- Службы компонентов
- Роли, службы ролей и компоненты, отсутствующие в Windows Server — Server Core Roles, Role Services, and Features not in Windows Server — Server Core
- Роли, не являющиеся базовыми для сервера Roles not in Server Core
- Службы ролей не в Server Core Role Services not in Server Core
- Directory Services component updates
- What You Will Learn
- Domain and Forest Functional Levels
- Overview
- New DFL and FFL
- The Windows Server 2012 R2 Domain Functional Level enables support for the following:
- Minimum DFL enforced on new domain creation
- Lowering the forest and domain functional levels
- ADPREP
- Deprecation of NTFRS
- Overview
- LDAP Query Optimizer changes
- Overview
- Background
- Details of change
- Comparison between old and new algorithm
- Sample results using the new algorithm
- To enable the Stats control in LDP
- Try This: Use LDP to return query statistics
- Additional Resources
- 1644 Event improvements
- Overview
- Background
Службы компонентов





Службы компонентов полностью интегрированы с другими компонентами и службами Windows 2000 Server. Интеграция со службами Internet Information Services и Active Server Pages упрощает создание приложений в среде Интернет/интрасети. Интеграция с кластерными службами повышает отказоустойчивость. Интеграция со службой обработки очередей сообщений (MSMQ) обеспечивает надежную, постоянную связь между приложениями.
Возможности Microsoft Transaction Server (MTS) были объединены с «классической» технологией СОМ и образовали технологию СОМ+, которая интегрирована в операционную систему Windows 2000. Оснастка ММС для управления СОМ+ — Службы компонентов (Component Services) доступна из меню Администрирование (Пуск | Программы | Администрирование | Службы компонентов).
В состав служб компонентов входит переработанный инструмент управления, реализованный в виде оснастки ММС, с помощью которого можно устанавливать пакеты MTS в СОМ+ (рис. 22.13). Ранее для этого применялись специальные инструменты MTS. Сразу после установки пакета можно использовать такие новые возможности СОМ+, как базы данных, хранящиеся в оперативной памяти (In-Memory DataBase, IMDB), или новая система поддержки событий.
Роли, службы ролей и компоненты, отсутствующие в Windows Server — Server Core Roles, Role Services, and Features not in Windows Server — Server Core
Область применения: Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016 и Windows Server (половина ежегодного канала) Applies to: Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, and Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel)
Следующие роли, службы ролей и компоненты были удалены из варианта установки Server Core Windows Server. The following roles, role services, and features have been removed from the Server Core installation option of Windows Server. Используйте эти сведения, чтобы определить, работает ли параметр Server Core для вашей среды. Use this information to help figure out if the Server Core option works for your environment.
Вы также можете просмотреть список ролей, служб ролей и компонентов, входящих в Server Core. You can also see a list of the roles, role services, and features that ARE included in Server Core. Это очень большой список, поэтому для получения наилучших результатов найдите в списке конкретную роль или интересующую вас функцию. It’s a very large list, so for best results, search that list for the specific role or feature you’re interested in.
Роли, не являющиеся базовыми для сервера Roles not in Server Core
- Факс-сервер (Факс) Fax Server (Fax)
- Службы MultiPoint (мултипоинтсерверроле) MultiPoint Services (MultiPointServerRole)
- Службы политики сети и доступа (NPAS) Network Policy and Access Services (NPAS)
- Службы развертывания Windows (WDS) (до windows Server версии 1803) Windows Deployment Services (WDS) (before Windows Server version 1803)
Службы ролей не в Server Core Role Services not in Server Core
Обратите внимание, что некоторые службы роли удаленный рабочий стол включены в Server Core (посредник подключений, лицензирование, узел виртуализации), а другие — нет (шлюз, узел сеансов удаленных рабочих столов, Веб-доступ). Note that some Remote Desktop role services are included in Server Core (Connection Broker, Licensing, Virtualization Host), but others are NOT (Gateway, RD Session Host, Web Access).
- Службы печати и документов \ сервер распределенного сканирования (Printing-Scan-Server) Print and Document Services \ Distributed Scan Server (Print-Scan-Server)
- Службы печати и документов \ печать в Интернете (Печать — Интернет) Print and Document Services \ Internet Printing (Print-Internet)
- Шлюз службы удаленных рабочих столов \ удаленный рабочий стол (RDS-Gateway) Remote Desktop Services \ Remote Desktop Gateway (RDS-Gateway)
- Узел сеансов службы удаленных рабочих столов \ удаленный рабочий стол (RDS-RD-Server) Remote Desktop Services \ Remote Desktop Session Host (RDS-RD-Server)
- Службы удаленных рабочих столов \ удаленный рабочий стол Веб-доступ (RDS-Web-Access) Remote Desktop Services \ Remote Desktop Web Access (RDS-Web-Access)
- Веб-сервер службы ролей (IIS) \ средства управления \ консоль управления IIS (Web Management-Console) Role Service Web Server (IIS) \ Management Tools \ IIS Management Console (Web-Mgmt-Console)
- Веб-сервер службы ролей (IIS) \ средства управления \ совместимость управления IIS 6 \ консоль управления IIS 6 (Web-лгци-Management-Console) Role Service Web Server (IIS) \ Management Tools \ IIS 6 Management Compatibility \ IIS 6 Management Console (Web-Lgcy-Mgmt-Console)
- Службы развертывания Windows \ сервер развертывания (WDS-развертывание) Windows Deployment Services \ Deployment Server (WDS-Deployment)
- Службы развертывания Windows \ транспортный сервер (WDS-транспорт) (до Windows Server версии 1803) Windows Deployment Services \ Transport Server (WDS-Transport) (before Windows Server version 1803)
Directory Services component updates
Applies To: Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012
Author: Justin Turner, Senior Support Escalation Engineer with the Windows group
This content is written by a Microsoft customer support engineer, and is intended for experienced administrators and systems architects who are looking for deeper technical explanations of features and solutions in Windows Server 2012 R2 than topics on TechNet usually provide. However, it has not undergone the same editing passes, so some of the language may seem less polished than what is typically found on TechNet.
This lesson explains the Directory Services component updates in Windows Server 2012 R2.
What You Will Learn
Explain the following new Directory Services component updates:
Explain the following new Directory Services component updates:
Domain and Forest Functional Levels
Overview
The section provides a brief introduction to the domain and forest functional level changes.
New DFL and FFL
With the release, there are new domain and forest functional levels:
Forest Functional Level: Windows Server 2012 R2
Domain Functional Level: Windows Server 2012 R2
The Windows Server 2012 R2 Domain Functional Level enables support for the following:
DC-side protections for Protected Users
Protected Users authenticating to a Windows Server 2012 R2 domain can no longer:
Authenticate with NTLM authentication
Use DES or RC4 cipher suites in Kerberos pre-authentication
Be delegated with unconstrained or constrained delegation
Renew user tickets (TGTs) beyond the initial 4 hour lifetime
New forest-based Active Directory policies which can be applied to accounts in Windows Server 2012 R2 domains to control which hosts an account can sign-on from and apply access control conditions for authentication to services running as an account
Authentication Policy Silos
New forest-based Active Directory object which can create a relationship between user, managed service and computer accounts to be used to classify accounts for authentication policies or for authentication isolation.
See How to Configure Protected Accounts for more information.
In addition to the above features, the Windows Server 2012 R2 domain functional level ensures that any domain controller in the domain runs Windows Server 2012 R2. The Windows Server 2012 R2 forest functional level does not provide any new features, but it ensures that any new domain created in the forest will automatically operate at the Windows Server 2012 R2 domain functional level.
Minimum DFL enforced on new domain creation
Windows Server 2008 DFL is the minimum functional level supported on new domain creation.
The deprecation of FRS is accomplished by removing the ability to install a new domain with a domain functional level lower than Windows Server 2008 with Server Manager or via Windows PowerShell.
Lowering the forest and domain functional levels
The forest and domain functional levels are set to Windows Server 2012 R2 by default on new domain and new forest creation but can be lowered using Windows PowerShell.
To raise or lower the forest functional level using Windows PowerShell, use the Set-ADForestMode cmdlet.
To set the contoso.com FFL to Windows Server 2008 mode:
To raise or lower the domain functional level using Windows PowerShell, use the Set-ADDomainMode cmdlet.
To set the contoso.com DFL to Windows Server 2008 mode:
Promotion of a DC running Windows Server 2012 R2 as an additional replica into an existing domain running 2003 DFL works.
New domain creation in an existing forest
ADPREP
There are no new forest or domain operations in this release.
These .ldf files contain schema changes for the Device Registration Service.
Work Folders:
MSODS:
Authentication Policies and Silos
Deprecation of NTFRS
Overview
FRS is deprecated in Windows Server 2012 R2. The deprecation of FRS is accomplished by enforcing a minimum domain functional level (DFL) of Windows Server 2008. This enforcement is present only if the new domain is created using Server Manager or Windows PowerShell.
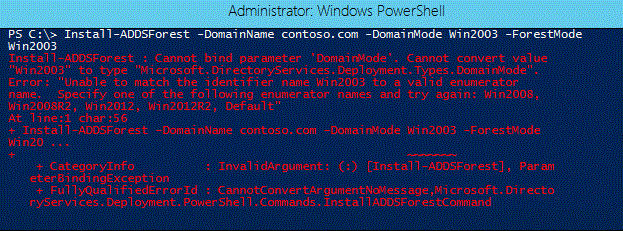
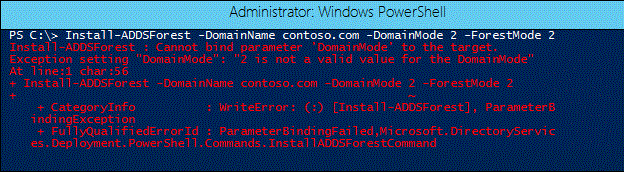
You use the -DomainMode parameter with the Install-ADDSForest or Install-ADDSDomain cmdlets to specify the domain functional level. Supported values for this parameter can be either a valid integer or a corresponding enumerated string value. For example, to set the domain mode level to Windows Server 2008 R2, you can specify either a value of 4 or «Win2008R2». When executing these cmdlets from Server 2012 R2 valid values include those for Windows Server 2008 (3, Win2008) Windows Server 2008 R2 (4, Win2008R2) Windows Server 2012 (5, Win2012) and Windows Server 2012 R2 (6, Win2012R2). The domain functional level cannot be lower than the forest functional level, but it can be higher. Since FRS is deprecated in this release, Windows Server 2003 (2, Win2003) is not a recognized parameter with these cmdlets when executed from Windows Server 2012 R2.
LDAP Query Optimizer changes
Overview
The LDAP query optimizer algorithm was reevaluated and further optimized. The result is the performance improvement in LDAP search efficiency and LDAP search time of complex queries.
From the Developer:improvements in the performance of searches through improvements in the mapping from LDAP query to ESE query. LDAP filters beyond a certain level of complexity prevent optimized index selection, resulting in drastically decreased performance (1000x or more). This change alters the way in which we select indices for LDAP queries to avoid this problem.
A complete overhaul of the LDAP query optimizer algorithm, resulting in:
- Faster search times
- Efficiency gains allow DCs to do more
- Less support calls regarding AD Performance issues
- Back ported to Windows Server 2008 R2 (KB 2862304)
Background
The ability to search Active Directory is a core service provided by domain controllers. Other services and line of business applications rely on Active Directory searches. Business operations can cease to a halt if this feature is not available. As a core and heavily used service, it is imperative that domain controllers handle LDAP search traffic efficiently. The LDAP query optimizer algorithm attempts to make LDAP searches efficient as possible by mapping LDAP search filters to a result set that can be satisfied via records already indexed in the database. This algorithm was reevaluated and further optimized. The result is the performance improvement in LDAP search efficiency and LDAP search time of complex queries.
Details of change
An LDAP search contains:
A location (NC head, OU, Object) within the hierarchy to begin the search
A search filter
A list of attributes to return
The search process can be summarized as follows:
Simplify the search filter if possible.
Select a set of Index Keys that will return the smallest covered set.
Perform one or more intersections of Index Keys, to reduce the covered set.
For each record in the covered set, evaluate the filter expression as well as the security. If the filter evaluates to TRUE and access is granted, then return this record to the client.
The LDAP query optimization work modifies steps 2 and 3, to reduce the size of the covered set. More specifically, the current implementation selects duplicate Index Keys and performs redundant intersections.
Comparison between old and new algorithm
The target of the inefficient LDAP search in this example is a Windows Server 2012 domain controller. The search completes in approximately 44 seconds as a result of failing to find a more efficient index.
Sample results using the new algorithm
This example repeats the exact same search as above but targets a Windows Server 2012 R2 domain controller. The same search completes in less than a second due to the improvements in the LDAP query optimizer algorithm.
If unable to optimize the tree:
For example: an expression in the tree was over a column not indexed
Record a list of indices that prevent optimization
Exposed via ETW tracing and event ID 1644
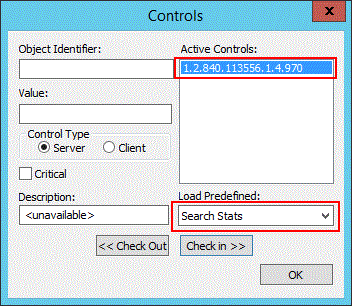
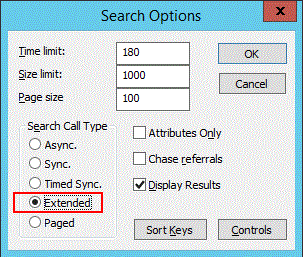
To enable the Stats control in LDP
Open LDP.exe, and connect and bind to a domain controller.
On the Options menu, click Controls.
On the Controls dialog box, expand the Load Predefined pull-down menu, click Search Stats and then click OK.
On the Browse menu, click Search
In the Search dialog box, select the Options button.
Ensure the Extended check box is selected on the Search Options dialog box and select OK.
Try This: Use LDP to return query statistics
Perform the following on a domain controller, or from a domain-joined client or server that has the AD DS tools installed. Repeat the following targeting your Windows Server 2012 DC and your Windows Server 2012 R2 DC.
Using LDP, enable search statistics (see To enable the Stats control in LDP)
Conduct several LDAP searches and observe the statistical information at the top of the results. You will repeat the same search in other activities so document them in a notepad text file.
Perform an LDAP search that the query optimizer should be able to optimize because of attributes indices
Attempt to construct a search that takes a long time to complete (you may want to increase the Time limit option so the search does not timeout).
Additional Resources
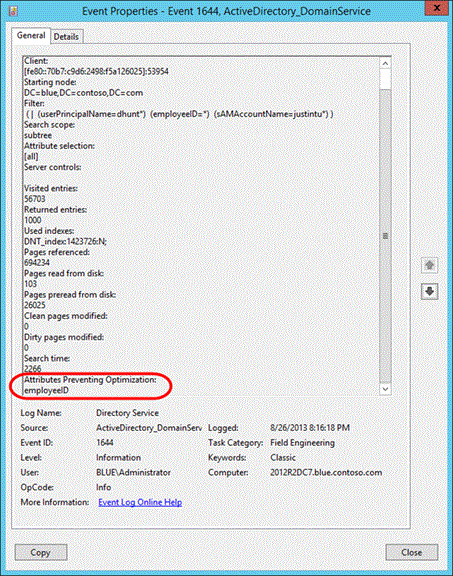
951581 LDAP queries are executed more slowly than expected in the AD or LDS/ADAM directory service and Event ID 1644 may be logged
1644 Event improvements
Overview
This update adds additional LDAP search result statistics to event ID 1644 to aid in troubleshooting purposes. Additionally, there is a new registry value that can be used to enable logging on a time-based threshold. These improvements were made available in Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 via KB 2800945 and will be made available to Windows Server 2008 SP2.
- Additional LDAP search statistics are added to event ID 1644 to aid in troubleshooting inefficient or expensive LDAP searches
- You can now specify a Search Time Threshold (eg. Log event 1644 for searches taking longer than 100ms) instead of specifying the Expensive and Inefficient search result threshold values
Background
While troubleshooting Active Directory performance problems, it becomes apparent that LDAP search activity may be contributing to the problem. You decide to enable logging so that you can see expensive or inefficient LDAP queries processed by domain controller. In order to enable the logging, you must set the Field Engineering diagnostics value and can optionally specify the expensive / inefficient search results threshold values. Upon enabling the Field Engineering logging level to a value of 5, any search that meets these criteria is logged in the Directory Services event log with an event ID 1644.