- Windows Error Reporting
- Для чего нужна служба «Windows Error Reporting» и как отключить ее в Windows 7, 8.1 и 10
- Отключение Error Reporting в Windows 7 и 8.1
- Отключение Error Reporting в Windows 10
- Универсальный способ отключения Error Reporting
- Troubleshooting a Failover Cluster using Windows Error Reporting
- Enabling event channels
- Gathering Logs
- Gathering Windows Error Reporting reports
- Troubleshooting using Windows Error Reporting reports
- Physical disk failed to come online
- Physical disk timed out
- How to enable or disable Windows 10 Error Reporting Service
- How the Windows 10 Error Reporting Service Works and Why
- Should I disable the Windows error reporting service?
- Steps to disable Window 10 Error Reporting Service
- Method One: Use Command to disable Window 10 Error Report
- Method Two: Use the Registry Editor
Windows Error Reporting
Applies to
This is a 300 level topic (moderately advanced).
See Resolve Windows 10 upgrade errors for a full list of topics in this article.
When Windows Setup fails, the result and extend code are recorded as an informational event in the Application log by Windows Error Reporting as event 1001. The event name is WinSetupDiag02. You can use Event Viewer to review this event, or you can use Windows PowerShell.
To use Windows PowerShell, type the following commands from an elevated Windows PowerShell prompt:
The following source will be available only if you have updated from a previous version of Windows 10 to a new version. If you installed the current version and have not updated, the source named WinSetupDiag02 will be unavailable.
To use Event Viewer:
- Open Event Viewer and navigate to Windows Logs\Application.
- Click Find, and then search for winsetupdiag02.
- Double-click the event that is highlighted.
Note: For legacy operating systems, the Event Name was WinSetupDiag01.
Ten parameters are listed in the event:
| Parameters |
|---|
| P1: The Setup Scenario (1=Media,5=WindowsUpdate,7=Media Creation Tool) |
| P2: Setup Mode (x=default,1=Downlevel,5=Rollback) |
| P3: New OS Architecture (x=default,0=X86,9=AMD64) |
| P4: Install Result (x=default,0=Success,1=Failure,2=Cancel,3=Blocked) |
| P5: Result Error Code (Ex: 0xc1900101) |
| P6: Extend Error Code (Ex: 0x20017) |
| P7: Source OS build (Ex: 9600) |
| P8: Source OS branch (not typically available) |
| P9: New OS build (Ex: 16299> |
| P10: New OS branch (Ex: rs3_release> |
The event will also contain links to log files that can be used to perform a detailed diagnosis of the error. An example of this event from a successful upgrade is shown below.
Для чего нужна служба «Windows Error Reporting» и как отключить ее в Windows 7, 8.1 и 10
Когда в работе какой-то программы происходит ошибка, Windows автоматически регистрирует это событие и запускает штатную утилиту Windows Error Reporting, которая формирует отчет и предлагает отправить его на сервера Microsoft. Отправка лога не осуществляется автоматически, более того, большинство пользователей предпочитают не делиться информацией о программных ошибках и были бы не прочь отключить эту функцию вообще.
В Windows 7 и 8.1 это можно сделать через графический интерфейс системы, если же вы хотите отключить Windows Error Reporting в Windows 10, нужно отредактировать один ключ в реестре или изменить значение соответствующей ему политики в редакторе gpedit.msc . Существует и универсальный способ, одинаково подходящий для всех версий Windows, но о нём будет сказано ниже.
Отключение Error Reporting в Windows 7 и 8.1
Откройте через окошко «Выполнить» ( Win + R ) Центр поддержки командой wscui.cpl апплет «Центр поддержки».
Нажмите в меню справа ссылку «Параметры центра поддержки».
На следующей странице нажмите ссылку «Параметры отчета о неполадках».
И активируйте радиокнопку «Не проверять на наличие новых решений».
Отключение Error Reporting в Windows 10
В Windows 10 опция «Параметры отчета о неполадках» была удалена из окна параметров центра поддержки, поэтому для отключения формирования отчетов о программных ошибках в этой версии системы придется действовать в обход.
Откройте через окошко «Выполнить» одноименной командой редактор реестра Regedit и раскройте ключ:
HKLM\SOFTWARE\MicrosoftWindows\Windows Error Reporting
Справа создайте новый DWORD -параметр.
Назовите его Disabled и задайте в качестве его значения единицу.
Сохраните настройки, закройте редактор реестра и перезагрузите компьютер.
Описание примера отключения функции Error Reporting через редактор групповых политик мы опускаем, поскольку его результат является эквивалентным применяемому твику реестра, к тому же редактор gpedit.msc доступен не всех редакциях Windows.
Универсальный способ отключения Error Reporting
Предложенный ниже способ является универсальным и одинаково работает в Windows 7, 8.1 и Windows 10.
Вызовите окошко «Выполнить» и выполните в нём команду services.msc , чтобы открыть оснастку управления службами.
Отыщите справа службу «Служба регистрации ошибок Windows», откройте ее свойства и выставьте параметры так, как показано на скриншоте после чего сохраните настройки.
Любители командной строки могут отключить ее через консоль.
Запустив командную строку или PowerShell от имени администратора и выполните в ней команду:
sc config wersvc start=disabled
gpupdate /force
Чтобы обновить политику без перезагрузки компьютера.
Troubleshooting a Failover Cluster using Windows Error Reporting
Applies to: Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server
Windows Error Reporting (WER) is a flexible event-based feedback infrastructure designed to help advanced administrators or Tier 3 support gather information about the hardware and software problems that Windows can detect, report the information to Microsoft, and provide users with any available solutions. This reference provides descriptions and syntax for all WindowsErrorReporting cmdlets.
The information on troubleshooting presented below will be helpful for troubleshooting advanced issues that have been escalated and that may require data to be sent to Microsoft for triaging.
Enabling event channels
When Windows Server is installed, many event channels are enabled by default. But sometimes when diagnosing an issue, we want to be able to enable some of these event channels since it will help in triaging and diagnosing system issues.
You could enable additional event channels on each server node in your cluster as needed; however, this approach presents two problems:
- You have to remember to enable the same event channels on every new server node that you add to your cluster.
- When diagnosing, it can be tedious to enable specific event channels, reproduce the error, and repeat this process until you root cause.
To avoid these issues, you can enable event channels on cluster startup. The list of enabled event channels on your cluster can be configured using the public property EnabledEventLogs. By default, the following event channels are enabled:
Here’s an example of the output:
The EnabledEventLogs property is a multistring, where each string is in the form: channel-name, log-level, keyword-mask. The keyword-mask can be a hexadecimal (prefix 0x), octal (prefix 0), or decimal number (no prefix) number. For instance, to add a new event channel to the list and to configure both log-level and keyword-mask you can run:
If you want to set the log-level but keep the keyword-mask at its default value, you can use either of the following commands:
If you want to keep the log-level at its default value, but set the keyword-mask you can run the following command:
If you want to keep both the log-level and the keyword-mask at their default values, you can run any of the following commands:
These event channels will be enabled on every cluster node when the cluster service starts or whenever the EnabledEventLogs property is changed.
Gathering Logs
After you have enabled event channels, you can use the DumpLogQuery to gather logs. The public resource type property DumpLogQuery is a mutistring value. Each string is an XPATH query as described here.
When troubleshooting, if you need to collect additional event channels, you can a modify the DumpLogQuery property by adding additional queries or modifying the list.
To do this, first test your XPATH query using the get-WinEvent PowerShell cmdlet:
Next, append your query to the DumpLogQuery property of the resource:
And if you want to get a list of queries to use, run:
Gathering Windows Error Reporting reports
Windows Error Reporting Reports are stored in %ProgramData%\Microsoft\Windows\WER
Inside the WER folder, the ReportsQueue folder contains reports that are waiting to be uploaded to Watson.
Here’s an example of the output:
Inside the WER folder, the ReportsArchive folder contains reports that have already been uploaded to Watson. Data in these reports is deleted, but the Report.wer file persists.
Here’s an example of the output:
Windows Error Reporting provides many settings to customize the problem reporting experience. For further information, please refer to the Windows Error Reporting documentation.
Troubleshooting using Windows Error Reporting reports
Physical disk failed to come online
To diagnose this issue, navigate to the WER report folder:
Here’s an example of the output:
Next, start triaging from the Report.wer file — this will tell you what failed.
Since the resource failed to come online, no dumps were collected, but the Windows Error Reporting report did collect logs. If you open all .evtx files using Microsoft Message Analyzer, you will see all of the information that was collected using the following queries through the system channel, application channel, failover cluster diagnostic channels, and a few other generic channels.
Here’s an example of the output:
Message Analyzer enables you to capture, display, and analyze protocol messaging traffic. It also lets you trace and assess system events and other messages from Windows components. You can download Microsoft Message Analyzer from here. When you load the logs into Message Analyzer, you will see the following providers and messages from the log channels.
You can also group by providers to get the following view:
To identify why the disk failed, navigate to the events under FailoverClustering/Diagnostic and FailoverClustering/DiagnosticVerbose. Then run the following query: EventLog.EventData[«LogString»] contains «Cluster Disk 10». This will give you give you the following output:
Physical disk timed out
To diagnose this issue, navigate to the WER report folder. The folder contains log files and dump files for RHS, clussvc.exe, and of the process that hosts the «smphost» service, as shown below:
Here’s an example of the output:
Next, start triaging from the Report.wer file — this will tell you what call or resource is hanging.
The list of services and processes that we collect in a dump is controlled by the following property: PS C:\Windows\system32> (Get-ClusterResourceType -Name «Physical Disk»).DumpServicesSmphost
How to enable or disable Windows 10 Error Reporting Service
The Windows 10 error reporting service is designed to help ensure your PC works optimally. The central idea behind Windows Error Report (WER) is to keep Microsoft informed about user issues working with Windows.
However, every Windows OS version has the service enabled on default settings. But an individual user can choose to disable if the need arises. This article explores how to enable or disable the error reporting service on Windows 10.
How the Windows 10 Error Reporting Service Works and Why
Windows 10 Error Report focuses on discovering hardware and software issues from the user’s PC and report to Microsoft. With a database of likely complaints experienced with using the Windows 10, Microsoft can then send solutions for troubleshooting.
While working with the PC, some users experience pop-ups or alerts requesting the submission of the problem report. Windows error report usually occurs after a system failure, program crashes, refused to load properly or operating system errors. Windows usually prompt the user to submit an error report online to help proffer solutions in the future. The problem report may include program name, date, time of error and version.
Should I disable the Windows error reporting service?
Windows users often disable error reporting due to disk space or privacy issues but might need to exercise restraint. Error reporting service for Windows 10 offers dual benefits to Microsoft and the PC users.
Each error report helps Microsoft develop more advanced service packs for dealing with glitches. That means better user experience with Windows 10 based on the information gathered.
Steps to disable Window 10 Error Reporting Service
- Use Command to disable Window 10 Error Report
- Use the Registry Editor to disable Window 10 Error Report
Just like other versions, Windows 10 does have a slightly different graphical user interface for disabling error reports. Lower versions of Windows OS have error reporting under Action Center Setting. On Windows 10 it is the Security & Maintenance function requiring working with registries.
Method One: Use Command to disable Window 10 Error Report
It’s a simple and straightforward process. Here are the steps to follow:
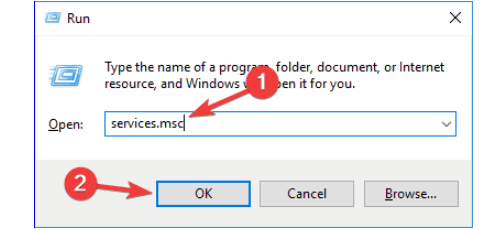
- Use the shortcut key. From the keyboard press down the Windows key+R. It should navigate to the Run dialog box.
- Into the open space of the dialog box type service.msc.
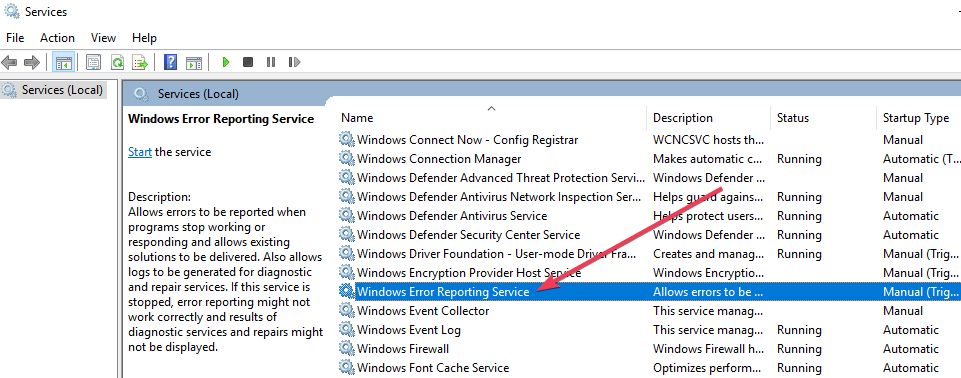
- Move the cursor to Windows Error Reporting Service and right-click it.
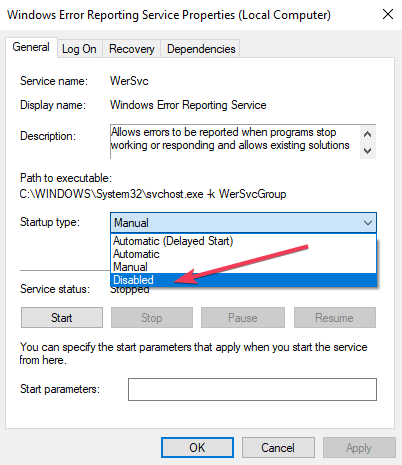
- Locate Startup types and scroll through the drop down menu list on the right.
- Click Disabledwhich is at the bottom of the list.
- Click ‘OK‘ or apply to complete the action.
- Close the service window to exit. Now the process has been completed.
- RELATED: 5 best software to fix runtime errors in Windows 10
Note:
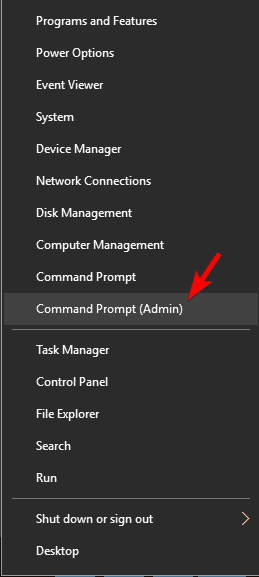
In some cases, the Startup type which is close to disabled might appear as gray. That means the user needs admin rights to continue the process. Therefore, log out and log in as an administrator. Or locate the administrative command prompt by pressing Windows key+ X to select command prompt admin.
Method Two: Use the Registry Editor
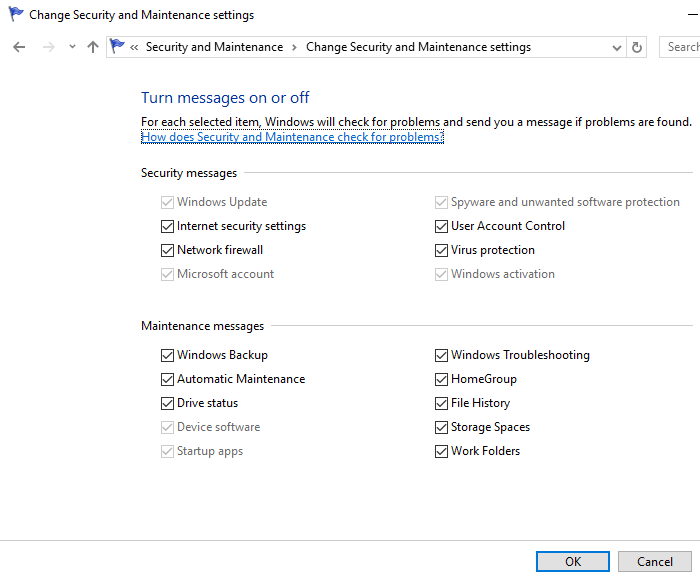
Using the Registry Editor is another way to safely disable the Windows 10 Error Reporting Service. This second method for disabling Windows error reporting service includes tweaking the registry. But first, you need to check for error report issues:
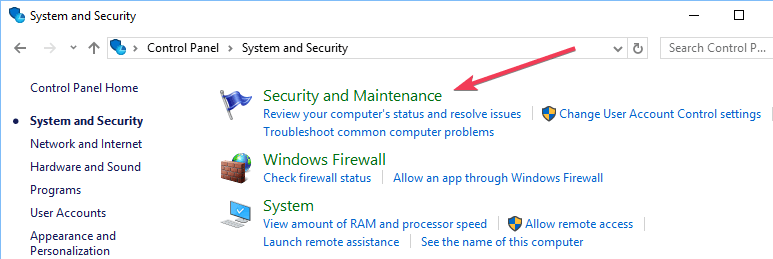
- Locate Control Panel from Windows startup.
- Click Control Panel> System and Security> Security and Maintenance.
- Look out for Report problems. Report problems should by default display ‘On’.
- RELATED: Fix Blue Screen of Death errors with these 4 software solutions
Steps to disable Windows Error Reporting Service using the Registry Editor
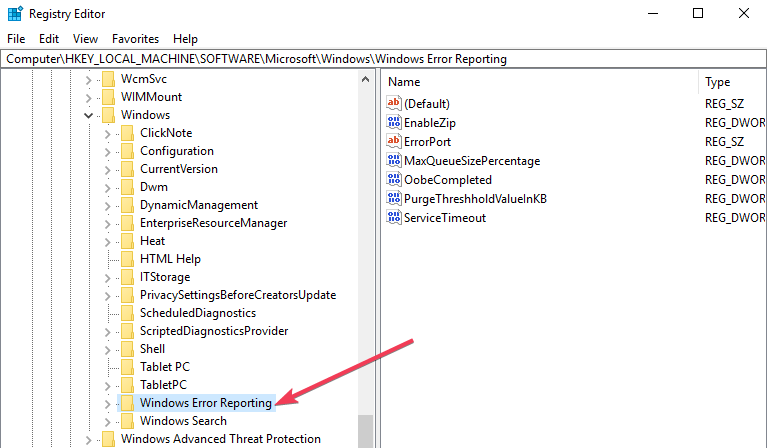
- Locate the registry editor app below:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\Windows Error Reporting
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\Windows Error Reporting
- To the right of your window, locate the registry key in the dialog box.
- Click on the option ‘disabled’ so the dialog box can appear. Replace the value ‘0’ with ‘1’.
- If there is no value then create a new one with the same name, ‘Disabled’.
- Then set the new 32-Bit DWORD value to ‘1’.
- Tap ‘OK’ to effect changes.
Note:
- To confirm that the Windows error reporting service has been disabled, go to Security and Maintenance. Check the comment on the report problem to see if it reads on or off.
- To re-enable error reporting service on Windows 10 simply set the disabled value back to zero. Another option would be to delete the disabled value.
- To create a new DWORD from the registry editor one needs to locate Edit > New on the menu.
It’s quite simple to disable and enable Windows 10 error reporting service anytime. And understanding how to use the Registry Editor or finder makes everything much simpler.