picker. In the following example, a new terminal is created with two tabs of different colors:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and \; separates commands.
When —tabColor is set for a tab, it is associated with the first pane of this tab. Hence in a tab with multiple panes, the color will be applied only if the first pane is in focus. To set the tab color for additional panes, you will need to add the —tabColor parameter to the split-pane subcommand as well. In the example below, a tab with two panes is created with tab colors specified for each pane:
Color scheme (Preview)
To open a new terminal instance with a specific color scheme (instead of the colorScheme set in the profile), use the —colorScheme argument. This argument overrides the value defined in the profile.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and \; separates commands.
This feature is only available in Windows Terminal Preview.
Tab focus
To open a new terminal instance with a specific tab in focus, use the -t flag (or —target ), along with the tab-index number. To open your default profile in the first tab and the «Ubuntu-18.04» profile focused in the second tab ( -t 1 ), enter:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; backslash + semicolon separates commands.
Examples of multiple commands from PowerShell
Windows Terminal uses the semicolon character ; as a delimiter for separating commands in the wt command line. Unfortunately, PowerShell also uses ; as a command separator. To work around this, you can use the following tricks to run multiple wt commands from PowerShell. In all the following examples, a new terminal window is created with three panes — one running Command Prompt, one with PowerShell, and the last one running WSL.
The following examples use the Start-Process command to run wt . For more information on why the terminal uses Start-Process , see Using start below.
Single quoted parameters
In this example, the wt parameters are wrapped in single quotes ( ‘ ). This syntax is useful if nothing is being calculated.
Escaped quotes
When passing a value contained in a variable to the wt command line, use the following syntax:
Note the usage of ` to escape the double-quotes ( » ) around «Windows PowerShell» in the -p parameter to the split-pane parameter.
Using start
All the above examples explicitly used start to launch the terminal.
The following examples do not use start to run the command line. Instead, there are two other methods of escaping the command line:
- Only escaping the semicolons so that PowerShell will ignore them and pass them straight to wt .
- Using —% , so PowerShell will treat the rest of the command line as arguments to the application.
In both of these examples, the newly created Windows Terminal window will create the window by correctly parsing all the provided command-line arguments.
However, these methods are not recommended currently, as PowerShell will wait for the newly-created terminal window to be closed before returning control to PowerShell. By default, PowerShell will always wait for Windows Store applications (like Windows Terminal) to close before returning to the prompt. Note that this is different than the behavior of Command Prompt, which will return to the prompt immediately.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Heinz-Tschabitsche-c6d01096ad5f47b8800846cebc7d99b1.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/large-cursor-over-speech-bubble-on-computer-monitor-475158513-57bde1ca3df78ca3c0437610-5c866be646e0fb00017b312e.jpg)