- Как удалить файл в Linux через терминал
- Удаление файлов с помощью rm
- Синтаксис и опции команды rm
- Поиск и удаление файлов с помощью find
- How To: Linux / UNIX delete a file using rm command
- Syntax: rm command to remove a file
- Unix Remove or delete a file example
- Linux delete multiple files
- Linux recursively delete all files
- Linux delete a file and prompt before every removal
- Force rm command to explain what is being done with file
- How to delete empty directories
- How to read a list of all files to delete from a text file
- How do I delete a file named -foo.txt or a directory named -bar?
- Never run rm -rf / as an administrator or normal UNIX / Linux user
- Conclusion
- Linux: Delete file & folder using command line terminal
- In Linux, delete a file using terminal
- Delete Linux empty folder using terminal
- Delete empty directory / folder
- Delete Linux directory/folder that contains files
- Command to remove file with dash ‘-‘
- Delete everything
Как удалить файл в Linux через терминал
В операционной системе Linux практически все операции можно выполнить с помощью терминала. Для этого в системе предусмотрено мужество очень мощных и гибких команд и утилит, которые позволяют очень тонко управлять системой.
В этой инструкции мы рассмотрим удаление файлов. Это типичная и очень простая процедура, выполнять которую должен уметь любой пользователь. Здесь вы узнаете, как удалить файл в Linux через терминал и какие команды для этого понадобятся. Статья будет актуальной для любого дистрибутива Linux, например, Ubuntu Linux, Debian и т. д.
Удаление файлов с помощью rm
Для того чтобы удалить файл в Linux через терминал необходимо использовать команду « rm » (от английского «remove»). Данная команда удаляет все указанные ей файлы, но по умолчанию не удаляет каталоги. Чтобы позволить команде « rm » удалять каталоги нужно добавить опцию « -r » или « -R ». Более подробно об этом во второй половине статьи.
Также нужно отметить, что команда « rm » не выполняет физическое удаление данных, вместо этого указанные файлы просто удаляются из файловой системы, а занимаемое ими место маркируется как свободное. Это означает, что после удаления данные остаются на диске и пока они не будут перезаписаны другими данными, их можно будет восстановить с помощью специальных программ. Для физического удаления данных с перезаписью диска следует использовать команду « shred ».
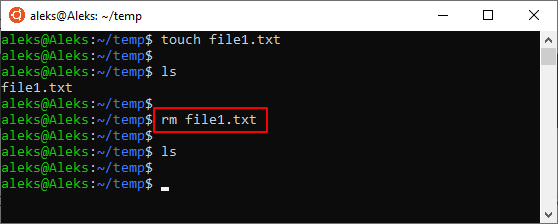
В общем случае для удаления файла в Linux через терминал достаточно просто ввести в терминал « rm » и указать имя документа. Например, для того чтобы удалить « file1.txt » из текущего каталога нужно выполнить вот такую команду:
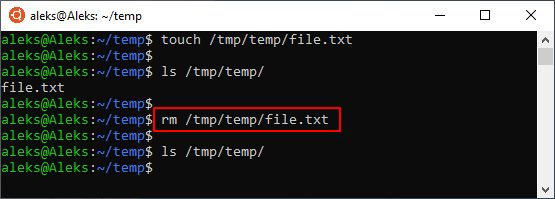
Если удаляемый файл находится не в текущем каталоге, то в терминале нужно указать полный путь. Например, это может выглядеть вот так:
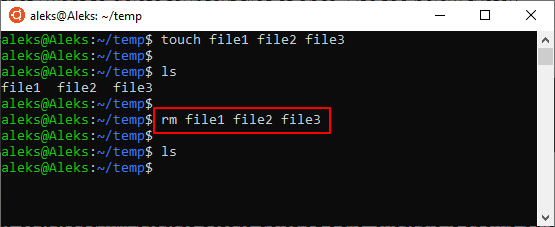
При необходимости, с помощью команды « rm » можно удалить сразу несколько файлов. Для этого просто введите « rm » и перечислите имена через пробел, например:
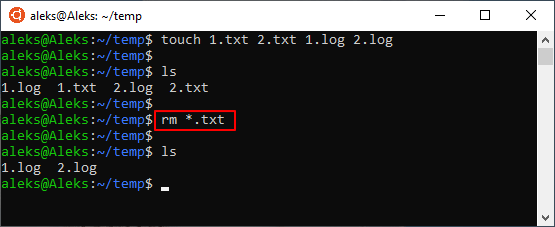
Для удаления большого количества похожих файлов можно использовать маски. Например, чтобы удалить все документы с расширением txt нужно выполнить вот такую команду:
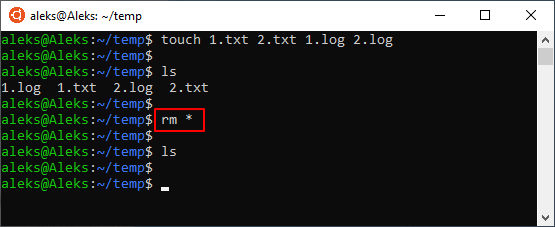
Также маску можно использовать для удаления вообще всех файлов. Например, чтобы удалить все файлы в текущей папке нужно выполнить:
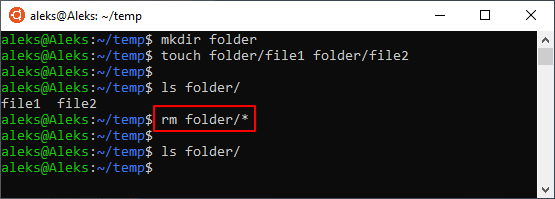
Аналогичным способом можно удалить все файлы в определенной папке:
Главное, соблюдать осторожность, так как при использовании масок можно удалить что-то лишнее.
Синтаксис и опции команды rm
Команда « rm » имеет множество опций, что позволяет очень тонко управлять процессом удаления файлов. Вы можете изучить все доступные опции если введете в терминал Linux команду « man rm ». Здесь же мы будем рассматривать самые простые и часто используемые опции.
Синтаксис команды « rm » выглядит следующим образом:
Разберем основные опции команды rm:
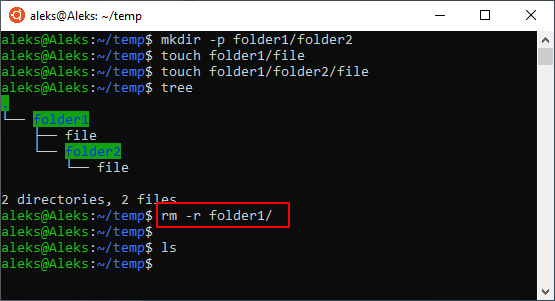
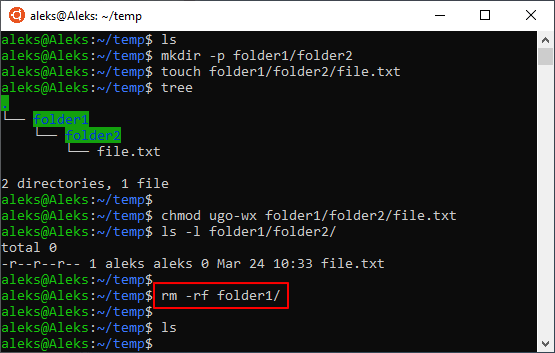
Теперь разберем некоторые опции, которые часто используются при удалении файлов в Linux через терминал. Например, очень часто возникает необходимость удалить папку вместе с всем содержимым. Для этого нужно использовать опцию «-r», которая включает рекурсивный обход папок. Например, для того чтобы удалить папку «folder1» и все ее содержимое нужно выполнить:
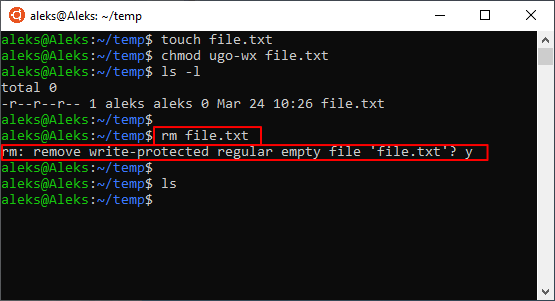
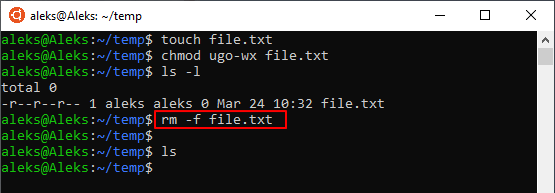
Если права доступа к файлу разрешают только чтение, то в терминале Linux появится запрос подтверждения, и чтобы продолжить вам нужно будет ввести букву « y » (от англ. «yes»).
Чтобы избежать такой ситуации и удалять все файлы без предупреждения нужно использовать опцию « -f ». Например:
Не редко возникает необходимость удалить папку вместе со всеми файлами и без запросов на подтверждение. В этом случае нужно комбинировать опции « -r » и « -f ». В результате команда выглядит вот так:
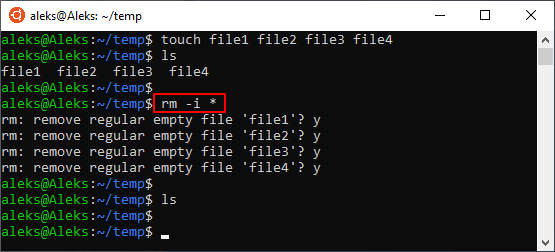
Если вы, наоборот, хотите каждый раз получать запрос подтверждения, то команду « rm » нужно выполнять с опцией « -i ». Например, для того чтобы удалить все файлы в текущем каталоге с запросом подтверждения нужно выполнить:
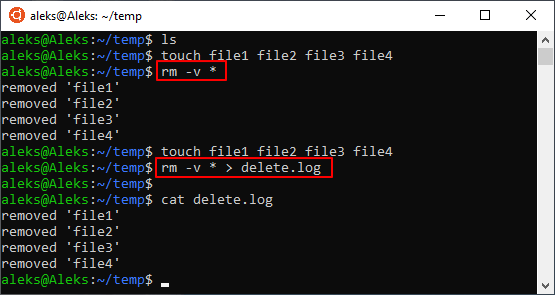
Также бывает полезной опция « -v ». При ее использовании в терминале будет появляться подробная информация о выполняемых действиях. Например, для того чтобы удалить все файлы в текущем каталоге и вывести информацию в терминал нужно выполнить:
Также вывод информации можно перенаправить в файл. Для этого после команды нужно использовать оператор перенаправления вывода ( > ) и указать название файла. Например:
Естественно все эти опции можно комбинировать, в зависимости от ваших задач.
Поиск и удаление файлов с помощью find
Также нужно отметить, что существуют и альтернативные способы удаления файлов. Например, вы можете использовать команду поиска « find ». Команда « find » будет полезна в тех случаях, когда вам нужно удалить определенные файлы в целом ряде папок.
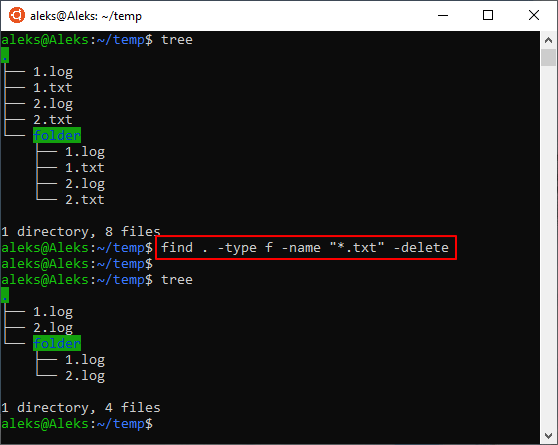
Например, для того чтобы найти и удалить все txt-файлы в текущей и во всех вложенных папках можно выполнить вот такую команду:
Чтобы узнать больше об использовании « find » введите в терминал команду « man find ».
Источник
How To: Linux / UNIX delete a file using rm command
H ow do I delete a file under a Linux / UNIX / *BSD / AIX / HP-UX operating system using command line options?
To remove or delete a file or directory in Linux, FreeBSD, Solaris, macOS, or Unix-like operating systems, use the rm command or unlink command. This page explains how to delete a given file on a Linux or Unix like system using the command line option.

| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | No |
| Requirements | rm and unlink command on Linux or Unix |
| Est. reading time | 4 minutes |
Syntax: rm command to remove a file
rm (short for remove) is a Unix / Linux command which is used to delete files from a filesystem. Usually, on most filesystems, deleting a file requires write permission on the parent directory (and execute permission, in order to enter the directory in the first place). The syntax is as follows to delete the specified files and directories:
- -f : Forcefully remove file
- -r : Remove the contents of directories recursively
When rm command used just with the file names, rm deletes all given files without confirmation by the user.
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Warning : Be careful with filenames as Unix and Linux, by default, won’t prompt for confirmation before deleting files. Always keep verified backups of all critical files and data.
Unix Remove or delete a file example
Say you have a file named abc.txt and you want to remove it:
$ rm abc.txt
Linux delete multiple files
Delete three files named foo.mp4, bar.doc, and demo.txt, run:
Linux recursively delete all files
Remove all files and sub-directories from a directory (say deltree like command from MS-DOS world), enter:
$ rm -rf mydir
Linux delete a file and prompt before every removal
To request confirmation before attempting to remove each file pass the -i option to the rm command:
$ rm -i filename
Sample outputs:
Gif 01: rm command demo
Force rm command to explain what is being done with file
Pass the -v option as follows:
$ rm -v moiz.list.txt bios-updates.doc
removed ‘moiz.list.txt’
removed ‘bios-updates.doc’
How to delete empty directories
To remove empty directory use rmdir command and not the rm command:
$ rmdir mydirectory
$ rmdir dirNameHere
$ rmdir docs
How to read a list of all files to delete from a text file
The rm command is often used in conjunction with xargs to supply a list of files to delete. Create a file called file.txt:
$ cat file.txt
List of to delete:
Now delete all file listed in file.txt, enter:
$ xargs rm
How do I delete a file named -foo.txt or a directory named -bar?
To delete a file called -foo.txt :
rm — -foo.txt
OR
rm — ./-foo.txt
To delete a directory called -bar :
rm -r -f — -bar
The two — dashes tells rm command the end of the options and rest of the part is nothing but a file or directory name begins with a dash.
Never run rm -rf / as an administrator or normal UNIX / Linux user
WARNING! These examples will delete all files on your computer if executed.
$ rm -rf /
$ rm -rf *
rm -rf (variously, rm -rf /, rm -rf *, and others) is frequently used in jokes and anecdotes about Unix disasters. The rm -rf / variant of the command, if run by an administrator, would cause the contents of every writable mounted filesystem on the computer to be deleted. Do not try these commands.
Conclusion
You learned how to delete files on Linux and Unix-like operating systems. Here are all important options for GNU rm command (read man page here)
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -f | Ignore nonexistent files and arguments, never prompt |
| -i | Prompt before every file removal |
| -I | Prompt once before removing more than three files, or when removing recursively; less intrusive than -i, while still giving protection against most mistakes —interactive[=WHEN] prompt according to WHEN: never, once (-I), or always (-i); without WHEN, prompt always |
| —one-file-system | when removing a hierarchy recursively, skip any directory that is on a file system different from that of the corresponding command line argument |
| —no-preserve-root | do not treat ‘/’ specially |
| —preserve-root[=all] | do not remove ‘/’ (default); with ‘all’, reject any command line argument on a separate device from its parent |
| -r | remove directories and their contents recursively |
| -R | same as above |
| -d | rmove empty directories |
| -v | Explain what is being done |
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
Linux: Delete file & folder using command line terminal
As we know Linux is slightly different from Windows for various tasks even in deleting files and folders. And here we will see the quick Linux commands to delete a file and directory using the terminal.
However, just like in Windows, system files or the important folders are only accessible by admin, in Linux, they are under sudo or root users. Therefore, if want to delete any system file on Linux using GUI, then you should log in as root but that is a bit risky because you don’t want to run all your applications under an admin user.
Therefore, under the standard sudo user, we can use the command terminal to easily delete and files and folders including the empty ones.
Note: If you get permission denied error while using any command given below then use sudo with that.
In Linux, delete a file using terminal
To delete a file in Linux follows the below-given steps. Here we are using Ubuntu, however, the steps will be the same for all the available distros.
- Open command terminal, the shortcut key of doing that is [ Ctrl ] + [ Alt ] + [ T ].
- Switch to the directory where the files are located that you want to delete using a command cd filename. For example, a file in the /opt directory, so to switch into that type- cd /opt.
- Now, to know whether the file which we want to remove, is in the current directory, we can use ls command.
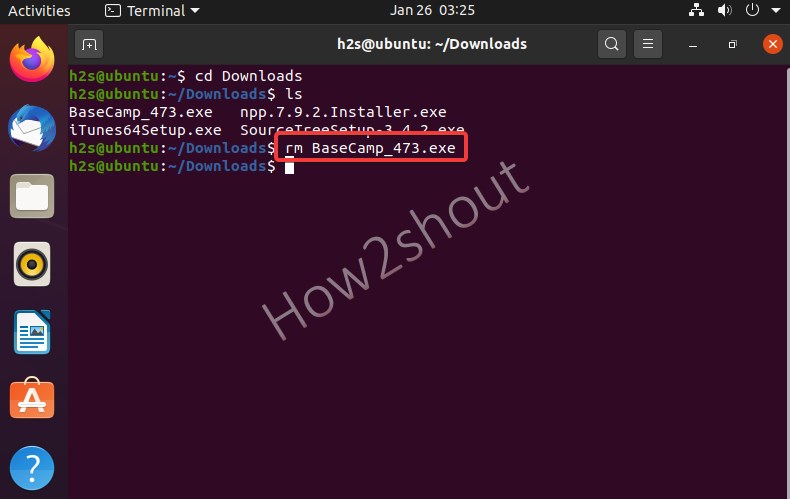
- To delete a file, you now type: rm filename .
- The command rm stands for “remove”. For example, here we have a file BaseCamp_473.exe then the command will be rm BaseCamp_473.exe. The file with this name will then be deleted if that is available in the directory.
- One thing that needs to be noted, using the command terminal and the rm command, the files will be deleted directly and it not going to be moved to the recycle bin.
Delete Linux empty folder using terminal
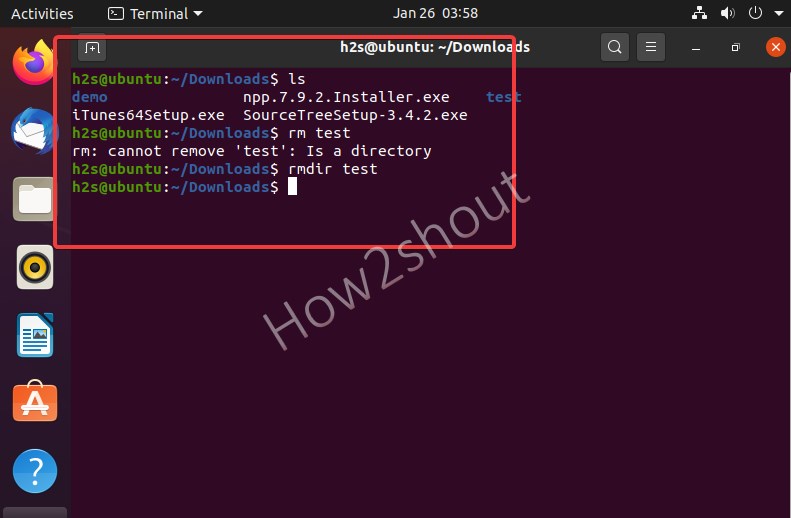
The process to remove directories is also the same as files, however, the command will slightly be different because if we use rm command then that will give an error such as “rm: cannot remove ‘test’: Is a directory“. Therefore, using it you cannot delete files in the terminal. Moreover, Linux also differentiates between empty and filled folders, and how to deal with them is given below.
Delete empty directory / folder
- Go to Applications and open Terminal, whereas Ubuntu, Manjaro, and other user-friendly Linux can also use the key combination [ Ctrl ] + [ Alt ] + [ T ] to open it.
- With the help of cd command switch to the directory from where you want to remove the empty folder.
- To check whether the directory is in the currently selected folder, you can ls use the command.
- Type in the command rmdir foldername , replace the foldername in the command with the directory you want to delete, and then press the [ Enter ] key.
- Example for the terminal: rmdir test
- Remember, the command rmdir stands for “remove directory” and only deletes empty directories.
Delete Linux directory/folder that contains files
Now, if there is some folder that contains files and folder then we cannot use rmdir command, for that simply use rm with -r flag will be in use. Moreover, we can even use this for empty directories as well.
- Press the key combination [ Ctrl ] + [ Alt ] + [ T ] to open a terminal.
- Go to the directory from where you want to remove the folder along with its file. To switch between folders we can use cd command.
- Again just like we did above, first, confirm the folder you want to remove is actually there or not using ls use the command.
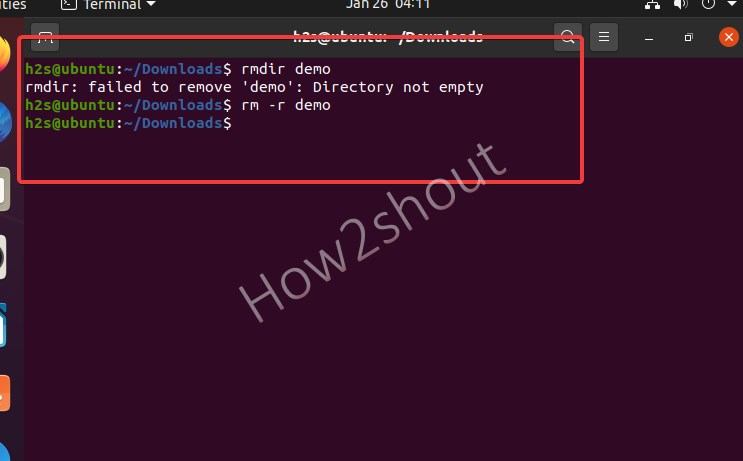
- Type in the command rm -r , followed by the directory you want to delete, and press [ Enter ].
- For Example in the terminal: rm -r demo
- The command rm -r is the abbreviation for “remove recursive” and deletes filled directories. Sometimes, if any folder is not getting deleted, we can use the -f flag means force, as well. Example– rm -rf foldername
Command to remove file with dash ‘-‘
To remove a file whose name starts with a ‘-‘, for example ‘-h2s’,
use one of these commands:
Delete everything
This is really a disastrous command because it will remove all essential files on your Linux system and left nothing but an unbootable panic system, thus this here just for knowledge, and don’t try it on the system you are working. Inshort your Linux will delete all directories on all hard drives and partitions.
The above command will give a warning, that this will remove everything, thus in case you want to use it then type – sudo rm -rf / —no-preserve-root
Источник