- How to Copy All Files from a Directory to another Directory in Linux
- How to Copy Files with “cp” Command in Linux:
- Copy a file with the same name:
- Copy a file with a different name:
- Copy Multiple Files with “cp” Command:
- How to Copy files with the “rsync” command in Linux:
- Conclusion:
- About the author
- Wardah Batool
- Linux Copy File Command [ cp Command Examples ]
- cp Command Syntax
- Linux Copy File Examples
- Copy a file to another directory
- Verbose option
- Preserve file attributes
- Copying all files
- Recursive copy
- Linux copy file command with interactive option
- Verbose output with cp command
- Conclusion
- How to Copy files and folders in Linux
- What is cp command?
- Common syntax for cp command:
- Common options for cp command:
- 1) Copying files with cp command
- 2) Copying files with a different name
- 3) Copying multiple files in Linux
- 4) How to copy directories recursively
- 5) Copying multiple directories recursively
- 6) Copying specific format files in Linux
- 7) Copying all files at once in Linux
- 8) How to copy hidden files (‘.’ dot files) in Linux
- 9) Backup the file with cp command
- 10) Copying files with attributes
- 11) How to avoid file overwriting with cp command?
- 12) Prompting confirmation with cp command
- 13) Copying link files in Linux
- Conclusion:
How to Copy All Files from a Directory to another Directory in Linux
Sometimes, we need to copy the files or folders rather than having a backup program. The files can be copied with the same name, or you can change the name as well.
Copying a file, folder, or directory is a simple and basic task in the Linux operating system. Rename, delete or copy commands are used as daily purpose operations while working with the command-line interface.
Although there are multiple commands to copying the files, the “cp” and “rsync” command are widely used simplest approaches.
How to Copy Files with “cp” Command in Linux:
The “cp” command is one of the commonly used commands to perform the copy operation. You can copy files or folders from source to destination, i-e, one directory through this command.
The syntax of the “cp” command is:
Let’s take a look at an example to understand the “cp” command tool better.
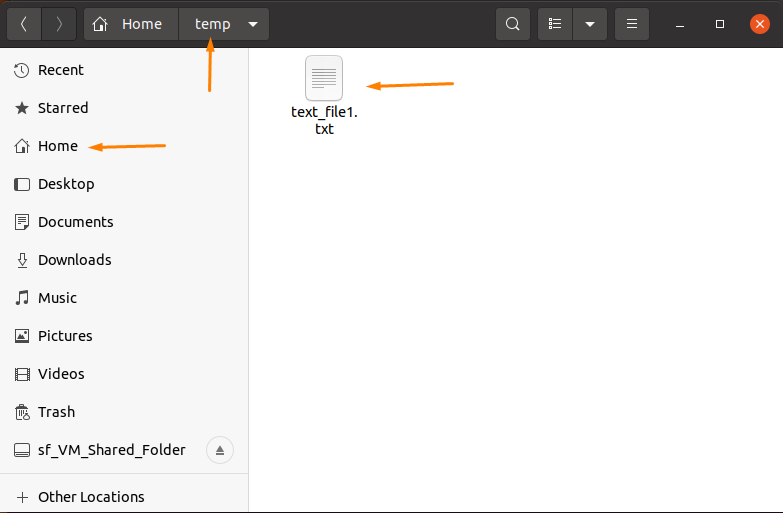
In the home directory, create a “temp” folder with the text file named “text_file1.txt” and add random content to it.
Copy a file with the same name:
To copy a “text_file1.txt” file directory with the same name, open the terminal and type the mentioned “cp” command with the right path.
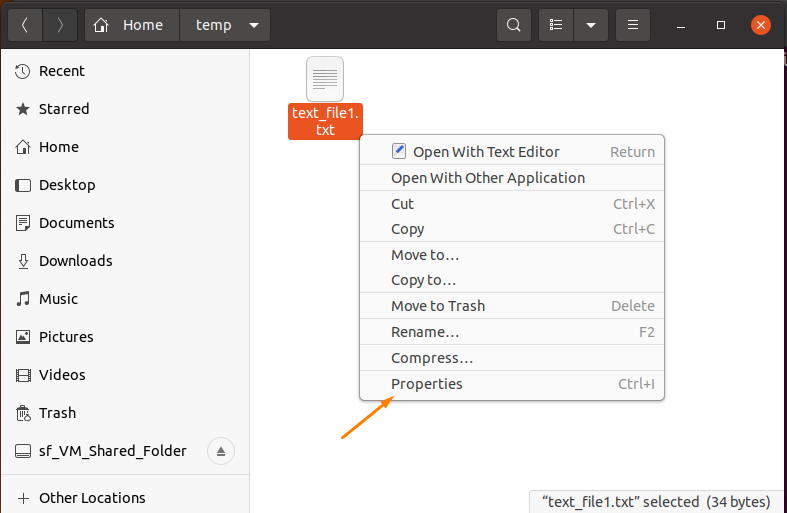
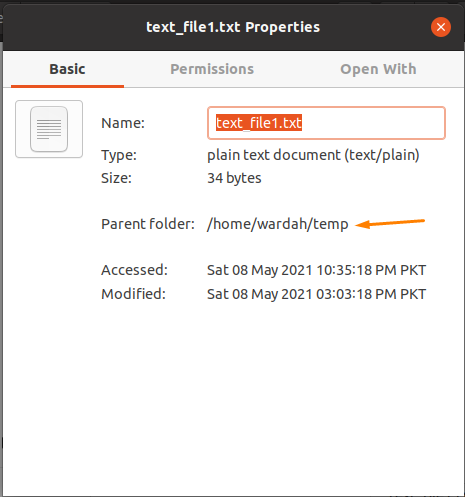
Get the folder’s path by right-clicking on the file and navigate to the “Properties” option (it is the easy way to get the path link).
A dialogue box will open with the complete path of a text file:
Use this path with the “cp” command to copy file:
This command will copy the “text_file1.txt” file to the “temp2” folder.
To verify it, type the “ls” command in the terminal:
Copy a file with a different name:
To copy the file in the current working directory with the different name, type the following “cp” command with file location:
Verify it using the “ls” command”:
Copy Multiple Files with “cp” Command:
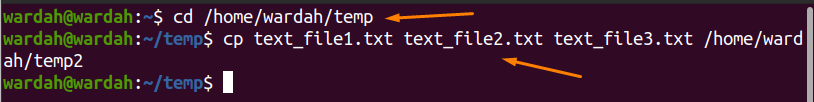
To copy multiple files with the “cp” command, navigate the terminal to the directory where files are saved and then run the “cp” command with the file names you want to copy and the destination path.
$ cd / home / wardah / temp
$ cp text_file1.txt text_file2.txt text_file3.txt / home / wardah / temp2
Run the mentioned command to verify if files are copied successfully:
Above mentioned scenarios are how to copy a single or selected file in a directory. Now, use the wildcard character (*) to copy present files of one directory to any other specific directory.
Let’s check how it works:
Run the “ls” command to check how many files exist in the temp directory:
Instead of mentioning all file names in the terminal, use the wildcard (*) with the directory path to copy all the files into destination:
Now, run the “ls” command again to check if all files are copied in the “temp2” directory:
How to Copy files with the “rsync” command in Linux:
The “rsync” command is another versatile Linux tool to synchronize and copy files and directories locally as well as remotely.
The syntax of the “rsync” command is to copy files is:
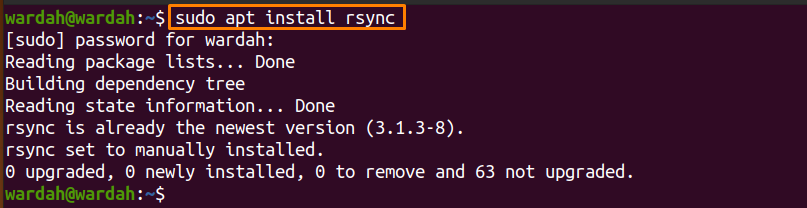
It is a pre-built tool in many Linux distribution. However, if you don’t get it on your system, install it by executing the following command:
To copy a file from one place to another, run the following command:
To confirm, type:
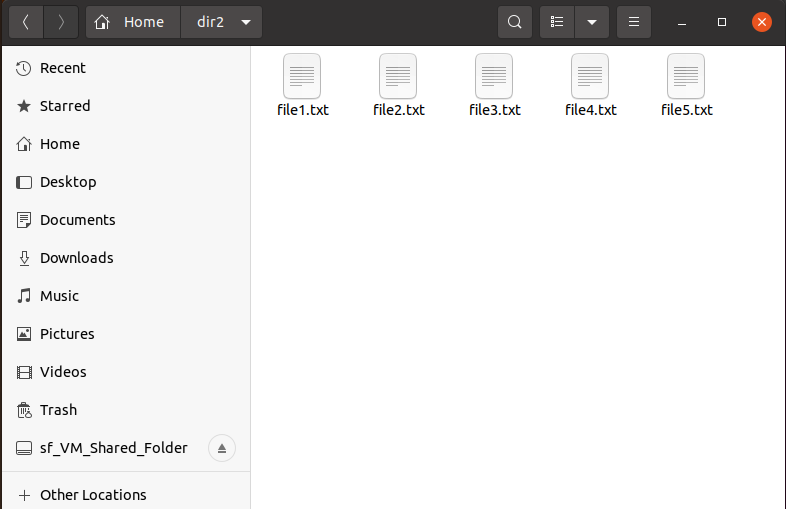
To copy all the directory files to another location, the command would be:
(The “-a” with the “rsync” command is used to copy directories recursively)
Here are the two concepts:
If you add a trailing slash (/) with the path, it will copy the content of the source directory to the destination directory, just like shown in the image:
But, if you don’t add it, it will copy the source directory inside the destination directory, like:
The above command will copy a “dir1” directory to the “dir2” directory.
Conclusion:
Copying a file or directory is the basic command one can operate. One can use it multiple times while using Linux operating system.
This guide has seen the two simplest approaches, the “cp” command and the “rsync” command. Using these commands, we have learned how to copy a single file, multiple files, and even copy one directory to another.
About the author
Wardah Batool
I am a Software Engineer Graduate and Self Motivated Linux writer. I also love to read latest Linux books. Moreover, in my free time, i love to read books on Personal development.
Источник
Linux Copy File Command [ cp Command Examples ]
cp Command Syntax
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | No |
| Requirements | Terminal app/Shell prompt |
| Est. reading time | 3 mintues |
The syntax is as follows to copy files and directories using the cp command:
cp SOURCE DEST
cp SOURCE DIRECTORY
cp SOURCE1 SOURCE2 SOURCE3 SOURCEn DIRECTORY
cp [OPTION] SOURCE DEST
cp [OPTION] SOURCE DIRECTORY
Where,
- In the first and second syntax you copy SOURCE file to DEST file or DIRECTORY.
- In the third syntax you copy multiple SOURCE(s) (files) to DIRECTORY.
Note: You need to type the cp command at the dollar sign ($) prompt. This prompt means that the shell is ready to accept your typed commands. Do not type the dollar ($) sign. You need to open the Terminal app to use cp command on a Linux.
Linux Copy File Examples
To make a copy of a file called file.doc in the current directory as newfile.doc, enter:
$ cp file.doc newfile.doc
$ ls -l *.doc
Sample outputs:
You can copy multiple files simultaneously into another directory. In this example, copy the files named main.c, demo.h and lib.c into a directory named backup:
$ cp main.c demo.h libc. backup
If backup is located in /home/project, enter:
$ cp main.c demo.h libc. /home/project backup
Copy a file to another directory
To copy a file from your current directory into another directory called /tmp/, enter:
$ cp filename /tmp
$ ls /tmp/filename
$ cd /tmp
$ ls
$ rm filename
Verbose option
To see files as they are copied pass the -v option as follows to the cp command:
Preserve file attributes
To copy a file to a new file and preserve the modification date, time, and access control list associated with the source file, enter:
$ cp -p file.txt /dir1/dir2/
$ cp -p filename /path/to/new/location/myfile
This option ( -p ) forces cp to preserve the following attributes of each source file in the copy as allowed by permissions:
- Modification time/date
- Access time
- File flags
- File mode
- User ID (UID)
- Group ID (GID)
- Access Control Lists (ACLs)
- Extended Attributes (EAs)
Copying all files
The star wildcard represents anything i.e. all files. To copy all the files in a directory to a new directory, enter:
$ cp * /home/tom/backup
The star wildcard represents anything whose name ends with the .doc extension. So, to copy all the document files (*.doc) in a directory to a new directory, enter:
$ cp *.doc /home/tom/backup
Recursive copy
To copy a directory, including all its files and subdirectories, to another directory, enter (copy directories recursively):
$ cp -R * /home/tom/backup
Linux copy file command with interactive option
You can get prompt before overwriting file. For example, if it is desired to make a copy of a file called foo and call it bar and if a file named bar already exists, the following would prompt the user prior to replacing any files with identical names:
cp -i foo bar
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Verbose output with cp command
If you pass the -v to the cp, it makes tells about what is going on. That is verbose output:
cp -v file1 file2
cp -avr dir2 /backups/
Conclusion
This page explained cp command that is used for copying files under Linux and Unix-like systems. For more info see man pages: ls(1).
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
How to Copy files and folders in Linux
Being a Linux user, copying files and directories is one of the most common tasks.
Linux users don’t spend a day without using the cp (copy) command according to my personal experience. cp command is used to copy a single file or group of files or directory.
To perform the copy operation, you must have at least read permission in the source file and write permission in the target directory.
In this article, we will explain how to use the cp command.
To perform remote file copy, use the commands such as rsync command or scp command or pscp command.
What is cp command?
‘cp’ command is one of the basic and most widely used Linux commands for copying files and directories from one location to another.
When copying files from source to destination, the source file remains the same and the target file may have the same or different name.
Common syntax for cp command:
Common options for cp command:
| Options | Description |
|---|---|
| -v | Verbose mode (Show progress) |
| -r/R | Copy directories recursively |
| -n | Don’t overwrite an existing file |
| -d | Copy a link file |
| -i | Prompt before overwrite |
| -p | Preserve the specified attributes |
| -b | Make a backup of each existing destination file |
To demonstrate file copy operation in detail, we will be performing a copy operation between user1 and user2 .
1) Copying files with cp command
Use the following command to copy a file from one location to another.
In the following example, we will copy the source file “/home/user1/cp-demo.txt” to the target directory “/home/user2” with the same name:
You can check whether the specific file is copied to the target directory using the ls command as shown below:
2) Copying files with a different name
Use the following command to copy a file from one place to another with a different name. You need to give a new name to the target file.
In the following example, we will copy a file named “/home/user1/cp-demo.txt” to the target directory with a new name “/home/user2/cp-demo11.txt” :
Use the ls command to verify this:
3) Copying multiple files in Linux
The following cp command copies multiple files from one location to another.
In this example, we will copy the following three files named “cp-demo.txt, cp-demo-1.txt and cp-demo-9.txt” to the target.
No additional option is required to copy multiple files, and the file name(s) must be separated with a space as shown below:
Use the ls command to verify the copied files. You should see them in the target directory as shown below:
4) How to copy directories recursively
To copy a directory recursively from one location to another, use the -r/R option with the cp command. It copies everything, including all its files and subdirectories.
In the following example, we will copy the ‘/home/user1/cp-demo-folder’ directory to ‘/home/user2/’ and the target directory name will remain the same:
Use the ls command to verify the outcome. You should see them in the target directory as shown below:
5) Copying multiple directories recursively
Use the following command to copy multiple directories at once. In the following example, we will copy the public_html & public_ftp folders to the target directory named /home/2daygeek/cp-test.
Output can be verified using the ls command:
6) Copying specific format files in Linux
Sometimes you may have to copy files with a specific extension for a certain purpose. If so, you should use the cp command with the «wildcard (*)» option and the file extension name.
In the following example, we will copy all the files containing the *.sh extension from the source to the target directory. Similarly, you can copy any file extensions such as .jpg, .png, .txt, .php, and .html.
This can be verified using the ls command:
7) Copying all files at once in Linux
To copy all the files except the directory from one location to another, use the following cp command with wildcard (*) option.
cp command excludes directories by default, and the -r option must be added to copy them.
In this example, we will copy all the files from ‘/home/user1/’ to ‘/home/user2′ :
Verify the output using the ls command as shown below:
8) How to copy hidden files (‘.’ dot files) in Linux
By default, the cp command does not copy “dot (.)” or ‘hidden’ files in Linux.
Use the following command to copy all types of files, including link files (soft link or hard link), folders and hidden or dot files from source to destination.
This example is very useful to copy user’s home directory which has several hidden files:
You can verify this by using the ls command with the “-a” option:
9) Backup the file with cp command
cp command allows you to backup the file if the same file name exists in the target directory using the —backup option.
In this example, we will copy the /home/user1/passwd-up.sh file to the target directory /home/user2/.
It will backup the “passwd-up.sh” file in the target directory during the copy operation, if you say “yes” when you see the message below:
It adds the “Tilde (
)” symbol at the end of the old file, the same can be verified in the following output.
10) Copying files with attributes
By default, Linux replaces file attributes such as username, group name, date and time when copying files from a user, and does not carry the original file attributes.
To preserve the original attributes of the files, use the -p option with the cp command.
Upon querying we can see that the file “service-1.sh” has retained its original attributes as shown below:
11) How to avoid file overwriting with cp command?
When copying a file, use the -n option with the cp command to avoid overwriting an existing file.
It will only copy the source file, if the target directory does not have a file with the same name. If a duplicate file exists in the target, then the command will run, but won’t make any changes:
Upon querying using the ls command, it can be seen that no action is taken against the file because it still has the old attributes, which can be seen in the above example (refer section 10):
12) Prompting confirmation with cp command
Use the -i option with the cp command to prompt for confirmation before overwriting the file, in case the file exists in the target location.
The following example prompts for confirmation when copying the “cp-demo-9.txt” file because the file already exists in the target directory:
13) Copying link files in Linux
By default, the cp command excludes link files while performing the copy operation. Use the -d option with the cp command to copy the link files as shown below:
It has been successfully copied, and the soft link file can be found in the below output:
Conclusion:
In this tutorial, we have demonstrated 13 methods that are widely used by the Linux administrators in their daily operations. If you would like to explore other options, please visit the man page of the cp command by using the following command:
Источник