- How to Downgrade Windows Server Datacenter to Standard Edition?
- Downgrade редакции в Windows Server с Datacenter до Standard
- Upgrade Options for Windows Server 2012 R2
- Upgrading previous retail versions of Windows Server to Windows Server 2012 R2
- Per-server-role considerations for upgrading
- Converting a current evaluation version to a current retail version
- Converting a current retail version to a different current retail version
- Converting a current volume-licensed version to a current retail version
How to Downgrade Windows Server Datacenter to Standard Edition?
When analyzing the server licenses used in our corporate network (with a KMS server deployed) we found that a more expensive Windows Server Datacenter edition is installed on one of the host. At the same time the server does not use Datacenter features such as virtualization, S2D, Azure Stack, Storage Replica, etc. There was an idea to change (downgrade) the installed Windows Server 2016 Datacenter to Standard edition to save money. We did not consider clean Windows Server reinstallation, because some roles are already configured, and additional software with hardware-related licenses had been installed on the server.
Although Microsoft supports only Windows Server edition upgrade using DISM (see the article on how to convert Windows Server Evaluation to licensed version), you can also perform a reverse procedure and downgrade the Datacenter edition to Standard one keeping all current settings, installed roles and apps.
We strongly recommend to backup your operating system image before performing a downgrade (at least through Windows Server Backup).
Also be very careful when downgrading a Windows Server with the ADDS domain controller role installed. It is better to transfer the FSMO roles and demote it from a DC to domain-member server (before you do it, backup your domain controller and you can restore the DC from a backup in case of any issues).
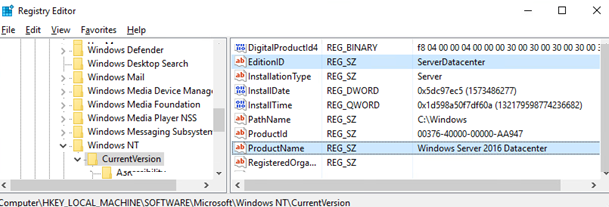
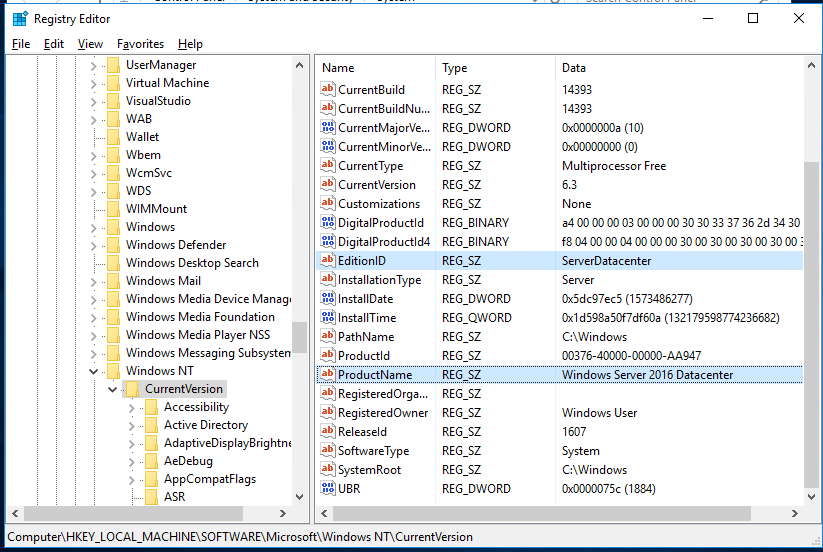
- On a running Windows Server 2016 Datacenter, open the Registry Editor and go to reg key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion;
- Check the values of the following REG_SZ parameters: EditionID = ServerDatacenter, ProductName = Windows Server 2016 Datacenter;
- Change the values as follows: EditionID to ServerStandard, ProductName to Windows Server 2016 Standard;
- Close the rgedit.exe;
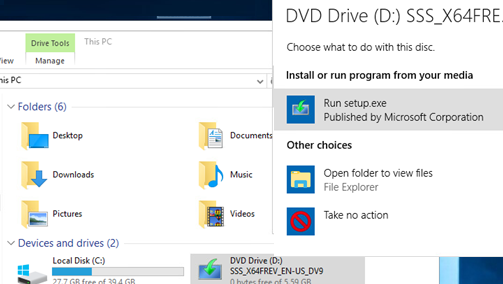
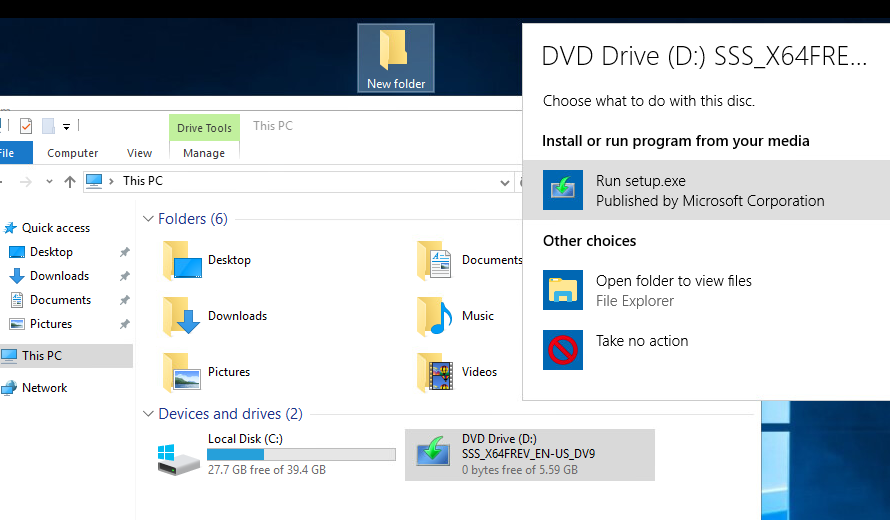
- Mount the installation Windows Server 2016 ISO image and run the setup wizard (setup.exe);
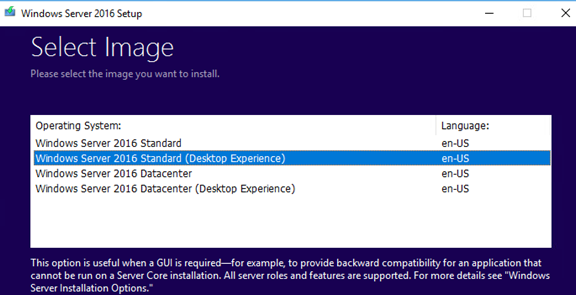
- When selecting the install options in the Windows Server Setup window, select Upgrade and Windows Server 2016 Standard (Desktop Experience) edition;
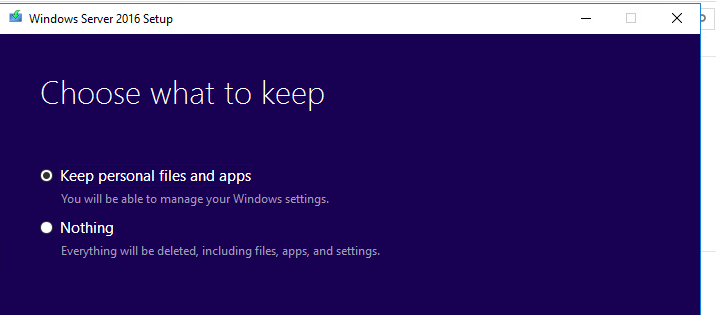
- Check the option Keep personal files and apps (if this option is unavailable with the message “ You can’t keep Windows settings, personal files, and apps because your current version of Windows might be installed in a unsupported directory ”, check the following post);
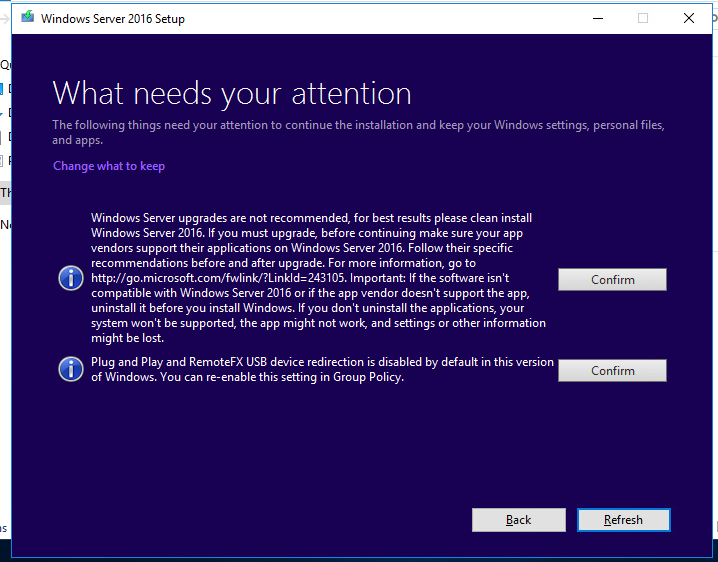
- Click on the Confirm button for items found. In my case, the first item said that a Windows Server upgrade is not recommended, and it was better to clean install the OS, and the second one said that PnP and RemoteFX USB device redirection were disabled in this Windows version by default;
- Start the Windows Server update. Wait till it is over and after several restarts make sure that Windows 2016 Standard edition is now running on the host.
This downgrade method should work for all supported Windows Server versions (2012R2/2016/2019). Also you can use it to downgrade and update the version, for example from Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter to Windows Server 2019 Standard (although it is not recommended either).
Downgrade редакции в Windows Server с Datacenter до Standard
При анализе используемых серверных лицензий в сети с KMS сервером мы обнаружили, что на одном из серверов установлена значительно более дорогая редакция Windows Server Datacenter, чем требуют задачи, запущенные на сервере (на сервере не используется виртуализация, S2D, Azure Stack, Storage Replica и прочее). Возникала идея изменить (понизить) редакцию установленного Windows Server 2016 Datacenter на Standard в целях экономии более дорогих лицензий. Чистую переустановку Windows Server мы не рассматривали, потому что на сервере уже настроены ряд ролей и установлено дополнительное ПО, лицензии которого жестко привязаны к ОС и железу.
Несмотря на то, что Microsoft поддерживает только апгрейд редакции Windows Server с младшей на старшую с помощью DISM (см. статью о конвертировании ознакомительной версии Windows Server), вы можете выполнить и обратную процедуру – downgrade версии Datacenter до Standard с сохранением всех текущих настроек и установленных ролей, программ.
Настоятельно рекомендуем перед выполнением даунгрейда сделать бэкап системы (хотя бы через Windows Server Backup).
Также будьте внимательны при выполнении даунгрейда Windows Server с ролью контроллера домена AD. Желательно сначала перенести с него FSMO роли и понизить его до рядового сервера домена (предварительно сделайте бэкап DC, к которому можно будет вернуться при проблемах).
- На работающем Windows Server 2016 Datacenter запустите редактор реестра и перейдите в ветку HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion;
- Проверьте значения следующих REG_SZ параметров: EditionID = ServerDatacenter, ProductName = Windows Server 2016 Datacenter;
- Измените значения параметров следующим образом: EditionID на ServerStandard, ProductName на Windows Server 2016 Standard;
- Закройте редактор реестра;
- Смонтируйте установочный ISO образ с Windows Server 2016 и запустите мастер установки (setup.exe);
- При выборе вариантов установки в окне Windows Server Setup выберите Upgrade и редакцию Windows Server 2016 Standard (Desktop Experience);
- Укажите, что вы хотите сохранить персональные данные и установленные программы — Keep personal files and apps (если эта опция недоступна, проверьте каталог установки Windows);
- Нажмите на кнопку Confirm у каждого обнаруженного пункта. В моем случае в первом пункте было указано, что апгрейд версии Windows Server не рекомендуется, лучше выполнить чистую установку; во втором – в этой версии Windows по-умолчанию отключены PnP и RemoteFX USB перенаправление устройств;
- Запустите обновление Windows, дождитесь его окончания и после нескольких перезагрузок проверьте, что теперь на сервере запущена редакция Windows 2016 Standard.
Данный способ даунгрейда должен работать во всех поддерживаемых версиях Windows Server (2012R2/2016/2019). Кроме того, вы можете использовать его для даунгрейда с обновлением версии, например, с Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter до Windows Server 2019 Standard (хотя это также не рекомендуемый сценарий).
Upgrade Options for Windows Server 2012 R2
Applies To: Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2
This topic includes information about upgrading to Windows ServerВ® 2012 R2 from a variety of previous operating systems using a variety of methods.
The process of moving to Windows Server 2012 R2 might vary greatly depending on which operating system you are starting with and the pathway you take. We use the following terms to distinguish among different actions, any of which could be involved in a new Windows Server 2012 R2 deployment.
Installation is the basic concept of getting the new operating system on your hardware. Specifically, a clean installation requires deleting the previous operating system. For information about installing Windows Server 2012 R2, see System Requirements and Installation Information for Windows Server 2012 R2. For information about installing other versions of Windows Server, see Windows Server Installation and Upgrade.
Upgrade means moving from your existing operating system release to a more recent release, while staying on the same hardware. For example, if your server is running Windows Server 2012, you can upgrade it to Windows Server 2012 R2. You can upgrade from an evaluation version of the operating system to a retail version, from an older retail version to a newer version, or, in some cases, from a volume-licensed edition of the operating system to an ordinary retail edition.
License conversion in some operating system releases, you can convert a particular edition of the release to another edition of the same release in a single step with a simple command and the appropriate license key. We call this “license conversion.” For example, if you are running Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard, you can convert it to Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter.
Migration means moving from your existing operating system to Windows Server 2012 R2 by transferring to a different set of hardware. Migration, which might vary considerably depending on the server roles you have installed, is discussed in detail at https://technet.microsoft.com/windowsserver/dn458795.
Depending on your scenario, you might encounter a variety of different upgrade pathways.
Upgrading previous retail versions of Windows Server to Windows Server 2012 R2
The table below briefly summarizes which already licensed (that is, not evaluation) Windows operating systems can be upgraded to which editions of Windows Server 2012 R2.
Note the following general guidelines for supported paths:
In-place upgrades from 32-bit to 64-bit architectures are not supported. All editions of Windows Server 2012 R2 are 64-bit only.
In-place upgrades from one language to another are not supported.
In-place upgrades from one build type (fre to chk, for example) are not supported.
If the server is a domain controller, see https://technet.microsoft.com/library/hh994618.aspx for important information.
Upgrades from pre-release versions of Windows Server 2012 R2 are not supported. Perform a clean installation to Windows Server 2012 R2.
Upgrades that switch from a Server Core installation to the Server with a GUI mode of Windows Server 2012 R2 in one step (and vice versa) are not supported. However, after upgrade is complete, Windows Server 2012 R2 allows you to switch freely between Server Core and Server with a GUI modes. For more information about these installation options, how to convert between them, and how to use the new Minimal Server Interface and Features on Demand, see https://technet.microsoft.com/library/hh831786.
If you do not see your current version in the left column, upgrading to this release of Windows Server 2012 R2 is not supported.
If you see more than one edition in the right column, upgrade to either edition from the same starting version is supported.
If you are running:
You can upgrade to these editions:
Windows ServerВ 2008В R2 Datacenter with SP1
Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter
Windows ServerВ 2008В R2 Enterprise with SP1
Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard or Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter
Windows ServerВ 2008В R2 Standard with SP1
Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard or Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter
Windows Web ServerВ 2008В R2 with SP1
Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard
Windows Server 2012 Datacenter
Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter
Windows Server 2012 Standard
Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard or Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter
Hyper-V Server 2012
Hyper-V Server 2012 R2
Windows Storage Server 2012 Standard
Windows Storage Server 2012 R2 Standard
Windows Storage Server 2012 Workgroup
Windows Storage Server 2012 R2 Workgroup
Per-server-role considerations for upgrading
Even in supported upgrade paths from previous retail versions to Windows Server 2012 R2, certain server roles that are already installed might require additional preparation or actions for the role to continue functioning after the upgrade. Consult the specific TechNet Library topics for each server role you intend to install for details of additional steps that might be required.
Converting a current evaluation version to a current retail version
You can convert the evaluation version of Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard to either Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard (retail) or Datacenter (retail). Similarly, you can convert the evaluation version of Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter to the retail version.
Before you attempt to convert from evaluation to retail, verify that your server is actually running an evaluation version. To do this, do either of the following:
From an elevated command prompt, run slmgr.vbs /dlv; evaluation versions will include “EVAL” in the output.
From the Start screen, open Control Panel. Open System and Security, and then System. View Windows activation status in the Windows activation area of the System page. Click View details in Windows activation for more information about your Windows activation status.
If you have already activated Windows, the Desktop shows the time remaining in the evaluation period.
If the server is running a retail version instead of an evaluation version, see the “Upgrading previous retail versions of Windows Server to Windows Server 2012 R2” section of this topic for instructions to upgrade to Windows Server 2012.
For Windows Server 2012 Essentials: You can convert to the full retail version by entering a retail, volume license, or OEM key in the command slmgr.vbs.
If the server is running an evaluation version of Windows Server 2012 Standard or Windows Server 2012 Datacenter, you can convert it to a retail version as follows:
If the server is a domain controller, you cannot convert it to a retail version. In this case, install an additional domain controller on a server that runs a retail version and remove AD DS from the domain controller that runs on the evaluation version. For more information, see https://technet.microsoft.com/library/hh994618.aspx.
Read the license terms.
From an elevated command prompt, determine the current edition name with the command DISM /online /Get-CurrentEdition. Make note of the edition ID, an abbreviated form of the edition name. Then run DISM /online /Set-Edition: /ProductKey:XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX /AcceptEula, providing the edition ID and a retail product key. The server will restart twice.
For the evaluation version of Windows Server 2012 Standard, you can also convert to the retail version of Windows Server 2012 Datacenter in one step using this same command and the appropriate product key.
Converting a current retail version to a different current retail version
At any time after installing Windows Server 2012, you can run Setup to repair the installation (sometimes called “repair in place”) or, in certain cases, to convert to a different edition.
You can run Setup to perform a “repair in place” on any edition of Windows Server 2012; the result will be the same edition you started with.
For Windows Server 2012 Standard, you can convert the system to Windows Server 2012 Datacenter as follows: From an elevated command prompt, determine the current edition name with the command DISM /online /Get-CurrentEdition. Make note of the edition ID, an abbreviated form of the edition name. Then run DISM /online /Set-Edition: /ProductKey:XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX /AcceptEula, providing the edition ID and a retail product key. The server will restart twice.
Converting a current volume-licensed version to a current retail version
At any time after installing Windows Server 2012, you can freely convert it between a volume-licensed version, a retail version, or an OEM version. The edition remains the same during this conversion.
To do this, from an elevated command prompt, run:
slmgr /ipk
Where is the appropriate volume-license, retail, or OEM product key.