- О приложении «Служба каталогов»
- Доступ к домену Open Directory
- Доступ к домену Active Directory
- Доступ к каталогам LDAP
- How to repair a Mac disk with Disk Utility
- Open Disk Utility
- Select your disk in Disk Utility
- Repair volumes, then containers, then disks
- If Disk Utility found errors that it can’t repair
- If your disk doesn’t appear in Disk Utility
- FAQ: Зачем нужна Служба каталогов?
О приложении «Служба каталогов»
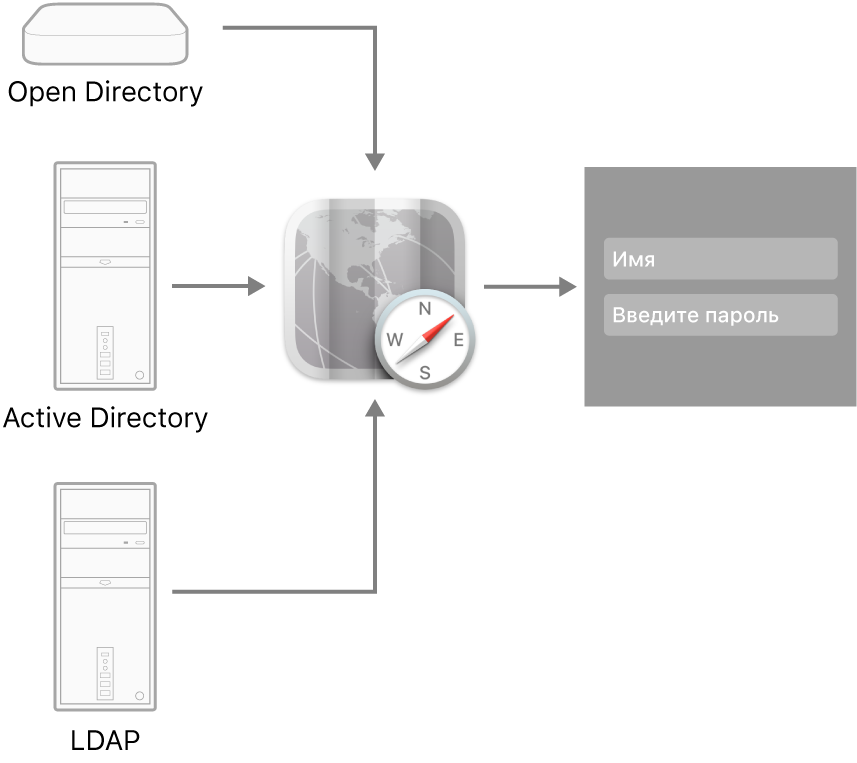
В Службе каталогов можно добавлять и настраивать расширенные подключения к серверам каталогов. Компьютер Mac обращается к серверам каталогов за сведениями о пользователях и другими административными данными, хранящимися в домене каталогов серверов каталогов. Компьютер Mac может подключаться к серверам Open Directory, Active Directory и LDAP.
Когда Вы добавляете сервер каталогов в список «Службы» в приложении «Служба каталогов» (или удаляете из этого списка), настройки подключения для этого сервера каталогов также добавляются в списки «Аутентификация» и «Контакты» (или удаляются из них). Но если Вы удаляете настройки соответствующего подключения из списков «Аутентификация» и «Контакты», сервер каталогов не удаляется из списка «Службы».
Расширенные функции Службы каталогов позволяют настраивать записи, службы, политики поиска и параметры удаленных компьютеров Mac с приложением macOS Server.
Далее перечислены расширенные функции Службы каталогов.
Службы. Настройка подключения к серверам каталогов (Open Directory, Active Directory и LDAP), доступным пользователю.
Политика поиска. Настройка областей, в которых компьютер Mac будет искать информацию для идентификации пользователей и контактные данные.
Подключение. Настройка удаленных компьютеров Mac с приложением macOS Server.
Редактор каталогов. Настройка типов записей и атрибутов в аутентифицированном домене каталогов или в локальной службе каталогов.
Доступ к домену Open Directory
Настройте компьютер Mac для доступа к определенному домену Open Directory. См. раздел Настройка доступа к Open Directory.
Доступ к домену Active Directory
На Mac с macOS или приложением macOS Server настройте доступ к домену Active Directory на сервере Windows 2000 или новее. См. раздел Настройка доступа к домену.
Доступ к каталогам LDAP
На Mac с macOS или приложением macOS Server настройте доступ к определенным каталогам LDAP. См. разделы Настройка доступа к каталогу LDAP и Настройка доступа к каталогу LDAP вручную.
Источник
How to repair a Mac disk with Disk Utility
Use the First Aid feature of Disk Utility to find and repair disk errors.
Disk Utility can find and repair errors related to the formatting and directory structure of a Mac disk. Errors can lead to unexpected behavior when using your Mac, and significant errors might even prevent your Mac from starting up completely.
Before proceeding, make sure that you have a current backup of your Mac, in case you need to recover damaged files or Disk Utility finds errors that it can’t repair.
Open Disk Utility
In general, you can just open Disk Utility from the Utilities folder of your Applications folder. However, if your Mac doesn’t start up all the way, or you want to repair the disk your Mac starts up from, open Disk Utility from macOS Recovery:
- Determine whether you’re using a Mac with Apple silicon, then follow the appropriate steps:
- Apple silicon: Turn on your Mac and continue to press and hold the power button until you see the startup options window. Click the gear icon labeled Options, then click Continue.
- Intel processor: Turn on your Mac, then immediately press and hold these two keys until you see an Apple logo or other image: Command (⌘) and R.
- You may be asked to select a user you know the password for. Select the user, then click Next and enter their administrator password.
- From the utilities window in macOS Recovery, select Disk Utility and click Continue.
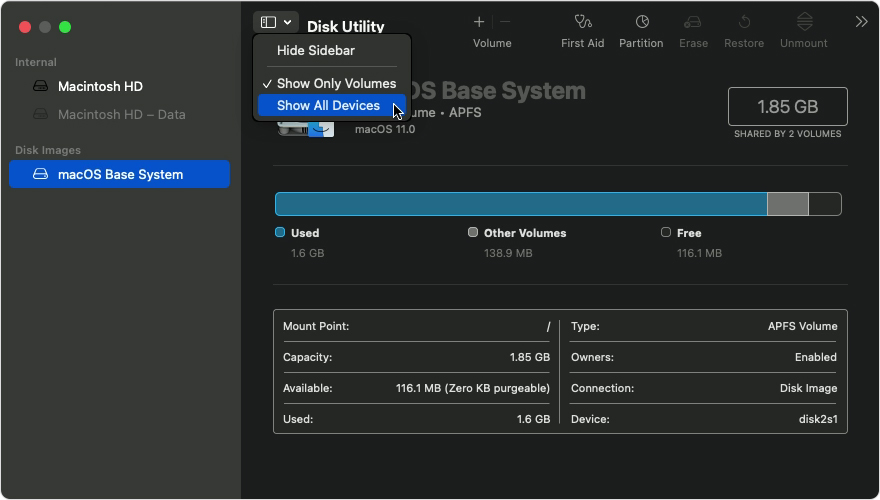
Select your disk in Disk Utility
Choose View > Show All Devices (if available) from the menu bar or toolbar in Disk Utility.
The sidebar in Disk Utility should now show each available disk or other storage device, beginning with your startup disk. And beneath each disk you should see any containers and volumes on that disk. Don’t see your disk?
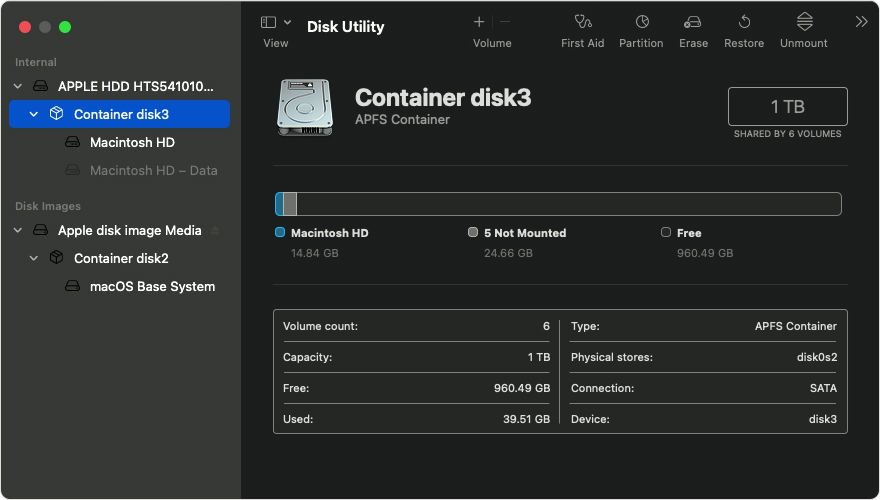
In this example, the startup disk (APPLE HDD) has one container and two volumes (Macintosh HD, Macintosh HD — Data). Your disk might not have a container, and it might have a different number of volumes.
Repair volumes, then containers, then disks
For each disk that you’re repairing, start by selecting the last volume on that disk, then click the First Aid button or tab.
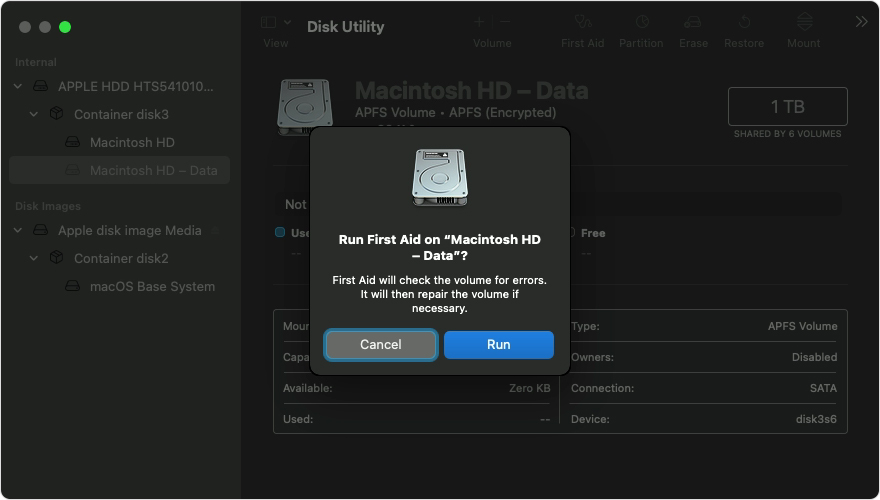
In this example, the last volume on the disk is Macintosh HD — Data.
Click Run to begin checking the selected volume for errors.
- If there is no Run button, click the Repair Disk button instead.
- If the button is dimmed and you can’t click it, skip this step for the disk, container, or volume you selected.
- If you’re asked for a password to unlock the disk, enter your administrator password.
After Disk Utility is done checking the volume, select the next item above it in the sidebar, then run First Aid again. Keep moving up the list, running First Aid for each volume on the disk, then each container on the disk, then finally the disk itself.
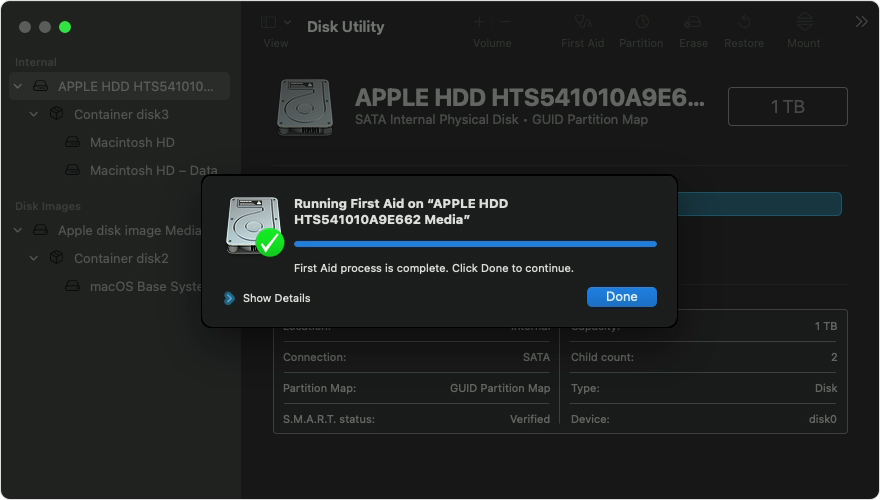
In this example, the repair order is Macintosh HD — Data, then Macintosh HD, then Container disk3, then APPLE HDD.
If Disk Utility found errors that it can’t repair
If Disk Utility found errors that it could not repair, use Disk Utility to erase (format) your disk.
If your disk doesn’t appear in Disk Utility
If Disk Utility can’t see your disk, it also can’t see any containers or volumes on that disk. In that case, follow these steps:
- Shut down your Mac, then unplug all nonessential devices from your Mac.
- If you’re repairing an external drive, make sure that it’s connected directly to your Mac using a cable that you know is good. Then turn the drive off and back on.
- If your disk still doesn’t appear in Disk Utility, your Mac might need service. If you need help, please contact Apple Support.
Источник
FAQ: Зачем нужна Служба каталогов?

К нам поступил следующий вопрос:
Это утилита управления директориями 🙂 Поскольку такой ответ вас точно не устроит, поясним, что эта служебная программа нужна для организации и управления доступом к различным службам сетевых каталогов, например, к LDAP.
Рядовому пользователю Служба каталогов вряд ли когда-нибудь вообще понадобится. Поэтому она и спрятана очень глубоко — даже не в /Applications/Utilities, а вообще в /System/Library/CoreServices. Другое дело — серверные версии Mac OS X, где Служба каталогов по умолчанию сидит прямо в Доке.
Единственное более-менее полезное применение Службы каталогов для обычного маковода — эксклюзивная возможность включить на Маке учётную запись рут-админа, от имени которого можно будет входить в систему и делать с ней абсолютно всё, что в голову взбредёт, потому что для root-пользователя не существует никаких ограничений и запретов. Обычно к этому трюку прибегают для переименования папки пользователя, которую никак иначе переименовать не получится. Но всегда нужно помнить, что неограниченные возможности могут повлечь за собой неограниченно негативные последствия для системы 😉
Источник