- How to Create Symbolic Links in Linux
- What are Linux Symbolic Links
- How to Create Symbolic Links in Linux?
- Create Symbolik Link in Linux for Files
- Create Symbolic Link in Linux for Folders
- How to Change or Remove Symbolic Link in Linux?
- Wrapping up
- What is Symbolic Links in Linux? How to Create Symbolic Links?
- What is Symbolic link in Linux and why is it used?
- How to create a symbolic link in Linux
- Things to keep in mind about symbolic links
- Changes made to link are reflected in the original file
- Does it link to a file or a directory? You may not know!
- You can create links to non-existent file or directory
- The symbolic links are created with 777 permission but it means nothing
- You can link to a link of a link aka chained symbolic link
- linux-notes.org
- Создание ссылок (symlink) в Unix/Linux
- How to: Linux / UNIX create soft link with ln command
- Two types of links
- How do I create soft link / symbolic link under Unix and Linux?
- How to use the ln command
- Creating Symlink to a directory
- How to overwrite symlinks/Soft link
- How to delete or remove symlinks/soft links
- Getting help about the ln command
- Conclusion
How to Create Symbolic Links in Linux
Learning Linux symbolic commands is a great way of improving your potential in the Linux terminal. In this tutorial, we’ll cover a few commands to learn symbolic links in a quick and easy way. Before we begin, let’s overview what are symbolic links.
What are Linux Symbolic Links
Symbolic Links are not only helpful in creating shortcuts and file management in operating systems like Linux. They also serve as a way to create various locations for primary user folders, for instance, Documents, Pictures, Downloads, and much more!
Symbolic Links act like a string creating pathways for different files, folders, and directories in the computer system. They are capable of creating and storing multiple files in different places refer to one single file. Thus, increasing efficiency by locating all the specific documents in one command.
These links are stored in the mainframe, so even if the original file is deleted, you’ll have a backup for most of the important files. Symbolic links help create invalid link pathways to store pieces of information as per the requirement of the user.
Due to the user-friendly features in Linux, even Microsoft is following it to create Symbolic Links. Symbolic links, also known as Soft links or Symlinks, are not unique to Linux but they are just like a Search option in Windows where one can search a specific file or directory in a disk by executing various commands.
How to Create Symbolic Links in Linux?
Let’s look at how you can create file and folder links in Linux:
Create Symbolik Link in Linux for Files
Generally, to create links use we use the ln command and the -s option to specify Symbolic links. This is the easiest way to ensure a flexible approach that allows experimenting with the language as much as possible. There is nothing hard in creating Symbolic links in Linux – you just need to follow one simple step.
The ln command in Linux creates links between source files and directories.
- -s – the command for Symbolic Links.
- [target file] – name of the existing file for which you are creating the link
- [Symbolic filename] – name of the symbolic link.
Created links can be verified by directory listing using detailed list command:
However, if you do not specify the [Symbolic filename], the command will automatically create a new link in the existing directory.
Create Symbolic Link in Linux for Folders
Creating symbolic links for folders is not difficult either. The command used to create the folder symbolic link is:
For example, to link the /user/local/downloads/logo directory to /devisers folder, use the following command:
Once a Symbolic link is created and attached to the folder /devisers, it will lead to /user/local/downloads/logo. When the user changes directory – cd – to /devisers, the system will automatically change to the specific file and write it in the command directory.
Symbolic link options are called command line switches. Here are the most common ones and their descriptions:
| Command Switch | Description |
| –backup[=CONTROL] | backup each existing destination file |
| -d, -F, –directory | superuser is allowed to attempt hard link |
| -f, –force | existing destination file is removed |
| -I, –interactive | prompt before removing destination files |
| -L, –logical | deference targets that are symbolic links |
| -n, –non-dereference | symbolic links to directory are treated as files |
| -P, –physical | make hard links directly to symbolic links |
| -r, –relative | create symbolic links relative to link location |
| -s, –symbol | make symbolic links instead of hard links |
| -S, –suffix=SUFFIX | override usual backup suffix |
| -v, –verbose | print name of each linked file |
How to Change or Remove Symbolic Link in Linux?
You can remove existing links attached to files or directories by the unlink or rm command. This is how you can do it with the unlink command:
Removing symbolic link using the rm command is similar to the unlink command which is as under:
Wrapping up
Remember, if the source is no longer in the current location, then you should delete the symbolic files to avoid creating duplicates, which might slow down your work.
Linux is a wonderful platform for creating an interactive and dynamic application, where you can experiment and innovate. A strong foundation is critical. Learn the basic of the language thoroughly to use it to its full potential. We hope this tutorial helped you improve your skills with another useful tool!
Edward is an expert communicator with years of experience in IT as a writer, marketer, and Linux enthusiast. IT is a core pillar of his life, personal and professional. Edward’s goal is to encourage millions to achieve an impactful online presence. He also really loves dogs, guitars, and everything related to space.
Источник
What is Symbolic Links in Linux? How to Create Symbolic Links?
What is Symbolic link in Linux and why is it used?
A symbolic link, also known as a symlink or a soft link, is a special type of file that simply points to another file or directory just like shortcuts in Windows. Creating symbolic link is like creating alias to an actual file.
If you try to access the symbolic link, you actually access the target file to which the symlink points to. Changes performed on the content of the link file changes the content of the actual target file.
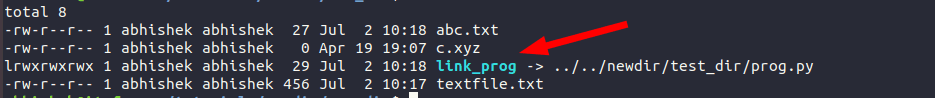
If you use the ls command with option -l, this is what a symbolic link looks like:
In most Linux distributions, the links are displayed in a different color than the rest of the entries so that you can distinguish the links from the regular files and directories.
Symbolic links offer a convenient way to organize and share files. They provide quick access to long and confusing directory paths. They are heavily used in linking libraries in Linux.
Now that you know a little about the symbolic links, let’s see how to create them.
How to create a symbolic link in Linux
To create a symbolic link to target file from link name, you can use the ln command with -s option like this:
The -s option is important here. It determines that the link is soft link. If you don’t use it, it will create a hard link. I’ll explain the difference between soft links and hard links in a different article.
Things to keep in mind about symbolic links
Symbolic links could be confusing at times therefore you should keep note of a few things.
Changes made to link are reflected in the original file
That’s the whole purpose of the links after all. You access the target file by accessing the link. You can make changes to the target file through the links. Let’s see with example.
I have a file prog.py in newdir/test_dir. It has the following attributes:
Now, I’ll create a soft link to this file in my present directory:
Here are the attributes of the newly created link:
Notice the l (it’s L, not one) at the beginning of the line? If you are familiar with the file permissions in Linux, you would know that the ‘l’ signifies link and thus it tells you that this file is actually a link. To refresh your memory, – means file, and d means directory.
Now if I use this link to change the content or the attributes, the same will be reflected in the target file. For example, I am using touch command on the soft link and you’ll notice that it changes the timestamp of the target file.
Does it link to a file or a directory? You may not know!
How would you know if the link points to file or a directory? You cannot know that until you follow the path and access the target file itself.
You can create links to non-existent file or directory
Yes, that’s totally possible. This is why you should be careful while creating soft links in Linux. The target file to which you are linking doesn’t need to exist. You won’t get any error or warning for creating link to a file/directory that does not exist.
You’ll get error only when you try to access the target file, either through the link or on its own. The ls command will still work though.
The symbolic links are created with 777 permission but it means nothing
Did you notice the file permission on the symbolic link? The symlinks are always created with 777 permission (rwxrwxrwx). For regular file, this would mean that anyone can access the file. But that’s not the case for the links.
If the file permissions on the links were treated as it is, any user could create a symlink to a secure file and access it freely. That would be a major security issue. Thankfully, that doesn’t happen. Because the permission on the target files matter, not the permission on links.
You may use the chmod command to change the permission on the link but it will change the permission of the linked file, not the link itself.
You can link to a link of a link aka chained symbolic link
You can make a symbolic link that points to another link and so on. This is called chained symbolic link. It’s better to avoid them as it creates more confusion.
Well, that’s it. I presume you have a better knowledge of the soft links now and you know how to create symbolic links in Linux. You may read about the symlinks command that can help you find broken symlinks in Linux and manage them easily.
If you have questions or suggestions, please leave a comment below.
Источник
linux-notes.org
Хотелось бы рассказать как можно создавать ссылки (симлинки) в ОС Unix/Linux. В своей теме «Создание ссылок (symlink) в Unix/Linux» я на готовом примере покажу как это делается. Существуют несколько видов ссылок, и я расскажу в чем разница между ними.
Симлинк или мягкая ссылка представляет собой особый тип файла, который содержит ссылку на другой файл или каталог в виде абсолютного или относительного пути.
Жёсткой ссылкой — это структурная составляющая файла которая описывает его элемент каталога.
Создание ссылок (symlink) в Unix/Linux
В этом подразделе, я расскажу какие бывают симлинки и в чем они отличаются.
Мягкая ссылка (Soft link):
- Мягкие ссылки используют различные номера инод чем основные файлы.
- Мягкие ссылки становится полезными, если исходный файл был удален.
- Мягкие ссылки могут быть созданы из каталогов.
- Мягкая ссылка может быть создана на пересечении файловых систем.
Для того чтобы создать симлинк в линукс используется следующая команда:
И так, я создал симлинк linux-notes.org.conf на на тот же файл но который будет расположен в другой директории. После создания симлинка, необходимо сменить права на него:
Для проверки номера иноды:
Я создал симлинк на файл, так же, можно создавать симлинка на целую папку, для этого используйте:
И так, я создал симлинк symlink-to-opt-dir на папку /opt/directory. После создания симлинка, необходимо сменить права на него:
Вот и все, очень просто, и полезно.
Для проверки номера иноды:
Чтобы удалить, используйте:
И аналогично для каталогов.
Если вы удалите мягкую ссылку (/home/captain/linux-notes.org-softlink.txt), то сам файл данных будет по-прежнему находится там же (/home/captain/linux-notes.org.txt). Тем не менее, если вы удалите /home/captain/linux-notes.org.txt, то /home/captain/linux-notes.org-softlink.txt станет сломанной ссылкой и данные будут потеряны.
Жесткие ссылки (Hard Links):
- Жесткие ссылки использует тот же номер иноды что и основные файлы.
- Нельзя создать жесткие ссылки на каталоги.
- Жесткие ссылки не могут быть созданы на пересечении файловых систем.
- Жесткие ссылки всегда относится к источнику, даже если они перемещаются или удаляется.
Чтобы создать «жесткую ссылку», используйте:
Проверяем номер иноды:
Оба файла имеют одинаковые иноды (одинаковое количество индексных дескрипторов). Если нужно удалить «жесткую ссылку», то используйте команду:
Если вы удалите жесткую ссылку, ваши данные будут там. Если вы удалите /home/captain/linux-notes.org.txt то файл будет по-прежнему доступен через жесткую ссылку
Жесткие ссылки (Hardlink) vs Мягкие ссылки (Softlink) в UNIX/Linux
- Как я говорил ранее, жесткие ссылки не могут быть созданы для директорий.
- Жесткие ссылки не могут использоваться на пересечении границ файловых систем ( Нельзя создать сылку /tmp и примонтированную на /tmp ко 2-му HDD который смонтирован на/harddisk2).
- Символические ссылки (мягкие ссылки) ссылаются на символичный путь с указанием абстрактного расположение другого файла.
- Жесткие ссылки, ссылаются к определенному местоположению физических данных.
На этом, моя тема «Создание ссылок (symlink) в Unix/Linux» завершена. Не сильно сложная тема, но очень полезная.
Источник
How to: Linux / UNIX create soft link with ln command
Symbolic links can be made to directories as well as to files on different filesystems or different partitions.
Two types of links
- symbolic links (also known as “soft links” or “symlinks”): Refer to a symbolic path indicating the abstract location of another file.
- hard links : Refer to the specific location of physical data.
How do I create soft link / symbolic link under Unix and Linux?
Soft links are created with the ln command. For example, the following would create a soft link named link1 to a file named file1, both in the current directory
$ ln -s file1 link1
To verify new soft link run:
$ ls -l file1 link1
Sample outputs:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
From the above outputs it is clear that a symbolic link named ‘link1’ contains the name of the file named ‘file1’ to which it is linked.
How to use the ln command
So the syntax is as follows to create a symbolic link in Unix or Linux, at the shell prompt:
$ ln -s < source-filename >< symbolic-filename >
For example create a softlink for /webroot/home/httpd/test.com/index.php as /home/vivek/index.php, enter the following command:
$ ln -s /webroot/home/httpd/test.com/index.php /home/vivek/index.php
$ ls -l
Sample outputs:
You can now edit the soft link named /home/vivek/index.php and /webroot/home/httpd/test.com/index.php will get updated:
$ vi /home/vivek/index.php
Your actual file /webroot/home/httpd/test.com/index.php remains on disk even if you deleted the soft link /home/vivek/index.php using the rm command:
$ rm /home/vivek/index.php ## ##
## But original/actual file remains as it is ##
$ ls -l /webroot/home/httpd/test.com/index.php
Creating Symlink to a directory
The syntax remains same:
$ ln -s
For example, create a symbolic link from the /home/lighttpd/http/users/vivek/php/app/ directory to the /app/ directory you would run:
$ ln -s /home/lighttpd/http/users/vivek/php/app/ /app/
Now I can edit files using /app/
$ cd /app/
$ ls -l
$ vi config.php
How to overwrite symlinks/Soft link
Pass the -f to the ln command to overwrite links:
ln -f -s /path/to/my-cool-file.txt link.txt
How to delete or remove symlinks/soft links
Use the rm command to delete a file including symlinks:
rm my-link-name
unlink /app/
rm /home/vivek/index.php
Getting help about the ln command
Type the following ln command:
$ man ln
$ ln —help
| ln command option | Description |
|---|---|
| —backup | make a backup of each existing destination file |
| -b | like —backup but does not accept an argument |
| -d | allow the superuser to attempt to hard link directories (note: will probably fail due to system restrictions, even for the superuser) |
| -f | remove existing destination files |
| -i | prompt whether to remove destinations |
| -L | dereference TARGETs that are symbolic links |
| -n | treat LINK_NAME as a normal file if it is a symbolic link to a directory |
| -P | make hard links directly to symbolic links |
| -r | create symbolic links relative to link location |
| -s | make symbolic links instead of hard links |
| -S | override the usual backup suffix |
| -t | specify the DIRECTORY in which to create the links |
| -T | treat LINK_NAME as a normal file always |
| -v | print name of each linked file |
| —help | display this help and exit |
| —version | output version information and exit |
Conclusion
You learned how to create a symbolic link in Linux using the ln command by passing the -s option. See ln command man page here for more information.
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник