- 990x.top
- Простой компьютерный блог для души)
- Драйвер INF — что это?
- Драйвер INF — что это такое?
- Заключение
- Установка драйвера из INF-файла
- Читайте также
- Установка размера файла, инициализация файла и разреженные файлы
- Пример: установка меток времени файла
- 5.5.2.4. Проверка драйвера
- Установка драйвера с помощью программы установки
- 16.3. Откат драйвера
- Драйвера и их назначение
- Установка драйвера и настройка источников данных
- 2.2 Компиляция и установка драйвера.
- Как писать драйвера (часть 1)
- Как писать драйвера (часть 2)
- Часть 2. API для WDM драйвера.
- Откат драйвера
- INF Driver-Version Entry
- Installing a File System Driver
- About Driver Installation
- Creating an INF File for a File System Driver
- Sections in a File System Driver INF File
- Version Section (required)
- DestinationDirs Section (optional but recommended)
- SourceDisksNames Section (required)
- SourceDisksFiles Section (required)
- DefaultInstall Section (required)
- DefaultInstall.Services Section (required)
- ServiceInstall Section (required)
- DefaultUninstall Section (optional)
- DefaultUninstall.Services Section (optional)
- Strings Section (required)
990x.top
Простой компьютерный блог для души)
Драйвер INF — что это?
Приветствую. Данная заметка коротко расскажет что такое драйвер INF. Постараюсь написать простыми словами.
Драйвер INF — что это такое?
Конфигурационный файл, в котором содержится информация об оборудовании, а также драйвере для него.

На файлах INF построена база драйверов, а также большинство системных инсталляционных пакетов Microsoft Windows.
Большинство дров используют при установке INF-файлы. А также некоторые приложения, например Internet Explorer, Media Player, компоненты обновлений, Java VM.
INF это старая технология, в 2000 году Microsoft придумала MSI, которое представляет из себя архив cabinet-формата, нечто похожее на ZIP, но содержит меньше функций. К cabinet-архиву пришиты дополнительные модули, включая компоненты интерфейса.
Если простыми словами — INF это некоторые инструкции для операционной системы, какие именно дрова устанавливать и куда. Часто прописано также какое ПО нужно ставить, какие файлы копировать. Как правило файлы INF находятся в папке с архивом, который необходимо распаковать и стандартно запустить установщик, который может называться например setup.exe, в котором уже прописано, какой именно нужно запускать INF-файл.
INF-файл можно запустить (правой кнопкой > установить) и вручную, если вы точно знаете какой. Он установит драйвер и дополнительное программное обеспечение (при наличии). Однако их нежелательно устанавливать используя INF-файл, лучше использовать автоматические проверенные установщики дровишек, например утилита DevID Agent:
Или приложение Intel Driver Support Assistant:
Данные инструменты помогут автоматически найти и установить дровишки при их отсутствии.
Заключение
- Драйвер INF — конфигурационный файл оборудования, содержащий инструкции установки драйвера для операционной системе.
Установка драйвера из INF-файла
Установка драйвера из INF-файла
Рассмотрим ситуацию, когда для установки оборудования используется набор из INF-файлов.
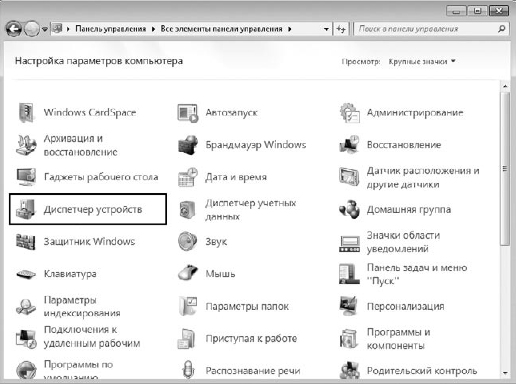
Откройте Панель управления и запустите механизм Диспетчер устройств. В результате откроется окно, в котором вы можете видеть список всех устройств, обнаруженных операционной системой на компьютере (рис. 16.1).
Большую его часть составляют устройства, находящиеся на материнской плате, и лишь некоторые записи свидетельствуют об устройствах, которые установлены в виде платы расширения или подключены с использованием внешних портов.
Наша задача – установить драйвер для устройства, не обнаруженного операционной системой. Если устройство еще не подключено к компьютеру, самое время это сделать.
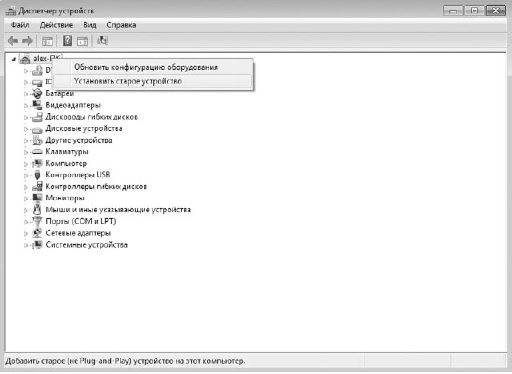
Если устройство уже подключено к компьютеру, то щелкните правой кнопкой мыши на названии компьютера в самом верху списка и в появившемся меню выберите пункт Установить старое устройство (рис. 16.2). Это приведет к запуску мастера установки оборудования, который будет вам помогать и направлять ваши действия при установке оборудования (рис. 16.3).
Рис. 16.1. Запускаем механизм Диспетчер устройств
Рис. 16.2. Выбираем пункт Установить старое устройство
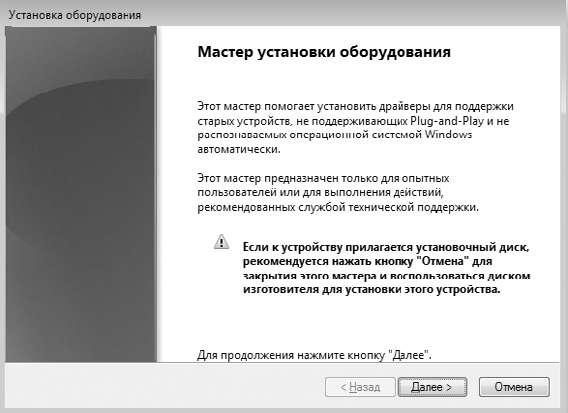
Прочитав вступительную речь и приготовив диск с драйверами, если он нужен, нажмите кнопку Далее, чтобы начать процесс установки устройства.
Рис. 16.3. Мастер установки оборудования
Мастер установки на выбор предлагает два варианта дальнейших действий: автоматическую и ручную установку оборудования (рис. 16.4). Автоматическая установка ничего не даст, так как операционная система уже пыталась сделать это в процессе установки. По этой причине сразу же необходимо переходить ко второму варианту действий. Установите переключатель в положение Установка оборудования, выбранного из списка вручную и нажмите кнопку Далее.
Рис. 16.4. Выбираем вариант действия
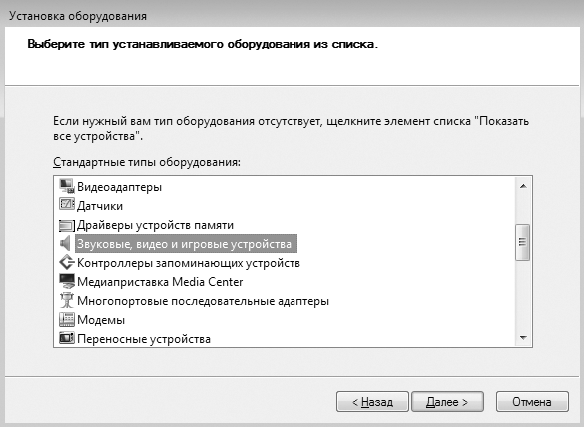
В следующем окне вы увидите список устройств разного типа, драйверы к которым имеются в операционной системе (рис. 16.5).
Рис. 16.5. Указываем тип устройства, которое нужно установить
Рассмотрим сначала вариант, когда вы обнаружили в списке производителей и драйверов нужный вам драйвер. Отметив его, нажмите кнопку Далее, чтобы перейти к его установке.
В следующем окне мастер установки оборудования покажет список всех имеющихся в системе драйверов для выбранного типа устройства, отсортированных по производителю оборудования. Если вы уверены в том, что для вашего оборудования подойдет один из предложенных драйверов, то в левой части окна выберите нужного производителя, а в правой – необходимый драйвер. После этого можно попробовать его установить, нажав кнопку Далее (рис. 16.6). Это приведет к появлению подтверждающего окна, в котором еще раз нужно нажать кнопку Далее (рис. 16.7).
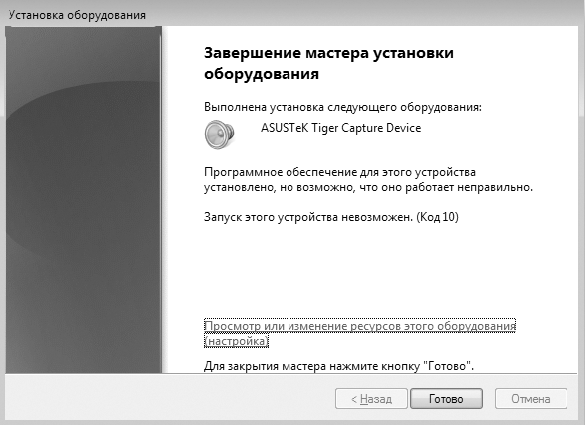
После того как установка драйверов подтверждена, мастер установки оборудования копирует необходимые драйверы в систему и пытается инициализировать устройство. Если инициализация устройства прошла успешно, вы увидите окно с сообщением о том, что драйвер для устройства был установлен корректно и устройство готово к работе. В противном случае мастер сообщит о том, что установка завершилась неудачей и запуск устройства невозможен, или о том, что есть какие-то трудности (рис. 16.8).
Рис. 16.6. Указываем драйвер для устройства
Рис. 16.7. Подтверждаем установку драйвера
В этой ситуации единственный выход – попробовать установить другой драйвер, например идущий в комплекте с устройством или скачанный с веб-сайта производителя в Интернете.
Рис. 16.8. Неудачная установка драйвера
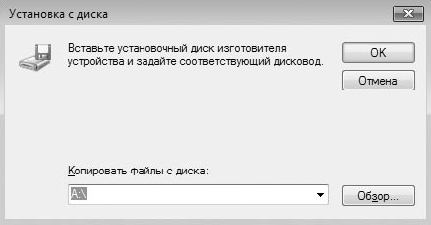
Чтобы установить другой драйвер, нажмите кнопку Установить с диска (см. рис. 16.6). В результате появится окно, в котором нужно нажать кнопку Обзор (рис. 16.9) и в открывшемся окне выбора файла указать расположение файла с драйвером.
Рис. 16.9. Устанавливаем драйвер из другого источника
После нажатия кнопки ОК мастер попытается установить драйвер. Если данный драйвер сможет работать в Windows 7, он будет установлен и устройство сможет функционировать.
Данный текст является ознакомительным фрагментом.
Продолжение на ЛитРес
Читайте также
Установка размера файла, инициализация файла и разреженные файлы
Установка размера файла, инициализация файла и разреженные файлы Функция SetEndOfFile позволяет переустановить размер файла, используя текущее значение указателя файла для определения его размера. Возможно как расширение, так и усечение файла. В случае расширения файла
Пример: установка меток времени файла
Пример: установка меток времени файла Программа 3.3 реализует UNIX-команду touch, предназначенную для изменения кода защиты файлов и обновления меток времени до текущих значений системного времени. В упражнении 3.11 от вас требуется расширить возможности функции touch таким
5.5.2.4. Проверка драйвера
5.5.2.4. Проверка драйвера После загрузки убедитесь, что драйвер установлен и используется. Нажмите ‹Alt+F2›, введите system-config-display, перейдите в раскрывшемся окне на вкладку Оборудование и щелкните на кнопке Настроить напротив строки с идентификацией видеокарты. В
Установка драйвера с помощью программы установки
Установка драйвера с помощью программы установки Часто для установки старого оборудования используется программа установки, и стандартный подход установки драйверов, описанный выше, при этом не подходит. Однако при запуске программы установки она отказывается
16.3. Откат драйвера
16.3. Откат драйвера Иногда приходится не только ставить драйверы с нуля, но и обновлять старые драйверы. Необходимость установки нового драйвера объясняется достаточно просто: новый драйвер практически всегда представляет собой исправленную версию старого драйвера
Драйвера и их назначение
Драйвера и их назначение Для того чтобы подключить оборудование к компьютеру, недостаточно просто физически подсоединить его к системному блоку. Чтобы операционная система распознала это оборудование, необходимо наличие специальной программы – драйвер. Только после
Установка драйвера и настройка источников данных
Установка драйвера и настройка источников данных Дистрибутив драйвера состоит из одного исполнимого файла с именем ibgem_21_desk.exe (для настольной редакции драйвера версии 2.1). Чтобы установить драйвер, необходимо запустить этот файл.Существует два способа создания
2.2 Компиляция и установка драйвера.
2.2 Компиляция и установка драйвера. Проект, сгенерированный DriverWizard, находится в каталоге XDSP. В этом каталоге расположены файлы рабочего пространства (Workspace) VC++: XDSP.dsw, XDSP.ncd и XDSP.opt и два каталога – sys и exe. Здесь же находится файл XDSPioctl.h. В нем описаны управляющие коды,
Как писать драйвера (часть 1)
Как писать драйвера (часть 1) Предисловие. Драйвера под Windows являются для большей массы программистов, «тайной за семью печатями». И вовсе не потому, что это что-то архисложное, сколько по причине абсолютной недокументированности идеологии.Начав заниматься этой темой я
Как писать драйвера (часть 2)
Как писать драйвера (часть 2) Прежде, чем хвататься за описание самого драйвера, давайте определимся с типами существующих драйверов.По существующему в DDK разделению сам Microsoft подразделяет драйвера на следующие типы:– Kernel-Mode Drivers;– Kernel Streaming Drivers;– Graphics Drivers;– Network
Часть 2. API для WDM драйвера.
Часть 2. API для WDM драйвера. Большинство функций драйверного API, которые нас интересуют, предоставляются модулем ntoskrnl.exe.Для их использования надо сделать следующее:1) Объявить типы данных и определить константы.Большинство определений для C находятся в файлах ntdef.h и wdm.h.2)
Откат драйвера
Откат драйвера Иногда случается, что при установке новой версии драйвера устройства, например видеокарты, система начинает работать нестабильно. Естественно, это недопустимо, поскольку создает множество неудобств. Все ухудшается еще и тем, что, как правило, дистрибутивы
INF Driver-Version Entry
The INF file in a driver package specifies the driver-version information for the drivers that are installed by the INF. The version information in the file identifies the driver package as a whole, in contrast to the internal and external version numbers for the individual driver files within the package.
The file specifies each driver’s date and version number in an INF DriverVer directive with the following format:
The date parameter mm/dd/yyyy consists of a two-digit month code mm, two-digit day code dd, and four-digit year code yyyy. This parameter specifies the date of the driver package and applies to all the driver files, including the INF file. A hyphen (-) can be used as the date-field separator in place of the slash (/). The operating system uses the DriverVer date to perform driver-version comparisons when selecting between two versions of a driver. This date also appears in the Driver Date value displayed by the Device Manager.
The optional version number x.y.v.z , which is shown in brackets above, is used for display purposes only (for example, in the Driver Version number displayed by the Device Manager). The operating system does not use this value for driver selection. When compiling driver files, make sure that the internal version number that is specified in the FILEVERSION parameter in the driver’s resource file matches the DriverVer version number in the INF file.
When the operating system searches for drivers, it chooses a driver with a more recent DriverVer date over a driver with an earlier date. If an INF file has no DriverVer entry or is unsigned, the operating system applies the default date of 00/00/0000.
In Windows 2000, Windows XP and later, the INF file for a driver package must provide a DriverVer directive.
Installing a File System Driver
About Driver Installation
The Setup application programming interface (SetupAPI) provides the functions that control Windows setup and driver installation, including the installation of file system and file system filter drivers.
The installation process is controlled by INF files. For more information about INF files:
For file system driver-specific INF file information, see below
For more information about general driver installation (including information about driver packages, INF files, and driver signing), see Device and Driver Installation.
After creating an INF file, you will typically write the source code for your setup application. The setup application calls user-mode setup functions to access the information in the INF file and perform installation operations.
The following information regarding installing and uninstalling file system filter drivers also applies to file system drivers:
Creating an INF File for a File System Driver
A file system driver’s INF file provides instructions that SetupAPI uses to install the driver. The INF file is a text file that specifies the files that must be present for your driver to run and the source and destination directories for the driver files. An INF file also contains driver configuration information that SetupAPI stores in the registry, such as the driver’s start type and load order group.
You can create a single INF file to install your driver on multiple versions of the Windows operating system. For more information about creating such an INF file, see Creating INF Files for Multiple Platforms and Operating Systems and Creating International INF Files.
Starting with 64-bit versions of Windows Vista, all kernel-mode components, including non-PnP (Plug and Play) drivers such as file system drivers (file system, legacy filter, and minifilter drivers), must be signed in order to load and execute. For these versions of the Windows operating system, the following list contains information that is relevant to file system drivers.
INF files for non-PnP drivers, including file system drivers, are not required to contain [Manufacturer] or [Models] sections.
The SignTool command-line tool, located in the \bin\SelfSign directory of the WDK installation directory, can be used to directly «embed sign» a driver SYS executable file. For performance reasons, boot-start drivers must contain an embedded signature.
Given an INF file, the Inf2Cat command-line tool can be used to create a catalog (.cat) file for a driver package.
With Administrator privileges, an unsigned driver can still be installed on x64-based systems starting with Windows Vista. However, the driver will fail to load (and thus execute) because it is unsigned.
For detailed information about the driving signing process, including the driving signing process for 64-bit versions of Windows Vista, see Kernel-Mode Code Signing Walkthrough.
All kernel-mode components, including custom kernel-mode development tools, must be signed. For more information, see Signing Drivers during Development and Test (Windows Vista and Later).
INF files cannot be used to read information from the registry or to launch a user-mode application.
Sections in a File System Driver INF File
To construct your own file system driver INF file, use the following information as a guide. You can use the InfVerif tool to check the syntax of your INF file.
An INF file for a file system driver generally contains the following sections.
Version Section (required)
The Version section specifies the driver version information, as shown in the following code example.
The following table shows the values that file system filter drivers should specify in the Version section.
| Entry | Value |
|---|---|
| Signature | «$WINDOWS NT$» |
| Provider | In your own INF file, you should specify a provider other than Microsoft. |
| DriverVer | See INF DriverVer directive |
| CatalogFile | Leave this entry blank. In the future, it will contain the name of a WHQL-supplied catalog file for signed drivers. |
DestinationDirs Section (optional but recommended)
The DestinationDirs section specifies the directories where the file system driver files will be copied.
In this section and in the ServiceInstall section, you can specify well-known system directories by using system-defined numeric values. For a list of these values, see INF DestinationDirs Section. In the following code example, the value «12» refers to the Drivers directory (%windir%\system32\drivers).
SourceDisksNames Section (required)
The SourceDisksNames section specifies the distribution media to be used.
In the following code example, the SourceDisksNames section lists a single distribution media for the file system driver. The unique identifier for the media is 1. The name of the media is specified by the %Disk1% token, which is defined in the Strings section of the INF file.
SourceDisksFiles Section (required)
The SourceDisksFiles section specifies the location and names of the files to be copied.
In the following code example, the SourceDisksFiles section lists the file to be copied for the file system driver and specifies that the files can be found on the media whose unique identifier is 1 (This identifier is defined in the SourceDisksNames section of the INF file.)
DefaultInstall Section (required)
In the DefaultInstall section, a CopyFiles directive copies the file system driver’s driver files to the destination that is specified in the DestinationDirs section.
The CopyFiles directive should not refer to the catalog file or the INF file itself; SetupAPI copies these files automatically.
You can create a single INF file to install your driver on multiple versions of the Windows operating system. This type of INF file is created by creating additional DefaultInstall, DefaultInstall.Services, DefaultUninstall, and DefaultUninstall.Services sections for each operating system version. Each section is labeled with a decoration (for example, .ntx86, .ntia64, or .nt) that specifies the operating system version to which it applies. For more information about creating this type of INF file, see Creating INF Files for Multiple Platforms and Operating Systems.
In the following code example, the CopyFiles directive copies the files that are listed in the ExampleFileSystem.DriverFiles section of the INF file.
DefaultInstall.Services Section (required)
The DefaultInstall.Services section contains an AddService directive that controls how and when the services of a particular driver are loaded.
In the following code example, the AddService directive adds the file system service to the operating system. The %ServiceName% token contains the service name string, which is defined in the Strings section of the INF file. ExampleFileSystem.Service is the name of the file system driver’s ServiceInstall section.
ServiceInstall Section (required)
The ServiceInstall section adds subkeys or value names to the registry and sets values. The name of the ServiceInstall section must appear in an AddService directive in the DefaultInstall.Services section.
The following code example shows the ServiceInstall section for the file system driver.
The DisplayName entry specifies the name for the service. In the preceding example, the service name string is specified by the %ServiceName% token, which is defined in the Strings section of the INF file.
The Description entry specifies a string that describes the service. In the preceding example, this string is specified by the %ServiceDesc% token, which is defined in the Strings section of the INF file.
The ServiceBinary entry specifies the path to the executable file for the service. In the preceding example, the value 12 refers to the Drivers directory (%windir%\system32\drivers).
The ServiceType entry specifies the type of service. The following table lists the possible values for ServiceType and their corresponding service types.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| 0x00000001 | SERVICE_KERNEL_DRIVER (Device driver service) |
| 0x00000002 | SERVICE_FILE_SYSTEM_DRIVER (File system or file system filter driver service) |
| 0x00000010 | SERVICE_WIN32_OWN_PROCESS (Microsoft Win32 service that runs in its own process) |
| 0x00000020 | SERVICE_WIN32_SHARE_PROCESS (Win32 service that shares a process) |
The ServiceType entry should always be set to SERVICE_FILE_SYSTEM_DRIVER for a file system driver.
The StartType entry specifies when to start the service. The following table lists the possible values for StartType and their corresponding start types.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| 0x00000000 | SERVICE_BOOT_START |
| 0x00000001 | SERVICE_SYSTEM_START |
| 0x00000002 | SERVICE_AUTO_START |
| 0x00000003 | SERVICE_DEMAND_START |
| 0x00000004 | SERVICE_DISABLED |
For detailed descriptions of these start types to determine which one is appropriate for your file system driver, see What Determines When a Driver Is Loaded.
Starting with x64-based Windows Vista systems, the binary image file of a boot-start driver (a driver that has a start type of SERVICE_BOOT_START) must contain an embedded signature. This requirement ensures optimal system boot performance. For more information, see Kernel-Mode Code Signing Walkthrough.
For information about how the StartType and LoadOrderGroup entries determine when the driver is loaded, see What Determines When a Driver Is Loaded.
The ErrorControl entry specifies the action to be taken if the service fails to start during system startup. The following table lists the possible values for ErrorControl and their corresponding error control values.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| 0x00000000 | SERVICE_ERROR_IGNORE (Log the error and continue system startup.) |
| 0x00000001 | SERVICE_ERROR_NORMAL (Log the error, display a message to the user, and continue system startup.) |
| 0x00000002 | SERVICE_ERROR_SEVERE (Switch to the registry’s LastKnownGood control set and continue system startup. |
| 0x00000003 | SERVICE_ERROR_CRITICAL (If system startup is not using the registry’s LastKnownGood control set, switch to LastKnownGood and try again. If startup still fails, run a bug-check routine. Only the drivers that are needed for the system to startup should specify this value in their INF files.) |
The LoadOrderGroup entry must always be set to «File System» for a file system driver. This is different from what is specified for a file system filter driver or file system minifilter driver where the LoadOrderGroup entry is set to one of the file system filter load order groups. For more information about the load order groups that are used for file system filter drivers and file system minifilter drivers, see Load Order Groups for File System Filter Drivers and Load Order Groups and Altitudes for Minifilter Drivers.
The AddReg directive refers to one or more INF writer-defined AddRegistry sections that contain any information to be stored in the registry for the newly installed service.
If the INF file will also be used for upgrading the driver after the initial install, the entries that are contained in the AddRegistry section should specify the 0x00000002 (FLG_ADDREG_NOCLOBBER) flag. Specifying this flag preserves the registry entries in HKLM\CurrentControlSet\Services when subsequent files are installed. For example:
DefaultUninstall Section (optional)
The DefaultUninstall section is optional but recommended if your driver can be uninstalled. It contains DelFiles and DelReg directives to remove files and registry entries.
In the following code example, the DelFiles directive removes the files that are listed in the ExampleFileSystem.DriverFiles section of the INF file.
The DelReg directive refers to one or more INF writer-defined DelRegistry sections that contain any information to be removed from the registry for the service that is being uninstalled.
DefaultUninstall.Services Section (optional)
The DefaultUninstall.Services section is optional but recommended if your driver can be uninstalled. It contains DelService directives to remove the file system driver’s services.
In the following code example, the DelService directive removes the file system driver’s service from the operating system.
The DelService directive should always specify the 0x200 (SPSVCINST_STOPSERVICE) flag to stop the service before it is deleted.
There are certain classes of file system products that cannot be completely uninstalled. In this situation, it is acceptable to just uninstall the components of the product that can be uninstalled and leave installed the components of the product that cannot be uninstalled. An example of such a product is the Microsoft Single Instance Store (SIS) feature.
Strings Section (required)
The Strings section defines each %strkey% token that is used in the INF file.
For example, the file system driver defines the following strings in its INF file.
You can create a single international INF file by creating additional locale-specific Strings.LanguageID sections in the INF file. For more information about international INF files, see Creating International INF Files.