- Команда exit для начинающих
- Команда exit в Linux
- Определение ловушек (trap)
- Заключение
- Bash get exit code of command on a Linux / Unix
- What is an exit code in bash shell?
- How to find out the exit code of a command
- Bash get exit code of command – How to use exit codes in shell scripts
- How do I set an exit code for my own shell scripts?
- A sample shell script to get the exit code of a command
- Recommend exit code for your shell scripts
- How to deal with the exit codes of all piped commands
- Conclusion
- How to Exit a File in Vi / Vim Editor in Linux
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
Команда exit для начинающих
Оригинал: Linux exit Command Explained for Beginners (with Examples)
Автор: Himanshu Arora
Дата публикации: 4 сентября 2019 года
Перевод: А. Кривошей
Дата перевода: март 2020 г.
Если вы новичок в Linux, и ваша работа связана с работой в командной строке, то само собой разумеется, что вы должны проводить много времени в терминале. Как вы, вероятно, согласитесь, есть некоторые команды, которые мы обычно используем очень часто, например, ls, cp и rm. Однако есть некоторые другие, которые используются намного реже. В этом посте мы обсудим одну такую, менее часто используемую команду: Exit.
Обратите внимание, что все примеры и инструкции, упомянутые в этой статье, были протестированы в оболочке Bash, работающей в Ubuntu 18.04LTS.
Команда exit в Linux
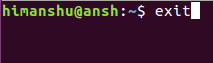
Команда exit позволяет вам выйти из оболочки, где она запущена.
Если в вашем окне оболочки есть несколько вкладок, то эта команда выходит из вкладки, в которой она выполняется. Учитывая, что это встроенная команда, весьма вероятно, что вы не найдете выделенную справочную страницу для exit. Чтобы получить доступ к ее официальной документации, выполните следующую команду:
В моей системе вышеупомянутая команда выдала следующий вывод:
Теперь некоторые из вас могут спросить, почему (или, скорее, когда) требуется N. Это значение, которое является состоянием выхода, используется в основном, когда команда используется внутри скрипта (сценария bash). В некоторых случаях это значение отображается на понятную человеку ошибку, предупреждение или уведомление.
Кроме того, как ясно из вышеприведенного вывода справочной команды, если значение N не указано явно, то этим значением считается состояние завершения последней выполненной команды.
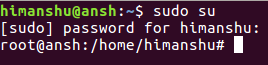
Давайте рассмотрим простой пример: я переключил учетные записи пользователей и вошел в оболочку root:
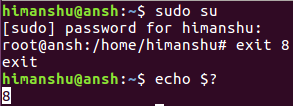
Затем я вышел из оболочки с помощью команды exit. Кроме того, я использовал 8 в качестве значения состояния выхода.
Теперь в родительской оболочке (куда я вернулся) я использовал следующую команду для проверки состояния выхода:
Вы можете видеть, что это то же значение состояния, которое было передано команде выхода в оболочке root. Таким образом, мы можем получить доступ к статусу, а затем делать все, что намечено.
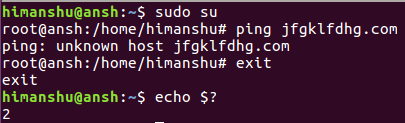
Вот еще один пример, в котором я явно не передавал какой-либо статус выхода из оболочки root, но при запросе в родительской оболочке было возвращено состояние выхода последней команды, которая была выполнена в оболочке root:
Определение ловушек (trap)
Если вы хотите, вы также можете определить некоторые действия, которые вы хотите, чтобы система выполняла при выходе из оболочки. Например, вы можете удалить один или несколько файлов при выходе. Для этого вам нужно установить ловушку (trap), которую вы можете создать следующим образом:
Какое бы действие вы ни предприняли при выходе из системы, вам нужно указать соответствующую команду в двойных кавычках выше. Например, я использовал следующую команду:
Дело в том, что в моей системе такого файла нет, поэтому после выполнения команды exit оболочка должна отобразить ошибку для нее. И вот что на самом деле произошло — см. ниже:
Таким образом, вы можете установить ловушки на выходе. Для получения дополнительной информации о ловушках выполните следующую команду:
Заключение
Когда дело доходит до команды exit, не требуется особой кривой обучения, особенно если вы новичок в командной строке. И вы, вероятно, согласитесь с этим. Так что просто попробуйте все, что мы здесь обсудили, и начните использовать команду exit (если вы этого еще не сделали).
Источник
Bash get exit code of command on a Linux / Unix
I am a new Linux system user. How do I get the exit code of a command? How do I get the exit code or status of Linux or Unix shell command and store it into a shell variable?
Introduction – Each Linux or Unix shell command returns a status when it terminates normally or abnormally. For example, if backup.sh script is unsuccessful, and it returns a code which tells the shell script to send an e-mail to sysadmin.
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | No |
| Requirements | Bash on Linux, macOS or Unix-like OS |
| Est. reading time | 2 minutes |
What is an exit code in bash shell?
Every Linux or Unix command executed by the shell script or user has an exit status. Exit status is an integer number. 0 exit status means the command was successful without any errors. A non-zero (1-255 values) exit status means command was a failure.
How to find out the exit code of a command
You need to use a particular shell variable called $? to get the exit status of the previously executed command. To print $? variable use the echo command or printf command:
date
echo $?
date-foo-bar
printf ‘%d\n’ $?
How to get the exit code of a command such as date and date-foo-bar
Bash get exit code of command – How to use exit codes in shell scripts
So how do you store exit status of the command in a shell variable? Simply assign $? to a shell variable. The syntax is:
How do I set an exit code for my own shell scripts?
The exit command cause normal shell script termination. It exits the shell with a status of N. The syntax is:
A sample shell script to get the exit code of a command
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Recommend exit code for your shell scripts
| Exit status | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Catchall for general errors |
| 2 | Misuse of shell builtins (according to Bash documentation) |
| 126 | Command invoked cannot execute |
| 127 | Command not found |
| 128 | Invalid argument to exit command |
| 128+n | Fatal error signal “n” |
| 130 | Bash script terminated by Control-C |
| 255* | Exit status out of range |
How to deal with the exit codes of all piped commands
Conclusion
This page showed how to use exit codes on Linux or Unix based system and how to get the exit status/code of command. See man pages by typing the man command or help command:
man bash
help exit
For more info see:
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
| Category | List of Unix and Linux commands |
|---|---|
| Documentation | help • mandb • man • pinfo |
| Disk space analyzers | df • duf • ncdu • pydf |
| File Management | cat • cp • less • mkdir • more • tree |
| Firewall | Alpine Awall • CentOS 8 • OpenSUSE • RHEL 8 • Ubuntu 16.04 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Linux Desktop Apps | Skype • Spotify • VLC 3 |
| Modern utilities | bat • exa |
| Network Utilities | NetHogs • dig • host • ip • nmap |
| OpenVPN | CentOS 7 • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Debian 8/9 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Package Manager | apk • apt |
| Processes Management | bg • chroot • cron • disown • fg • glances • gtop • jobs • killall • kill • pidof • pstree • pwdx • time • vtop |
| Searching | ag • grep • whereis • which |
| Shell builtins | compgen • echo • printf |
| Text processing | cut • rev |
| User Information | groups • id • lastcomm • last • lid/libuser-lid • logname • members • users • whoami • who • w |
| WireGuard VPN | Alpine • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Firewall • Ubuntu 20.04 |
Comments on this entry are closed.
One of the best Unix exit code tutorial with examples. Thank you. I used it on my macOS macMini desktop.
Hi, I just completed 9 captchas- 18 3×3 grids. I come here for a quick tutorial to remind myself of something I already know, in most cases, for one minute so as not to lose my train of thought. Thank-you! But I don’t have the time for the captchas. Please find another solution to whatever problem you are trying to solve.
Captchas are only needed when posting comments to avoid spam. However, Cloudflare might trigger Captchas when it detects IP address with bad reputation.
Hi Vivek,
Love your site, and I’ve learned a lot from it. It’s a great resource.
I normally use a self-administered proxy/VPN when using a browser for privacy reasons. Unfortunately I can’t control which IP address I get without becoming an ISP or a cloud provider myself. Cloudflare probably sees my IP address and knows that it is in the range for cloud provider X, and not from a company or residential IP address, which triggers the captcha.
So in this case it is unfortunately targetting a normal/not-spamming user. I understand that you are doing this so as to not have to deal with spam or other issues; and my behaviour is probably that of only a tiny percentage of users.
Trade-offs and unintended consequences, right? Anyway, I thought it might be useful to hear from someone for whom this was causing issues. In order to check on this and reply today, I ‘only’ had to do 4 captchas.
Thank you kindly for your excellent website.
Источник
How to Exit a File in Vi / Vim Editor in Linux
In this article, we will learn how to exit Vi/Vim (after referred to as Vim) text editor using simple commands. In a previous article, we explained a simple tip on how to save a file in Vi or Vim after making changes to a file.
Before we move any further, if you are new to Vim, then we recommend reading through these 10 reasons why you should stick to using Vi/Vim text editor in Linux.
To open or create a new file using Vi/Vim, simply type the commands below, then press i to switch to insert mode (insert text):

After making changes to a file, press [Esc] to shift to the command mode and press :w and hit [Enter] to save a file.

To exit Vi/Vim, use the :q command and hit [Enter] .

To save a file and exit Vi/Vim simultaneously, use the :wq command and hit [Enter] or 😡 command.

If you make changes to a file but try to quite Vi/Vim using ESC and q key, you’ll receive an error as shown in the scrrenshot below.

To force this action, use ESC and :q! .

Additionally, you can use shortcut methods. Press the [Esc] key and type Shift + Z Z to save and exit or type Shift+ Z Q to exit without saving the changes made to the file.
Having learned the above commands, you can now proceed to learn advanced Vim commands from the links provided below:
In this article, we learned how to exit Vim text editor using simple commands. Do you have any questions to ask or any thoughts to share? Please, use the feedback form below.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник