- Windows Temporary Files – Everything you want to know
- Windows Temporary Files
- What are Temporary Files in Windows 10
- Why are Temporary Files created
- Temporary Files Location
- Change the location of the Temp folder
- Empty Temporary Files folder
- How to change TEMP folder and allocate free space on your system disk
- Step 1: Create a new folder for Temp files:
- Step 2: Open Environment Variables settings.
- Step 3. Change Environment Variables values.
- Full household PC Protection — Protect up to 3 PCs with NEW Malwarebytes Anti-Malware Premium!
- 3 Comments
- How to create a unique temporary file path in command prompt without external tools? [duplicate]
- 3 Answers 3
- Creating temporary folders
- 13 Answers 13
Windows Temporary Files – Everything you want to know
We have already seen the nature of some temporary files like Temporary Internet Files, Index.dat file, Cookies, and Prefetch Files. In this article, we shall have a look at a few aspects of the Windows Temporary Files, which your computer creates, during the course of its normal running.
Windows Temporary Files
What are Temporary Files in Windows 10
Temporary Files in Windows are those junk files whose use is only temporary and become redundant once the task in hand is completed. Such temporary files are created to hold data temporarily while a file is being created or processed or used.
Why are Temporary Files created
Windows Temporary files are created by the operating system during the normal course of its running when there may not be enough memory allocated for the task.
Software that uses large amounts of data like Graphics, Video, or Media editing software also creates temporary files. Such created temporary files are more often than not, left behind even when the task is over, leading to their wasting disk space.
Temporary Files are also created for backup purposes, by programs. For instance, Microsoft Office saves a Temporary File of the open document every few minutes. If you save the document and exit, the Temporary File gets deleted. If the program crashes unexpectedly, the Temporary File is not deleted. They can thus be useful to help recover lost data if the program or the system crashes.
Ideally, the Temporary Files should get deleted once the program exits. But this is not always the case, leading to wasted disk space.
Temporary Files Location
The Temporary Files in Windows are typically found located in two locations:
- %systemdrive%\Windows\Temp
- %userprofile%\AppData\Local\Temp
If you click on C:\Windows\Temp you will receive a message You don’t currently have permission to access this folder. Click on Continue to do so. You will see that most of its contents are .tmp, .temp and .txt files.
The other folder typically located at C:\Users\username\AppData\Local\Temp, is created for each User. It’s a hidden folder and you will have to first ‘un-hide’ System folders from the Folder Options before you can see it.
The Temporary files created by the Windows operating system are usually stored in the %system%\Windows\Temp folder, whereas the ones created by the User when running any software is stored in his user profile at %userprofiles%\AppData\Local\.
Temporary Files of a particular software may also be located in a sub-folder, inside the parent folder of the particular software.
On rare occasions, a temporary file or a temporary files folder may get created into the root directory of the C (System) drive. You may want to examine the folder in details, and then delete it if you are sure, if it indeed contains temporary files.
Change the location of the Temp folder
If you wish, you can change the location of the Temporary Files folder. To do so, open System Properties via the Control Panel > Environment Variables > Edit the System and/or the User variables as you wish.
But do remember that it is never a good idea to combine the temporary directories together for all the user profiles, for security reasons, since there have been cases of security vulnerabilities with temporary files, due to a particular software’s incorrect file permissions or race conditions.
Empty Temporary Files folder
There are several different ways to delete Temporary Files. You can use freeware junk file cleaners or the in-built Disk Cleanup utility to easily empty the contents of the Temp folders.
Planning to empty the contents of your Windows Installer Folder or WinSxS directory due to its sheer large size!? Think again!
Date: February 5, 2018 Tags: Files, Folder
How to change TEMP folder and allocate free space on your system disk
Last updated on September 28th, 2013
If you are running out of space in your system disk, then an easy solution to allocate free space, is to clear (delete) temporary files that were created from Windows services or programs installed on your computer. The cleaning procedure of these files is a safety operation and you don’t lose any critical files that are needed from your system to operate normally.
Windows uses (minimum) two temporary folders to store all temporary files created by computer usage: The system temporary folder: “C:\Windows\Temp” (that stores all System temporary files) and the user temporary folder that stores temporary files from each user. The user temporary folder is created inside each user’s profile and the full path depends from the operating system installed on the computer:
For Windows 8,7, VIsta OS the user temporary folder path is: %USERPROFILE%\AppData\Local\Temp
For Windows XP the user temporary folder path is: %USERPROFILE%\Local Settings\Temp
Moving the Temporary folder to another location helps you easily find and delete all your temporary files (from inside Temporary folder) and maximize your system disk’s free space. This procedure works better in the case of the existence of a second hard drive on your system.
In this article I’ll show you the way to move the temporary store folders to another disk location.
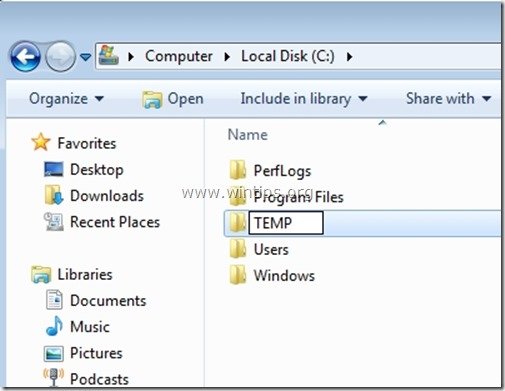
Step 1: Create a new folder for Temp files:
1. Open Windows explorer and create a new folder at the location that you prefer your temporary files to be stored.
(e.g. “C:\TEMP” or “D:\TEMP” if you have a secondary hard disk).
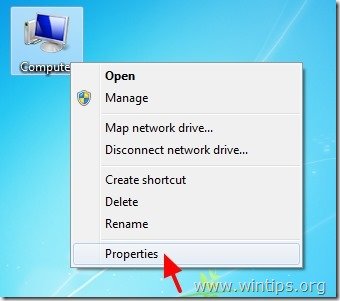
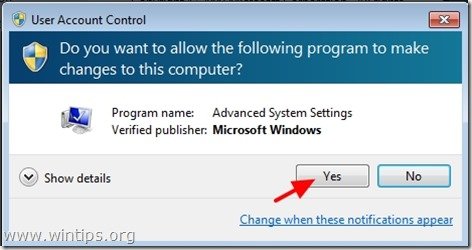
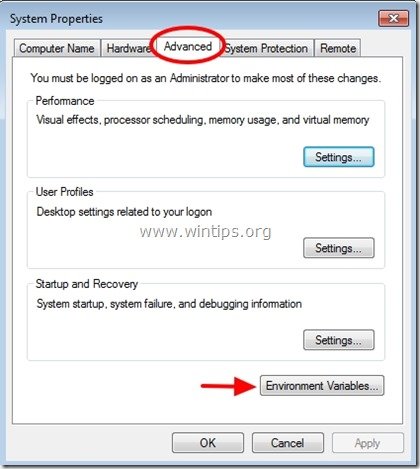
Step 2: Open Environment Variables settings.
1. Right click on the Computer icon and select Properties.
2. Click in Advanced system settings on the left pane.
3. Ask “Yes” on the “UAC Warning” message.
4. Inside Advanced settings click on “Environment Variables”
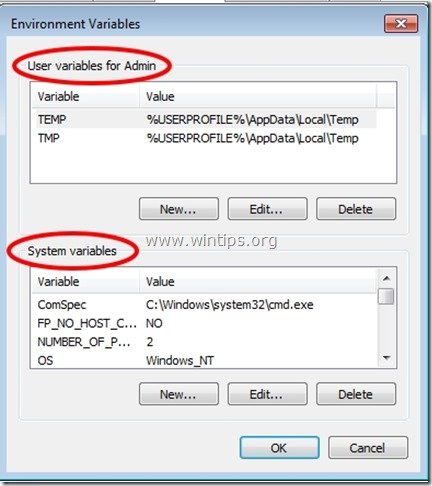
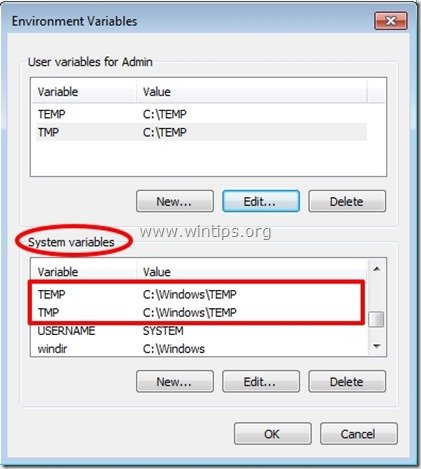
5. Inside Environment Variables you see two sections:
a. User variables for the current user (e.g. Admin)
b. System variables
From here you’ll be able to change the default location for temporary files.
Step 3. Change Environment Variables values.
A. To change current user’s temp files store location:
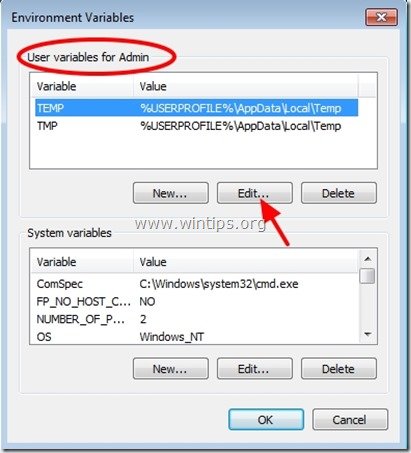
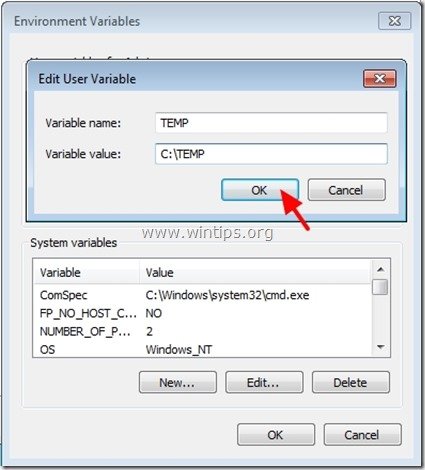
1. Go inside “User variables” section select the “TEMP” variable and press “Edit”.
2. In “Variable Value” box delete the default TEMP location (%USERPROFILE%\AppData\Local\Temp) and then type the new TEMP folder location (e.g. C:\TEMP). Press “OK” when finished.
3. Repeat the same procedure for the “TMP” variable.
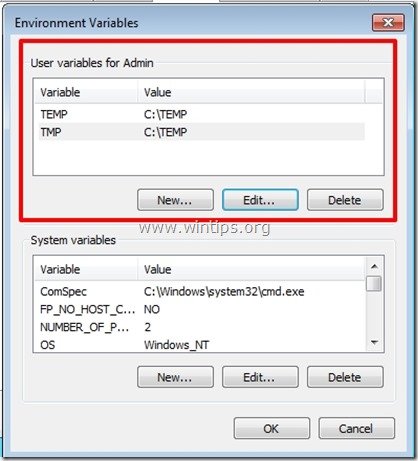
After you have finished, the “User variables” section should be like this:
5. Press “OK” twice and restart your computer for changes to take effect if you don’t want to change System’s Temp store location.
B. To change System’s temp files store location:
1. Go inside “System variables” section and scroll down until you find “TEMP” & “TMP” variables.
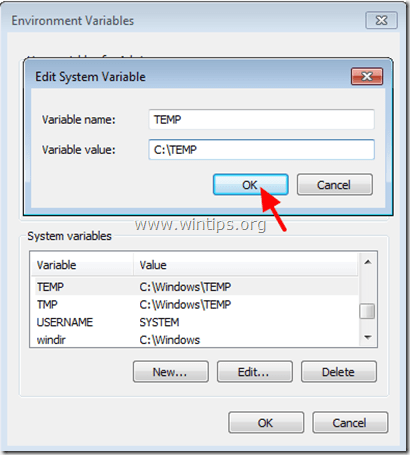
2. Select the “TEMP” variable and press “Edit”.
3. In “Variable Value” box delete the default TEMP location (%SystemRoot%\TEMP) and then type the new SYSTEM TEMP folder location. (e.g. C:\TEMP). Press “OK” when finished.
4. Repeat the same procedure for the “TMP” variable.
After you have finished, the “User variables” section should be like this:
5. Press “OK” twice and restart your computer for changes to take effect.
From now on, you can easily find and safely delete all the contents inside your new TEMP folder and allocate disk space.
Full household PC Protection — Protect up to 3 PCs with NEW Malwarebytes Anti-Malware Premium!
3 Comments
Bruce
February 22, 2018 @ 3:48 pm
Very good information. Can I delete everything in the user\app data\local\temp folder without causing any issues?
lakonst
February 22, 2018 @ 6:34 pm
June
August 22, 2013 @ 5:25 am
Thank you for such a complete step by step explanation. It made it so easy for me and was gratifying when it worked so smoothly.
How to create a unique temporary file path in command prompt without external tools? [duplicate]
I am trying to create the path to a temporary file to be used in a batch file.
There are the environment variables %TEMP% and %TMP% to get the temporary directory for the current user. But how to build a file name that does surely not yet exist?
Of course I can use the built-in variable %RANDOM% and create something like bat
%RANDOM%.tmp , but this method does not ensure that the file is currently inexistent (or that it will be created coincidentally by another application, before I first create it on disk and write to it) — although this all is very unlikely.
I know I could just reduce the probability of such collisions by appending also %DATE% / %TIME% , or by just adding multiple %RANDOM% instances, but this is not what I want.
Note: According to this post, there is a method in .NET ( Path.GetTempFileName() ) which does exactly what I am asking for (besides the wrong programming language obviously).
3 Answers 3
Try next code snippet:
or create procedures
- :uniqGet : create a file of a fix filename template ( bat
%RANDOM%.tmp in your case);
:uniqGetByMask : create a file of a variable filename template. Note quadrupled percent signs of %random% reference in a procedure call: prefix%%%%random%%%%suffix.ext . Also note advanced usage: CALL ing internal commands in call set «_uniqueFileName=%
2″ inside the procedure.
The code could be as follows:
Output:
I suggest you one of two methods. The «technical approach» is to use JScript’s FileSystemObject.GetTempName method. JScript is a programming language that comes pre-installed in all Windows versions from XP on, and its use in Batch via a «Batch-JScript» hybrid script is very simple:
However, the simplest approach is to store a number in a data file and every time that you want a new name, get the number, increment it and store it back in the same file. This will work for «just» 2147483647 times!
Firstly, using a separate folder will significantly reduce the chances of other programs intruding. So lets store the temp file in a private folder that’s really long and specific to prevent any name competition.
When generating the name, you could always use %random% and try generating a name which does not exist, however the more times this operation is use, the more ineffective it becomes. If you plan to use this process 10’s of thousands of times as the random function is limited to 32000 (approximately) your program will spend forever generating random attempts.
The next best approach is to start a counter at one and increase it till you have an unused name. That way you can guarantee your program will eventually find a name in a reasonable amount of time, however again your files will pile up (which is never a good experience)
What some people do (and I would recommend for your situation) is combine these to processes to effectively cut the fat in selecting a name, while using a reliable method (the best of both worlds):
Creating temporary folders
I am working on a program that needs to create a multiple temporary folders for the application. These will not be seen by the user. The app is written in VB.net. I can think of a few ways to do it such as incremental folder name or random numbered folder names, but I was wondering, how other people solve this problem?
13 Answers 13
Update: Added File.Exists check per comment (2012-Jun-19)
Here’s what I’ve used in VB.NET. Essentially the same as presented, except I usually didn’t want to create the folder immediately.
The advantage to use GetRandomFilename is that it doesn’t create a file, so you don’t have to clean up if your using the name for something other than a file. Like using it for folder name.
Random Filename Example:
C:\Documents and Settings\username\Local Settings\Temp\u3z5e0co.tvq
Here’s a variation using a Guid to get the temp folder name.
guid Example:
C:\Documents and Settings\username\Local Settings\Temp\2dbc6db7-2d45-4b75-b27f-0bd492c60496
You have to use System.IO.Path.GetTempFileName()
Creates a uniquely named, zero-byte temporary file on disk and returns the full path of that file.
You can use System.IO.Path.GetDirectoryName(System.IO.Path.GetTempFileName()) to get only the temp folder information, and create your folders in there
They are created in the windows temp folder and that’s consider a best practice
Just to clarify:
returns just the folder path to the temp folder.
returns the fully qualified file name (including the path) so this:
There’s a possible race condition when:
- creating a temp file with GetTempFileName() , deleting it, and making a folder with the same name, or
- using GetRandomFileName() or Guid.NewGuid.ToString to name a folder and creating the folder later
With GetTempFileName() after the delete occurs, another application could successfully create a temp file with the same name. The CreateDirectory() would then fail.
Similarly, between calling GetRandomFileName() and creating the directory another process could create a file or directory with the same name, again resulting in CreateDirectory() failing.
For most applications it’s OK for a temp directory to fail due to a race condition. It’s extremely rare after all. For them, these races can often be ignored.
In the Unix shell scripting world, creating temp files and directories in a safe race-free way is a big deal. Many machines have multiple (hostile) users — think shared web host — and many scripts and applications need to safely create temp files and directories in the shared /tmp directory. See Safely Creating Temporary Files in Shell Scripts for a discussion on how to safely create temp directories from shell scripts.