- Getting Stuck at Starting Windows Screen for long periods of time.
- Windows 7 Stuck on starting Windows Screen
- Replies (9)
- Advanced troubleshooting for Stop error or blue screen error issue
- What causes Stop errors?
- General troubleshooting steps
- Memory dump collection
- Pagefile Settings
- Memory dump analysis
- Advanced troubleshooting steps
- Advanced debugging references
- Debugging steps
- Video resources
- Advanced troubleshooting using Driver Verifier
- Common Windows Stop errors
Getting Stuck at Starting Windows Screen for long periods of time.
Starting on Saturday, When I start my computer it gets stuck at the starting windows screen. The first time this happened I ran a Start up repair, and I was able to start my computer like normal. However, the next time I shut off my computer and attempted to turn it on the problem came up again. I attempted to do the same thing I did the first time, but now I get stuck at the starting windows screen for at least 10 minutes before it will allow me the option to get to my desktop. My computer did recently go through the microsoft updates, and it was after when the problems started. Is there any known solution?
Try these steps:
Step 1 : Start the computer in safe mode and check if you can boot to your desktop normally.
If you can start the computer normally in safe mode, then we can assume that a third party startup program or service is causing the problem. To isolate the program, you
can perform a clean boot.
Step 2 : Perform a clean boot.
Refer this KB article for more information about clean boot:
How to troubleshoot a problem by performing a clean boot in Windows Vista or in Windows 7
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/929135
Steps to perform a clean boot:
a. Click the start orb on your desktop
b. Type msconfig in the Start Search box, and then press ENTER.
If you are prompted for an administrator password or for a confirmation, type the password, or click Continue.
c. On the General tab, click Selective Startup.
d. Under Selective Startup, click to clear the Load Startup Items check box.
e. Click the Services tab, click to select the Hide All Microsoft Services check box, and then click Disable All.
f. Click OK.
g. When you are prompted, click Restart.
NOTE : Please ensure to start the computer in normal mode after troubleshooting. Follow step 7 from the KB article.
Step 3: Perform a system restore to restore the computer to an earlier point in time before the problem started.
Regards,
Afzal Taher — Microsoft Support.
Visit our Microsoft Answers Feedback Forum and let us know what you think.
Windows 7 Stuck on starting Windows Screen
Replies (9)
Thank you for posting your query in Microsoft Community.
From your issue description I understand that, computer stuck on start screen.I see that you have performed many troubleshooting steps that should fix the issue. Don’t worry; we will certainly help you.
Let’s follow the methods from this link and check if it fixes the issue.
Windows hangs or freezes
Anti Virus Disclaimer: Any data files that are infected may only be cleaned by deleting the file entirely, which means there is a potential for data loss.
Hope this will be helpful. Incase if you still have further queries please reply with more details and we will be happy to help you.
Was this reply helpful?
Sorry this didn’t help.
Great! Thanks for your feedback.
How satisfied are you with this reply?
Thanks for your feedback, it helps us improve the site.
How satisfied are you with this reply?
Thanks for your feedback.
4 people found this reply helpful
Was this reply helpful?
Sorry this didn’t help.
Great! Thanks for your feedback.
How satisfied are you with this reply?
Thanks for your feedback, it helps us improve the site.
How satisfied are you with this reply?
Thanks for your feedback.
As the computer freezes during the startup repair, let’s perform system restore using Windows 7 installation disk.
Try booting your system with Windows 7 installation disc.
When it gets to the main setup window, click on Repair from the lower left corner.
Select system restore from the System recovery option and check if computer works fine.
2 people found this reply helpful
Was this reply helpful?
Sorry this didn’t help.
Great! Thanks for your feedback.
How satisfied are you with this reply?
Thanks for your feedback, it helps us improve the site.
How satisfied are you with this reply?
Thanks for your feedback.
2 people found this reply helpful
Was this reply helpful?
Sorry this didn’t help.
Great! Thanks for your feedback.
How satisfied are you with this reply?
Thanks for your feedback, it helps us improve the site.
How satisfied are you with this reply?
Thanks for your feedback.
Was this reply helpful?
Sorry this didn’t help.
Great! Thanks for your feedback.
How satisfied are you with this reply?
Thanks for your feedback, it helps us improve the site.
How satisfied are you with this reply?
Thanks for your feedback.
1 person found this reply helpful
Was this reply helpful?
Sorry this didn’t help.
Great! Thanks for your feedback.
How satisfied are you with this reply?
Thanks for your feedback, it helps us improve the site.
How satisfied are you with this reply?
Thanks for your feedback.
I have a dell studio 1747 win 7 ultimate sp1. I cannot get past the loading windows . when choosing win repair it runs and says win cannot repair try system restore, then that fails saying I have no restore points.
I have tried starting in safe mode / networking but it does not load and hangs up on loading windows files and drivers. this all happened after having to shut it down by power button after coming from sleep mode.
I use Norton 360 for security and have noticed it recently makes the pc very hot and it will also not run IE11 without crashing it.
Was this reply helpful?
Sorry this didn’t help.
Great! Thanks for your feedback.
How satisfied are you with this reply?
Thanks for your feedback, it helps us improve the site.
How satisfied are you with this reply?
Thanks for your feedback.
Check if the Laptop fan is working fine. Move the laptop near to a fan or cool place and check if it freezes.
Perform a hard reset and check if it helps.
- Turn off the computer.
- Disconnect all peripheral devices and remove all USB devices and media cards.
- Disconnect the AC power adapter and remove the battery.
- Press and hold the power button for at least 15 seconds.
- Reconnect the AC power adapter, but do not connect the battery.
If the above does not help, perform startup repair using Windows 7 reinstallation disk.
Refer to the suggestions from this link.
Keep us posted on the status of the issue.
Was this reply helpful?
Sorry this didn’t help.
Great! Thanks for your feedback.
How satisfied are you with this reply?
Thanks for your feedback, it helps us improve the site.
Advanced troubleshooting for Stop error or blue screen error issue
If you’re not a support agent or IT professional, you’ll find more helpful information about Stop error («blue screen») messages in Troubleshoot blue screen errors.
What causes Stop errors?
A Stop error is displayed as a blue screen that contains the name of the faulty driver, such as any of the following example drivers:
There is no simple explanation for the cause of Stop errors (also known as blue screen errors or bug check errors). Many different factors can be involved. However, various studies indicate that Stop errors usually are not caused by Microsoft Windows components. Instead, these errors are generally related to malfunctioning hardware drivers or drivers that are installed by third-party software. This includes video cards, wireless network cards, security programs, and so on.
Our analysis of the root causes of crashes indicates the following:
- 70 percent are caused by third-party driver code
- 10 percent are caused by hardware issues
- 5 percent are caused by Microsoft code
- 15 percent have unknown causes (because the memory is too corrupted to analyze)
The root cause of Stop errors is never a user-mode process. While a user-mode process (such as Notepad or Slack) may trigger a Stop error, it is merely exposing the underlying bug which is always in a driver, hardware, or the OS.
General troubleshooting steps
To troubleshoot Stop error messages, follow these general steps:
Review the Stop error code that you find in the event logs. Search online for the specific Stop error codes to see whether there are any known issues, resolutions, or workarounds for the problem.
As a best practice, we recommend that you do the following:
Make sure that you install the latest Windows updates, cumulative updates, and rollup updates. To verify the update status, refer to the appropriate update history for your system:
Make sure that the BIOS and firmware are up-to-date.
Run any relevant hardware and memory tests.
Run the Machine Memory Dump Collector Windows diagnostic package. This diagnostic tool is used to collect machine memory dump files and check for known solutions.
Run Microsoft Safety Scanner or any other virus detection program that includes checks of the Master Boot Record for infections.
Make sure that there is sufficient free space on the hard disk. The exact requirement varies, but we recommend 10–15 percent free disk space.
Contact the respective hardware or software vendor to update the drivers and applications in the following scenarios:
The error message indicates that a specific driver is causing the problem.
You are seeing an indication of a service that is starting or stopping before the crash occurred. In this situation, determine whether the service behavior is consistent across all instances of the crash.
You have made any software or hardware changes.
If there are no updates available from a specific manufacturer, it is recommended that you disable the related service.
You may also want to consider the option of rolling back changes or reverting to the last-known working state. For more information, see Roll Back a Device Driver to a Previous Version.
Memory dump collection
To configure the system for memory dump files, follow these steps:
Extract the .zip file and navigate to Source Code folder.
Run the tool DumpConfigurator.hta, and then select Elevate this HTA.
Select Auto Config Kernel.
Restart the computer for the setting to take effect.
Stop and disable Automatic System Restart Services (ASR) to prevent dump files from being written.
If the server is virtualized, disable auto reboot after the memory dump file is created. This lets you take a snapshot of the server in-state and also if the problem recurs.
The memory dump file is saved at the following locations:
| Dump file type | Location |
|---|---|
| (none) | %SystemRoot%\MEMORY.DMP (inactive, or grayed out) |
| Small memory dump file (256 kb) | %SystemRoot%\Minidump |
| Kernel memory dump file | %SystemRoot%\MEMORY.DMP |
| Complete memory dump file | %SystemRoot%\MEMORY.DMP |
| Automatic memory dump file | %SystemRoot%\MEMORY.DMP |
| Active memory dump file | %SystemRoot%\MEMORY.DMP |
You can use the Microsoft DumpChk (Crash Dump File Checker) tool to verify that the memory dump files are not corrupted or invalid. For more information, see the following video:
More information on how to use Dumpchk.exe to check your dump files:
Pagefile Settings
Memory dump analysis
Finding the root cause of the crash may not be easy. Hardware problems are especially difficult to diagnose because they may cause erratic and unpredictable behavior that can manifest itself in various symptoms.
When a Stop error occurs, you should first isolate the problematic components, and then try to cause them to trigger the Stop error again. If you can replicate the problem, you can usually determine the cause.
You can use the tools such as Windows Software Development KIT (SDK) and Symbols to diagnose dump logs. The next section discusses how to use this tool.
Advanced troubleshooting steps
Advanced troubleshooting of crash dumps can be very challenging if you are not experienced with programming and internal Windows mechanisms. We have attempted to provide a brief insight here into some of the techniques used, including some examples. However, to really be effective at troubleshooting a crash dump, you should spend time becoming familiar with advanced debugging techniques. For a video overview, see Advanced Windows Debugging and Debugging Kernel Mode Crashes and Hangs. Also see the advanced references listed below.
Advanced debugging references
Debugging steps
Verify that the computer is set up to generate a complete memory dump file when a crash occurs. See the steps here for more information.
Locate the memory.dmp file in your Windows directory on the computer that is crashing, and copy that file to another computer.
On the other computer, download the Windows 10 SDK.
Start the install and choose Debugging Tools for Windows. This installs the WinDbg tool.
Open the WinDbg tool and set the symbol path by clicking File and then clicking Symbol File Path.
If the computer is connected to the Internet, enter the Microsoft public symbol server (https://msdl.microsoft.com/download/symbols) and click OK. This is the recommended method.
If the computer is not connected to the Internet, you must specify a local symbol path.
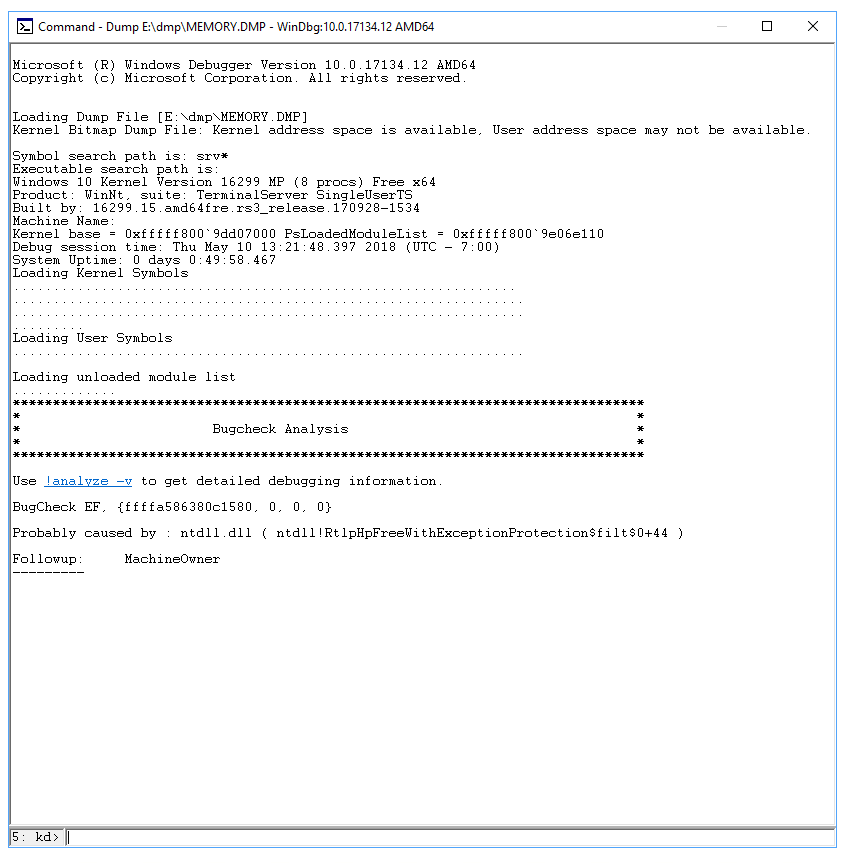
Click on Open Crash Dump, and then open the memory.dmp file that you copied. See the example below.
There should be a link that says !analyze -v under Bugcheck Analysis. Click that link. This will enter the command !analyze -v in the prompt at the bottom of the page.
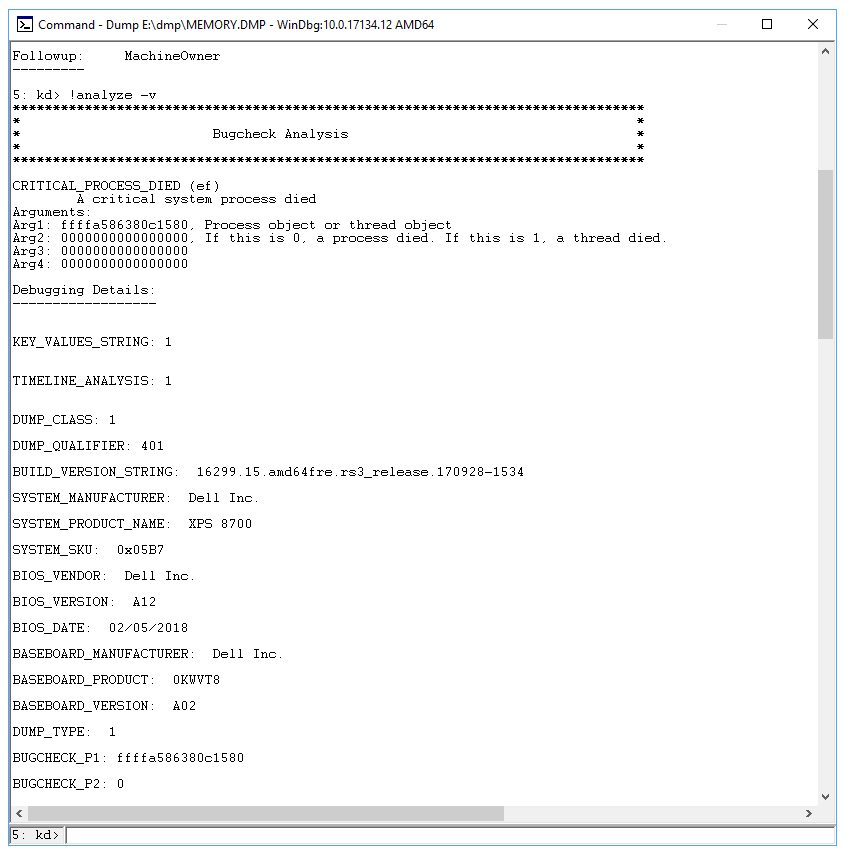
A detailed bugcheck analysis will appear. See the example below.
Scroll down to the section where it says STACK_TEXT. There will be rows of numbers with each row followed by a colon and some text. That text should tell you what DLL is causing the crash and if applicable what service is crashing the DLL.
See Using the !analyze Extension for details about how to interpret the STACK_TEXT output.
There are many possible causes of a bugcheck and each case is unique. In the example provided above, the important lines that can be identified from the STACK_TEXT are 20, 21, and 22:
(HEX data is removed here and lines are numbered for clarity)
The problem here is with mpssvc which is a component of the Windows Firewall. The problem was repaired by disabling the firewall temporarily and then resetting firewall policies.
Additional examples are provided in the Debugging examples section at the bottom of this article.
Video resources
The following videos illustrate various troubleshooting techniques for analyzing dump files.
Advanced troubleshooting using Driver Verifier
We estimate that about 75 percent of all Stop errors are caused by faulty drivers. The Driver Verifier tool provides several methods to help you troubleshoot. These include running drivers in an isolated memory pool (without sharing memory with other components), generating extreme memory pressure, and validating parameters. If the tool encounters errors in the execution of driver code, it proactively creates an exception to let that part of the code be examined further.
Driver Verifier consumes lots of CPU and can slow down the computer significantly. You may also experience additional crashes. Verifier disables faulty drivers after a Stop error occurs, and continues to do this until you can successfully restart the system and access the desktop. You can also expect to see several dump files created.
Don’t try to verify all the drivers at one time. This can degrade performance and make the system unusable. This also limits the effectiveness of the tool.
Use the following guidelines when you use Driver Verifier:
Test any “suspicious” drivers (drivers that were recently updated or that are known to be problematic).
If you continue to experience non-analyzable crashes, try enabling verification on all third-party and unsigned drivers.
Enable concurrent verification on groups of 10–20 drivers.
Additionally, if the computer cannot boot into the desktop because of Driver Verifier, you can disable the tool by starting in Safe mode. This is because the tool cannot run in Safe mode.
For more information, see Driver Verifier.
Common Windows Stop errors
This section doesn’t contain a list of all error codes, but since many error codes have the same potential resolutions, your best bet is to follow the steps below to troubleshoot your error.
The following table lists general troubleshooting procedures for common Stop error codes.
| Stop error message and code | Mitigation |
|---|---|
| VIDEO_ENGINE_TIMEOUT_DETECTED or VIDEO_TDR_TIMEOUT_DETECTED Stop error code 0x00000141, or 0x00000117 | Contact the vendor of the listed display driver to get an appropriate update for that driver. |
| DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL Stop error code 0x0000000D1 | Apply the latest updates for the driver by applying the latest cumulative updates for the system through the Microsoft Update Catalog website.Update an outdated NIC driver. Virtualized VMware systems often run “Intel(R) PRO/1000 MT Network Connection” (e1g6032e.sys). This driver is available at http://downloadcenter.intel.com. Contact the hardware vendor to update the NIC driver for a resolution. For VMware systems, use the VMware integrated NIC driver (types VMXNET or VMXNET2 , VMXNET3 can be used) instead of Intel e1g6032e.sys. |
| PAGE_FAULT_IN_NONPAGED_AREA Stop error code 0x000000050 | If a driver is identified in the Stop error message, contact the manufacturer for an update.If no updates are available, disable the driver, and monitor the system for stability. Run Chkdsk /f /r to detect and repair disk errors. You must restart the system before the disk scan begins on a system partition. Contact the manufacturer for any diagnostic tools that they may provide for the hard disk subsystem. Try to reinstall any application or service that was recently installed or updated. It’s possible that the crash was triggered while the system was starting applications and reading the registry for preference settings. Reinstalling the application can fix corrupted registry keys.If the problem persists, and you have run a recent system state backup, try to restore the registry hives from the backup. |
| SYSTEM_SERVICE_EXCEPTION Stop error code c000021a | Use the System File Checker tool to repair missing or corrupted system files. The System File Checker lets users scan for corruptions in Windows system files and restore corrupted files. For more information, see Use the System File Checker tool. |
| NTFS_FILE_SYSTEM Stop error code 0x000000024 | This Stop error is commonly caused by corruption in the NTFS file system or bad blocks (sectors) on the hard disk. Corrupted drivers for hard disks (SATA or IDE) can also adversely affect the system’s ability to read and write to disk. Run any hardware diagnostics that are provided by the manufacturer of the storage subsystem. Use the scan disk tool to verify that there are no file system errors. To do this, right-click the drive that you want to scan, select Properties, select Tools, and then select the Check now button.We also suggest that you update the NTFS file system driver (Ntfs.sys), and apply the latest cumulative updates for the current operating system that is experiencing the problem. |
| KMODE_EXCEPTION_NOT_HANDLED Stop error code 0x0000001E | If a driver is identified in the Stop error message, disable or remove that driver. Disable or remove any drivers or services that were recently added. If the error occurs during the startup sequence, and the system partition is formatted by using the NTFS file system, you might be able to use Safe mode to disable the driver in Device Manager. To do this, follow these steps: |