- Как установить и использовать Docker в Debian 10 Linux
- Установить Docker на Debian
- Выполнение команды Docker без Sudo
- Использование Docker
- Образы Docker
- Контейнеры Docker
- Выводы
- Install Docker Engine on Debian
- Prerequisites
- OS requirements
- Uninstall old versions
- Installation methods
- Install using the repository
- Set up the repository
- Install Docker Engine
- Upgrade Docker Engine
- Install from a package
- Upgrade Docker Engine
- Install using the convenience script
- Install pre-releases
- Upgrade Docker after using the convenience script
- Uninstall Docker Engine
Как установить и использовать Docker в Debian 10 Linux
Docker — это платформа контейнеризации, которая позволяет быстро создавать, тестировать и развертывать приложения в виде переносимых самодостаточных контейнеров, которые могут работать практически где угодно.
В этом руководстве мы объясним, как установить Docker на Debian 10 Buster, и изучим основные концепции и команды Docker.
Установить Docker на Debian
Выполните следующие шаги, чтобы установить последнюю стабильную версию Docker из репозиториев Docker.
Установите пакеты, необходимые для добавления нового репозитория через HTTPS:
Импортируйте GPG-ключ репозитория с помощью следующей команды curl :
В случае успеха команда вернет OK .
Добавьте стабильный репозиторий Docker APT в список репозиториев программного обеспечения вашей системы:
$(lsb_release -cs) вернет имя дистрибутива Debian . В данном случае это buster .
Обновите список пакетов apt и установите последнюю версию Docker CE (Community Edition):
После завершения установки служба Docker запустится автоматически. Чтобы проверить это, введите:
На момент написания последней стабильной версии Docker была 19.03.1 :
Выполнение команды Docker без Sudo
По умолчанию только root и пользователь с привилегиями sudo могут выполнять команды Docker.
Если вы хотите выполнять команды Docker без добавления sudo вам необходимо добавить своего пользователя в группу докеров, которая создается во время установки пакета Docker CE. Для этого введите:
$USER — это переменная среды, в которой хранится ваше имя пользователя.
Выйдите из системы и войдите снова, чтобы членство в группе обновилось.
После этого убедитесь, что вы можете запускать команды docker без ввода sudo :
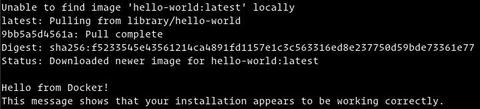
Команда загрузит тестовое изображение, запустит его в контейнере, напечатает сообщение «Hello from Docker» и выйдет. Результат должен выглядеть следующим образом:
Использование Docker
Теперь, когда вы установили на свой Debian 10, давайте рассмотрим основные концепции и команды докеров.
Образы Docker
Образ Docker состоит из ряда слоев файловой системы, представляющих инструкции в файле Dockerfile образа, которые составляют исполняемое программное приложение. Изображение — это неизменяемый двоичный файл, включающий приложение и все другие зависимости, такие как библиотеки, двоичные файлы и инструкции, необходимые для запуска приложения.
Большинство образов Docker доступны в Docker Hub . Это облачная служба реестра, которая, помимо прочего, используется для хранения образов Docker в общедоступном или частном репозитории.
Чтобы найти изображение в реестре Docker Hub, используйте команду docker search . Например, чтобы найти образ Debian, вы должны ввести:
Контейнеры Docker
Экземпляр изображения называется контейнером. Контейнер представляет среду выполнения для отдельного приложения, процесса или службы.
Возможно, это не самое подходящее сравнение, но если вы программист, вы можете думать об образе Docker как о классе, а контейнер Docker — как об экземпляре класса.
Для запуска, остановки, удаления и управления контейнером используйте команду docker container . Например, следующая команда запустит контейнер Docker на основе образа Debian. Если у вас нет образа локально, сначала он будет загружен:
Контейнер Debian остановится сразу же после загрузки, потому что у него нет длительного процесса и никакой другой команды не предоставляется. Контейнер загрузился, запустил пустую команду и завершил работу.
-it позволяет вам взаимодействовать с контейнером через командную строку. Чтобы запустить интерактивный контейнер, введите:
Как видно из выходных данных выше, после запуска контейнера командная строка изменяется, что означает, что теперь вы работаете изнутри контейнера .
Если у вас нет работающих контейнеров, вывод будет пустым.
Чтобы просмотреть все контейнеры, передайте ему переключатель -a :
Чтобы удалить один или несколько контейнеров, просто скопируйте идентификатор контейнера (или идентификаторы) и вставьте их после команды container rm :
Выводы
Установить Docker на Debian 10 — относительно простая задача. Docker де-факто является стандартом для контейнерных технологий и является важным инструментом для инженеров DevOps и их конвейера непрерывной интеграции и доставки.
Для получения дополнительной информации ознакомьтесь с официальной документацией Docker .
Если у вас есть вопросы, оставьте комментарий ниже.
Источник
Install Docker Engine on Debian
Estimated reading time: 11 minutes
To get started with Docker Engine on Debian, make sure you meet the prerequisites, then install Docker.
Prerequisites
OS requirements
To install Docker Engine, you need the 64-bit version of one of these Debian or Raspbian versions:
- Debian Bullseye 11 (stable)
- Debian Buster 10 (oldstable)
- Raspbian Bullseye 11 (stable)
- Raspbian Buster 10 (oldstable)
Docker Engine is supported on x86_64 (or amd64 ), armhf , and arm64 architectures.
Uninstall old versions
Older versions of Docker were called docker , docker.io , or docker-engine . If these are installed, uninstall them:
It’s OK if apt-get reports that none of these packages are installed.
The contents of /var/lib/docker/ , including images, containers, volumes, and networks, are preserved. The Docker Engine package is now called docker-ce .
Installation methods
You can install Docker Engine in different ways, depending on your needs:
Most users set up Docker’s repositories and install from them, for ease of installation and upgrade tasks. This is the recommended approach, except for Raspbian.
Some users download the DEB package and install it manually and manage upgrades completely manually. This is useful in situations such as installing Docker on air-gapped systems with no access to the internet.
In testing and development environments, some users choose to use automated convenience scripts to install Docker. This is currently the only approach for Raspbian.
Install using the repository
Before you install Docker Engine for the first time on a new host machine, you need to set up the Docker repository. Afterward, you can install and update Docker from the repository.
Raspbian users cannot use this method!
For Raspbian, installing using the repository is not yet supported. You must instead use the convenience script.
Set up the repository
Update the apt package index and install packages to allow apt to use a repository over HTTPS:
Add Docker’s official GPG key:
Use the following command to set up the stable repository. To add the nightly or test repository, add the word nightly or test (or both) after the word stable in the commands below. Learn about nightly and test channels.
Note: The lsb_release -cs sub-command below returns the name of your Debian distribution, such as helium . Sometimes, in a distribution like BunsenLabs Linux, you might need to change $(lsb_release -cs) to your parent Debian distribution. For example, if you are using BunsenLabs Linux Helium , you could use stretch . Docker does not offer any guarantees on untested and unsupported Debian distributions.
Install Docker Engine
This procedure works for Debian on x86_64 / amd64 , armhf , arm64 , and Raspbian.
Update the apt package index, and install the latest version of Docker Engine and containerd, or go to the next step to install a specific version:
Got multiple Docker repositories?
If you have multiple Docker repositories enabled, installing or updating without specifying a version in the apt-get install or apt-get update command always installs the highest possible version, which may not be appropriate for your stability needs.
To install a specific version of Docker Engine, list the available versions in the repo, then select and install:
a. List the versions available in your repo:
b. Install a specific version using the version string from the second column, for example, 5:18.09.1
Verify that Docker Engine is installed correctly by running the hello-world image.
This command downloads a test image and runs it in a container. When the container runs, it prints a message and exits.
Docker Engine is installed and running. The docker group is created but no users are added to it. You need to use sudo to run Docker commands. Continue to Linux postinstall to allow non-privileged users to run Docker commands and for other optional configuration steps.
Upgrade Docker Engine
To upgrade Docker Engine, first run sudo apt-get update , then follow the installation instructions, choosing the new version you want to install.
Install from a package
If you cannot use Docker’s repository to install Docker Engine, you can download the .deb file for your release and install it manually. You need to download a new file each time you want to upgrade Docker.
Go to https://download.docker.com/linux/debian/dists/ , choose your Debian version, then browse to pool/stable/ , choose amd64 , armhf , or arm64 , and download the .deb file for the Docker Engine version you want to install.
To install a nightly or test (pre-release) package, change the word stable in the above URL to nightly or test . Learn about nightly and test channels.
Install Docker Engine, changing the path below to the path where you downloaded the Docker package.
The Docker daemon starts automatically.
Verify that Docker Engine is installed correctly by running the hello-world image.
This command downloads a test image and runs it in a container. When the container runs, it prints a message and exits.
Docker Engine is installed and running. The docker group is created but no users are added to it. You need to use sudo to run Docker commands. Continue to Post-installation steps for Linux to allow non-privileged users to run Docker commands and for other optional configuration steps.
Upgrade Docker Engine
To upgrade Docker Engine, download the newer package file and repeat the installation procedure, pointing to the new file.
Install using the convenience script
Docker provides a convenience script at get.docker.com to install Docker into development environments quickly and non-interactively. The convenience script is not recommended for production environments, but can be used as an example to create a provisioning script that is tailored to your needs. Also refer to the install using the repository steps to learn about installation steps to install using the package repository. The source code for the script is open source, and can be found in the docker-install repository on GitHub.
Always examine scripts downloaded from the internet before running them locally. Before installing, make yourself familiar with potential risks and limitations of the convenience script:
- The script requires root or sudo privileges to run.
- The script attempts to detect your Linux distribution and version and configure your package management system for you, and does not allow you to customize most installation parameters.
- The script installs dependencies and recommendations without asking for confirmation. This may install a large number of packages, depending on the current configuration of your host machine.
- By default, the script installs the latest stable release of Docker, containerd, and runc. When using this script to provision a machine, this may result in unexpected major version upgrades of Docker. Always test (major) upgrades in a test environment before deploying to your production systems.
- The script is not designed to upgrade an existing Docker installation. When using the script to update an existing installation, dependencies may not be updated to the expected version, causing outdated versions to be used.
Tip: preview script steps before running
You can run the script with the DRY_RUN=1 option to learn what steps the script will execute during installation:
This example downloads the script from get.docker.com and runs it to install the latest stable release of Docker on Linux:
Docker is installed. The docker service starts automatically on Debian based distributions. On RPM based distributions, such as CentOS, Fedora, RHEL or SLES, you need to start it manually using the appropriate systemctl or service command. As the message indicates, non-root users cannot run Docker commands by default.
Use Docker as a non-privileged user, or install in rootless mode?
The installation script requires root or sudo privileges to install and use Docker. If you want to grant non-root users access to Docker, refer to the post-installation steps for Linux. Docker can also be installed without root privileges, or configured to run in rootless mode. For instructions on running Docker in rootless mode, refer to run the Docker daemon as a non-root user (rootless mode).
Install pre-releases
Docker also provides a convenience script at test.docker.com to install pre-releases of Docker on Linux. This script is equivalent to the script at get.docker.com , but configures your package manager to enable the “test” channel from our package repository, which includes both stable and pre-releases (beta versions, release-candidates) of Docker. Use this script to get early access to new releases, and to evaluate them in a testing environment before they are released as stable.
To install the latest version of Docker on Linux from the “test” channel, run:
Upgrade Docker after using the convenience script
If you installed Docker using the convenience script, you should upgrade Docker using your package manager directly. There is no advantage to re-running the convenience script, and it can cause issues if it attempts to re-add repositories which have already been added to the host machine.
Uninstall Docker Engine
Uninstall the Docker Engine, CLI, and Containerd packages:
Images, containers, volumes, or customized configuration files on your host are not automatically removed. To delete all images, containers, and volumes:
You must delete any edited configuration files manually.
Источник