- Cygwin
- This is the home of the Cygwin project
- . is it?
- . isn’t it?
- Cygwin version
- Installing Cygwin
- Support for Cygwin
- 32 bit Cygwin
- Cygwin
- Installing and Updating Cygwin Packages
- Installing and Updating Cygwin for 64-bit versions of Windows
- Installing and Updating Cygwin for 32-bit versions of Windows
- Signing key transition
- General installation notes
- Q: How do I add a package to my existing Cygwin installation?
- Q: Is there a command-line installer?
- Q: Why not use apt, yum, my favourite package manager, etc.?
- Q: How do I install everything?
- 5 Installing Cygwin and Starting the SSH Daemon
- 5.1 About the Cygwin Requirement for Installing Management Agents
- 5.2 Be fore You Begin Installing Cygwin
- 5.3 Installing Cygwin
- 5.4 Confi guring SSH
- 5.5 After Inst alling Cygwin and Configuring SSH
Cygwin
Get that Linux feeling — on Windows
This is the home of the Cygwin project
. is it?
- a large collection of GNU and Open Source tools which provide functionality similar to a Linux distribution on Windows.
- a DLL (cygwin1.dll) which provides substantial POSIX API functionality.
. isn’t it?
- a way to run native Linux apps on Windows. You must rebuild your application from source if you want it to run on Windows.
- a way to magically make native Windows apps aware of UNIX® functionality like signals, ptys, etc. Again, you need to build your apps from source if you want to take advantage of Cygwin functionality.
The Cygwin DLL currently works with all recent, commercially released x86_64 versions of Windows, starting with Windows Vista. For more information see the FAQ.
Cygwin version
The most recent version of the Cygwin DLL is 3.2.0.
Installing Cygwin
Use the setup program to perform a fresh install or to update an existing installation.
Keep in mind that individual packages in the distribution are updated separately from the DLL so the Cygwin DLL version is not useful as a general Cygwin distribution release number.
Support for Cygwin
For all Cygwin-related questions and observations, please check the resources available at this site, such as the FAQ, the User’s Guide and the mailing list archives. If you’ve exhausted these resources then please send email to an appropriate mailing list. This includes observations about web pages, setup questions, questions about where to find things, questions about why things are done a certain way, questions about the color preferences of Cygwin developers, questions about the meaning of the number 42, etc.
Please send notification of technical problems (bad html, broken links) concerning these web pages to the Cygwin mailing list.
Please do not send personal email with «quick questions» to individual Cygwin contributors. The Cygwin mailing lists are the places for all questions. Really. I mean it.
32 bit Cygwin
Address space is a very limiting factor for Cygwin. These days, a full 32 bit Cygwin distro is not feasible anymore, and will in all likelihood fail in random places due to an issue with the fork(2) system call.
Therefore we recommend using 32 bit Cygwin only in limited scenarios, with only a minimum of necessary packages installed, and only if there’s no way to run 64 bit Cygwin instead.
You have been warned. If you’re still sure you really need a 32 bit Cygwin, and there’s absolutely no way around it, you may run the setup-x86.exe installer.
The Cygwin DLL and utilities are Copyright © Cygwin authors. Other packages have other copyrights.
UNIX ® is a registered trademark of the Open Group in the United States and other countries.
Источник
Cygwin
Get that Linux feeling — on Windows
Installing and Updating Cygwin Packages
Installing and Updating Cygwin for 64-bit versions of Windows
Run setup-x86_64.exe any time you want to update or install a Cygwin package for 64-bit windows. The signature for setup-x86_64.exe can be used to verify the validity of this binary.
Installing and Updating Cygwin for 32-bit versions of Windows
Run setup-x86.exe any time you want to update or install a Cygwin package for 32-bit windows. The signature for setup-x86.exe can be used to verify the validity of this binary.
Signing key transition
See this mail for more details.
General installation notes
When installing packages for the first time, the setup program does not install every package. Only the minimal base packages from the Cygwin distribution are installed by default, which takes up about 100 MB.
Clicking on categories and packages in the setup program package installation screen allows you to select what is installed or updated.
Individual packages like bash, gcc, less, etc. are released independently of the Cygwin DLL, so the Cygwin DLL version is not useful as a general Cygwin release number. The setup program tracks the versions of all installed components and provides the mechanism for installing or updating everything available from this site for Cygwin.
Once you’ve installed your desired subset of the Cygwin distribution, the setup program will remember what you selected, so re-running it will update your system with any new package releases.
On Windows Vista and later, the setup program will check by default if it runs with administrative privileges and, if not, will try to elevate the process. If you want to avoid this behaviour and install under an unprivileged account just for your own usage, run setup with the --no-admin option.
Q: How do I add a package to my existing Cygwin installation?
A: Run the setup program and select the package you want to add.
Tip: if you don’t want to also upgrade existing packages, select ‘Keep’ at the top-right of the package chooser page.
Q: Is there a command-line installer?
A: Yes and no. The setup program understands command-line arguments which allow you to control its behavior and choose individual packages to install. While this provides some functionality similar to such tools as apt-get or yum it is not as full-featured as those package managers.
Q: Why not use apt, yum, my favourite package manager, etc.?
A: The basic reason for not using a more full-featured package manager is that such a program would need full access to all of Cygwin’s POSIX functionality. That is, however, difficult to provide in a Cygwin-free environment, such as exists on first installation. Additionally, Windows does not easily allow overwriting of in-use executables so installing a new version of the Cygwin DLL while a package manager is using the DLL is problematic.
Q: How do I install everything?
A: You do not want to do this! This will install an enormous number of packages that you will never use, including debuginfo and source for every package.
If you really must do this, clicking on the «Default» label next to the «All» category to change it to «Install» will mark every Cygwin package for installation. Be advised that this will download and install tens of gigabytes of files to your computer.
Источник
5 Installing Cygwin and Starting the SSH Daemon
This chapter explains how to install Cygwin and start the SSH daemon on Microsoft Windows hosts. This chapter is applicable only when you want to install a Management Agent on a Microsoft Windows host, using the Add Host Targets Wizard or EM CLI. In particular, this chapter covers the following:
If you do not want to install Cygwin to deploy Management Agents on Microsoft Windows hosts using the Add Host Targets Wizard or EM CLI, you can choose to deploy Management Agents on these hosts using the PsExec process utility. For information on how to deploy Management Agents on Microsoft Windows hosts using PsExec, see Appendix F.
5.1 About the Cygwin Requirement for Installing Management Agents
The Add Host Targets Wizard is an application built into the Enterprise Manager Cloud Control console. It offers GUI-rich, interactive screens that enable you to install Oracle Management Agents (Management Agents) on unmanaged hosts and convert them to managed hosts, so that they can be monitored and managed in Enterprise Manager Cloud Control.
When you use the Add Host Targets Wizard or EM CLI to install a Management Agent on a host running on Microsoft Windows, as a prerequisite, you must install Cygwin and start the SSH Daemon on the host. To do so, follow the steps listed in Section 5.3.
Cygwin is essentially a utility that offers a Linux-like environment on a Microsoft Windows host. Technically, it is a DLL ( cygwin1.dll ) that acts as a Linux API layer providing substantial Linux API functionality. Once you install Cygwin, you can configure the SSH Daemon on the host. The Add Host Targets Wizard is certified and supported with Cygwin 1.7.
The SSH Daemon enables the Add Host Targets Wizard to establish SSH connectivity between the OMS host and the host on which you want to install a Management Agent. Using this connectivity, the wizard transfers the Management Agent software binaries to the destination host over SSH protocol, installs the Management Agent, and configures it.
5.2 Be fore You Begin Installing Cygwin
Before starting with the SSHD setup, ensure you are not using OpenSSH and MKSNT when using the Add Host Targets Wizard. To do so, perform the following checks:
Ensure OpenSSH\bin and mksnt are not in your PATH environment variable. If they are, remove them by doing the following:
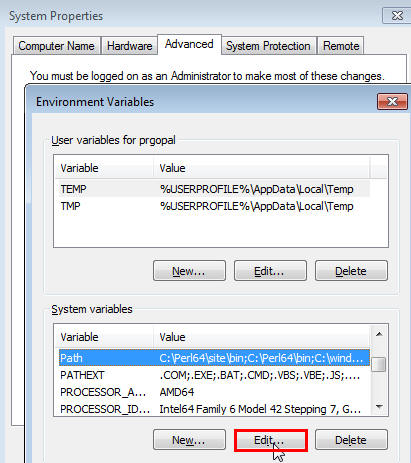
Right-click on My Computer and go to Properties .
In the System Properties window, click Advanced.
In this tab, click Environment Variables.
Here, search for the PATH system variable, select it, and if the OpenSSH\bin and mksnt are present in PATH, click Edit.
In the Edit System Variable dialog box, delete these two values from PATH, then click OK.
Stop the SSH Daemon if it is running from OpenSSH , MKS or any other vendor. If the SSH Daemon is running, stop it by doing the following:
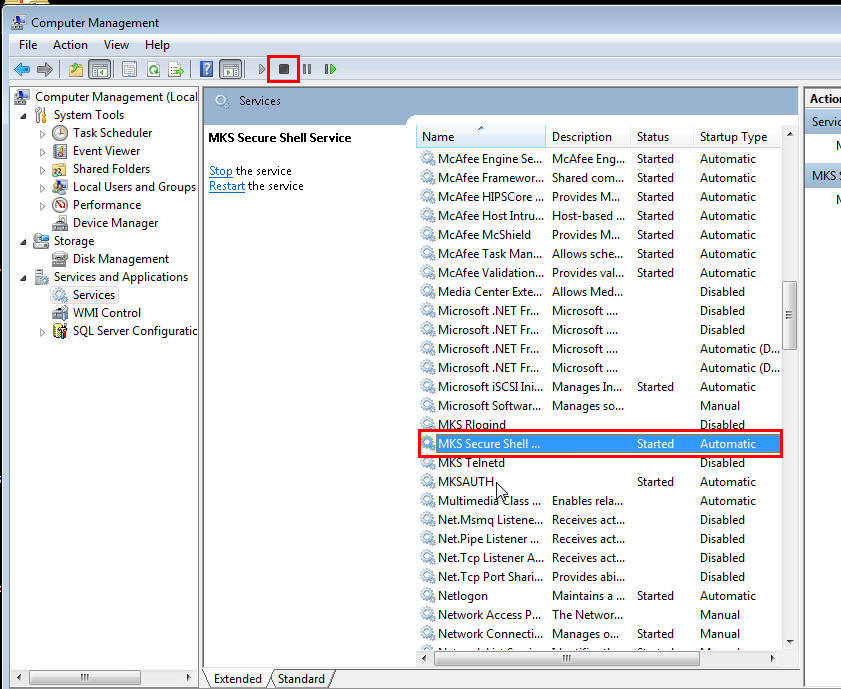
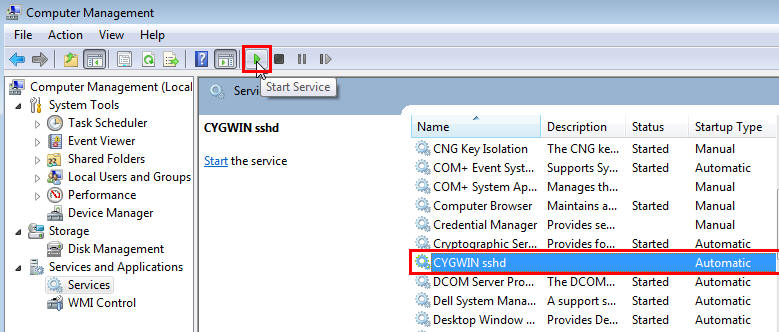
Right-click on My Computer , and select Manage.
In the Computer Management window, in the left pane, expand Services and Applications , and select Services .
In the right pane, click the SSH Daemon/MKS Secure Shell service, then click the Stop button.
The navigational steps described in this section may vary for different Microsoft Windows operating systems.
5.3 Installing Cygwin
To install Cygwin on a Microsoft Windows host, follow these steps:
Access the following URL, then click Install Cygwin:
Download the 32-bit version (if you are running a 32-bit version of Microsoft Windows) or the 64-bit version (if you are running a 64-bit version of Microsoft Windows) of the Cygwin setup executable.
Run the setup executable, then click Next to proceed.
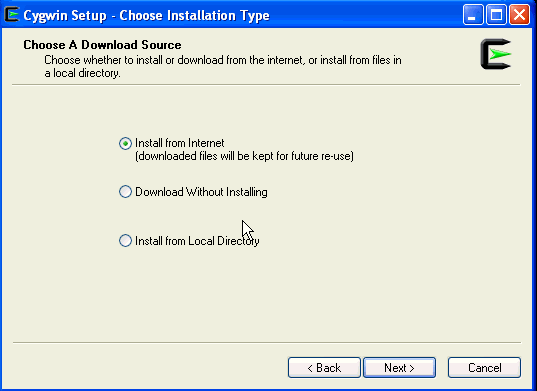
On the Choose Installation Type screen, select Install from Internet, then click Next.
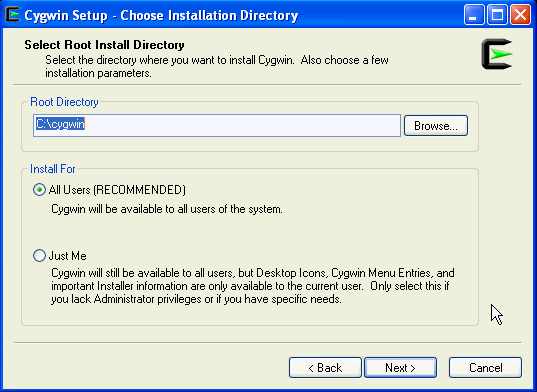
On the Choose Installation Directory screen, enter C:\cygwin as the Root Directory, then click Next.
If you choose to install Cygwin in a different directory, then ensure that you update the SSH_PATH, SCP_PATH, MKDIR_PATH, SH_PATH, CHMOD_PATH , and TRUE properties present in the $ \oui\prov\resources\ssPaths_msplats.properties file to their proper Cygwin binary values, after installing the Enterprise Manager system.
For example, if you choose to install Cygwin in the D:\software\cygwin directory, then update the specified properties in the following manner:
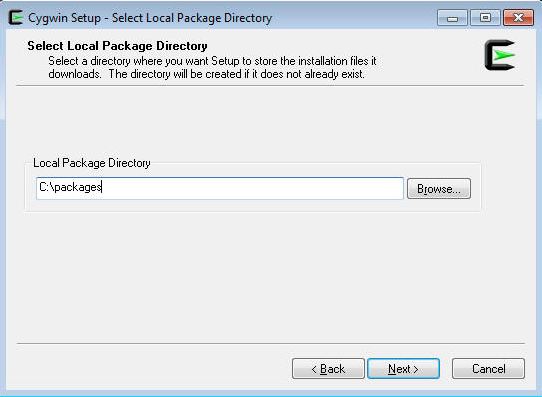
On the Select Local Package Directory screen, select a directory on your local machine where you want to store the downloaded installation files, then click Next.
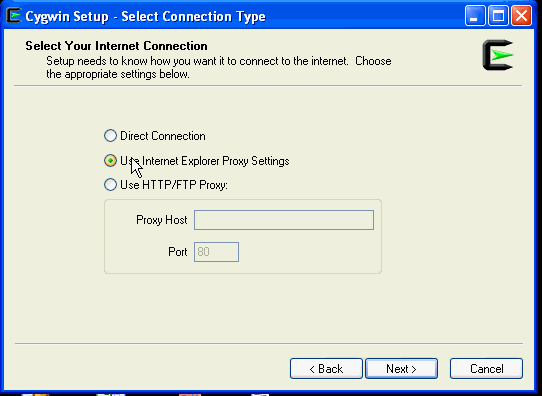
On the Select Connection Type screen, select appropriate settings to connect to the internet, then click Next.
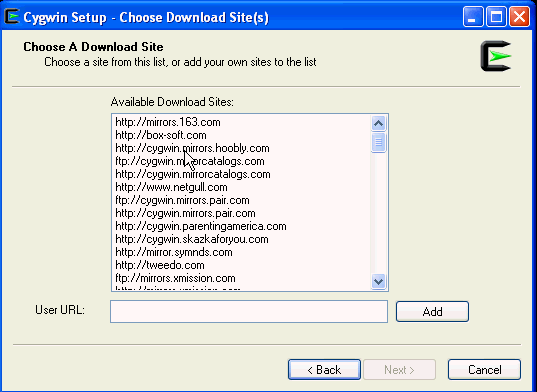
On the Choose Download Site(s) screen, select any site from the available list, then click Next.
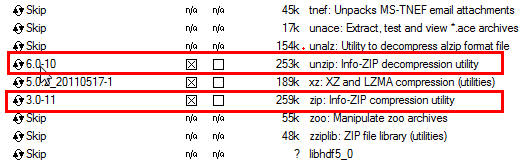
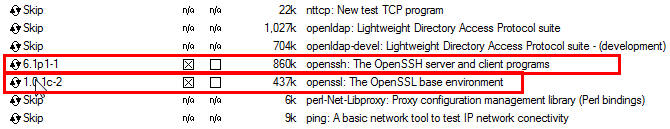
On the select pac kages screen, ensure that you select the following packages, then click Next :
From the Archive category, select unzip and zip as follows:
From the Net category, select openssh and openssl as follows:
After selecting the packages and clicking Next, the Resolving Dependencies screen is displayed. Click Next to proceed.
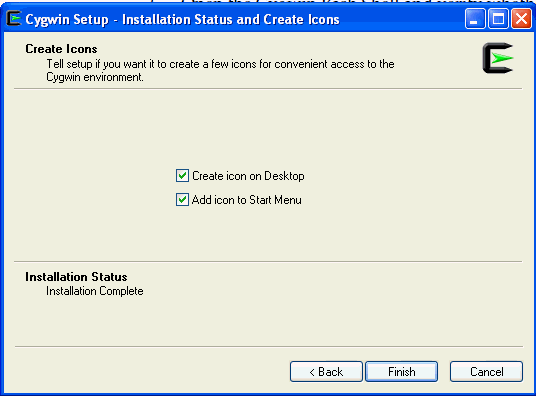
On the Installation Status and Create Icons screen, do not make any changes. Click Finish to complete the installation process.
5.4 Confi guring SSH
This section describes how to configure SSH and test your Cygwin setup after installing Cygwin on a host.
While configuring SSH, you may need to run the cygwin.bat script. While running cygwin.bat in Microsoft Windows Server 2008 and Microsoft Windows Vista, ensure that you invoke it in administrator mode. To do this, right-click the cygwin.bat file and select Run as administrator.
To configure SSH and test your Cygwin setup, follow these steps:
After you install Cygwin, navigate to the C:\cygwin directory, open the Cygwin.bat file in edit mode using any editor, and add the following line before invoking the bash shell.
set CYGWIN=binmode ntsec
For example, here are the contents for the Cygwin.bat file after adding the above line:
To verify if Cygwin ( cygrunsrv) is installed properly, run C:\cygwin\Cygwin.bat , and execute the following command:
If Cygwin is installed properly, then all the Cygwin help options are displayed on the screen. However, if this command returns an error message, then you may have to reinstall Cygwin.
To configure the SSHD service, run C:\cygwin\Cygwin.bat , and execute the following command:
After running the command, you are prompted the following questions:
At this point, if you want to use the same name, that is cyg_server, enter no. You are then prompted the following questions:
However, if you want to use a different name, enter yes. You are then prompted the following questions:
If the configuration is successful, you will see the following message:
Backup the c:\cygwin\etc\passwd file and then use any editor to open the file in edit mode. Remove only those entries of the user that you will use to connect to the host on which you want to install a Management Agent. Ask the user to make a backup of the c:\cygwin\etc\passwd file before editing.
If the user that you are employing to connect to the host on which you want to install the Management Agent is a local user, run C:\cygwin\Cygwin.bat and execute the following:
If the user you are employing to connect to the host on which you want to install the Management Agent running is a domain user, run C:\cygwin\Cygwin.bat and execute the following:
(Only if the Cygwin software you have installed is of version 1.7.32 or higher) Open C:\cygwin\etc\sshd_config in a text editor and add the following line to the end of the file:
(For a domain user only) If the user you are employing to connect to the host on which you want to install the Management Agent is a domain user, do the following to start the SSH daemon:
Right-click on My Computer , and select Manage .
In the Computer Management dialog box that appears, go to Services and Applications, and select CYGWIN sshd .
Right-click CYGWIN sshd and select Properties .
In the Properties dialog box, go to the Log On tab.
Here, specify the domain/user name and password. Click Apply.
Run C:\cygwin\Cygwin.bat , and execute the following:
If /var/log/sshd.log does not exist, you do not have to execute the following commands:
Perform one of the following steps to start the SSH daemon:
Run C:\cygwin\Cygwin.bat and execute the following command:
Run C:\cygwin\Cygwin.bat and execute the following command:
cygrunsrv -S sshd
Perform these steps:
Right-click on My Computer , and select Manage .
In the Computer Management dialog box that appears, go to Services and Applications, and select CYGWIN sshd .
Click CYGWIN sshd, then click the Start button.
If the SSH daemon does not start up, view the c:\cygwin\var\log\sshd.log file for information on why the start up failed.
You can now test your Cygwin setup.
To do this, go to a different machine (that has the ssh client running), and execute the following command:
This command will prompt you to specify the password. When you specify the correct password, the command should return the accurate date.
If you experience a process fork failure, memory leak error, or a file access error after configuring SSH, view the following website for a workaround:
If you are unable to find a workaround for your problem, report your problem to the Cygwin community using the following website:
5.5 After Inst alling Cygwin and Configuring SSH
After installing Cygwin (as described in Section 5.3) and configuring SSH (as described in Section 5.4), follow these steps:
If the OMS host runs on a Microsoft Windows platform, perform the following on the OMS host:
Right click My Computer, then select Properties. In the window that appears, select Advanced system settings, then select Environment Variables. In the System Variables section, create the CYGWIN variable, and specify its value as nodosfilewarning
You do not need to restart the host after performing this step.
Navigate to the Cygwin install directory (that is, C:\cygwin if you chose to install Cygwin in the default location), open the Cygwin.bat file in edit mode using any editor, then edit the following line:
For example, these are the contents of the Cygwin.bat file after editing the above line:
From the Start menu, select Run. For Open, enter services.msc, then click OK. Search for the Cygwin SSHD service and stop it.
Navigate to the Cygwin install directory (that is, C:\cygwin if you chose to install Cygwin in the default location), then run Cygwin.bat. Run the following command to start the SSHD service:
Running this command may return an error mentioning that /var/empty must be owned by the root user. If you encounter this error, run the following from the Cygwin terminal:
After running this command, retry the $ /usr/sbin/sshd command.
Perform the tasks mentioned in Step 1 on all the Microsoft Windows target hosts (on which you want to install Management Agents using the Add Host Targets Wizard or EM CLI).
Источник