- Which version of Windows operating system am I running?
- Find operating system info in Windows 10
- Related links
- Find operating system info in Windows 8.1 or Windows RT 8.1
- Related links
- Find operating system info in Windows 7
- Related links
- Operating System Version
- Determine whether your computer is running a 32-bit version or 64-bit version of the Windows operating system
- Support for Office 2010 ended on October 13, 2020
- Determine the operating system bit count
- Windows 7 or Windows Vista
- Windows XP Professional
- 32-bit and 64-bit Windows: Frequently asked questions
- Windows 10 and Windows 8.1
- Windows 7
- Windows 10 and Windows 8.1
- Windows 7
- Computer Basics —
- Understanding Operating Systems
- Computer Basics: Understanding Operating Systems
- Lesson 8: Understanding Operating Systems
- What is an operating system?
- The operating system’s job
- Types of operating systems
- Microsoft Windows
- macOS
- Linux
- Operating systems for mobile devices
Which version of Windows operating system am I running?
Find operating system info in Windows 10
To find out which version of Windows your device is running, press the Windows logo key + R, type winver in the Open box, and then select OK.
Here’s how to learn more:
Select the Start button > Settings > System > About .
Under Device specifications > System type, see if you’re running a 32-bit or 64-bit version of Windows.
Under Windows specifications, check which edition and version of Windows your device is running.
Related links
If you’re having a problem with activation, see Activate in Windows 10.
If you forgot the password you use to sign in to Windows devices or email, see How to reset your Microsoft password.
For info about updating Windows, see Windows Update: FAQ.
Find operating system info in Windows 8.1 or Windows RT 8.1
To find out which version of Windows your device is running, press the Windows logo key + R, type winver in the Open box, and then select OK.
If your device is running Windows 8.1 or Windows RT 8.1, here’s how to learn more:
If you’re using a touch device, swipe in from the right edge of the screen, tap Settings, and then tap Change PC settings. Continue to step 3.
If you’re using a mouse, point to the lower-right corner of the screen, move the mouse pointer up, click Settings, and then click Change PC settings.
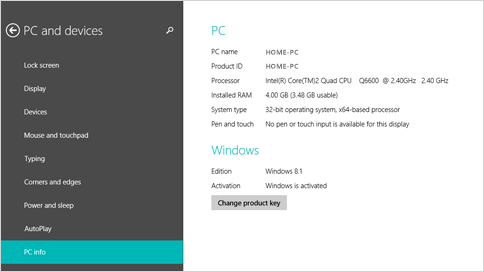
Select PC and devices > PC info.
Under Windows you’ll see which edition and version of Windows your device is running.
Under PC > System type you’ll see if you’re running a 32-bit or 64-bit version of Windows.
Related links
If you’re having a problem with activation, see Activate Windows 7 or Windows 8.1
If you forgot the password you use to sign in to Windows devices or email, see How to reset your Microsoft password.
For info about updating Windows, see Windows Update: FAQ.
Find operating system info in Windows 7
Select the Start 
Under Windows edition, you’ll see the version and edition of Windows that your device is running.
Support for Windows 7 ended on January 14, 2020
We recommend you move to a Windows 10 PC to continue to receive security updates from Microsoft.
Related links
If you’re having a problem with activation, see Activate Windows 7 or Windows 8.1.
If you forgot the password you use to sign in to Windows devices or email, see How to reset your Microsoft password.
For info about updating Windows, see Windows Update: FAQ.
Operating System Version
The Version API Helper functions are used to determine the version of the operating system that is currently running. For more information, see Getting the System Version.
The following table summarizes the most recent operating system version numbers.
| Operating system | Version number |
|---|---|
| Windows 10 | 10.0* |
| Windows Server 2019 | 10.0* |
| Windows Server 2016 | 10.0* |
| Windows 8.1 | 6.3* |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | 6.3* |
| Windows 8 | 6.2 |
| Windows Server 2012 | 6.2 |
| Windows 7 | 6.1 |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | 6.1 |
| Windows Server 2008 | 6.0 |
| Windows Vista | 6.0 |
| Windows Server 2003 R2 | 5.2 |
| Windows Server 2003 | 5.2 |
| Windows XP 64-Bit Edition | 5.2 |
| Windows XP | 5.1 |
| Windows 2000 | 5.0 |
* For applications that have been manifested for Windows 8.1 or Windows 10. Applications not manifested for Windows 8.1 or Windows 10 will return the Windows 8 OS version value (6.2). To manifest your applications for Windows 8.1 or Windows 10, refer to Targeting your application for Windows.
Identifying the current operating system is usually not the best way to determine whether a particular operating system feature is present. This is because the operating system may have had new features added in a redistributable DLL. Rather than using the Version API Helper functions to determine the operating system platform or version number, test for the presence of the feature itself.
To determine the best way to test for a feature, refer to the documentation for the feature of interest. The following list discusses some common techniques for feature detection:
- You can test for the presence of the functions associated with a feature. To test for the presence of a function in a system DLL, call the LoadLibrary function to load the DLL. Then call the GetProcAddress function to determine whether the function of interest is present in the DLL. Use the pointer returned by GetProcAddress to call the function. Note that even if the function is present, it may be a stub that just returns an error code such as ERROR_CALL_NOT_IMPLEMENTED.
- You can determine the presence of some features by using the GetSystemMetrics function. For example, you can detect multiple display monitors by calling GetSystemMetrics(SM_CMONITORS).
- There are several versions of the redistributable DLLs that implement shell and common control features. For information about determining which versions are present on the system your application is running on, see the topic Shell and Common Controls Versions.
If you must require a particular operating system, be sure to use it as a minimum supported version, rather than design the test for the one operating system. This way, your detection code will continue to work on future versions of Windows.
Note that a 32-bit application can detect whether it is running under WOW64 by calling the IsWow64Process function. It can obtain additional processor information by calling the GetNativeSystemInfo function.
Determine whether your computer is running a 32-bit version or 64-bit version of the Windows operating system
Support for Office 2010 ended on October 13, 2020
Upgrade to Microsoft 365 to work anywhere from any device and continue to receive support.
When you install Microsoft Lync 2010 communications software, depending on your computer’s operating system you will need to choose between a 32-bit version or a 64-bit version installer.
The minimum operating system requirements for Lync 2010 is Window 7, Windows Vista, or Windows XP Professional with Service Pack 3 (SP3). For more information about system requirements, see Lync Online and Online Meeting Add-in for Microsoft Lync 2010 System Requirements.
Determine the operating system bit count
Windows 7 or Windows Vista
If you have Windows Vista or Windows 7, there are two methods to determine whether you are running a 32-bit or a 64-bit version. If one does not work, try the other.
Method 1: View System window in Control Panel
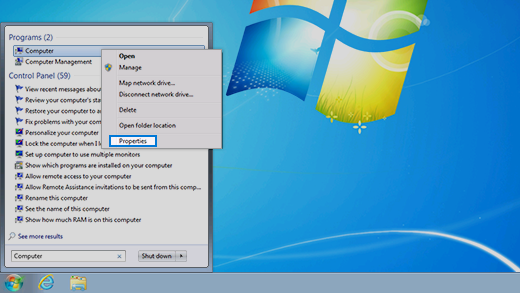
Click Start, type system in the search box, and then click System in the Control Panel list.
The operating system is displayed as follows:
For a 64-bit version operating system: 64-bit Operating System appears for the System type under System.
For a 32-bit version operating system: 32-bit Operating System appears for the System type under System.
Method 2: View System Information window
Click Start, type system in the search box, and then click System Information in the Programs list.
When System Summary is selected in the navigation pane, the operating system is displayed as follows:
For a 64-bit version operating system: X64-based PC appears for the System Type under Item.
For a 32-bit version operating system: X86-based PC appears for the System Type under Item.
Windows XP Professional
If you have Windows XP, there are two methods to determine whether you are running a 32-bit or a 64-bit version. If one does not work, try the other.
Method 1: View System Properties in Control Panel
Click Start, and then click Run.
Type sysdm.cpl, and then click OK.
Click the General tab. The operating system is displayed as follows:
For a 64-bit version operating system: Windows XP Professional x64 Edition Version appears under System.
For a 32-bit version operating system: Windows XP Professional Version appears under System.
Method 2: View System Information window
Click Start, and then click Run.
Type winmsd.exe, and then click OK.
When System Summary is selected in the navigation pane, locate Processor under Item in the details pane. Note the value.
If the value that corresponds to Processor starts with x86, the computer is running a 32-bit version of Windows.
If the value that corresponds to Processor starts with ia64 or AMD64, the computer is running a 64-bit version of Windows.
32-bit and 64-bit Windows: Frequently asked questions
Here are answers to some common questions about the 32-bit and 64-bit versions of Windows.
Upgrading from the 32-bit version to the 64-bit version of Windows requires that you reformat your hard disk, install the 64-bit version of Windows, and then reinstall everything else that you had on your device.
Windows 10 and Windows 8.1
Select the Start button, then select Settings > System > About .
Open About settings
At the right, under Device specifications, see System type.
Windows 7
Select the Start button 
Under System, see the system type.
To install a 64-bit version of Windows, you need a CPU that’s capable of running a 64-bit version of Windows. The benefits of using a 64-bit operating system are most apparent when you have a large amount of random access memory (RAM) installed on your computer, typically 4 GB of RAM or more. In such cases, because a 64-bit operating system can handle large amounts of memory more efficiently than a 32-bit operating system, a 64-bit system can be more responsive when running several programs at the same time and switching between them frequently.
To run a 64-bit version of Windows, your computer must have a 64-bit-capable processor. To find out if your processor is 64-bit-capable, do the following.
Windows 10 and Windows 8.1
Select the Start button, then select Settings > System > About .
Open About settings
At the right, under Device specifications, see System type.
Windows 7
Select the Start button 
Select View and print detailed performance and system information.
In the System section, you can see what type of operating system you’re currently running under System type, and whether or not you can run a 64-bit version of Windows under 64-bit capable. (If your computer is already running a 64-bit version of Windows, you won’t see the 64-bit capable listing.)
Computer Basics —
Understanding Operating Systems
Computer Basics: Understanding Operating Systems
Lesson 8: Understanding Operating Systems
What is an operating system?
An operating system is the most important software that runs on a computer. It manages the computer’s memory and processes, as well as all of its software and hardware. It also allows you to communicate with the computer without knowing how to speak the computer’s language. Without an operating system, a computer is useless.
Watch the video below to learn more about operating systems.
Looking for the old version of this video? You can still view it here.
The operating system’s job
Your computer’s operating system (OS) manages all of the software and hardware on the computer. Most of the time, there are several different computer programs running at the same time, and they all need to access your computer’s central processing unit (CPU), memory, and storage. The operating system coordinates all of this to make sure each program gets what it needs.
Types of operating systems
Operating systems usually come pre-loaded on any computer you buy. Most people use the operating system that comes with their computer, but it’s possible to upgrade or even change operating systems. The three most common operating systems for personal computers are Microsoft Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Modern operating systems use a graphical user interface, or GUI (pronounced gooey). A GUI lets you use your mouse to click icons, buttons, and menus, and everything is clearly displayed on the screen using a combination of graphics and text.
Each operating system’s GUI has a different look and feel, so if you switch to a different operating system it may seem unfamiliar at first. However, modern operating systems are designed to be easy to use, and most of the basic principles are the same.
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft created the Windows operating system in the mid-1980s. There have been many different versions of Windows, but the most recent ones are Windows 10 (released in 2015), Windows 8 (2012), Windows 7 (2009), and Windows Vista (2007). Windows comes pre-loaded on most new PCs, which helps to make it the most popular operating system in the world.
Check out our tutorials on Windows Basics and specific Windows versions for more information.
macOS
macOS (previously called OS X) is a line of operating systems created by Apple. It comes preloaded on all Macintosh computers, or Macs. Some of the specific versions include Mojave (released in 2018), High Sierra (2017), and Sierra (2016).
According to StatCounter Global Stats, macOS users account for less than 10% of global operating systems—much lower than the percentage of Windows users (more than 80%). One reason for this is that Apple computers tend to be more expensive. However, many people do prefer the look and feel of macOS over Windows.
Check out our macOS Basics tutorial for more information.
Linux
Linux (pronounced LINN-ux) is a family of open-source operating systems, which means they can be modified and distributed by anyone around the world. This is different from proprietary software like Windows, which can only be modified by the company that owns it. The advantages of Linux are that it is free, and there are many different distributions—or versions—you can choose from.
According to StatCounter Global Stats, Linux users account for less than 2% of global operating systems. However, most servers run Linux because it’s relatively easy to customize.
To learn more about different distributions of Linux, visit the Ubuntu, Linux Mint, and Fedora websites, or refer to our Linux Resources. For a more comprehensive list, you can visit MakeUseOf’s list of The Best Linux Distributions.
Operating systems for mobile devices
The operating systems we’ve been talking about so far were designed to run on desktop and laptop computers. Mobile devices such as phones, tablet computers, and MP3 players are different from desktop and laptop computers, so they run operating systems that are designed specifically for mobile devices. Examples of mobile operating systems include Apple iOS and Google Android . In the screenshot below, you can see iOS running on an iPad.
Operating systems for mobile devices generally aren’t as fully featured as those made for desktop and laptop computers, and they aren’t able to run all of the same software. However, you can still do a lot of things with them, like watch movies, browse the Web, manage your calendar, and play games.
To learn more about mobile operating systems, check out our Mobile Devices tutorials.