- How to base64 encode and decode from command-line
- Overiew
- How to base64 encode on Ubuntu, Debian, OSX, and Red Hat
- Why Base64 Encode Data
- Base64 is not Encryption
- Base64 Encoding a String
- Base64 Encoding a File
- Decoding Strings
- Decoding Files
- Conclusion
- Bash base64 encode and decode
- base64 [OPTION] [INFILE] [OUTFILE]
- Options:
- Example#1: Encoding text data
- Example#2: Decoding text data
- Example#3: Encoding text file
- Example#4: Decoding text file
- Example#5: Encoding any user-defined text
- Example#6: Checking user validity by decoding text
- Conclusion:
- References:
- About the author
- Fahmida Yesmin
- Base64 Encode and Decode From Command Line
- Base64 Syntax
- Options
- Encoding String
- Decoding String
- Encoding Text File
- Decoding Text File
- Encoding User Input
- Validating User key
- About the author
- Karim Buzdar
How to base64 encode and decode from command-line
Overiew
In this tutorial, you will learn how to base64 encode and decode from the command-line on Linux. You will also learn what base64 encoding is and why it should never be used to protect data from unauthorized access.
Base64 encoding and decoding data has many use cases. One being is ensuring data integrity when transferring data over the network, while another is storing Secrets in Kubernetes.
After reading this tutorial you will understand how to easily encode files or strings, and then decode them back.
How to base64 encode on Ubuntu, Debian, OSX, and Red Hat
If you are running popular linux distributions, such as Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, or Red Hat, the base64 command-line tool is typically pre-installed. You should not have to perform any additional steps.
OSX also comes bundled with its own version of base64.
Why Base64 Encode Data
Transferring an ASCII file over the network can cause corruption if not decoded correctly. The reason is ASCII files are string converted to bytes, and when those bytes are decoded incorrectly back to ASCII your data becomes corrupt.
Base64 was introduced as a way to convert your ASCII data into arbitrary bytes, where they could then be transferred as bytes, and decoded correctly back to ASCII.
In short, base64 encoding ensures the integrity of our data when transferred over the network.
Base64 is not Encryption
Encoding files is not encryption and should never be used to secure sensitive data on disk. Rather it is a useful way of transferring or storing large data in the form of a string.
While it may obfuscate that actual data from should surfers, anyone who has access to base64 encoded data can easily decode it.
Base64 Encoding a String
To base64 encode string you can pipe an echo command into the base64 command-line tool. To ensure no extra, hidden characters are added use the -n flag.
Without the -n flag you may capture a hidden characters, like line returns or spaces, which will corrupt your base64 encoding.
Which will output the following
Base64 Encoding a File
To base64 encode a file
This will output a very long, base64 encoded string. You may want to write the stdout to file instead.
Decoding Strings
To decode with base64 you need to use the —decode flag. With encoded string, you can pipe an echo command into base64 as you did to encode it.
Using the example encoding shown above, let’s decode it back into its original form.
Provided your encoding was not corrupted the output should be your original string.
Decoding Files
To decode a file with contents that are base64 encoded, you simply provide the path of the file with the —decode flag.
As with encoding files, the output will be a very long string of the original file. You may want to output stdout directly to a file.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you learned how to base64 encode files and strings. This something commonly done to transfer files in such a way that it remains
Источник
Bash base64 encode and decode
base64 [OPTION] [INFILE] [OUTFILE]
You can use different types of options with base64 command. Data can be taken from any file or standard input while encoding or decoding. After encode or decode, you can send the output in a file or print the output in the terminal.
Options:
-e or –encode
This option is used to encode any data from standard input or from any file. It is the default option.
-d or –decode
This option is used to decode any encoded data from standard input or from any file.
-n or –noerrcheck
By default, base64 checks error while decoding any data. You can use –n or –noerrcheck option to ignore checking at the time of decoding.
-u or –help
This option is used to get information about the usage of this command.
-i, –ignore-garbage
This option is used to ignore non-alphabet character while decoding.
–copyright
It is used to get copyright information.
–version
It is used to get the version information.
How you use the base64 command in Linux is shown in this tutorial by using some examples.
Example#1: Encoding text data
You can encode any text data by using base64 in the command line. When you want to encode any data using base64 then using -e or –encode option is optional. So, if you don’t mention any option with base64 then it will work for encoding. The following command will encode the data, ‘linuxhint.com’ and print the encoded data as output.
Output:
Example#2: Decoding text data
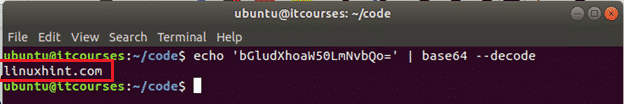
The following command will decode the encoded text, ‘bGludXhoaW50LmNvbQ==‘ and print the original text as output.
Output:
Example#3: Encoding text file
Create a text file named, ‘sample.txt’ with the following text that will be encoded by using base64.
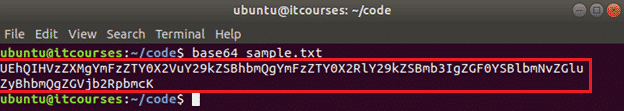
You can print the encoded text in the command line or store the encoded text into another file. The following command will encode the content of the sample.txt file and print the encoded text in the terminal.
Output:
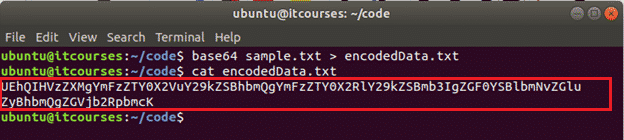
The following commands will encode the content of the sample.txt file and save the encoded text into the encodedData.txt file.
Output:
Example#4: Decoding text file
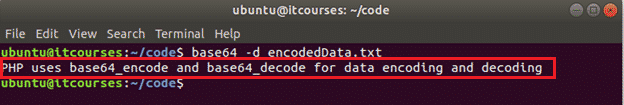
The following command will decode the content of the encodedData.txt file and print the output in the terminal
Output:
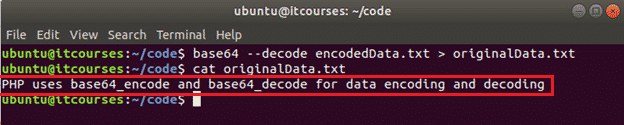
The following commands will decode the content of the encodedData.txt file and store the decoded content into the file, originalData.txt.
Output:
Example#5: Encoding any user-defined text
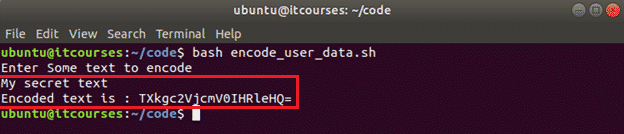
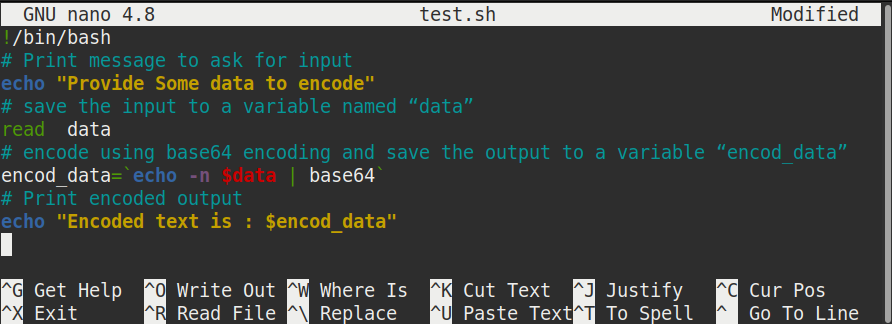
Create a bash file named encode_user_data.sh with the following code. The following script will take any text data as input, encode the text by using base64 and print the encoded text as output.
Output:
Example#6: Checking user validity by decoding text
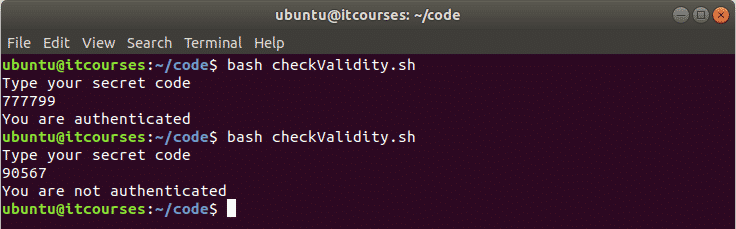
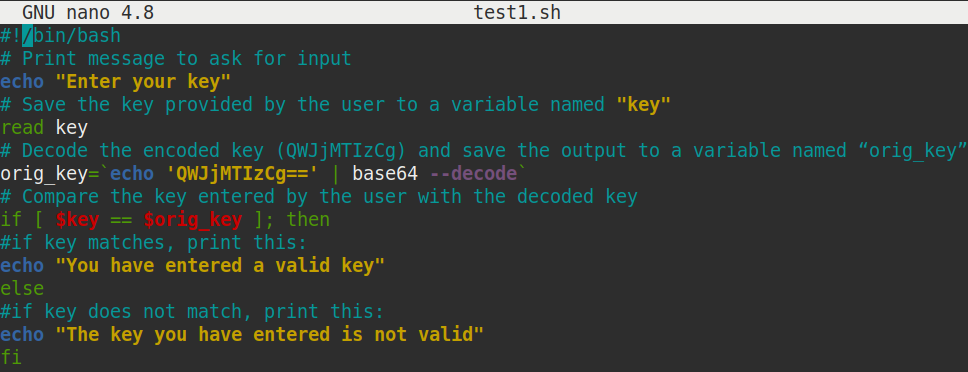
Create a bash file named checkValidity.sh and add the following code. In this example, a secret text is taken from the user. A predefined encoded text is decoded by base64 and compared with the user input. If both values are equal then the output will be ‘You are authenticated’ otherwise the output will be ‘You are not authenticated’. Using this simple decoding code, normal validation can be done very easily.
Output:
Conclusion:
For any sensitive data like password or any confidential data, encoding and decoding system is not suitable at all. You must use encryption and decryption system for securing these type of data.
References:
About the author
Fahmida Yesmin
I am a trainer of web programming courses. I like to write article or tutorial on various IT topics. I have a YouTube channel where many types of tutorials based on Ubuntu, Windows, Word, Excel, WordPress, Magento, Laravel etc. are published: Tutorials4u Help.
Источник
Base64 Encode and Decode From Command Line
Some of the uses of encoding are:
- Data compression
- Data hiding
- Transmission of data in another format
For encoding data, Base64 uses only alphabet, number and = symbol. For instance, c2FtcGxlCg== is a valid encoded data while b?HV3.Zh2J== is not a valid encoded data.
In this article, we will explain how to use the base64 command to encode and decode the data in a string or a file.
We have performed the commands on Ubuntu 20.04 Focal Fossa system. However, you can also run the same commands on other Linux distributions. For running the commands, we have used the command line Terminal application, which can be accessed using the Ctrl+Alt+T keyboard shortcut.
Base64 Syntax
Here is the syntax for encoding using Base64:
Options
Some of the command-line options that can be used with base64 command are:
Use this option to decode a file or a string.
Use this option to display help regarding the usage of base64.
Use this option while decoding to ignore non-alphabet characters
Use this option to display version information
Encoding String
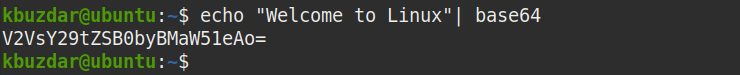
You can easily encode a string using the base64 command. For instance, to encode a sample text “Welcome to Linux” to base64, the command would be:
This command will encode the text in the string using base64 and print the encoded text to standard output as shown in the following screenshot
You can also save the encoded output to a file rather than printing to standard output using the redirection operator (>). The following command will encode the text and save the output to a file named “encodedfile.txt:
To view the encoded file, you can use the cat command:
Decoding String
You can also decode the base64 encoded text using the –decode or -d option. For instance to decode base64 encoded text “V2VsY29tZSB0byBMaW51eAo=”, the command would be:
This command will decode the base64 encoded text and print the original text on the standard output as shown in the following screenshot.
You can also save the decoded output to a file rather than printing to standard output using the redirection operator (>). The following command will decode the encoded text and save the original text to a file named “decodedfile.txt:
Encoding Text File
The base64 command can also be used to encode a text file. For instance, to encode a text file named “testfile.txt”, the command would be:
This command will encode the specified text file and print its encoded form on the standard output as shown in the following screenshot.
You can also save the encoded output to a file rather than printing to standard output using the redirection operator (>). The following command will convert the text in the file using base64 and save the output to another file named “encodedfile.txt:
To view the encoded file, you can use the cat command:
Decoding Text File
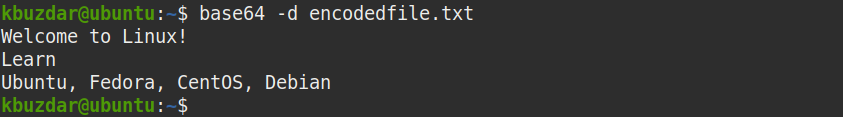
To decode an encoded text file, use the –decode or -d option. For instance to decode base64 encoded text file “encodedfile.txt”, the command would be:
This command will decode the base64 encoded text file and print the original text on the standard output as shown in the following screenshot.
You can also save the decoded output to a file rather than printing to standard output using the redirection operator (>). The following command will decode the encoded text and save the original text to a file named “decodedfile.txt which can be later viewed using the cat command.
Encoding User Input
Using the base64 encoding, we can encode any user-provided data. For this purpose, we will need to create a script that will take user input, encode it using base64 encoding, and print the encoded data on standard output.
Create a script “test.sh” with the following code:
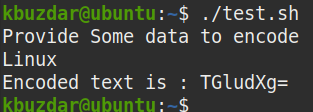
Run the script as follows:
After running the script, you will be asked to input the data that you want to encode. Type some data and press Enter, and you will receive the encoded output on the screen.
Validating User key
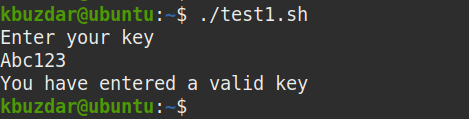
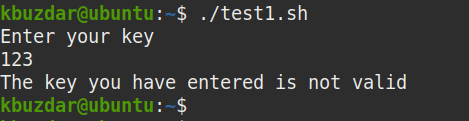
Now let’s see an example of base64 decoding. We will use the base64 decoding to check user validity. To do so, we will create a script that will ask the user for a key. Then it will match the input key with the predefined key, which will be first decoded by base64 decoding. If the key entered by the user matches with the predefined key, it will print “You have entered a valid key” message, otherwise, you will see “The key you have entered is not valid “printed on the screen.
Create a script “test1.sh” with the following code:
Run the script as follows:
After running the script, you will be asked for the key. Type the key and press Enter. If the entered key matches with the predefined decoded key, you will receive the ” You have entered a valid key” message, otherwise “The key you have entered is not valid ” message will be printed on the screen.
This is how you can use the base64 to encode and decode a string or a file from the command line. The results can be either printed on the standard output or save in a file. However, remember that encoding is not similar to encryption, and one can easily reveal the encoded data, so it is not recommended to use encoding for the transmission of sensitive data.
About the author
Karim Buzdar
Karim Buzdar holds a degree in telecommunication engineering and holds several sysadmin certifications. As an IT engineer and technical author, he writes for various web sites. He blogs at LinuxWays.
Источник