- 5 бесплатных программ для разметки разделов диска в Linux
- GParted
- GNOME Disks
- KDE Partition Manager
- Fdisk [Command Line]
- GNU Parted [Command Line]
- Заключение
- Disk editor для linux
- What is new in version 7
- What is new in version 6
- What is new in version 5
- Overview:
- The Main Features:
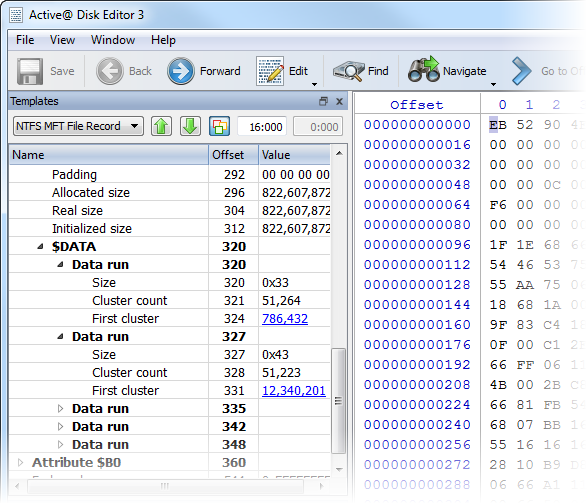
- 1. Enhanced template view
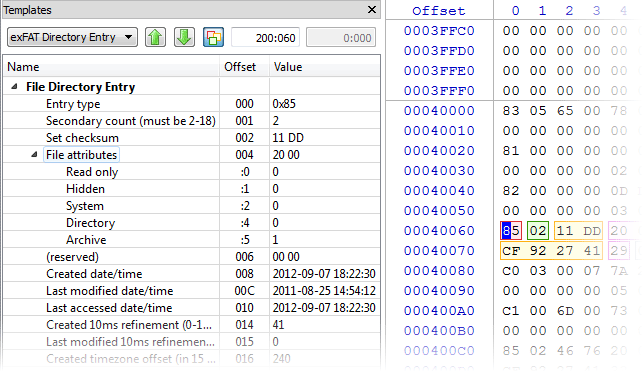
- 2. Detailed MFT record information
- 3. Side-by-side Compare and Edit
- 4. Fields coloring with data in tooltips
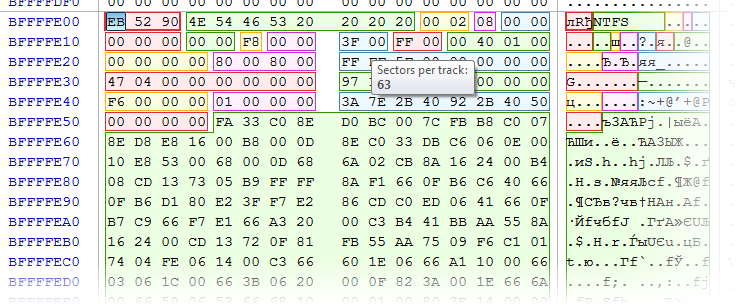
- 5. Extensive exFAT support
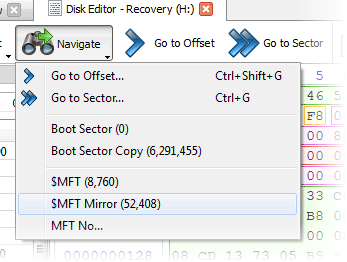
- 6. Fast navigation points
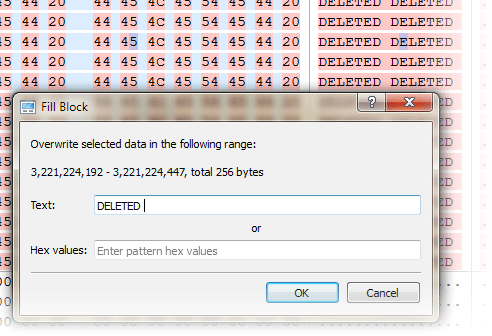
- 7. Filling selection with a pattern
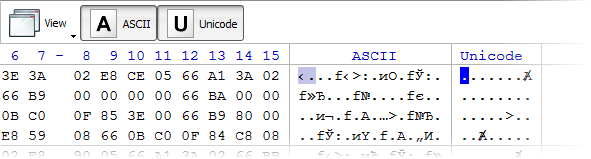
- 8. Unicode support
- 9. Quick Disk Info
- 10. Bookmarks
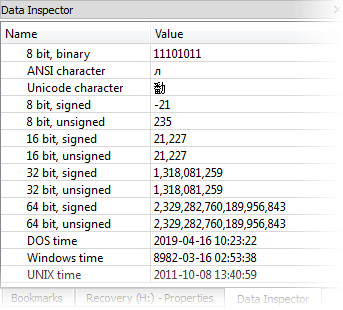
- 11. Inspector
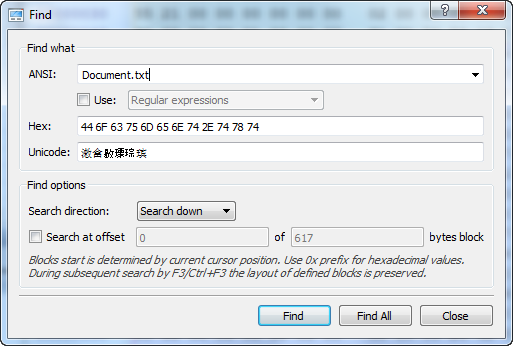
- 12. Search
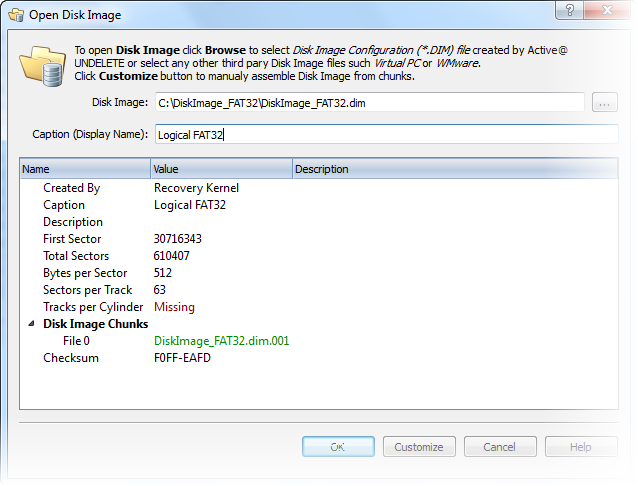
- 13. Working with images
- 14. Hyperlinks in templates
- Video Guide
- Integration with data recovery software
- Contacts:
5 бесплатных программ для разметки разделов диска в Linux
Представляем вам наш рекомендуемый список утилит для разметки жесткого диска в дистрибутивах Linux, которые позволят вам удалять, добавлять, настраивать или изменять размеры разделов диска.
Обычно вы изменяете разделы диска при установке ОС. Но что делать, если вам нужно изменить разделы через некоторое время после установки. Вы не сможете уже вернуться к экрану настройки. Именно здесь вам пригодятся менеджеры разделов (или, точнее, менеджеры разделов дисков).
В большинстве случаев нет необходимости отдельно устанавливать менеджер разделов, поскольку он обычно предустановлен в системе. Также стоит отметить, что вы можете выбрать либо менеджер разделов на базе команд терминала, либо что-то с графическим интерфейсом пользователя.
Внимание! Играть с разметкой диска — рискованная задача. Не делайте этого без особой необходимости. Если вы используете инструмент разметки из терминала, вам необходимо сначала изучить конкретные команды. Иначе можно запросто просто стереть весь диск.
GParted
Возможно, это самый популярный менеджер разделов на основе графического интерфейса пользователя, доступный для дистрибутивов Linux. Возможно, вы уже устанавливали его в некоторых дистрибутивах, но если вы этого не делали, просто найдите его в программном центре и установите.
При запуске программе необходима аутентификация с правами root. Таким образом вам нет необходимости здесь использовать терминал. После успешной аутентификации выполняется анализ устройств, а затем производится настройка разделов диска. Также в программе есть функция «Попробовать восстановить данные», используемая в случае потери данных или случайного удаления файлов.
GNOME Disks
Менеджер разделов с графическим интерфейсом, который поставляется в комплекте с Ubuntu или любыми дистрибутивами на базе Ubuntu, такими как Zorin OS.
Позволяет удалять, добавлять, изменять размер и настраивать разделы. Также поможет вам в форматировании USB в Ubuntu, если есть какая-то проблема с носителем.
С помощью этого инструмента можно даже попытаться восстановить раздел. Параметры также включают редактирование файловой системы, создание образа раздела, восстановление образа и тестирование раздела.
KDE Partition Manager
KDE Partition Manager должна быть предварительно установлена на дистрибутивы Linux на базе KDE. Но если ее там нет, установите из центра приложений.
В случае, если она не предустановлена вы можете получить уведомление о необходимости получения прав администратора при запуске. Без прав ничего не удастся сделать, поэтому лучше запускайте ее такой командой:
После запуска программа сканирует устройства, затем вы сможете перемещать, копировать, удалять и изменять разделы. Также есть возможность импорта/экспорта таблицы разделов и другие функции.
Fdisk [Command Line]
Fdisk — утилита командной строки, которая используется во всех Unix-подобных ОС. Не волнуйтесь, хотя и требуется от вас запуск терминала и ввод команд — это не так уж и сложно. Однако, если вы слишком запутались при использовании текстовой утилиты, вам следует придерживаться упомянутых выше приложений с графическим интерфейсом пользователя. Они все делают одно и то же.
Чтобы запустить fdisk, вы должны обладать правами root пользователя и указать устройство для управления разделами. Вот пример команды:
Вы можете подробнее ознакомиться со списком команд на соответствующем ресурсе.
GNU Parted [Command Line]
Еще одна утилита командной строки, которую вы можете найти предустановленной на вашем дистрибутиве Linux. Для начала достаточно ввести следующую команду:
Заключение
Я бы не забыл упомянуть QtParted в качестве одной из альтернатив списку менеджеров разделов. Однако она не поддерживается уже много лет, поэтому я не рекомендую ее использовать.
А что вы думаете о менеджерах разделов, упомянутых здесь? Я пропустил какую-нибудь из ваших любимых? Дайте мне знать, и я обновлю этот список менеджеров разделов для Linux с вашими предложениями.
Источник
Disk editor для linux

Active@ Disk Editor is a freeware advanced tool for viewing & editing raw data (sectors) on Physical Disks including Volumes, Partitions & Files
What is new in version 7
- Added templates for XFS and ReFS filesystem superblocks
- Adopted for HiDPI (high resolution displays)
- Improved navigation and search
- Improved user interface and bug fixes
- Linux package is now installer
What is new in version 6
- Enhanced Search & search results navigation
- Added template for BtrFS Superblock
- Improved Templates control & behavior
- Improved Open Object dialog
- Redesigned Bookmarks, Template View & File Cluster Chain
- Enhanced Settings, customizable Fonts & Look-n-Feel
What is new in version 5
- Ability to open and inspect particular files
- File preview panel renders and displays file content
- Added navigation through File Entries on opened volume
- Added Browse My Computer mode to easy access to disks, volumes and files
- Included both 64-bit and 32-bit versions
- Bug fixes and GUI tweaks
- Disk Editor for Linux version is now available for download!
Overview:
Active@ Disk Editor uses a simple, low-level disk viewer which displays information in binary and text modes at the same time. You can use this view to analyze the contents of data storage structure elements such as:
- Hard disk drives
- SSD & USB Disks
- Partitions & Volumes
- Files
- Other objects
The Main Features:
|
|
|
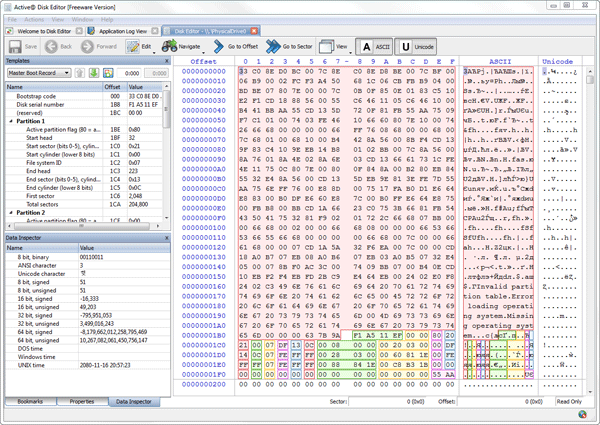
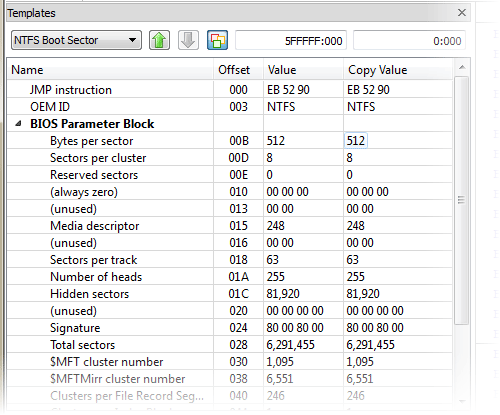
1. Enhanced template viewTemplate view shows parsed records of the most important areas on disk, allowing easily interpretation and editing. When you navigate to a point of interest, a proper template is selected automatically. The following templates are supported: MBR, GUID Partition table, NTFS boot sector, NTFS MFT file record, FAT boot sector, FAT32 boot sector, FAT directory entry, exFAT boot sector, exFAT directory entry, HFS+ Volume header, HFS+ Catalog Node, HFS+ File Record, Ext2/Ext3/Ext4 superblock, Ext2/Ext3/Ext4 inode, UFS superblock, UFS inode, LDM structures. As you edit data in Hex, ASCII or Unicode pane or in Templates window, modified data is fully synchronized between views. After each modification a template view is recalculated giving you an up-to-date interpretation of data. | 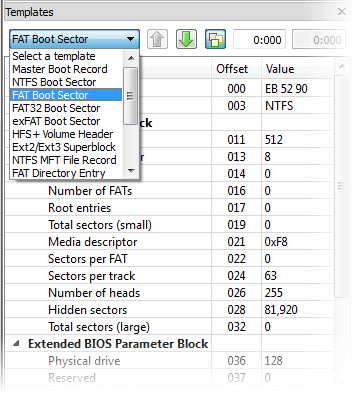 |
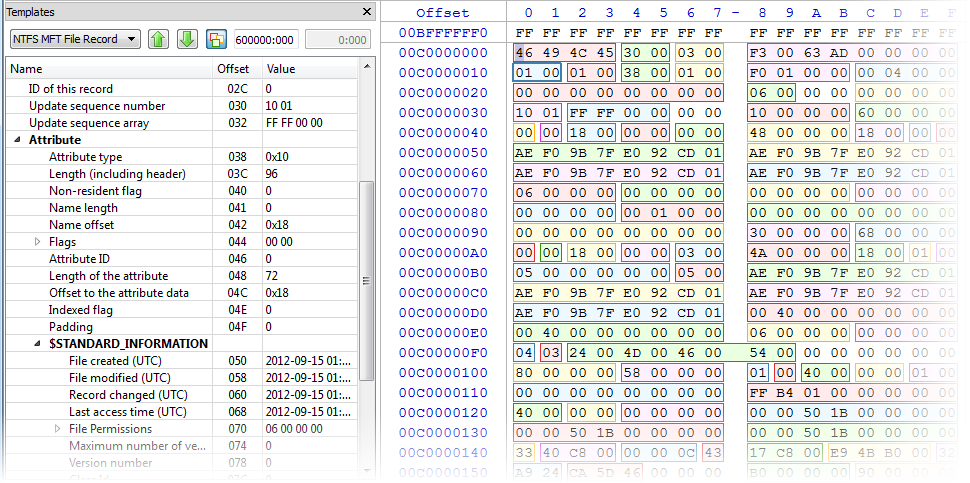
2. Detailed MFT record information
 |
 |
4. Fields coloring with data in tooltips
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Video Guide
This tutorial video eplains major features of Active@ Disk Editor such as viewing and editing raw content of a file or any sector on the drive in hexadecimal or text modes, easy navigation through logical partition stricture of hard disk and more.
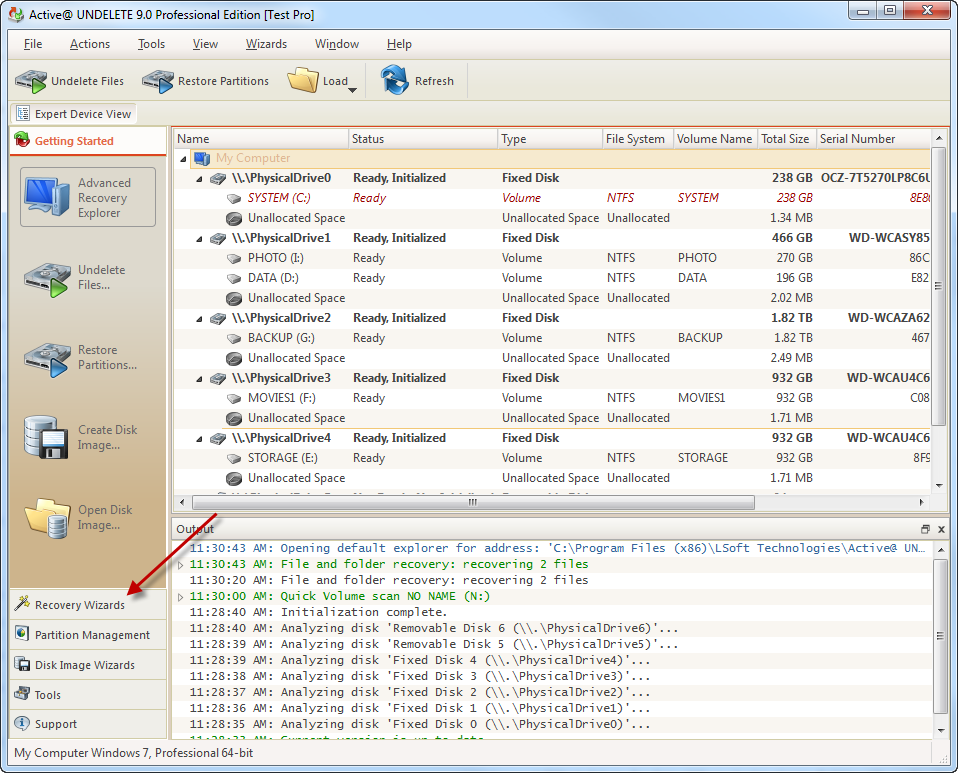
Integration with data recovery software
Active@ Disk Editor is a separate, lightweight module of Active @ UNDELETE — advanced data recovery and disk tool. For more features, like:
- Restore deleted or damaged partitions;
- Recover deleted files or files from deleted or damaged partitions.
- Create, format and resize disk partitions (volumes);
- Recover data from damaged RAID’s;
- Integrated Disk Editor tool and more please visit Active@ UNDELETE web site
Download DEMO version of Active@ UNDELETE for free:
Contacts:
| Postal address: | LSoft Technologies Inc. |
| 7177 Danton Promenade | |
| Mississauga, Ontario | |
| L5N 5P3 | |
| Canada | |
| Toll Free: | +1 (877) 403-8082 |
| Phone: | +1 (905) 812-8434 |
| Fax: | +1 (416) 352-7561 |
| Technical Support: | click here |
Active@ Disk Editor is developed by LSoft Technologies Inc.
Since its inception in 1999, LSoft’s mission has been to create software framework for your privacy protection. New unique technologies implementing security standards have been developed to serve this goal. LSoft’s vision is coupled today with a strong commitment to the latest technologies that expand the power and reach of PC for its users.
Active@ Disk Editor is preferred by universities as an essential tool in studying data forensics and security: Active@ Disk Editor presentation
Источник




