- Computer Basics —
- Understanding Operating Systems
- Computer Basics: Understanding Operating Systems
- Lesson 8: Understanding Operating Systems
- What is an operating system?
- The operating system’s job
- Types of operating systems
- Microsoft Windows
- macOS
- Linux
- Operating systems for mobile devices
- Five Common Operating Systems
- Related
- What Operating Systems Do
- Microsoft Windows
- Apple iOS
- Google’s Android OS
- Apple macOS
- Linux Operating System
- What is Operating System? Types of OS, Features and Examples
- What is an Operating System?
- History Of OS
- Examples of Operating System with Market Share
- Types of Operating System (OS)
- Batch Operating System
- Multi-Tasking/Time-sharing Operating systems
- Real time OS
- Distributed Operating System
- Network Operating System
- Mobile OS
- Functions of Operating System
- Features of Operating System (OS)
- Advantage of using Operating System
- Disadvantages of using Operating System
- What is a Kernel?
- Features of Kennel
- Types of Kernels
Computer Basics —
Understanding Operating Systems
Computer Basics: Understanding Operating Systems
Lesson 8: Understanding Operating Systems
What is an operating system?
An operating system is the most important software that runs on a computer. It manages the computer’s memory and processes, as well as all of its software and hardware. It also allows you to communicate with the computer without knowing how to speak the computer’s language. Without an operating system, a computer is useless.
Watch the video below to learn more about operating systems.
Looking for the old version of this video? You can still view it here.
The operating system’s job
Your computer’s operating system (OS) manages all of the software and hardware on the computer. Most of the time, there are several different computer programs running at the same time, and they all need to access your computer’s central processing unit (CPU), memory, and storage. The operating system coordinates all of this to make sure each program gets what it needs.
Types of operating systems
Operating systems usually come pre-loaded on any computer you buy. Most people use the operating system that comes with their computer, but it’s possible to upgrade or even change operating systems. The three most common operating systems for personal computers are Microsoft Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Modern operating systems use a graphical user interface, or GUI (pronounced gooey). A GUI lets you use your mouse to click icons, buttons, and menus, and everything is clearly displayed on the screen using a combination of graphics and text.
Each operating system’s GUI has a different look and feel, so if you switch to a different operating system it may seem unfamiliar at first. However, modern operating systems are designed to be easy to use, and most of the basic principles are the same.
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft created the Windows operating system in the mid-1980s. There have been many different versions of Windows, but the most recent ones are Windows 10 (released in 2015), Windows 8 (2012), Windows 7 (2009), and Windows Vista (2007). Windows comes pre-loaded on most new PCs, which helps to make it the most popular operating system in the world.
Check out our tutorials on Windows Basics and specific Windows versions for more information.
macOS
macOS (previously called OS X) is a line of operating systems created by Apple. It comes preloaded on all Macintosh computers, or Macs. Some of the specific versions include Mojave (released in 2018), High Sierra (2017), and Sierra (2016).
According to StatCounter Global Stats, macOS users account for less than 10% of global operating systems—much lower than the percentage of Windows users (more than 80%). One reason for this is that Apple computers tend to be more expensive. However, many people do prefer the look and feel of macOS over Windows.
Check out our macOS Basics tutorial for more information.
Linux
Linux (pronounced LINN-ux) is a family of open-source operating systems, which means they can be modified and distributed by anyone around the world. This is different from proprietary software like Windows, which can only be modified by the company that owns it. The advantages of Linux are that it is free, and there are many different distributions—or versions—you can choose from.
According to StatCounter Global Stats, Linux users account for less than 2% of global operating systems. However, most servers run Linux because it’s relatively easy to customize.
To learn more about different distributions of Linux, visit the Ubuntu, Linux Mint, and Fedora websites, or refer to our Linux Resources. For a more comprehensive list, you can visit MakeUseOf’s list of The Best Linux Distributions.
Operating systems for mobile devices
The operating systems we’ve been talking about so far were designed to run on desktop and laptop computers. Mobile devices such as phones, tablet computers, and MP3 players are different from desktop and laptop computers, so they run operating systems that are designed specifically for mobile devices. Examples of mobile operating systems include Apple iOS and Google Android . In the screenshot below, you can see iOS running on an iPad.
Operating systems for mobile devices generally aren’t as fully featured as those made for desktop and laptop computers, and they aren’t able to run all of the same software. However, you can still do a lot of things with them, like watch movies, browse the Web, manage your calendar, and play games.
To learn more about mobile operating systems, check out our Mobile Devices tutorials.
Five Common Operating Systems
Related
Whether it’s a desktop or laptop computer, a smartphone or a video game system, every modern computer needs an operating system. That’s the core software on the computer that sits between application software and the hardware, distributing memory and computing resources to apps, managing files and enforcing security rules.
Five of the most common operating systems are Microsoft Windows, Apple macOS, Linux, Android and Apple’s iOS.
What Operating Systems Do
Operating systems define how a computer stores files, switches between different applications, manages memory, keeps itself secure, and interacts with peripherals like printers and cameras. Different operating systems take different approaches to all of these, which is why you normally can’t run a Windows program on a Macintosh computer and why permissions look different on an Android phone than on an iPhone.
Some operating systems are designed by groups of people around the world, like the open source, freely available operating system Linux, while others are commercial products made by one company, such as Microsoft’s Windows and Apple’s macOS.
Different operating systems run on different types of hardware and are designed for different types of applications. For example, iOS is designed for iPhones and iPad tablets, while Mac desktops and laptops use macOS. Your computer or smartphone comes equipped with an OS, but you can install another one in some cases.
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows has existed in one form or another since 1985, and it remains the most popular operating system for home and office computers. Its latest versions, including Windows 10, are also used on some tablets, and the OS is used on some web and number-crunching server computers as well. Computers from a wide variety of manufacturers can use Windows.
Initial versions of Windows worked with an earlier Microsoft operating system called MS-DOS, providing a modern graphical interface on top of DOS’s traditional text-based commands. Signature features of Microsoft Windows’s user interface include windows themselves – rectangle-shaped, on-panel screens that represent individual applications. The Windows Start menu has helped generations of users find programs and files on their devices.
Efforts to use versions of the Windows OS for smartphones have been less successful.
Apple iOS
Apple’s iOS is one of the most popular smartphone operating systems, second only to Android. It runs on Apple hardware, including iPhones, iPad tablets and iPod Touch media players.
Signature features of iOS include the App Store where users buy apps and download free software, an emphasis on security including strong encryption to limit what unauthorized users can extract from the phone, and a simple, streamlined interface with minimal hardware buttons.
Google’s Android OS
Android is the most popular operating system in the world judging by the number of devices installed. Largely developed by Google, it’s chiefly used on smartphones and tablets. Unlike iOS, it can be used on devices made by a variety of different manufacturers, and those makers can tweak parts of its interface to suit their own needs.
Users can download custom versions of the operating system because large portions of it are open source, meaning anyone can legally modify it and publish their own. However, most people prefer to stick with the version that comes on their devices.
Android, like iOS, comes with an application and media store called the Play Store built by Google. Some phone manufacturers and other organizations also offer their own stores to install software and media.
Apple macOS
Apple’s macOS, successor to the popular OS X operating system, runs on Apple laptops and desktops. Based in part on the historic family of Unix operating systems dating back to research in the 1960s at AT&T’s Bell Labs, macOS shares some features with other Unix-related operating systems including Linux. While the graphical interfaces are different, many of the underlying programming interfaces and command line features are the same.
Signature elements of macOS include the dock used to find programs and frequently used files, unique keyboard keys including the Command key, and the stoplight-colored buttons used to resize open program windows. MacOS is known for its user-friendly features, which include Siri, a natural-voice personal assistant, and FaceTime, Apple’s video-calling application.
Linux Operating System
Unlike many other operating systems, development on Linux isn’t led by any one company. The operating system was created by Finnish programmer Linus Torvalds in 1991. Nowadays, programmers from all over the world collaborate on its open source code and submit tweaks to the central kernel software and other programs.
A wide assortment of commercial and open source software is available for Linux, and various Linux distributions provide custom user interfaces and tools for installing software onto machines running the operating system. A favorite of many programmers, Linux is widely used on corporate and scientific servers, including cloud computing environments. Linux can be run on a wide variety of hardware and is available free of charge over the internet.
Steven Melendez is an independent journalist with a background in technology and business. He has written for a variety of business publications including Fast Company, the Wall Street Journal, Innovation Leader and Business BVI. He was awarded the Knight Foundation scholarship to Northwestern University’s Medill School of Journalism.
What is Operating System? Types of OS, Features and Examples
What is an Operating System?
An Operating System (OS) is a software that acts as an interface between computer hardware components and the user. Every computer system must have at least one operating system to run other programs. Applications like Browsers, MS Office, Notepad Games, etc., need some environment to run and perform its tasks.
The OS helps you to communicate with the computer without knowing how to speak the computer’s language. It is not possible for the user to use any computer or mobile device without having an operating system. 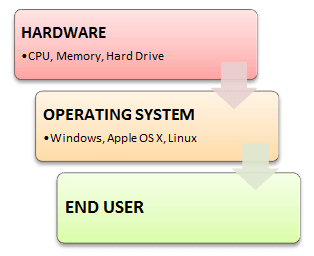
History Of OS
- Operating systems were first developed in the late 1950s to manage tape storage
- The General Motors Research Lab implemented the first OS in the early 1950s for their IBM 701
- In the mid-1960s, operating systems started to use disks
- In the late 1960s, the first version of the Unix OS was developed
- The first OS built by Microsoft was DOS. It was built in 1981 by purchasing the 86-DOS software from a Seattle company
- The present-day popular OS Windows first came to existence in 1985 when a GUI was created and paired with MS-DOS.
Examples of Operating System with Market Share
Following are the examples of Operating System with the latest Market Share
| OS Name | Share |
| Windows | 40.34 |
| Android | 37.95 |
| iOS | 15.44 |
| Mac OS | 4.34 |
| Linux | 0.95 |
| Chrome OS | 0.14 |
| Windows Phone OS | 0.06 |
Types of Operating System (OS)
Following are the popular types of Operating System:
- Batch Operating System
- Multitasking/Time Sharing OS
- Multiprocessing OS
- Real Time OS
- Distributed OS
- Network OS
- Mobile OS
Batch Operating System
Some computer processes are very lengthy and time-consuming. To speed the same process, a job with a similar type of needs are batched together and run as a group.
The user of a batch operating system never directly interacts with the computer. In this type of OS, every user prepares his or her job on an offline device like a punch card and submit it to the computer operator.
Multi-Tasking/Time-sharing Operating systems
Time-sharing operating system enables people located at a different terminal(shell) to use a single computer system at the same time. The processor time (CPU) which is shared among multiple users is termed as time sharing.
Real time OS
A real time operating system time interval to process and respond to inputs is very small. Examples: Military Software Systems, Space Software Systems are the Real time OS example.
Distributed Operating System
Distributed systems use many processors located in different machines to provide very fast computation to its users.
Network Operating System
Network Operating System runs on a server. It provides the capability to serve to manage data, user, groups, security, application, and other networking functions.
Mobile OS
Mobile operating systems are those OS which is especially that are designed to power smartphones, tablets, and wearables devices.
Some most famous mobile operating systems are Android and iOS, but others include BlackBerry, Web, and watchOS.
Functions of Operating System
Below are the main functions of Operating System: 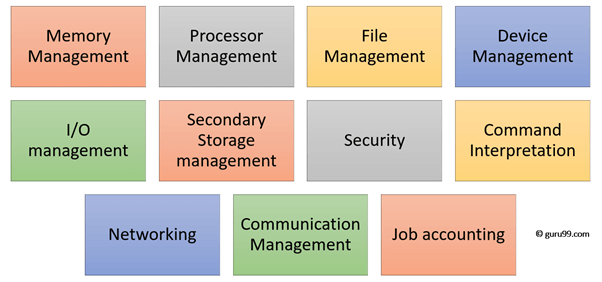
In an operating system software performs each of the function:
- Process management:- Process management helps OS to create and delete processes. It also provides mechanisms for synchronization and communication among processes.
- Memory management:- Memory management module performs the task of allocation and de-allocation of memory space to programs in need of this resources.
- File management:- It manages all the file-related activities such as organization storage, retrieval, naming, sharing, and protection of files.
- Device Management: Device management keeps tracks of all devices. This module also responsible for this task is known as the I/O controller. It also performs the task of allocation and de-allocation of the devices.
- I/O System Management: One of the main objects of any OS is to hide the peculiarities of that hardware devices from the user.
- Secondary-Storage Management: Systems have several levels of storage which includes primary storage, secondary storage, and cache storage. Instructions and data must be stored in primary storage or cache so that a running program can reference it.
- Security:- Security module protects the data and information of a computer system against malware threat and authorized access.
- Command interpretation: This module is interpreting commands given by the and acting system resources to process that commands.
- Networking: A distributed system is a group of processors which do not share memory, hardware devices, or a clock. The processors communicate with one another through the network.
- Job accounting: Keeping track of time & resource used by various job and users.
- Communication management: Coordination and assignment of compilers, interpreters, and another software resource of the various users of the computer systems.
Features of Operating System (OS)
Here is a list important features of OS:
- Protected and supervisor mode
- Allows disk access and file systems Device drivers Networking Security
- Program Execution
- Memory management Virtual Memory Multitasking
- Handling I/O operations
- Manipulation of the file system
- Error Detection and handling
- Resource allocation
- Information and Resource Protection

Advantage of using Operating System
- Allows you to hide details of hardware by creating an abstraction
- Easy to use with a GUI
- Offers an environment in which a user may execute programs/applications
- The operating system must make sure that the computer system convenient to use
- Operating System acts as an intermediary among applications and the hardware components
- It provides the computer system resources with easy to use format
- Acts as an intermediator between all hardware’s and software’s of the system
Disadvantages of using Operating System
- If any issue occurs in OS, you may lose all the contents which have been stored in your system
- Operating system’s software is quite expensive for small size organization which adds burden on them. Example Windows
- It is never entirely secure as a threat can occur at any time
What is a Kernel?
The kernel is the central component of a computer operating systems. The only job performed by the kernel is to the manage the communication between the software and the hardware. A Kernel is at the nucleus of a computer. It makes the communication between the hardware and software possible. While the Kernel is the innermost part of an operating system, a shell is the outermost one.
Features of Kennel
- Low-level scheduling of processes
- Inter-process communication
- Process synchronization
- Context switching
Types of Kernels
There are many types of kernels that exists, but among them, the two most popular kernels are:
1.Monolithic
A monolithic kernel is a single code or block of the program. It provides all the required services offered by the operating system. It is a simplistic design which creates a distinct communication layer between the hardware and software.
2. Microkernels
Microkernel manages all system resources. In this type of kernel, services are implemented in different address space. The user services are stored in user address space, and kernel services are stored under kernel address space. So, it helps to reduce the size of both the kernel and operating system.