- Fix Windows Update errors
- Fix Windows Update errors by using the DISM or System Update Readiness tool
- Symptom
- Resolution for Windows 8.1, Windows 10 and Windows Server 2012 R2
- Resolution for Windows 7 Service Pack 1 (SP1) and Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1
- Resolution — Download the package from Microsoft Update Catalog directly
- Description of the common corruption errors
- What does the System Update Readiness tool do
- Verify the integrity of resources
- Logging
- How to fix errors that are found in the CheckSUR log file
- Get help with Windows 10 upgrade and installation errors
- General fixes
- 0xC1900101 Errors
- Other Common Errors
Fix Windows Update errors
What does this guided walk-through do?
This guided walk-through provides steps to fix problems with Windows Updates for Windows 8.1 and 7, such as taking a long time to scan, or error codes while installing updates.
For help with Windows Update issues in Windows 10, see Troubleshoot problems updating Windows 10 instead.
A common cause of errors is inadequate drive space. If you need help freeing up drive space, see Tips to free up drive space on your PC.
Common error codes
The steps in this guided walk-through should help with all Windows Update errors and other issues— you don’t need to search for the specific error to solve it. As an example, here are some commonly seen error codes: 0x0xc1900223223; 0x80240034; 0x8007000E, 0x80242006, 0x80244018, 0x80D02002, 0x80246017, 0x80240438, 0x80070070, 0x8007000D, 0x80246008, 0x80096004, 0x80070020.
The steps provided here should help fix any errors that come up during the Windows Update process.
How does it work?
We’ll begin by asking you questions about the Windows version you’re using and the issue you’re experiencing. Next, we’ll take you through a series of troubleshooting steps that are specific to your situation. At the end of each step, you’ll be asked “Did this resolve the issue?” If it’s resolved, select Yes, and you’re done! If it isn’t resolved, select No and continue with the guided walk-through.
Fix Windows Update errors by using the DISM or System Update Readiness tool
Original product version: В Windows 10, version 1809 and later versions, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows 7 Service Pack 1, Windows Server 2008 R2 Service Pack 1
Original KB number: В 947821
Symptom
Windows updates and service packs may fail to install if there are corruption errors. For example, an update might not install if a system file is damaged. The DISM or System Update Readiness tool may help you to fix some Windows corruption errors.
This article is intended for Support agents and IT professionals. If you are home users and looking for more information about fixing Windows update errors, see Fix Windows Update errors.
Resolution for Windows 8.1, Windows 10 and Windows Server 2012 R2
To resolve this problem, use the inbox Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) tool. Then, install the Windows update or service pack again.
Open an elevated command prompt. To do this, open Start menu or Start screen, type Command Prompt, right-select Command Prompt, and then select Run as administrator. If you are prompted for an administrator password or for a confirmation, type the password, or select Allow.
Type the following command, and then press Enter. It may take several minutes for the command operation to be completed.
When you run this command, DISM uses Windows Update to provide the files that are required to fix corruptions. However, if your Windows Update client is already broken, use a running Windows installation as the repair source, or use a Windows side-by-side folder from a network share or from a removable media, such as the Windows DVD, as the source of the files. To do this, run the following command instead:
Replace the C:\RepairSource\Windows placeholder with the location of your repair source. For more information about using the DISM tool to repair Windows, reference Repair a Windows Image.
Type the sfc /scannow command and press Enter. It may take several minutes for the command operation to be completed.
Close the command prompt, and then run Windows Update again.
DISM creates a log file (%windir%/Logs/CBS/CBS.log) that captures any issues that the tool found or fixed. %windir% is the folder in which Windows is installed. For example, the %windir% folder is C:\Windows.
Resolution for Windows 7 Service Pack 1 (SP1) and Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1
To resolve this problem, use the System Update Readiness tool. Then, install the Windows update or service pack again.
Download the System Update Readiness tool.
select the download link in the following table that corresponds to the version of Windows that is running on your computer. For more information about how to find the version of Windows that you installed, see Find out if your computer is running the 32-bit or 64-bit version of Windows.
This tool is updated regularly, we recommend that you always download the latest version. This tool is not available in every supported language. Check the link below to see if it is available in your language.
| Operating system | Download link |
|---|---|
| x86-based (32-bit) versions of Windows 7 SP1 | Download the package now. |
| x64-based (64-bit) versions of Windows 7 SP1 | Download the package now. |
| x64-based (64-bit) versions of Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 | Download the package now. |
| Itanium-based versions of Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 | Download the package now. |
Install and run the tool.
Select Download on the Download Center webpage, then do one of the following:
- To install the tool immediately, select Open or Run, and then follow the instructions on your screen.
- To install the tool later, select Save, and then download the installation file to your computer. When you’re ready to install the tool, double-select the file.
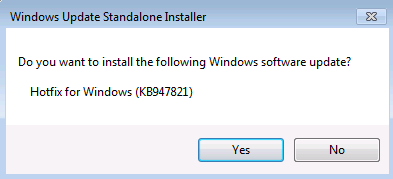
In the Windows Update Standalone Installer dialog box, select Yes.
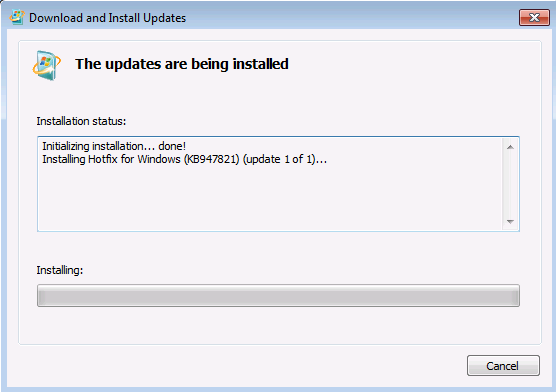
When the tool is being installed, it automatically runs. Although it typically takes less than 15 minutes to run, it might take much longer on some computers. Even if the progress bar seems to stop, the scan is still running, so don’t select Cancel.
When you see Installation complete, select Close.
Reinstall the update or service pack you were trying to install previously.
To manually fix corruption errors that the tool detects but can’t be fixed, see How to fix errors that are found in the CheckSUR log file.
Resolution — Download the package from Microsoft Update Catalog directly
You can also try to directly download the update package from Microsoft Update Catalog, and then install the update package manually.
For example, you may have problems when you try to install updates from Windows Update. In this situation, you can download the update package and try to install the update manually. To do this, follow these steps:
Open Microsoft Update Catalog in Internet Explorer.
In the search box, input the update number that you want to download. In this example, input 3006137. Then, select Search.
Find the update that applies to your operating system appropriately in the search results, and then select Add to add the update to your basket.
Select view basket to open your basket.
Select Download to download the update in your basket.
Select Browse to choose a location for the update you are downloading, and then select Continue.
Select Close after the download process is done. Then, you can find a folder that contains the update package in the location that you specified.
Open the folder, and then double-select the update package to install the update.
If the Windows update or service pack installed successfully, you are finished. If the problem is not fixed, or if System Update Readiness Tool cannot find the cause, contact us for more help.
Description of the common corruption errors
The following table lists the possible error code with Windows Update for your reference:
| Code | Error | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0x80070002 | ERROR_FILE_NOT_FOUND | The system cannot find the file specified. |
| 0x8007000D | ERROR_INVALID_DATA | The data is invalid. |
| 0x800F081F | CBS_E_SOURCE_MISSING | The source for the package or file not found. |
| 0x80073712 | ERROR_SXS_COMPONENT_STORE_CORRUPT | The component store is in an inconsistent state. |
| 0x800736CC | ERROR_SXS_FILE_HASH_MISMATCH | A component’s file does not match the verification information present in the component manifest. |
| 0x800705B9 | ERROR_XML_PARSE_ERROR | Unable to parse the requested XML data. |
| 0x80070246 | ERROR_ILLEGAL_CHARACTER | An invalid character was encountered. |
| 0x8007370D | ERROR_SXS_IDENTITY_PARSE_ERROR | An identity string is malformed. |
| 0x8007370B | ERROR_SXS_INVALID_IDENTITY_ATTRIBUTE_NAME | The name of an attribute in an identity is not within the valid range. |
| 0x8007370A | ERROR_SXS_INVALID_IDENTITY_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE | The value of an attribute in an identity is not within the valid range. |
| 0x80070057 | ERROR_INVALID_PARAMETER | The parameter is incorrect. |
| 0x800B0100 | TRUST_E_NOSIGNATURE | No signature was present in the subject. |
| 0x80092003 | CRYPT_E_FILE_ERROR | An error occurred while Windows Update reads or writes to a file. |
| 0x800B0101 | CERT_E_EXPIRED | A required certificate is not within its validity period when verifying against the current system clock or the time stamp in the signed file. |
| 0x8007371B | ERROR_SXS_TRANSACTION_CLOSURE_INCOMPLETE | One or more required members of the transaction are not present. |
| 0x80070490 | ERROR_NOT_FOUND | Windows could not search for new updates. |
| 0x800f0984 | PSFX_E_MATCHING_BINARY_MISSING | Matching component directory exist but binary missing |
| 0x800f0986 | PSFX_E_APPLY_FORWARD_DELTA_FAILED | Applying forward delta failed |
| 0x800f0982 | PSFX_E_MATCHING_COMPONENT_NOT_FOUND | Can’t identify matching component for hydration |
What does the System Update Readiness tool do
Verify the integrity of resources
The System Update Readiness tool verifies the integrity of the following resources:
- Files that are located in the following directories:
- %SYSTEMROOT%\Servicing\Packages
- %SYSTEMROOT%\WinSxS\Manifests
- Registry data that is located under the following registry subkeys:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Components
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Schema
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Component Based Servicing
This list may be updated at any time.
When the System Update Readiness tool detects incorrect manifests, Cabinets, or registry data, it may replace the incorrect data with a corrected version.
Logging
The System Update Readiness tool creates a log file that captures any issues that the tool found or fixed. The log file is located here:
How to fix errors that are found in the CheckSUR log file
To manually fix corruption errors that the System Update Readiness tool detects but can’t fix, follow these steps:
%SYSTEMROOT% is an environment variable that saves the folder in which Windows is installed. For example, generally the %SYSTEMROOT% folder is C:\Windows.
Identify the packages that the tool can’t fix. For example, you may find the following in the log file:
In this case, the package that is corrupted is KB958690.
Copy the package (.msu) to the %SYSTEMROOT%\CheckSUR\packages directory. By default, this directory doesn’t exist and you need to create the directory.
Get help with Windows 10 upgrade and installation errors
There are many reasons why you might receive an error message when upgrading or installing Windows 10, but common errors can be fixed with a few steps that you can do on your own. Note: An upgrade takes your device from an older version of Windows, such as Windows 7 or Windows 8.1, to Windows 10.
Before searching for a specific error code, try the tips listed in General fixes. If those don’t fix your upgrade or installation problem, check the table of error codes at the bottom of this article.
General fixes
Here are some things you can try to fix upgrade and installation errors:
Unplug any nonessential hardware devices. These could include headphones, printers, scanners speakers, USB flash drives, and external hard drives.
If you’re using a laptop and it’s plugged in to a docking station, undock it.
It’s a good idea to make sure that all important updates are installed before trying to upgrade Windows. This includes updates to hardware drivers on your device.
For information and to make sure you’re up-to-date, see Windows Update: FAQ.
Use Windows Defender to protect your device during the upgrade—non-Microsoft antivirus software can sometimes cause upgrade problems. As long as you have installation media and all required activation information, you can always reinstall the software after you upgrade.
To remove an antivirus application, go to Control Panel\Programs\Programs and Features. Select the program, and then select Uninstall. Select Yes to confirm.
Outdated software can cause problems with a Windows upgrade, so removing old or nonessential applications can help.
If you plan to reinstall the application later, make sure you have the installation media and all required activation information before removing it.
To uninstall software, go to Control Panel\Programs\Programs and Features. Select the program, and then select Uninstall. Select Yes to confirm.
To upgrade to Windows 10, you need enough space on your hard drive for the installation to take place.
To view how much hard drive space is available on your computer, select the Start button, then in the search box on the taskbar, type File Explorer (known as Windows Explorer in Windows 7).
Then select Computer or This PC and look under Hard Disk Drives or under Devices and drives. If there are multiple drives listed, the system drive is the drive that includes a Microsoft Windows logo above the drive icon. You’ll see the amount of available space under the drive.
If it looks like your drive is running low on space, see Tips to free up drive space on your PC.
0xC1900101 Errors
An error that begins with 0xC1900101 is usually a driver error. If you see any of these error codes, try the following steps first to fix the problem. If these steps don’t work, see Resolve Windows 10 upgrade errors for more detailed technical info.
Make sure that your device has enough space. Your device requires at least 16 GB of free space to upgrade a 32-bit OS, or 20 GB for a 64-bit OS. For more info, see Free up drive space in Windows 10.
Run Windows Update a few times. Download and install any available updates in Windows Update, including software updates, hardware updates, and some third-party drivers. Use the troubleshooter for Windows 10 to fix Windows Update errors.
Check third-party drivers and download any updates. You can find third-party drivers and installation instructions for any hardware you’ve added to your device on the manufacturer’s website.
Unplug extra hardware. Remove all external storage devices and drives, docks, and other hardware you might have plugged into your device that isn’t needed for basic functionality.
Check Device Manager for errors. Select the Start button, then in the search box on the taskbar, type device manager. Choose Device Manager from the results. In the window that pops up, look for any device with a yellow exclamation mark beside it (you may have to select each category to switch to the list of devices). Press and hold (or right-click) the device name and select either Update Driver Software or Uninstall to correct the errors.
Remove third-party security software. Make sure you know how to reinstall your programs and that any necessary product keys are on hand. Windows Defender will help protect your device in the meantime.
Repair hard-drive errors. Select the Start button, then in the search box on the taskbar, type command prompt. Choose Command Prompt from the list of results. In the window that pops up, type chkdsk/f C: and press the Enter key. Repairs automatically start on your hard drive, and you’ll be asked to restart your device.
Note: You must have administrator permissions on your device to do this.
Do a clean restart into Windows. Learn how.
Restore and repair system files. Select the Start button, then in the search box on the taskbar, type command prompt. Choose Command Prompt from the list of results. In the window that pops up, type DISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-image /Restorehealth and press the Enter key. (Learn to repair a Windows image)
Note: You must have administrator permissions on your device to do this.
Other Common Errors
The following table lists the most common upgrade and installation errors and some things you can try to fix them. If you continue having problems upgrading or installing Windows 10, contact Microsoft support.
What it means and how to fix it
This indicates that there was a problem downloading and installing the selected update. Windows Update will try again later and there is nothing you need to do at this time.
This could indicate that an incompatible app installed on your PC is blocking the upgrade process from completing. Check to make sure that any incompatible apps are uninstalled and then try upgrading again.
A cleanup operation from a previous installation attempt is still pending, and a system restart is required to continue the upgrade. Restart the device and run setup again. If restarting device does not resolve the issue, then use the Disk Cleanup utility and clean up the temporary files and the System files. For more information, see Disk cleanup in Windows 10.
A file needed by Windows Update is likely damaged or missing. Try repairing your system files: Select the Start button and type command prompt in the search box on the taskbar. Choose Command Prompt from the list of results. In the window that appears, type DISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-image /Restorehealth and press the Enter key.
This may signify that your PC doesn’t meet the minimum requirements to download or install the upgrade to Windows 10. Learn more about the minimum requirements for Windows 10
This might indicate that a driver or other software on your PC isn’t compatible with the upgrade to Windows 10. For info about how to fix this problem, contact Microsoft support.
This could mean that the upgrade process was interrupted because you accidentally restarted your PC or signed out of your PC. Try upgrading again and make sure your PC is plugged in and stays turned on.
This error might mean that your PC couldn’t connect to the Windows Update servers. If you’re using a VPN connection to connect to a work network, disconnect from the network and turn off the VPN software (if applicable) and try upgrading again.
The error could also mean there isn’t enough free space in the System Reserved partition. You might be able to fix this problem by using third-party software to increase the size of the System Reserved partition.
Error: We couldn’t complete the updates. Undoing changes. Don’t turn off your computer.
Error: Failure configuring Windows Updates. Reverting changes.
These are generic errors that might appear any time a Windows update fails. You’ll need to determine the specific error code to investigate how to best resolve this problem.
You can find the error code for the failed update by viewing your update history. Look for the update that wasn’t installed, note the error code, and then contact Microsoft support.
To view your update history in Windows 8.1:
Open Windows Update by swiping in from the right edge of the screen (or, if you’re using a mouse, pointing to the lower-right corner of the screen and moving the mouse pointer up), select Settings > Change PC settings > Update and recovery > View your update history.
To view your update history in Windows 7:
Select the Start 
Error: The update isn’t applicable to your computer.
This error might mean that your PC doesn’t have the required updates installed.
Check to make sure that all important updates are installed on your PC before you try upgrading.
This likely indicates that your PC doesn’t have enough space available to install the upgrade.
Free some space on the drive and try again. Get tips for freeing up drive space
The specified disk operation is not supported by the target disk, partition, or volume.
Make sure your machine meets the minimum requirements to install Windows 10.
The system cannot find the file specified.
If you have a disk or disks where you are not installing Windows 10 on, remove those disks.
A driver has caused a problem.
Disable or remove all 3rd party antivirus or antispyware from your system. Disconnect all peripheral devices that are connected to the system, except for the mouse, keyboard and display.
Contact your hardware vendor to obtain updated device drivers.
Windows Setup terminated unexpectedly due to another process running in the background.
When you start Windows by using a normal startup, several applications and services start automatically, and then run in the background. These programs include basic system processes, antivirus software, system utility applications, and other software that has been previously installed. These applications and services can cause interference when you attempt to upgrade to the latest version of Windows 10.
To help you determine whether a background program is interfering with the upgrade, a «clean boot» may be needed. See How to perform a clean boot in Windows.
Windows Setup terminated unexpectedly due to another process running in the background.
Uninstall any antivirus or antispyware software and update again.