- How to Create a File in Linux Using Terminal
- Introduction
- Create a file on Linux shell
- 1. Using cat command
- 2. Using touch command
- 3. Using Redirect > operator
- Conclusion
- Karim Buzdar
- 7 Ways to Create a File in Linux Terminal
- 1) Create a file with touch command
- 2) Create a file with cat command
- 3) Create a file with echo command
- 4) Create a file with printf command
- 5) Create a file with nano text editor
- 6) Create a file with vi text editor
- 7) Create a file with vim text editor
- Conclusion
- Как создать файл в терминале
- 1. Редактор nano
- 2. Редактор Vi
- 3. Оператор перенаправления >
- 4. Оператор перенаправления вывода >>
- 5. Оператор перенаправления 2>
- 6. Оператор перенаправления и head
- 7. Команда cp
- 8. touch
- 9. Утилита dd
- Создание специальных файлов в Linux
- Выводы
How to Create a File in Linux Using Terminal
As we all know, Linux is an operating system mainly used by geeks and developers, who are mostly keyboard people and like to write commands instead of using a graphical user interface (GUI). Unlike the Windows operating system, where most of the work is done with a few clicks, Linux has commands for everything, such as basic file manipulation, compression or extraction of files, etc. These commands run on the Linux command line known as the terminal or shell. The terminal or shell is a utility in Linux that is responsible for running the commands. Today, I will introduce various methods that you can use to create a file in Linux using the terminal.
Introduction
In a world where a lot of work has already been put into improving UI/UX and the UI is so much more intuitive and powerful, the command line still has a lot of advantages over the GUI. Typically, Linux is an operating system used in servers and mostly used by technical users, such as developers. Their main requirement is to have more control over the system, need fast performance, scripting capabilities, and much more, which the GUI, unfortunately, cannot provide. In server environments such as data centers, we usually don’t have GUI installed on the servers because the GUI takes a lot of time to load and is basically meant for the end-users. So to be a good technical user, you should have a good command of the shell, also known as the terminal.
Here a few advantages of a command-line interface over graphical user interfaces:
- Control over the system.
- Provide ease for many tasks like rename thousands of files in bulk.
- The ability to use scripts.
- Less memory and faster performance.
Now I am going to share different methods through which you can create a file in Linux.
Create a file on Linux shell
In Linux, there are a lot of commands through which a user can create files. Each command has its own significance. Some of the most used are:
1. Using ‘cat’ command.
2. Using ‘touch’ command.
3. Using redirect ‘>’ symbol
We are going to discuss them one by one.
For this tutorial, I am using the Ubuntu flavor of the Linux Operating system. So the screenshot for the demo purpose will be based on Ubuntu. But all commands are available on other Linux Distributions like Debian and CentOS too.
1. Using cat command
The ‘cat’ command also known as “concatenate” command is one the most frequently used command in Linux OS. There are multiple functionalities of the ‘cat’ command which includes
- Creation of single or multiple files.
- View the content of the file on the command line
- Redirect output of one file on the terminal screen or in another file
However, in this tutorial, we are only focused on the creation of a file. So, let’s see how we can create a file by using ‘cat’ command.
Step 1: First of all, open Terminal by clicking on Ubuntu launcher and search for Terminal.
Step 2: Now click on the Terminal and wait for the terminal to open. Advertisement
Step 3: By default, the terminal is on the ‘home’ location but to verify where the terminal is pointing right now we will use ‘pwd’ command. The ‘pwd’ will return the path to which the terminal is currently pointing. Right now, we are creating a file on the default location to which a terminal is pointing but if you want to create a file in some different location you can change the path by using ‘cd’ change directory command. The general syntax of cd command is “cd ‘path to folder’”.
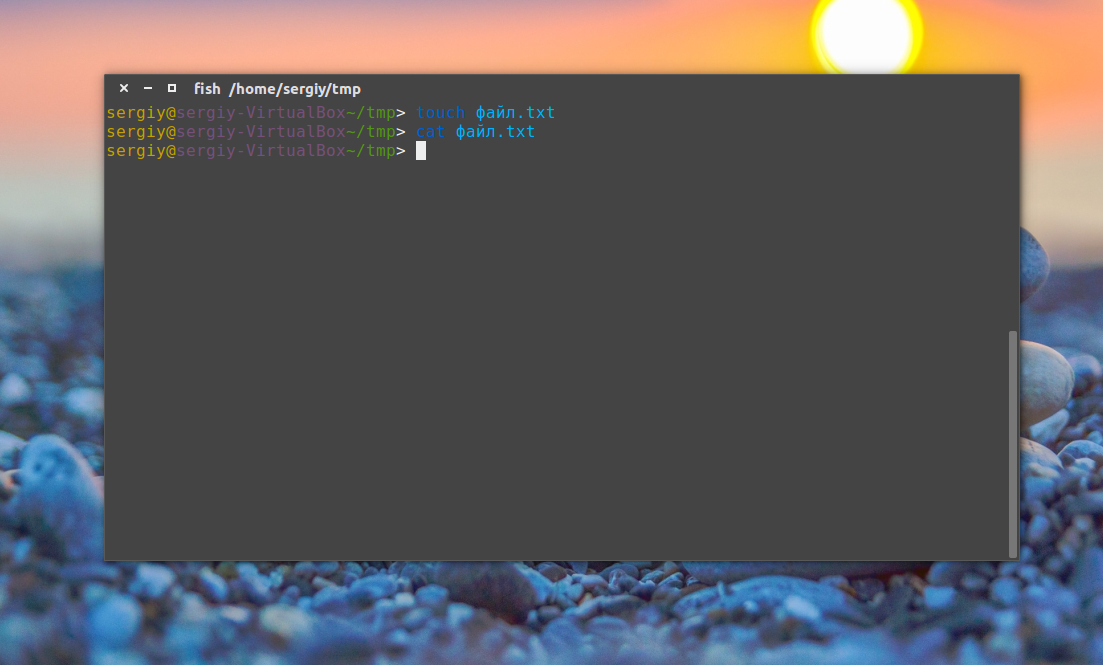
Step 4: Now to create a file write a command “cat > filename.ext” where filename will be the name of your file and ext will be an extension of the file. E.g. in the demo, I’m using dummy.txt
Step 5: Once the command is executed, a text file is created in the default path with the name you have provided. In our case it is the file dummy.txt
Now you can see the cursor is blinking awaits input from the user. Basically, the command is asking to type the desired text you want to write to a file. If you want to keep the file empty just press “ctrl+D” or if you want to write the content to the file, type it and then press “ctrl+D”. The content has been saved to the file and you will be returned to the main terminal.
You can verify the text by opening the file as shown in the screenshot.
Congratulations! Your file has been created with ‘cat’ command.
Note: Before creating a new file make sure that the file is not already created. To ensure this you can use “ls” command.
2. Using touch command
In Linux operating system, every file has timestamp details like the last time the file is accessed or modified etc. Every time the file is accessed or modified this timestamp is updated. The ‘touch’ command is a utility of Linux which is used to create, change or modify the timestamp of the file.
Let’s see how we can create a file by using ‘touch’ command.
Step 1: First of all, open Terminal by clicking on Ubuntu launcher and search for Terminal.
Step 2: Now click on the Terminal and wait for the terminal to open.
Step 3: By default, the terminal is on the ‘home’ location but to verify where the terminal is pointing right now we will use ‘pwd’ command. The ‘pwd’ will return the path to which the terminal is currently pointing. Right now, we are creating a file on the default location to which a terminal is pointing but if you want to create a file in some different location you can change the path by using ‘cd’ change directory command. The general syntax of the cd command is “cd ‘path to folder’”.
Step 4: Now to create a file write a command “touch filename.ext” where filename will be the name of your file and ext will be the extension of the file. E.g. in the demo I’m using dummy.txt. Once the command is executed the terminal will create a file on the path as shown in the following screenshots:
Congratulations! Your file has been created with ‘touch’ command.
Note: Before creating a new file make sure that the file is not already created. To ensure
this you can use “ls” command.
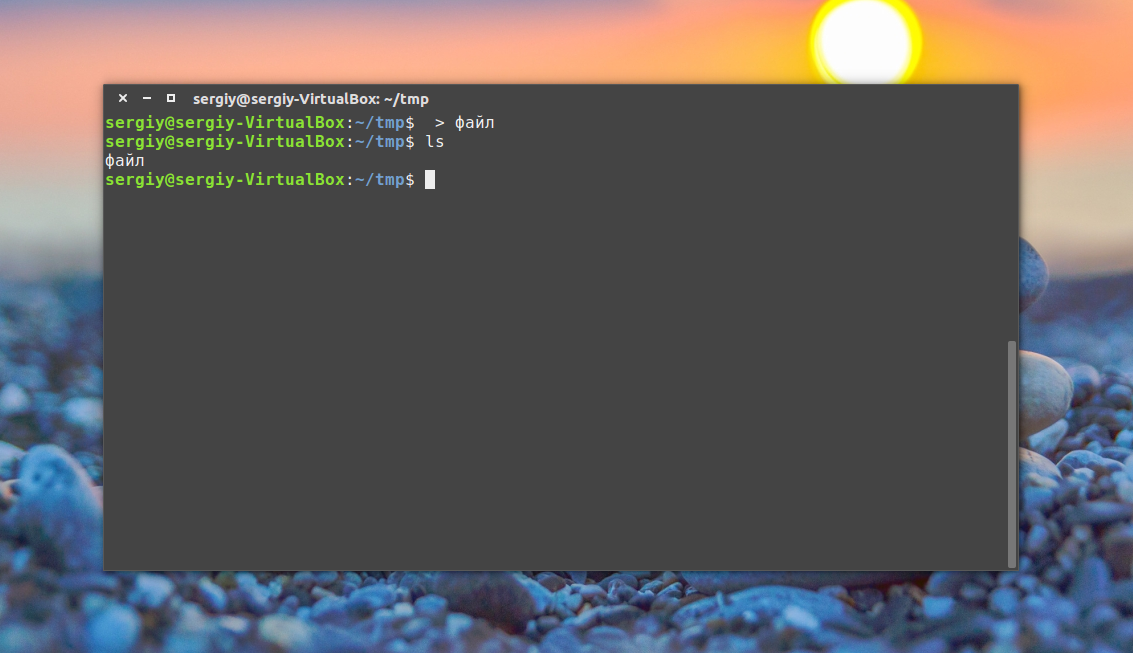
3. Using Redirect > operator
In Linux ‘>’ is known as output redirection operator provides an option to redirect the output of the command to a file instead of the standard terminal screen. We can also use the redirect operator to create a file.
let’s see how we can create a file by using ‘touch’ command.
Step 1: First of all, open Terminal by clicking on Ubuntu launcher and search for Terminal.
Step 2: Now click on the Terminal and wait for the terminal to open.
Step 3: By default, the terminal is on the ‘home’ location but to verify where the terminal is pointing right now we will use ‘pwd’ command. The ‘pwd’ will return the path to which the terminal is currently pointing. Right now, we are creating a file on the default location to which a terminal is pointing but if you want to create a file in some different location you can change the path by using ‘cd’ change directory command. The general syntax of cd command is “cd ‘path to folder’”.
Step 4: Now to create a file write a command “echo “this is a dummy text” > filename.ext” where filename will be the name of your file and ext will be the extension of the file. E.g. in
the demo I’m using dummy.txt. Once the command is executed the terminal will create a file on the path as shown in the following screenshot:
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have discussed the need for a command-line interface, its advantages, and the different methods to create a file in Linux by using the terminal.
Karim Buzdar
About the Author: Karim Buzdar holds a degree in telecommunication engineering and holds several sysadmin certifications. As an IT engineer and technical author, he writes for various web sites. You can reach Karim on LinkedIn
Источник
7 Ways to Create a File in Linux Terminal
In this tutorial, I will show you how to create a file from a Linux terminal. There are many text editors like (vim, nano, vi) and many commands like (cat, echo, printf, touch) to create a file in the Linux operating system via command line. Here will explain the following linux tools.
1) Create a file with touch command
We will use touch command with any extension to create file, this command will create an empty file touch.txt in your current directory as an example below.
To see the file type command below.
2) Create a file with cat command
We will use cat command to create file, this command will create an empty file cat.txt in your current directory as an example below, but you must add text in the file.
Add the text below.
To save the file hit Ctrl + d , and to see the file type command below.
To open the file, we will use cat command to open it.
3) Create a file with echo command
We will use echo command to create file, this command will create a file echo.txt in your current directory as an example below, but you should add text in the line command.
To see the file,type command below.
To open the file, we will use cat command to open it.
4) Create a file with printf command
We will use printf command to create file, this command will create a file printf.txt in your current directory as an example below, but you should add text in the line command.
To see the file type command below.
To open the file, we will use cat command to open it.
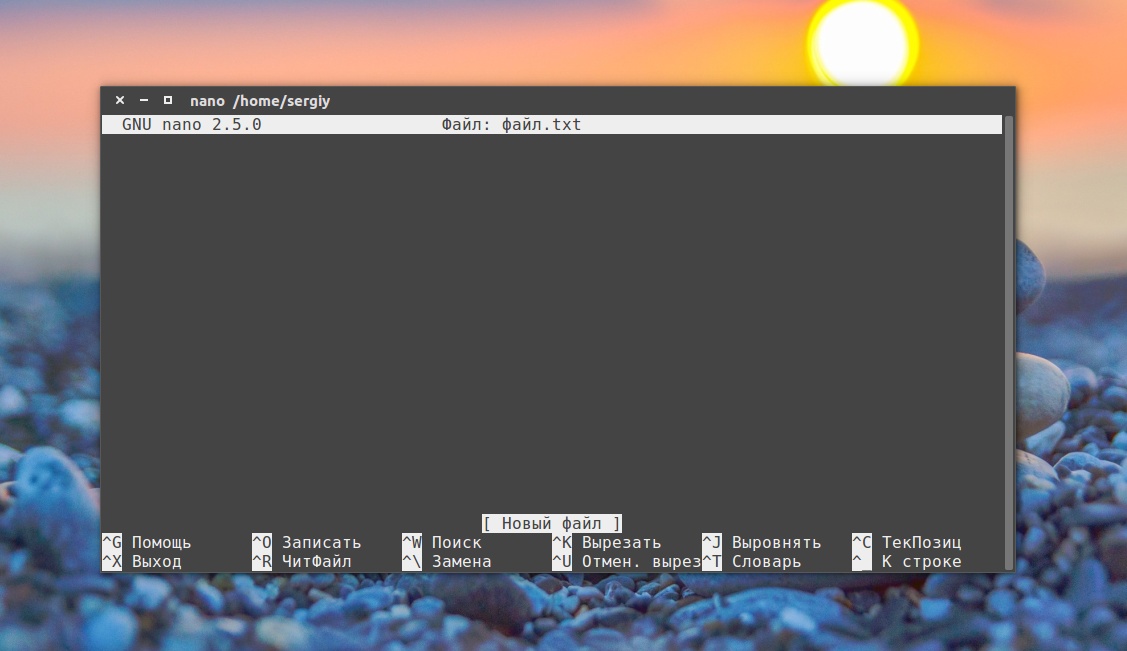
5) Create a file with nano text editor
To create a file using nano text editor, first install it, after that type command below and the text editor will be opened to adding text.
Add the text below.
To save the file type Ctrl + x and type y , to see the file type command below.
To open the file, We will use nano command to open it.
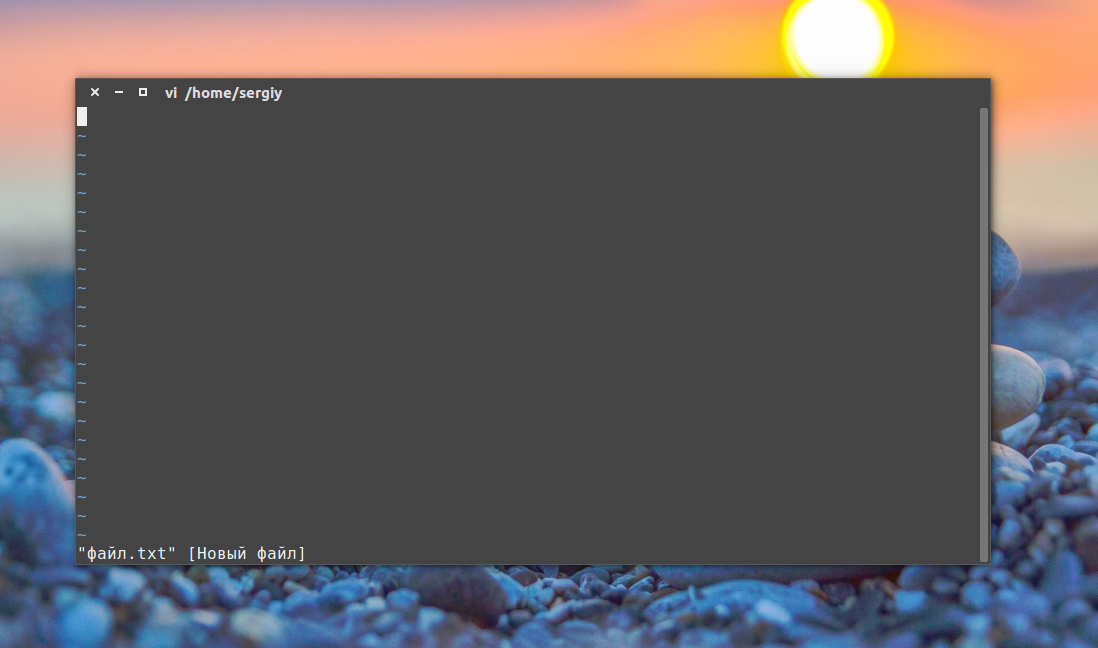
6) Create a file with vi text editor
To create a file using vi text editor, type command below and the text editor will open the file, but you can’t add any text before converting it to insert mode by typing i character.
Add the text below.
To save the file and exit hit Esc after that :wq , To see the file type command below.
To open the file, we will use vi command to open it.
7) Create a file with vim text editor
To create a file using vim text editor, type command below and the text editor will open the file, but you can’t add any text before converting it to insert mode by typing i character.
Add the text below.
To save the file and exit hit Esc after that :wq , to see the file type command below.
To open the file, we will use vim command to open it.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned the different ways to create a file from Linux terminal. Hope you enjoyed reading and please leave your comments in the below comment section.
Источник
Как создать файл в терминале
Философия Linux гласит — всё в системе есть файл. Мы ежедневно работаем с файлами, и программы, которые мы выполняем, — тоже файлы. В разных случаях нам может понадобиться создать в системе файлы определённого типа. Если вам интересно, какие типы файлов в Linux можно создать, смотрите отдельную статью.
Конечно, всё очень просто делается с помощью мышки и файлового менеджера. Но если вы дружите с клавиатурой, создать файл через терминал Linux намного быстрее и, как вы увидите, эффективнее. В терминале вы можете не только создавать пустые файлы, но и создавать файл с уже готовым содержимым, файлы определённого размера, и с нужными метаданными.
Как всё это делать, вы узнаете из этой статьи. Мы рассмотрим все доступные средства создания файлов в терминале Linux. Поехали!
1. Редактор nano
Самый распространённый способ создать текстовый файл в Linux — это использовать консольные текстовые редакторы. Например nano. После ввода команды открывается редактор, и вы прописываете нужный текст, например:
2. Редактор Vi
Тот же принцип, но программа намного серьёзнее:
Если вы в первый раз столкнулись с vim, то предупрежу — это необычный редактор. Здесь есть два режима: режим вставки и командный. Переключаться между ними можно с помощью кнопки Esc. Для выхода из редактора в командном режиме наберите :q, для сохранения файла — :w. Вообще, Vim — очень полезный инструмент. Чтобы узнать побольше о его возможностях и выучить основы, выполните: vimtutor.
Понятное дело, в этом пункте можно говорить и о других редакторах, в том числе и с графическим интерфейсом. Но мы их опустим и перейдём к другим командам создания файла в Linux.
3. Оператор перенаправления >
Это, наверное, самая короткая команда для создания файла в Linux:
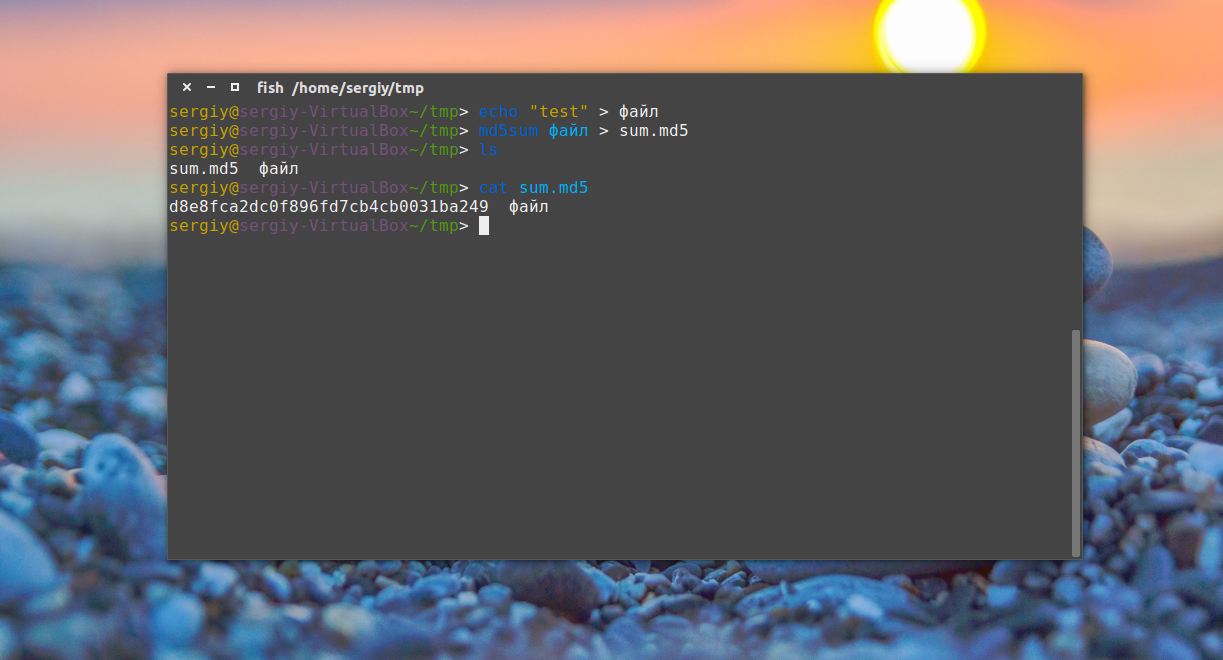
Оператор оболочки для перенаправления вывода позволяет записать вывод любой команды в новый файл. Например, можно подсчитать md5 сумму и создать текстовый файл в Linux с результатом выполнения.
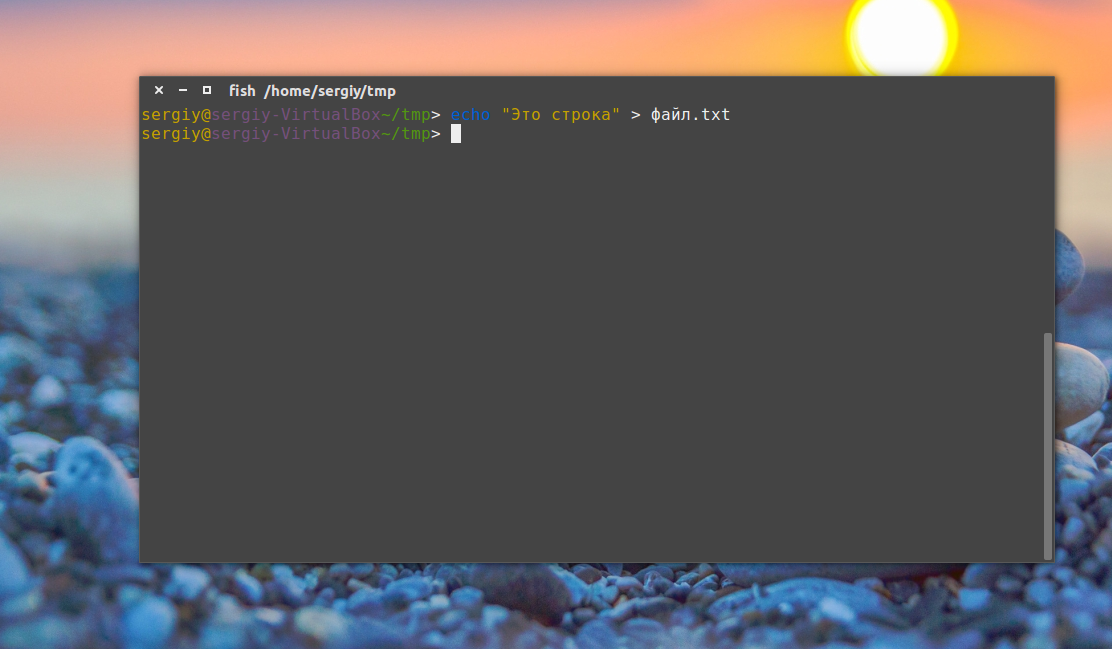
Это рождает ещё несколько способов создания файла в Linux, например, выведем строку в файл с помощью команды echo:
echo «Это строка» > файл.txt
Этот способ часто используется для создания конфигурационных файлов в Linux, так сказать, на лету. Но заметьте, что sudo здесь работать не будет. С правами суперпользователя выполниться echo, а запись файла уже будет выполнять оболочка с правами пользователя, и вы всё равно получите ошибку Access Denied.
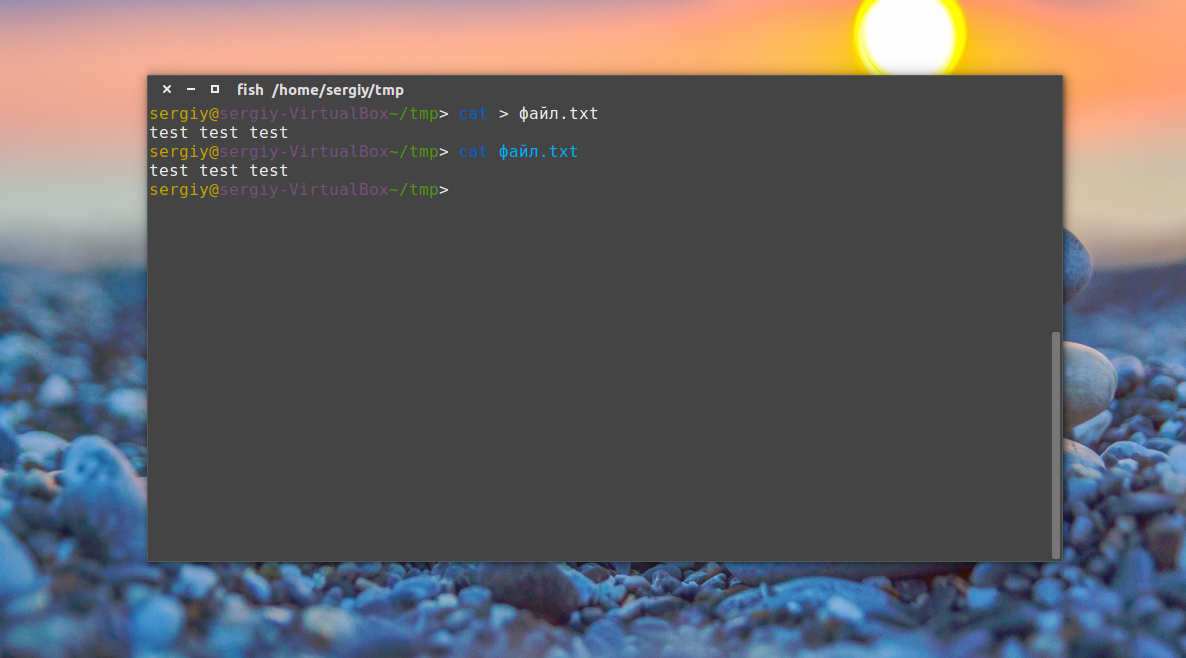
Ещё тем же способом можно сделать примитивный текстовый редактор для создания файла. Утилита cat без параметров принимает стандартный ввод, используем это:
После выполнения команды можете вводить любые символы, которые нужно записать в файл, для сохранения нажмите Ctrl+D.
А ещё есть утилита printf, и здесь она тоже поддерживает форматирование вывода:
printf «Это %d текстовая строка\n» 1 > файл
Этот способ создать файл в Linux используется довольно часто.
4. Оператор перенаправления вывода >>
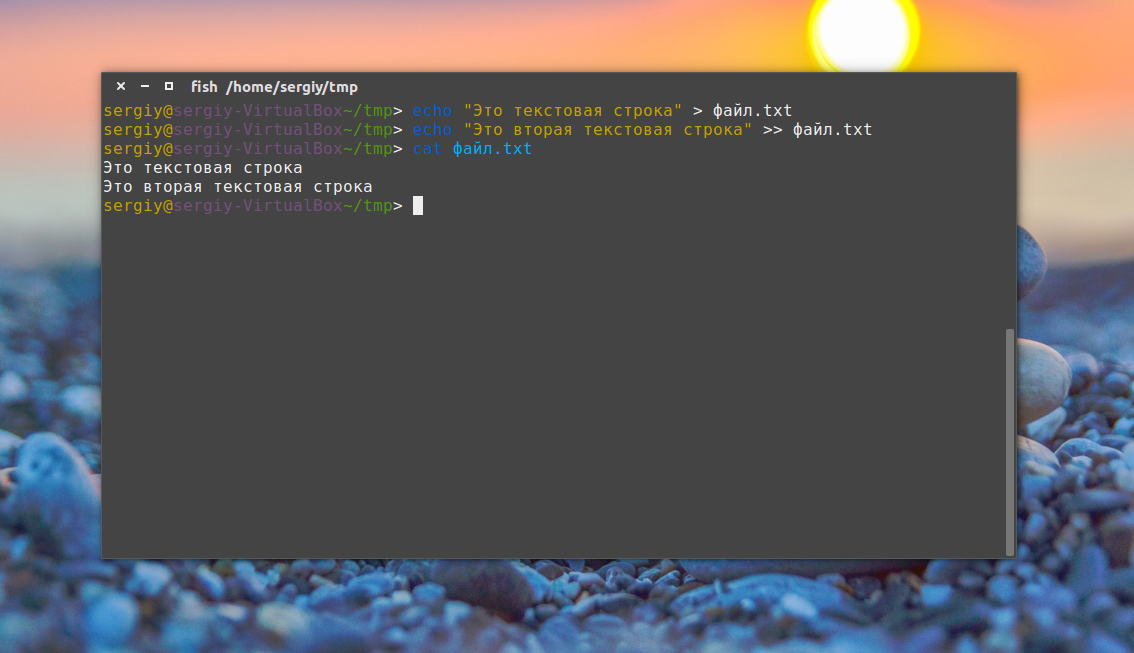
Также можно не только перезаписывать файл, а дописывать в него данные, с помощью перенаправления оператора >>. Если файла не существует, будет создан новый, а если существует, то строка запишется в конец.
echo «Это текстовая строка» > файл.txt
$ echo «Это вторая текстовая строка» >> файл.txt
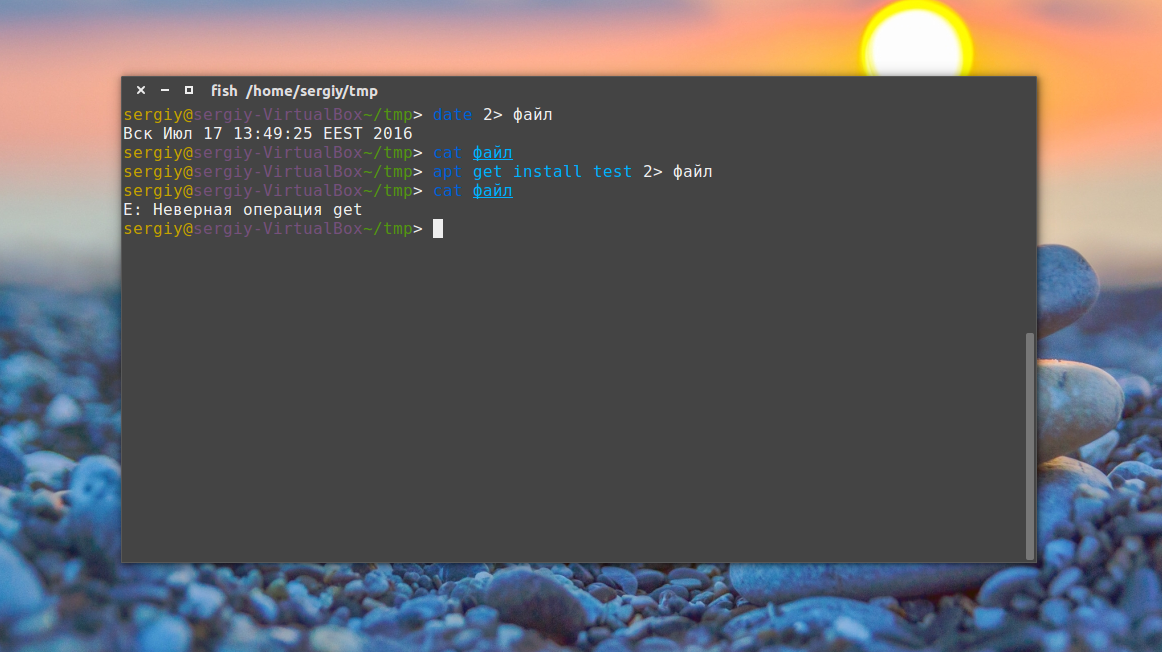
5. Оператор перенаправления 2>
Первые два оператора перенаправления вывода команды в файл использовали стандартный вывод. Но можно создать файл в терминале Ubuntu и перенаправить в него вывод ошибок:
Если команда не выдает ошибок, файл будет пустым.
6. Оператор перенаправления и head
С помощью команды head можно выбрать определённый объем данных, чтобы создать текстовый файл большого размера. Данные можно брать, например, с /dev/urandom. Для примера создадим файл размером 100 мегабайт:
base64 /dev/urandom | head -c 100M > файл
7. Команда cp
Команда cp используется для копирования файлов в Linux. Но с её помощью можно и создать файл. Например, чтобы создать пустой файл, можно просто скопировать /dev/null:
cp /dev/null файл
8. touch
Вот мы и подобрались к непосредственному созданию файлов через терминал, для этого в Linux есть специальная утилита touch. Она позволяет создать пустой файл в Linux, при этом указывать дату создания, права доступа и другие метаданные.
Чтобы создать пустой файл Linux, просто наберите:
Можно создать несколько пустых файлов сразу:
touch файл1 файл2
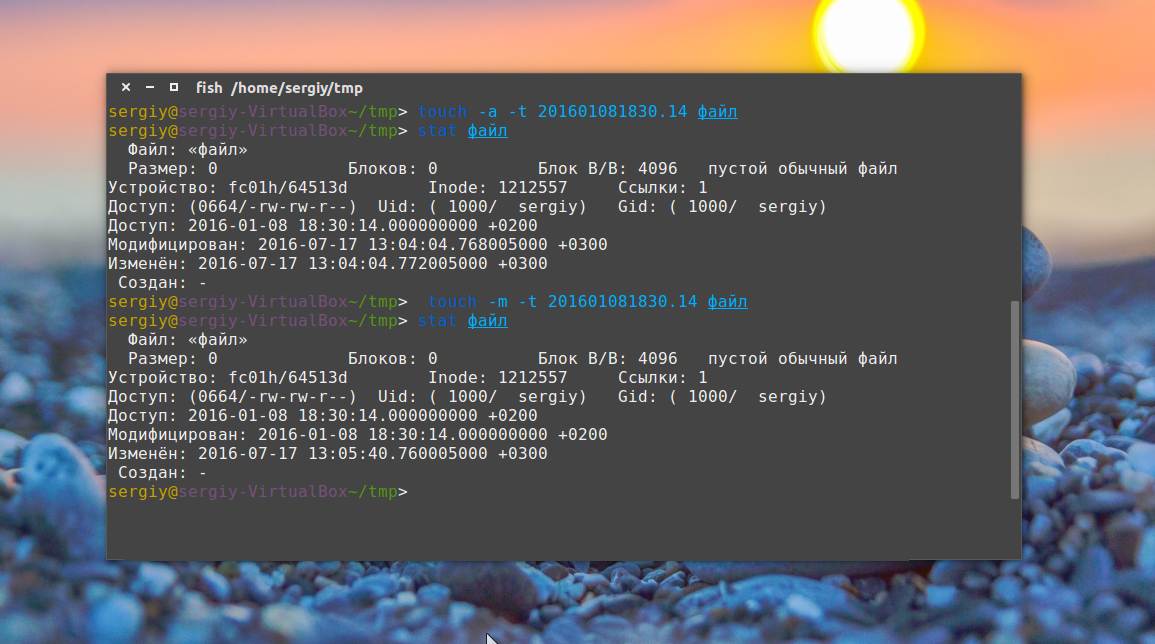
Опция -t позволяет установить дату создания. Дата указывается опцией -t в формате YYMMDDHHMM.SS. Если не указать, будет установлена текущая дата. Пример:
touch -t 201601081830.14 файл
Можно использовать дату создания другого файла:
touch -r шаблон файл
Также можно установить дату последней модификации, с помощью опции -m:
touch -m -t 201601081830.14 файл
Или дату последнего доступа:
touch -a -t 201601081830.14 файл
Чтобы посмотреть, действительно ли задаётся информация, которую вы указали, используйте команду stat:
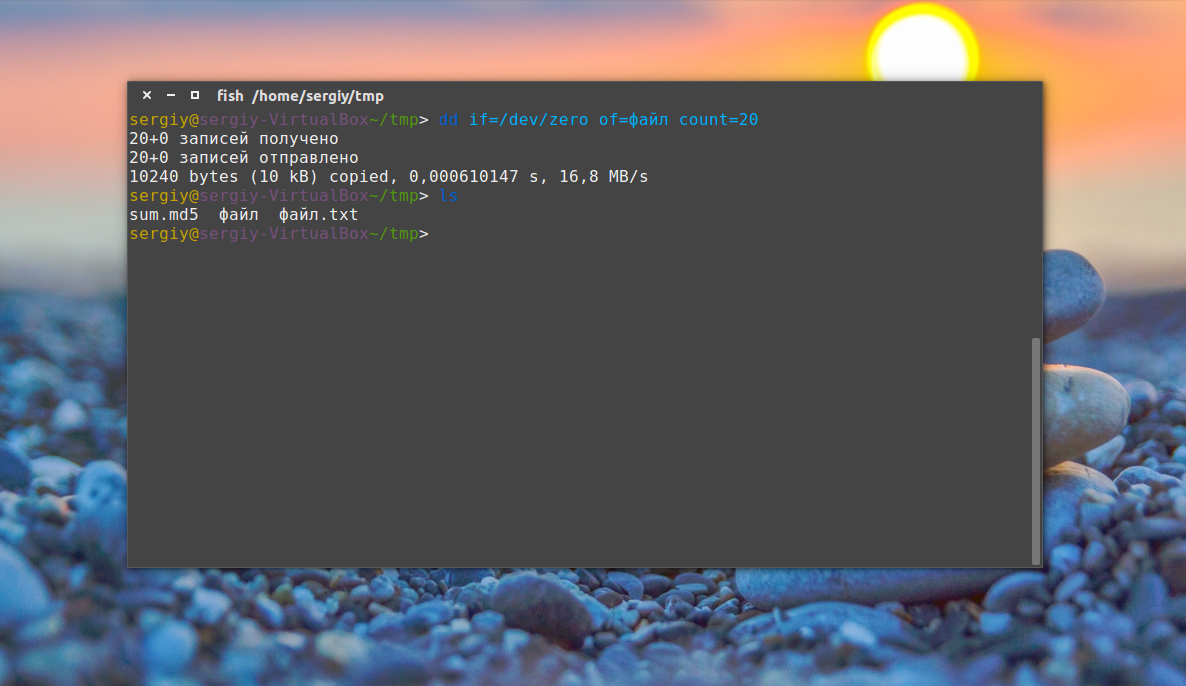
9. Утилита dd
Это утилита для копирования данных из одного файла в другой. Иногда необходимо создать файл определённого размера в Linux, тогда можно просто создать его на основе /dev/zero или /dev/random, вот так:
dd if=/dev/zero of=
Параметр if указывает, откуда брать данные, а of — куда записывать, count — необходимый размер. Ещё можно указать размер блока для записи с помощью bs, чем больше размер блока, тем быстрее будет выполняться копирование.
Создание специальных файлов в Linux
В Linux, кроме выше рассмотренных обычных текстовых и бинарных файлов, существуют ещё и специальные файлы. Это файлы сокетов и туннелей. Их нельзя создать обычными программами, но для этого существуют специальные утилиты, смотрите подробнее в статье, ссылку на которую я дал вверху.
Выводы
Это были все возможные команды для создания файла в Linux. Если вы знаете другие, которые следовало бы добавить в статью — поделитесь в комментариях.
Источник