- Rand/eng works
- Compiling and booting Linux headers
- Building
- Installing
- Enabling
- Altogether
- Компиляция программ Linux
- Подготовка системы
- Как выполняется компиляция?
- Компиляция программ Linux
- Получение исходников
- Настройка configure
- Сборка программы
- Выводы
- How To Compiling C Program And Creating Executable File Under a Linux / UNIX / *BSD
- Make Sure Compiler Is Installed On a Unix-like System
- Syntax
- Writing Your First C Program Under a Linux / UNIX-like system
- How Do I Compile My C Program?
Rand/eng works
Compiling and booting Linux headers
Although relatively straightforward, compiling and selecting the Linux headers is too manual and is only partially explained at several different documents in the codebase. This entry provides some guidelines and also scripts to automate a bit the process. Find the complete script at the bottom.
Building
First of all, move to the list of kernel sources. Browse through it to find the desired version of the headers. You may download the sources and uncompress them into the disk. In this sample script the kernel 4.14.151 is used.
Have a look at the Documentation/process/changes.rst file to understand the expected versions of the third-party libraries required for the compilation. Follow the process manually, then head to Documentation/admin-guide/README.rst .
First, the configuration must be defined. In this example we don’t tailor anything, so it will take a considerable amount of space (not being accurate, you should probably make sure you have 10GB+ of available disk).
It is now time to compile the headers and the kernel modules. The first command will prompt a lot of questions. After that, both commands will take a good amount of time to finish. In the example we are dedicating the full computing power (all the CPUs) to speed up the building process.
Installing
After the compilation it is now time to install the headers in the system and make them available for use. You may find issues with configurations such as the locales. Just fix it and retry as needed.
Enabling
After the installation, the system must know that this kernel is available for booting.
If you would wish to select this version of the kernel for the next boot, you can either:
- Enable the GRUB menu and select it manually
- Modify manually the configuration flags under etc/default/grub , then set the flags as desired. For instance, set something like GRUB_DEFAULT=”Advanced options for Ubuntu>Ubuntu, with Linux 4.14.151”
- Use some tool like grub-customizer. This one is handy when your VM is not able to show the GRUB menu. When running it, move to the “General settings” tab, then choose “default entry > predefined” and pick the specific version from the list
The latter option can be installed and run as follows:
Altogether
All the script put together, for convenience. Note that this works for building kernel 4.14.151 on an Ubuntu 16.04.4 LTS.
Technical guides, publications and snippets for easy deployment and development
Источник
Компиляция программ Linux
Все программы для компьютера представляют собой набор команд процессора, которые состоят из определенного набора бит. Этих команд несколько сотен и с помощью них выполняются все действия на вашем компьютере. Но писать программы непосредственно с помощью этих команд сложно. Поэтому были придуманы различные языки программирования, которые проще для восприятия человеку.
Для подготовки программы к выполнению, специальная программа собирает ее из исходного кода на языке программирования в машинный код — команды процессора. Этот процесс называется компиляция. Linux — это свободное программное обеспечение, а поэтому исходные коды программ доступны всем желающим. Если программы нет в репозитории или вы хотите сделать что-то нестандартное, то вы можете выполнить компиляцию программы.
В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как выполняется компиляция программ Linux, как происходит процесс компиляции, а также рассмотрим насколько гибко вы сможете все настроить.
Подготовка системы
Мы будем компилировать программы, написанные на Си или С++, так как это наиболее используемый язык для программ, которые требуют компиляции. Мы уже немного рассматривали эту тему в статье установка из tar.gz в Linux, но та статья ориентирована больше на новичков, которым нужно не столько разобраться, сколько получить готовую программу.
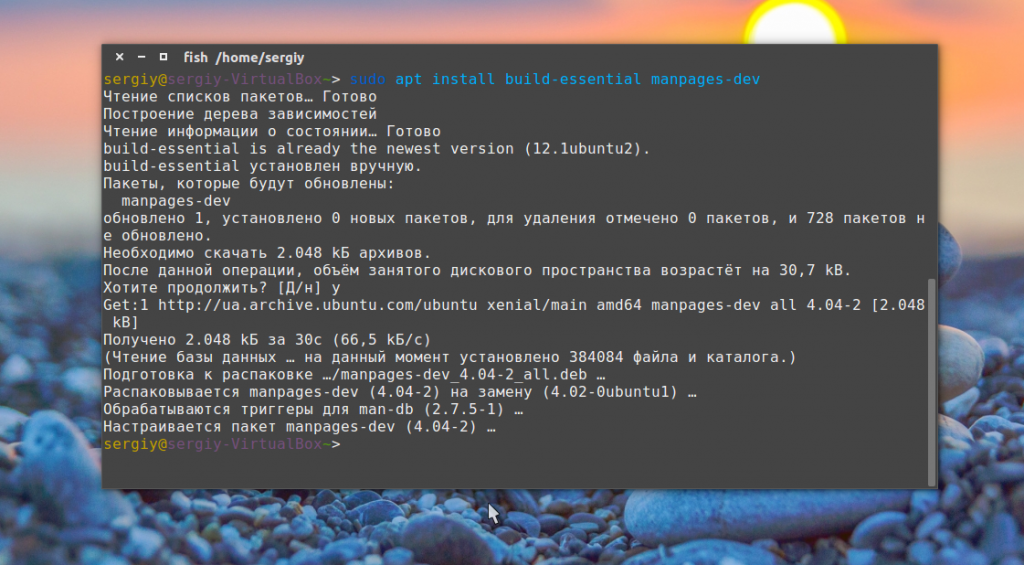
В этой же статье тема рассмотрена более детально. Как вы понимаете, для превращения исходного кода в команды процессора нужно специальное программное обеспечение. Мы будем использовать компилятор GCC. Для установки его и всех необходимых инструментов в Ubuntu выполните:
sudo apt install build-essential manpages-dev git automake autoconf
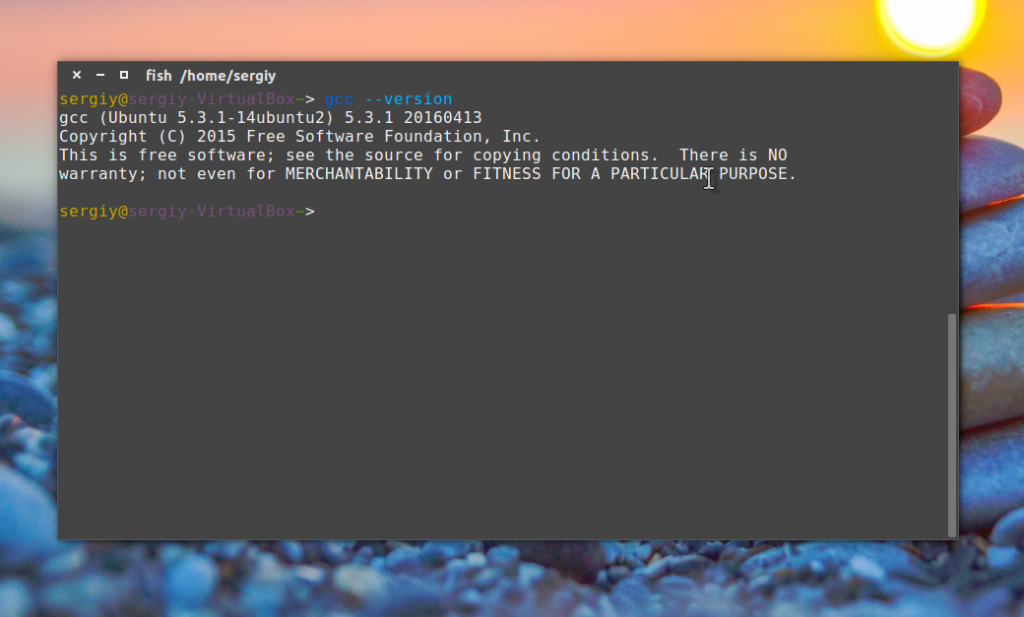
Затем вы можете проверить правильность установки и версию компилятора:
Но перед тем как переходить к самой компиляции программ рассмотрим более подробно составляющие этого процесса.
Как выполняется компиляция?
Компиляция программы Linux — это довольно сложный процесс. Все еще сложнее, потому что код программы содержится не в одном файле и даже не во всех файлах ее исходников. Каждая программа использует множество системных библиотек, которые содержат стандартные функции. К тому же один и тот же код должен работать в различных системах, содержащих различные версии библиотек.
На первом этапе, еще до того как начнется непосредственно компиляция, специальный инструмент должен проверить совместима ли ваша система с программой, а также есть ли все необходимые библиотеки. Если чего-либо нет, то будет выдана ошибка и вам придется устранить проблему.
Дальше идет синтаксический анализ и преобразование исходного кода в объектный код, без этого этапа можно было бы и обойтись, но это необходимо, чтобы компилятор мог выполнить различные оптимизации, сделать размер конечной программы меньше, а команды процессора эффективнее.
Затем все объектные файлы собираются в одну программу, связываются с системными библиотеками. После завершения этого этапа программу остается только установить в файловую систему и все. Вот такие основные фазы компиляции программы, а теперь перейдем ближе к практике.
Компиляция программ Linux
Первое что нам понадобиться — это исходники самой программы. В этом примере мы будем собирать самую последнюю версию vim. Это вполне нейтральная программа, достаточно простая и нужная всем, поэтому она отлично подойдет для примера.
Получение исходников
Первое что нам понадобиться, это исходные коды программы, которые можно взять на GitHub. Вы можете найти исходники для большинства программ Linux на GitHub. Кроме того, там же есть инструкции по сборке:
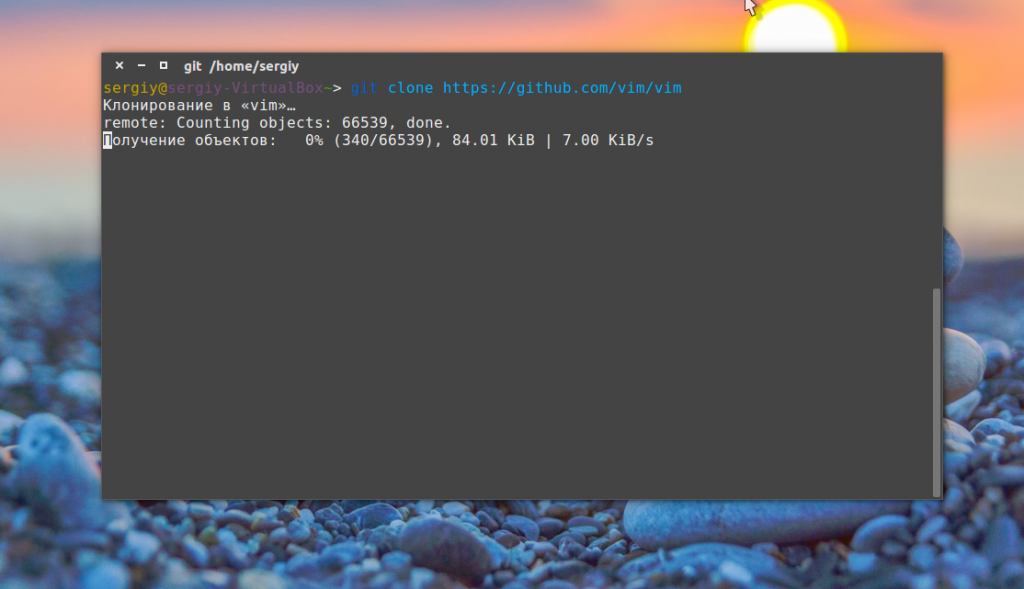
Давайте загрузим сами исходники нашей программы с помощью утилиты git:
git clone https://github.com/vim/vim
Также, можно было скачать архив на сайте, и затем распаковать его в нужную папку, но так будет удобнее. Утилита создаст папку с именем программы, нам нужно сделать ее рабочей:
Настройка configure
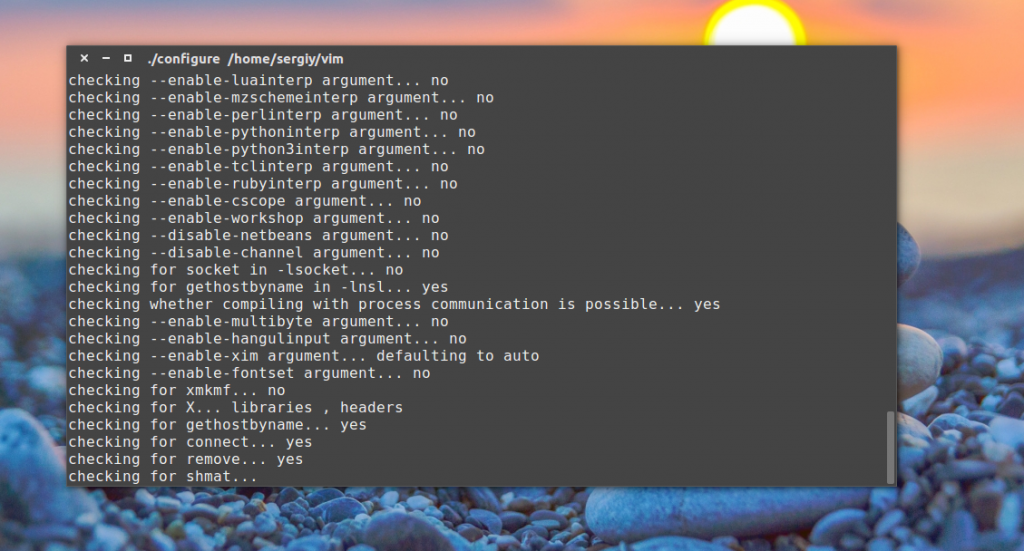
Дальше нам нужно запустить скрипт, который проверит нашу программу на совместимость с системой и настроит параметры компиляции. Он называется configure и поставляется разработчиками программы вместе с исходниками. Весь процесс компиляции описан в файле Makefile, его будет создавать эта утилита.
Если configure нет в папке с исходниками, вы можете попытаться выполнить такие скрипты чтобы его создать:
Также для создания этого скрипта можно воспользоваться утилитой automake:
aclocal
autoheader
automake —gnu —add-missing —copy —foreign
autoconf -f -Wall
Утилита automake и другие из ее набора генерируют необходимые файлы на основе файла Mackefile.am. Этот файл обязательно есть в большинстве проектов.
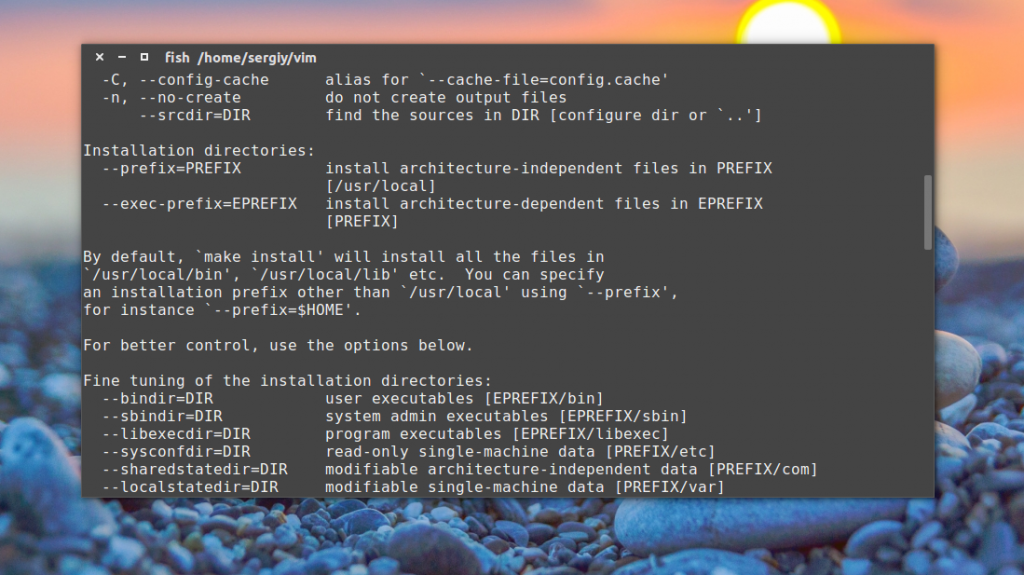
После того как вы получили configure мы можем переходить к настройке. Одним из огромных плюсов ручной сборки программ есть то, что вы можете сами выбрать с какими опциями собирать программу, где она будет размещена и какие дополнительные возможности стоит включить. Все это настраивается с помощью configure. Полный набор опций можно посмотреть, выполнив:
Рассмотрим наиболее часто используемые, стандартные для всех программ опции:
- —prefix=PREFIX — папка для установки программы, вместо /, например, может быть /usr/local/, тогда все файлы будут распространены не по основной файловой системе, а в /usr/local;
- —bindir=DIR — папка для размещения исполняемых файлов, должна находится в PREFIX;
- —libdir=DIR — папка для размещения и поиска библиотек по умолчанию, тоже в PREFIX;
- —includedir=DIR — папка для размещения man страниц;
- —disable-возможность — отключить указанную возможность;
- —enable-возможность — включить возможность;
- —with-библиотека — подобно enable активирует указанную библиотеку или заголовочный файл;
- —without-библиотека — подобное disable отключает использование библиотеки.
Вы можете выполнить configure без опций, чтобы использовать значения по умолчанию, но также можете вручную указать нужные пути. В нашем случае ./configure есть, и мы можем его использовать:
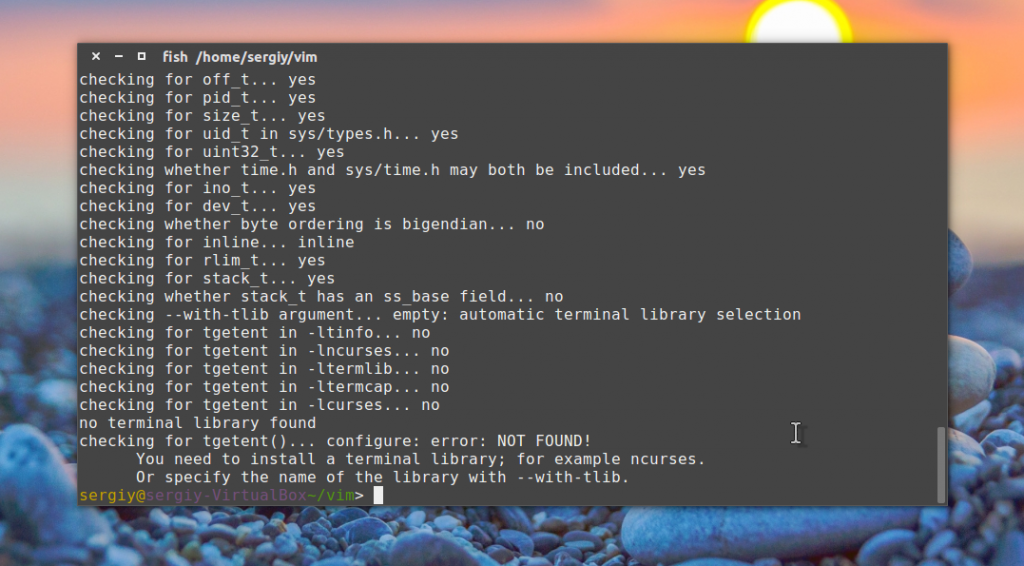
Во время настройки утилита будет проверять, есть ли все необходимые библиотеки в системе, и если нет, вам придется их установить или отключить эту функцию, если это возможно. Например, может возникнуть такая ошибка: no terminal library found checking for tgetent(). configure: error: NOT FOUND!
В таком случае нам необходимо установить требуемую библиотеку. Например, программа предлагает ncurses, поэтому ставим:
sudo apt install libncurces-dev
Приставка lib всегда добавляется перед библиотеками, а -dev — означает, что нам нужна библиотека со всеми заголовочными файлами. После удовлетворения всех зависимостей настройка пройдет успешно.
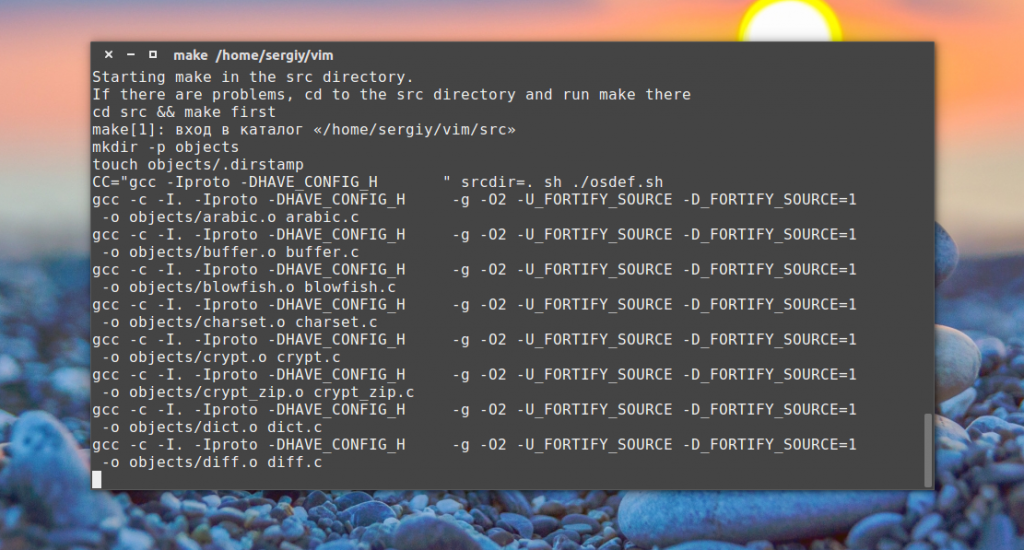
Сборка программы
Когда настройка будет завершена и Makefile будет готов, вы сможете перейти непосредственно к сборке программы. На этом этапе выполняется непосредственно преобразование исходного кода в машинный. Утилита make на основе Makefile сделает все необходимые действия:
Дальше осталось установить саму программу, если вы использовали опцию prefix, чтобы не устанавливать программу в основную файловую систему, то можно применить стандартную опцию make:
После этого программа будет установлена в указанную вами папку, и вы сможете ее использовать. Но более правильный путь — создавать пакет для установки программы, это делается с помощью утилиты checkinstall, она позволяет создавать как deb, так и rpm пакеты, поэтому может использоваться не только в Ubuntu. Вместо make install выполните:
Затем просто установите получившийся пакет с помощью dpkg:
sudo dpkg install vim.deb
После этого сборка программы полностью завершена и установлена, так что вы можете переходить к полноценному использованию.
Если вы устанавливали программу с помощью make install, то удалить ее можно выполнив в той же папке обратную команду:
sudo make uninstall
Команда удалит все файлы, которые были скопированы в файловую систему.
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели, как выполняется компиляция программы Linux. Этот процесс может быть сложным для новичков, но в целом, все возможно, если потратить на решение задачи несколько часов. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
На завершение видео о том, что такое компилятор и интерпретатор:
Источник
How To Compiling C Program And Creating Executable File Under a Linux / UNIX / *BSD
H ow do I compile C program and create an executable file under Linux or UNIX operating systems?
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | No |
| Requirements | C compiler |
| Est. reading time | 5m |
[/donotprint]But you can use gcc command to compile program. First make sure you have gcc C compiler installed:
Make Sure Compiler Is Installed On a Unix-like System
Type the following which command or type command or command command to verify that gcc is installed:
$ type -a gcc
$ command -V gcc
$ which gcc
Sample outputs:
Find out version of gcc, run:
$ gcc —version
Sample outpust:
Syntax
The syntax is as follows to compile a C program on a Unix-like operating system:
gcc program.c -o program-output
OR
cc program.c -o program-output
OR
make program
Writing Your First C Program Under a Linux / UNIX-like system
Use a text editor such as vi or gedit or nano to create a C program called first.c:
$ vi first.c
Type the following lines (program):
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
How Do I Compile My C Program?
To compile C program first.c, and create an executable file called first, enter:
$ gcc first.c -o first
OR
$ cc first.c -o first
To execute program first, enter:
$ ./first
Output:
However, both FreeBSD and Linux support direct make (GNU make utility to maintain groups of programs) command on C program without writing a make file. Remove, first program using the rm command:
$ rm first
$ make first
Output:
Execute program first:
$ ./first
Please note that above hack works with GNU/make only.
See also:
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
| Category | List of Unix and Linux commands |
|---|---|
| Documentation | help • mandb • man • pinfo |
| Disk space analyzers | df • duf • ncdu • pydf |
| File Management | cat • cp • less • mkdir • more • tree |
| Firewall | Alpine Awall • CentOS 8 • OpenSUSE • RHEL 8 • Ubuntu 16.04 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Linux Desktop Apps | Skype • Spotify • VLC 3 |
| Modern utilities | bat • exa |
| Network Utilities | NetHogs • dig • host • ip • nmap |
| OpenVPN | CentOS 7 • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Debian 8/9 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Package Manager | apk • apt |
| Processes Management | bg • chroot • cron • disown • fg • glances • gtop • jobs • killall • kill • pidof • pstree • pwdx • time • vtop |
| Searching | ag • grep • whereis • which |
| Shell builtins | compgen • echo • printf |
| Text processing | cut • rev |
| User Information | groups • id • lastcomm • last • lid/libuser-lid • logname • members • users • whoami • who • w |
| WireGuard VPN | Alpine • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Firewall • Ubuntu 20.04 |
Comments on this entry are closed.
Your c code is missing the filename of the #include directive.
Thanks for heads up.
Hi, I was just wondering how would you create an executable for numerous C programs? I am modifying the Windows Frotz interpreter for a college assignment with the aim to output the game data to a html page. The source for the interpreter contains numerous C files in a number of subdirectories. I have made the modifications but need to create the executable to see if it works properly. This is my first time creating an executable so i’m a bit unsure how to go about it. Any help would be greatly appreciated.
I just want to thank you. I am 57 years old and I just started computing two years ago. I have built three towers, which is no big deal; but, I have been running a lot of different systems. I want to learn c and c++ and you have helped me a lot. I am grateful for any help I can get. I usually do stuff on my own.I still wonder what the greatest difference is between BSD and Debian other than software installation. I do think that BSD is closer to being pure UNIX than Debian, but the kernels are so alike or an I wrong? It world be nice to know. Anyway, this letter is to thank you.
Nice to see at 57, you are learning BSD and C/C++ development.
*BSD is under BSD vs Linux is under GPL License
Network stack
Little change in command syntax for few utilities
A BSD and Linux kernel are different and follows different development methods and approach.
Please see this post along with discussion for more info.
i want a C program Compiler Code In VI editor
hi, i ve installed red hat linux.and trying to compile C++ prg.but getting a err msg saying that gcc not found.then i tried to see which compiler installed on my linx.To do so i am giving cmd – which
gcc – output is /usr/bin/which: – no gcc.
and i am not able to compile my prog..
plz help me in dis regard.
You need to install install update your repositories, and install it thru the RPM comander or do it with de packgesmanager.
install g++ . in redhat and centos or fedora yum install g++
king777 – you need to make sure the gcc development package is selected when you install redhat. Otherwise, you have to download/install gcc manually.
i don’t know about software creation iam from a village school of india
shall you pls send any program in c for me iam too interest in these
If using the Unix system
Follow the below steps:
$ vi welcome.c
Save the content written below (This is called programme)
include
int main(void)
<
printf(“WELCOME TO THE WORLD OF C\n”);
return 0;
>
Step 3 ) comiple the progamme
gcc welcome.c -o WELCOME
Step 4) For execution
$ ./WELCOME
THNX. very useful. 😀 😀 😀
After typing the following command “$ which gcc” to verify that gcc is installed, the Output was “/usr/bin/which: no gcc in (/usr/kerberos/bin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/X11R6/bin:/home/omar/bin)
” , instead of being “/usr/bin/gcc”. what i have to do now?
I would like to thank you very much. I am new user of linux and C language, I was trying to compile a small program for hours. You made it so easy thank you again and god bless you.
Many thanks for this! I love programming in C and perl and getting my feet wet with Linux/UNIX.
As a followup question, how would I take a program I’ve created (a calculator, for example), and package it so it can run as an executable on another computer (or even embed in a linux distro)?
i want to know how to create executable file.
when u compile any *.c file automatically the executable file is created, which is linked to ld further to get the output,the executable file created after compiling is called as intermediate object file or executable
I file con be executable thru the permitions
chmod +x program make in a sudo way
how to compile a user defined function in c using gcc.
what do you mean by segmentation fault.
Hi
i’m new linux worker.
befor linux i work on windows7 and now for robotic programing and… work in linux fedora12.
thank u for this note.
and i have a question!(excuse me for my bad english,becous i’m iranian)
–> how we can load and open the serial port in program??
–>how can i open the camera on linux?
–>and how we can comunicate with other laptop with wi-fi?
I followed the steps mentioned above.I m able to compile the code.But when i m givin “./first” to
run it its giving the following “-bash: ./first: Permission denied”. Please help me
Usually the compiled programm. If that’s not the case run
sudo chmod u+x
which gives the user permission to execute the file.
hii…iam on redhat 5.0….whenever i try to compile c program…iam gettin an error msg stating gcc command not found….explain me the easy way to install the gcc….please help me
i tried which gcc as you said but iam getting gcc not in and ./a.out is also not working…please someone help me out
HI! I’m new for linux and I’m using Fedora 13 actually I wnt to install compiler for c and c++ someone told me gcc is inbuilt in fedora 13, is it possible tell me how to know it’s installed or not or how to install it? how to create c or c++ programs in fedora 13 or any linux system, how to install other IDE’s for development. Please someone help me out……
I would like to know how can I execute the file “first” without using preceeding it
with the characters “./” . Any help is appreciated.
when i try to compile a C pogram in centos 5.2…i get the following error
$ cc prog.c
bash: cc: command not found
how to get rid of this prob…pls help
actually it is because gcc is not installed so type “yum install gcc” if u have a centos or fedora
i tried it as su -c’yum install gcc’
but it also get faliure.to install the gcc so hw could i hv 2 go for install.
yum only works if you have a yum repository… otherwise you have to do it manually..
when i try to compile a C pogram in Fedora 13 .i get the following error
$ cc prog.c
bash: cc: command not found
how to get rid of this prob…pls help
Dear friend,
I cannot also create,compile & execute C program in Fedora 15.Please help me to do this mailing me the required commands.
I can’t not compile program
TopDollar !! 🙂
My first c-compilation yummie!
And it works perfect following your instructions.
Peace out!
hi friends can any one say me how can i add libraries(.h) to my gcc compiler
This really doesn’t help me to understand how to make the compiled program executable. When I say executable I mean a *.exe file that I can call by name (such as typing “first_program.exe” in a terminal & having it execute), or by double clicking in a graphical environment.
Does ANYBODY know how to do THAT?!
Can I use script on Windows XP??
If we have a program with multible *.c or *.h files how do we compile those together? And how do we make this a *.exe file or some sort of exacutable?
i just want to know how to install gcc files in fedora. /
use the following command in terminal (it works for me in fedora 14)
yum groupinstall ‘Development Tools’
This will download (approx 105Mb) of data and automatically install it on your system. the best thing is you dont have to worry about the dependencies 😉
then type gcc and press enter
you should get this error “no input files selected” this means gcc is installed.
i tried but it says that you need to be root to perform this command. now what should i do?
Источник