- DebugView v4.90
- Introduction
- DebugView Capture
- DebugView Capabilities
- Installation and Use
- debugview — где его взять и как им пользоваться?
- Внимание
- How to Run DebugView 24×7 as a Windows Service with AlwaysUp
- Automatically start Sysinternals DebugView when your PC boots, before anyone logs in.
- DebugView not working properly as a Windows Service?
DebugView v4.90
By Mark Russinovich
Published: April 23, 2019

Run now from Sysinternals Live.
Introduction
DebugView is an application that lets you monitor debug output on your local system, or any computer on the network that you can reach via TCP/IP. It is capable of displaying both kernel-mode and Win32 debug output, so you don’t need a debugger to catch the debug output your applications or device drivers generate, nor do you need to modify your applications or drivers to use non-standard debug output APIs.
DebugView Capture
Under Windows 2000, XP, Server 2003 and Vista DebugView will capture:
- Win32 OutputDebugString
- Kernel-mode DbgPrint
- All kernel-mode variants of DbgPrint implemented in Windows XP and Server 2003
DebugView also extracts kernel-mode debug output generated before a crash from Window’s 2000/XP crash dump files if DebugView was capturing at the time of the crash.
DebugView Capabilities
DebugView has a powerful array of features for controlling and managing debug output.
Features new to version 4.6:
- Support for Windows Vista 32-bit and 64-bit
Features new to version 4.5:
- Support for log-file rollover: To better support long-running captures, DebugView can now create a new log file each day, optionally clearing the display when doing so.
Features new to version 4.4:
- Support for Windows Server 2003 64-bit Edition and Windows XP 64-bit Edition for x64:DebugView now captures kernel-mode debug output on 64-bit versions of Windows.
- Clock-time toggle: you can now toggle between clock time and elapsed time modes.
Features new to version 4.3:
- Support for Windows XP SP2:DebugView now captures kernel-mode debug output on Windows XP SP2.
- More highlighting filters: Many people have asked for more highlighting filters.
- Log file wrapping: A new log file option has DebugView wrap around to the start of the log file when the specified size limit is reached.
- Larger buffers: Larger Win32 and kernel-mode buffers lessen the chance of dropped debug output.
- Clear-output string: When DebugView sees the special debug output string «DBGVIEWCLEAR» it clears the output.
- Client minimize-to-tray: You can now run the client minimized in the tray.
Features new to version 4.2:
- Kernel-hook bug fixed:DebugView sometimes mistakenly report that it couldn’t hook kernel-mode debug output on Windows XP and Server 2003.
- Client global-capture option: A new option allows the client to capture console Win32 debug output on Terminal Server systems when run from a non-console session.
- Filtering improved: Filters can be much longer and now apply to Win32 process IDs when process IDs are included in the output.
- Crash-dump support improved: Several bugs related to extracting kernel-mode output from crash dumps are fixed and DebugView now loads resulting log files.
- More highlight filters:DebugView now has 10 highlight filters, up from 5.
- Insert comments: A new menu item lets you insert comments into output.
- New switches: New command-line switches allow you to specify history depth and load log files.
- Better balloon tips: If an output line is wider than the screen its mouse hover balloon tip word wraps.
Features new to version 4.1:
- Save and load filters: You can save and load filters, including the highlighting colors.
- Load saved logs: You can now load a log file back into the DebugView output window.
- Capture boot-time kernel-mode debug output: Under Windows 2000, you can use DebugView to capture debug output generated by drivers from the earliest point in the boot process.
Here is a list highlighting some of DebugView‘s other features:
- Remote monitoring: Capture kernel-mode and/or Win32 debug output from any computer accessible via TCP/IP — even across the Internet. You can monitor multiple remote computers simultaneously. DebugView will even install its client software itself if you are running it on a Windows 2000 system and are capturing from another Windows 2000 system in the same Network Neighborhood.
- Most-recent-filter lists:DebugView remembers your most recent filter selections, with an interface that makes it easy to reselect them.
- Process ID option: Toggle the display of process IDs for Win32 debug output.
- Clipboard copy: Select multiple lines in the output window and copy their contents to the clipboard.
- Log-to-file: Write debug output to a file as its being captured.
- Printing: Print all or part of captured debug output to a printer.
- One-file payload:DebugView is implemented as one file.
- Crash-Dump Support:DebugView can recover its buffers from a crash dump and save the output to a log file so that users can send you the output your Windows driver generated right up to the time of a crash.
The on-line help file describes all these features, and more, in detail.
Installation and Use
Simply execute the DebugView program file (dbgview.exe) and DebugView will immediately start capturing debug output. Note that if you run DebugView on Windows 2000/XP you must have administrative privilege to view kernel-mode debug output. Menus, hot-keys, or toolbar buttons can be used to clear the window, save the monitored data to a file, search output, change the window font, and more. The on-line help describes all of DebugView‘s features.
This is a screenshot of DebugView capturing Win32 debug output from a remote system. Note the presence of a highlighting filter.

Run now from Sysinternals Live.
debugview — где его взять и как им пользоваться?
Внимание
В одной из веток прочитал про отладчик (вернее про вывод отладочной информации) на экран. Речь шла о debugview.
Понял, что его надо откуда качать и как-то ставить, но не нашел в документации к Lua и Квику никаких упоминаний о нем.
Подскажите, что это за зверь такой, где его качать и как ставить и как пользоваться?
И можно хотя бы в двух словах объяснить, чем он отличается от обычного message?
Если я выполняю команду из примера в документации к PrintDbgStr:
PrintDbgStr(«test1»)
то ошибки не выдает, но и ничего нигде не выводит. В какое окно он это выводит?
| Цитата |
|---|
| Sergey Denegin написал: И можно хотя бы в двух словах объяснить, чем он отличается от обычного message? |
От обычного message отличается тем, что отладочный вывод вы видите только при запущенном внешнгем перехватчике таких сообщений (например — DebugView). Не запущен «перехватчик» — дебажный вывод практически не тормозит скрипт (особенно учитывая общую скорость Lua — так и вовсе незаметно). Удобно; можно оставлять вывод таких сообщений навсегда в своём коде.
| Цитата |
|---|
| Sergey Denegin написал: И можно хотя бы в двух словах объяснить, чем он отличается от обычного message? |
Если я выполняю команду из примера в документации к PrintDbgStr:
PrintDbgStr(«test1»)
то ошибки не выдает, но и ничего нигде не выводит. В какое окно он это выводит?
| Цитата |
|---|
| swerg написал: От обычного message отличается тем, что отладочный вывод вы видите только при запущенном внешнгем перехватчике таких сообщений (например — DebugView). |
| Цитата |
|---|
| Sergey Denegin написал: А как она по скорости? Быстрее чем обычный message? |
PrintDbgStr быстрее чем message
| Цитата |
|---|
| Sergey Denegin написал: И если я правильно понял, то если использовать DebugView, то значения переменных будут выводиться там, а обычные сообщения в обычном окне для message, и лично мне кажется, будет сложно совмещать по времени, что после чего следовало. Или такой проблемы не возникает? |
| Цитата |
|---|
| Андрей написал: на тормознутом DDE |
Тормознутый эксель, когда формулы в листе есть, бо пересчитывает каждый раз. Сам по себе DDE порвет большинство способов обмена информацией в среде Винды. Кстати, не поясните, какие имеются в виду, куда арке погуглить (и мне тоже, мало ли)?
| Цитата |
|---|
| Андрей написал: предназначена для манипулирования финансовыми средствами в немалых объемах |
Андрей, По молодости первое время пытался пользоваться отладчиком, пока не напоролся несколько раз на ситуацию, когда глючил сам отладчик. И какой ещё «редактор lua»? У меня это обыкновенный блокнот (точнее, редактор Far Manager), и лучшего не требуется. Что вообще можно отлаживать в интерпретаторе? Потерю управления между потоками? Так ведь не поможет тут никакой отладчик.
P.S. Мастдай 95 работал на пару порядков лучше нынешнего софта.
| Цитата |
|---|
| Андрей написал: В дополнение к вышесказанному хочу заметить, что для софтины, которая предназначена для манипулирования финансовыми средствами в немалых объемах, отсутствие собственного отладчика это полная лажа. Такая программа должна комплектоваться или комплектом ЯП-редактор-отладчик, либо полностью документированным открытым ВЫСОКОПРОИЗВОДИТЕЛЬНЫМ API. Создается впечатление, что у вас либо нет заинтересованности в поддержке и сопровождении этого проекта, либо вы просто его уже не вывозите. |
Мы зарегистрировали пожелание на доработку.
Ваше пожелание зарегистрировано. Мы постараемся рассмотреть его и сообщить Вам результаты анализа. Впоследствии, по результатам анализа, будет приниматься решение о реализации пожелания в будущих версиях ПО.
Отладка — это хорошо. Но писать тесты на свой код лучше и надежней.
Там где без отладочной информации не обойтись методика «print debug» помогает (я предпочитаю лог файлы). Если Вы пишите скрипты для себя, то, конечно, можете и отлаживать, а если для внешних клиентов, то как Вы будете у них отлаживать?
А если уже сравнивать с MT, то там отладка идет на исторических данных. Но и странно было бы ожидать отладку в реальном времени. Остановите поток данных?
Я не говорю, что если бы отладка была в Квике, то это не надо, но ее ценность не так велика. Плюс никто не мешает написать wrapper функций Квика и подкидывать данные из файлов для эмуляции потока, запуская на чистом lua. Тогда тесты станут еще более предсказуемыми.
How to Run DebugView 24×7 as a Windows Service with AlwaysUp
Automatically start Sysinternals DebugView when your PC boots, before anyone logs in.
DebugView is a free utility that captures diagnostic output from programs calling the OutputDebugString and DbgPrint API functions on your computer.
AlwaysUp will start DebugView whenever your PC reboots, making it possible for you to monitor Windows Services and other applications that are launched before you log in.
To run DebugView as a service with AlwaysUp:
If you don’t have DebugView installed, grab the zip file from Sysinternals and extract its contents to a new folder. We have placed our copy of DebugView in C:\Apps\DebugView so that directory will appear throughout this tutorial.
Next, compose the command line that you will use to run DebugView.
For your reference, the full set of command line options is revealed by running Dbgview.exe /?:

Since we want to capture global Win32 and kernel output to a new log file every day, we have chosen these options:
/v /l C:\DebugViewLogs\debugview-log.txt /g /n
And before moving on, make sure that your DebugView command line runs as expected! If it doesn’t work now, it won’t work under AlwaysUp.
Select Application > Add to open the Add Application window:
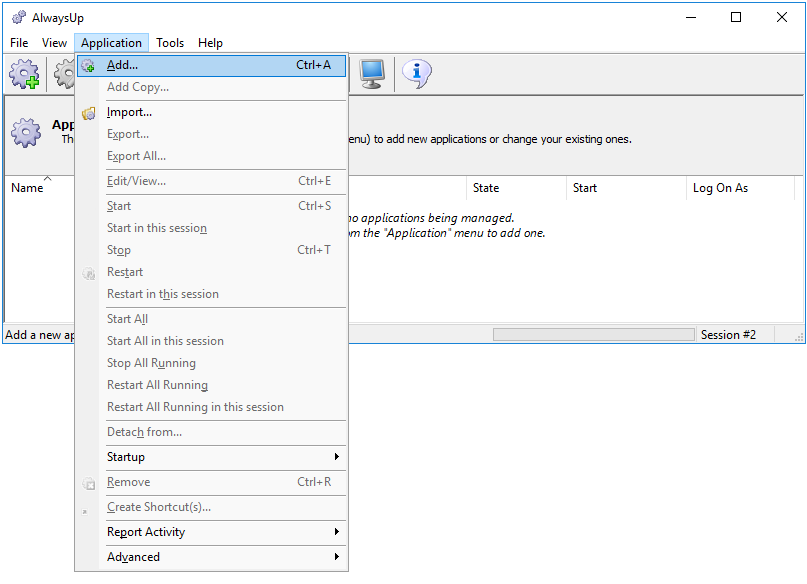
On the General tab:
In the Application field, enter the full path to the DebugView executable, Dbgview.exe. Look for it where you expanded the zip file you downloaded from Microsoft.
We have used (since we expanded the zip file to on our Windows Server 2016 system).
In the Arguments field, enter the command line parameters you will use to launch DebugView (see step 2).
In the Name field, enter the name that you will call this application in AlwaysUp. We have stuck with the default of Dbgview but you can specify another name if you like.
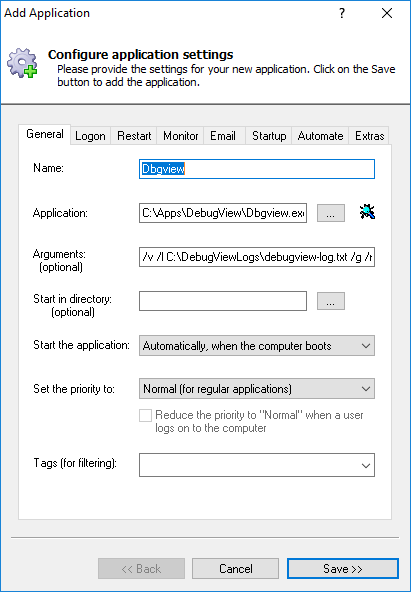
Click over to the Logon tab. Enter the user name and password of the Windows account where you run DebugView and have accepted the Sysinternals EULA.
If you don’t specify an account here, DebugView will run in the system account (where the EULA has not been accepted) and it may get stuck showing the EULA popup window in the background.
Click the Save >> button. In a couple of seconds, an application called Dbgview will appear in the AlwaysUp window. It is not yet running though (the state column will show Stopped).

To start DebugView from AlwaysUp, choose Application > Start «Dbgview». The state will transition to Running and DebugView will start working in the background.

And now would be a great time to open your log file and confirm that debug statements are being captured:
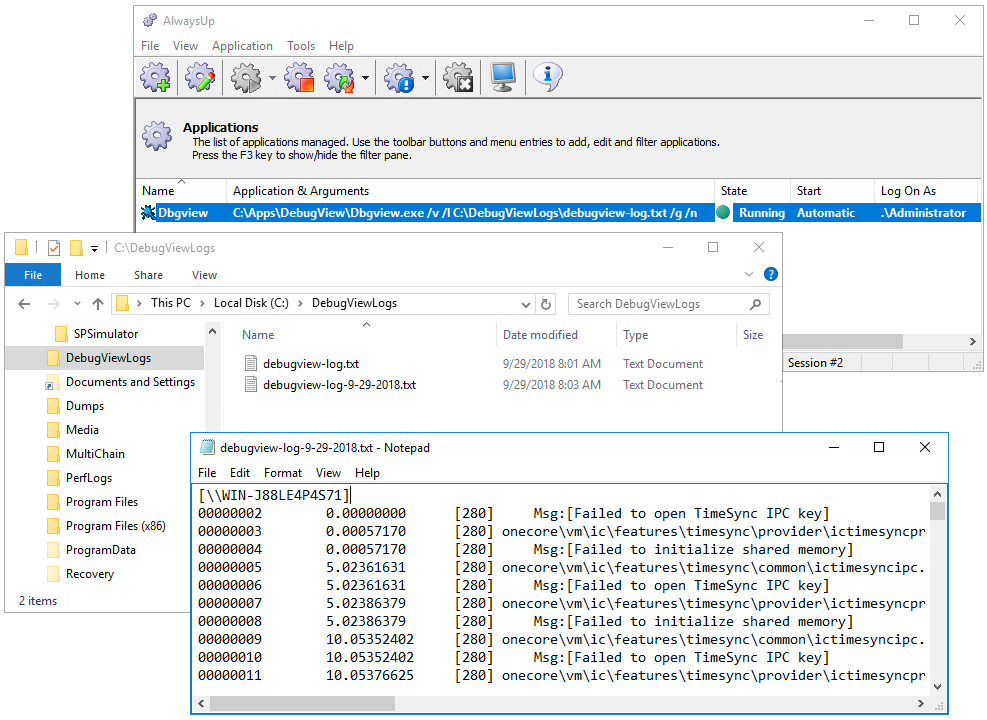
That’s it! Next time your computer boots, DebugView will start up immediately, before anyone logs on. We encourage you to edit DebugView in AlwaysUp and check out the many other settings that may be appropriate for your environment. Send email reports, boost priority, restart regularly, and much more.
DebugView not working properly as a Windows Service?
Consult the AlwaysUp Troubleshooter — our online tool that can help you resolve the most common problems encountered when running an application as a Windows Service.
From AlwaysUp, select Application > Report Activity > Today. to bring up a HTML report detailing the interaction between AlwaysUp and DebugView. The AlwaysUp Event Log Messages page explains the more obscure messages.
Browse the AlwaysUp FAQ for answers to commonly asked questions and troubleshooting tips.




