- Простая Dos атака с Golden Eye в Kali Linux
- Установка
- Атака
- Тесты
- Результат
- Анализ логов
- Заключение
- DDoS attack using SlowHTTPTest (Slowloris) in Kali Linux
- 1. Install slowhttptest
- 2. Running test
- DOS and DDOS Attacks in Kali Linux
- How to Launch a DoS Attack by using Metasploit Auxiliary
- Metasploit
- DoS Metasploit – Kali Linux Tutorial
- SYN flood
Простая Dos атака с Golden Eye в Kali Linux
В этой статье мы разберём один из самых простых способов Dos атак с помощью «Golden Eye»
DoS-атака представляет собой генерацию «мусорного» трафика с одного устройства (IP-адреса) на ресурс-«жертву» (например, сайт). Цель — исчерпать вычислительные и иные мощности «жертвы», чтобы заблокировать работу последней.
Не стоит путать DDos с Dos, хотя аббревиатуры различаются всего лишь на одну букву, за ней скрывается огромная фактическая разница. Dos атаку производит одна машина, а DDos атака зачастую делается с использованием ботнета.
Ботнет — это сеть компьютеров, зараженных вредоносным ПО. Киберпреступники используют специальные троянские программы, чтобы обойти систему защиты компьютеров, получить контроль над ними и объединить их в единую сеть (ботнет), которой можно управлять удаленно.
Действия в данной статье являются образовательными и будут проходить на собственном ресурсе. Автор никого не призывает к действиям и не несёт ответственности.
Установка
Для начала нам понадобится поставить на OC «Golden Eye». Выделим каталог под наш софт, в моём случае я создам новый.
Перейдём в него:
Теперь качаем архив:
Атака
Тесты
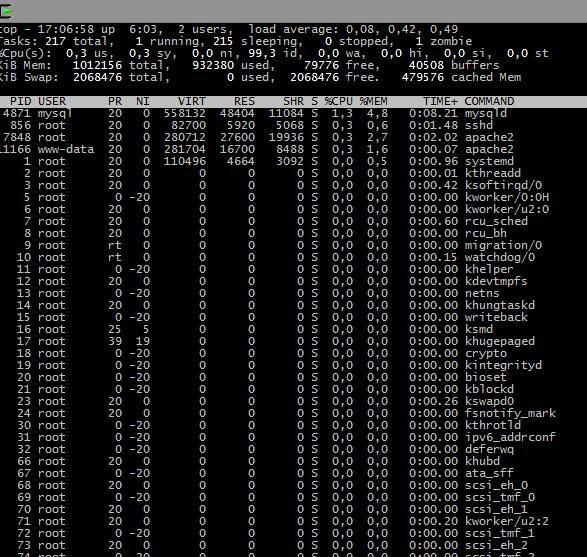
Следить за состоянием сервера я буду командой top:
Cервер находится в состоянии простоя, процесс полностью свободен, свободной оперативной памяти доступно 350 мегабайт.
Результат
Можно посмотреть по скриншоту, процессор по-прежнему практически бездействует, но количество свободной памяти резко сократилось, увеличилось количество спящих процессов.
Анализ логов
Одного взгляда на логи достаточно, что каждый запрос GET содержит различные строки, различные пользовательские агенты и различных реферов, среди которых Bing, Baidu, Yandex и другие рандомные поисковые системы.
Так что происходит, когда ваш веб-сервер встречается с этой атакой? Он анализирует входящий трафик, проверяет запрашиваемые URL, адреса источников и поле Referrer и пропускает их с кодом 200 OK. Почему? Потому что каждый браузер был различным.
Инструмент был создан остроумно так, чтобы любой сервер мог подумать, что это различные пользователи, пытающие зайти с одного IP (может быть IP прокси или большой организации?) с различными браузерами (Firefox, Chrome, MSIE, Safari и т. д.), различными операционными системами (Mac, Linux, Windows и т.д.) и даже с различными реферами. Да, возможно запрашиваемый URL был неправильным, но нормальные веб-сервера всё равно пропустят его, перенаправят на страницу ошибки в то время как соединение будет оставаться открытым (например, Apache worker/socket). Стандартный веб-сервер обычно позволяет X число одновременных пользователей с одного IP и с большим количеством соединений/используемых сокетов, этот тип атаке приводит к тяжёлому давлению на сервер и последующие пользователи получают ошибку (HTTP 503 или наподобии). Следовательно, атакующий с несколькими рандомными proxy/VPN может быстро истощить ресурсы сервера. Он даже может замедлить атаки на один IP для избежания начального выявления:
Вышеприведённая команда использует:
-w = 10 одновременные рабочие
-s = 10 одновременных соединений
-m = рандом, смесь GET и POST
Заключение
GoldenEye выглядит как расширенная (или схожая на) HTTP Flooder программа. Обе работают похожим образом, но NoCache и KeepAlive от GoldenEye делают большую разницу. Также она использует интересный способ перемешивания браузеров, операционных систем и рефереров, что может обмануть файервол.
В общем, это хороший инструмент для тестирования на нагрузку своего собственного веб-сайта (с разрешения вашей хостинг компании), вашего корпоративного веб-сайта и любых веб-приложений, которые позволяют входящие GET или POST запросы. Используйте её для обновления ваших правил файервола. WAF и благодаря этому избежите будущих атак.
Источник
DDoS attack using SlowHTTPTest (Slowloris) in Kali Linux
Most of web administrators that doesn’t care properly about the security of the servers, are often target of attacks that a lot of black hat hackers know how to perform in mass. One of those tricky attacks are the Slow HTTP attacks that target any kind of web server. Let’s explain quickly graphically what the attack looks like:
It’s just, pretty simple right? However for a bad configured server this can be the doom, the hardware won’t be pushed up to the limits, however it hangs basically for education … (bad example i know). Didn’t get it ? Imagine sending 100 old grandmas to a store, with all of them trying to tell a story from their childhood to the cashier so that no other customers can buy anything. For education, the cashier won’t kick the grandmas out of the store until they end up telling the story.
So, how you can perform such attack easily to a server and don’t die trying ? The SlowHTTPTest is a highly configurable tool that simulates some Application Layer Denial of Service attacks by prolonging HTTP connections in different ways. Use it to test your web server for DoS vulnerabilites, or just to figure out how many concurrent connections it can handle. SlowHTTPTest works on majority of Linux platforms, OS X and Cygwin – a Unix-like environment and command-line interface for Microsoft Windows, and comes with a Dockerfile to make things even easier.
Currently, the supported attacks by the slowhttptest library are:
- Slowloris
- Slow HTTP POST
- Apache Range Header
- Slow Read
In this article, we’ll teach you how to install slowhttptest on your Kali Linux system and how to use it to perform this attack on your servers.
1. Install slowhttptest
The Slowhttptest library is available from the repositories, so you can easily install it from the command line with the following command:
2. Running test
Slowloris and Slow HTTP POST DoS attacks rely on the fact that the HTTP protocol, by design, requires requests to be completely received by the server before they are processed. If an HTTP request is not complete, or if the transfer rate is very low, the server keeps its resources busy waiting for the rest of the data. If the server keeps too many resources busy, this creates a denial of service. This tool is sending partial HTTP requests, trying to get denial of service from target HTTP server.
Slow Read DoS attack aims the same resources as slowloris and slow POST, but instead of prolonging the request, it sends legitimate HTTP request and reads the response slowly. The command to run the attack to check if the server is the following one:
Note that this will make the server hang if there’s not protection against this attack implemented on the target server.
The command is described as next:
- -c : Specifies the target number of connections to establish during the test (in this example 500, normally with 200 should be enough to hang a server that doesn’t have protection against this attack).
- -H : Starts slowhttptest in SlowLoris mode, sending unfinished HTTP requests.
- -g : Forces slowhttptest to generate CSV and HTML files when test finishes with timestamp in filename.
- -o : Specifies custom file name, effective with -g .
- -i : Specifies the interval between follow up data for slowrois and Slow POST tests (in seconds).
- -r : Specifies the connection rate (per second).
- -t : Specifies the verb to use in HTTP request (POST, GET etc).
- -u : Specifies the URL or IP of the server that you want to attack.
- -x : Starts slowhttptest in Slow Read mode, reading HTTP responses slowly.
- -p : Specifies the interval to wait for HTTP response onprobe connection, before marking the server as DoSed (in seconds).
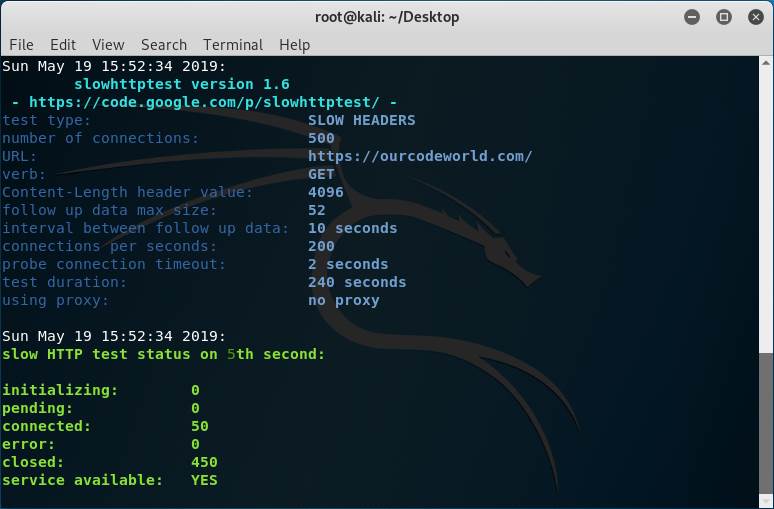
Now if we run the command with the target server, we get a similar output in the terminal:
As you can see, our target is our own website, however even with 500 connections, our server doesn’t hang at all because we do have protection against this kind of attacks. The service available will be always YES if the target is reachable. You can test with another computer/network if the website is still up indeed. The generate output in HTML created by our options, will be the following one:
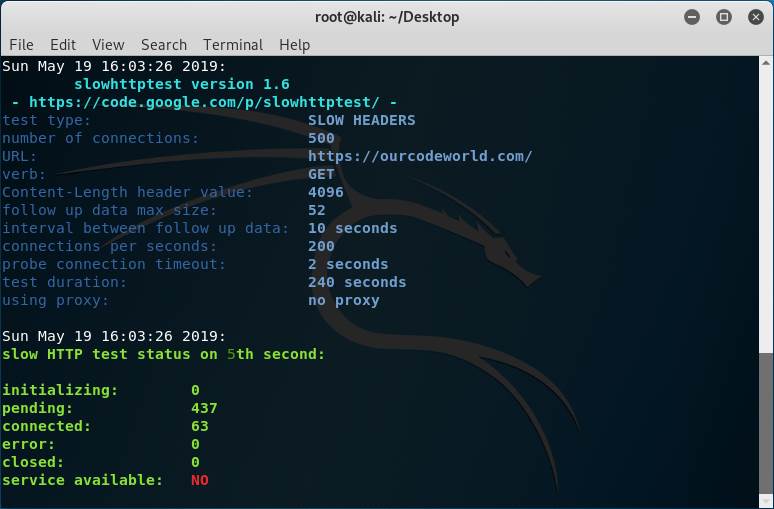
But, what if we disable the protection against Slow HTTP attacks in our server? Well, the output should be different and the website on the target server won’t be reachable:
Don’t trust always the service available message, just try accessing the real website from a browser and you will see if it works or not. The generated output this time is different because of the unreachable website:
Note that the Slow HTTP test needs to be executed on one of your own servers, do not run this kind of test on any third party server without its consent because this could get you in a lot of trouble (this is kind of illegal). This tool is meant to be used to test your own servers and implement protection against it.
Besides, do not try to run this attack on our website (spyboy.blog) as we do obviously have protection against this attack and your IP may get banned if we trace an intent of yours , thank you !!
Feel free to leave a comment below or reach me on Instagram @iamshubhamkumar__.
Источник
DOS and DDOS Attacks in Kali Linux
Today we are going to learn DOS and DDOS attack techniques. Denial-of-service (DOS) is an attack crashes a server, or make it extremely slow. DOS is typically accomplished by flooding the targeted machine or resource with superfluous requests in an attempt to overload systems and prevent some or all legitimate requests from being fulfilled. In simple words by DOS attack an attacker sends a lots of useless traffic to targeted website or server or network that because the system can’t handle this very huge amount of requests, and the system goes down, no one can use the system. As we all know that every server have traffic limits if the requests are more then the traffic limit at once the server becomes very slow or even it can crash. This technique is called DOS (Denial-Of-Service) attack.
DDOS is Distributed Denial-of-Service attack. DOS is the attack which performed from one computer to one targeted network, in DOS a single machine sends millions of useless traffic on a network but in the case of DDOS many attacker machine targets one network and every attacker machine is performing DOS. That means each and every attacker machine sends millions of traffics. DOS becomes useless against high capacity servers because larger servers easily manages millions of traffics. In such cases the attacker needs thousands or more machines from various networks to knee down the target, this is DDOS attack. To do this DDOS attacker need a organized group of hackers or botnets. Hacking group Anonymous is famous for their DDOS attacks.
Black hat hackers uses DDOS to slow down or crashes high profile web servers like banks or payment gateways, for revenges or blackmail and activism.
DOS attack can perform easily using various tools like
- Nemesy
- RUDY
- GolodenEye
- UDP flood
- PyLoris
- HULK
- ToR’s Hammer
- xerxess
- LOIC
- HOIC
- MetaSploit
There are also various types of DOS attack techniques:
- Distributed volume based DOS attack
- Degradation of service attacks
- Application-layer floods
- DDOS extortion
- HTTP POST DOS Attack
- Internet control message protocol (ICPM) flood
- R U Dead-Yet (RUDY)
- Nuke
- Peer-to Peer attacks
- Permanent denial-of-service attacks
- Reflected/spoofed attack
- shrew attack
- (S)SYN Attack
- Teardeop attacks
- Telephony denial-of-service (TDOS)
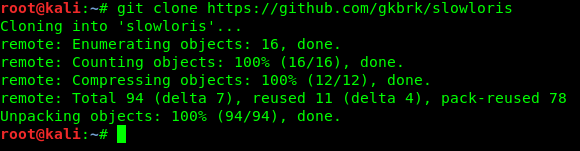
Now we practically do this on our localhost server using Slowloris. We clone Slowloris from it’s GitHub repository by using following command:
The screenshot of the command is following:
Then we type cd command to navigate in to Slowloris’s directory:
Then we need to run Slowloris Python script. Here we need the IP address of the targeted server or website in our case it is 127.0.0.1 that is our localhost. The command of DOS attack using Slowloris will be as following:
Источник
How to Launch a DoS Attack by using Metasploit Auxiliary
Mostly DDOS Attack targeting the Enterprise Networks so implement the DDoS Protection in Enterprise network is a more Important concern.
An organization should always ensure and focus on maximum Protection level for enterprise networks and you can try a free trial to Stop DDoS Attack in 10 Seconds.
Enterprise Networks should choose the best DDoS Attack prevention services to ensure the DDoS attack protection and prevent their network and website from future attacks Also Check your Companies DDOS Attack Downtime Cost.
In this Kali Linux Tutorial, we show you how attackers to launch a powerful DoS attack by using Metasploit Auxiliary.
Metasploit
Metasploit is a penetration testing platform that allows you to find, exploit, and validate vulnerabilities. Also, it provides the infrastructure, content, and tools to conduct penetration tests and comprehensive security auditing.
DoS Metasploit – Kali Linux Tutorial
In this tutorial, we are using Metasploit Auxilary SYN Flood to launch the attack “auxiliary/dos/tcp/synflood” .
SYN flood
It is a type of DoS attack which use to send a huge amount of Sync to consume all the resources of the target system.
Let’s start by launching Metasploit by simply typing msfconsole in your terminal Window. It will take a couple of minutes to launch the console.
Then use the select the auxiliary “auxiliary/dos/tcp/synflood” by typing the following command.
msf > use auxiliary/dos/tcp/synflood
Once the auxiliary got loaded type show options to list all the options with the auxiliary. you can define the settings as per your convenient.
Then you should setup RHOST and RPORT which is the target address and the port numbers respectively.
Then to Launch the attack just type exploit, so that sync flooding will start, we placed Wireshark in the target machine to show how many packets hit the machine.
We can see around 127252 packets captured within minutes after the attack launched.
Источник