- Ethical hacking and penetration testing
- InfoSec, IT, Kali Linux, BlackArch
- Kali Linux updating troubleshooting
- Error ‘E: Failed to fetch … Cannot initiate the connection’
- During the update, a window or request appears that does not respond to clicks
- What to do if the program asks about updating the configuration file
- Error: 1 404 Not Found [IP:
- Error “E: Could not access the lock file /var/lib/dpkg/lock”
- W: An error occurred during the signature verification. The repository is not updated and the previous index files will be used. GPG error:
- Kali Linux update is delayed for the whole day
- What to do when the update is broken?
- Failed to fetch InRelease
- The system occupies a lot of disk space
- Failed to update Kali «failed to fetch http.kali.org/kali» #1258
- Comments
- Maur1ch commented Jul 6, 2020 •
- Describe the bug
- Steps to reproduce the behavior
- deb-src https://http.kali.org/kali kali-rolling main contrib non-free
- Device Information
- Ethical hacking and penetration testing
- InfoSec, IT, Kali Linux, BlackArch
- Errors in Kali Linux ‘W: Failed to fetch’ and ‘W: Some index files failed to download. They have been ignored, or old ones used instead.’ (SOLVED)
- 1. Cannot update Kali Linux because errors
- 2. Specifying a certain Kali Linux update mirror
- 3. How to bypass ISP censorship to access Kali Linux servers
- 4. Redirecting traffic through the Tor network using Privoxy
- 5. How to bypass ISP censorship using free VPNs
Ethical hacking and penetration testing
InfoSec, IT, Kali Linux, BlackArch
Kali Linux updating troubleshooting
A full system update is performed as follows:
The update process requires:
- correct entry in repository list (application sources)
- Internet connection
Application sources (repositories) are written in the /etc/apt/sources.list file
To open a file, use the command
Lines that begin with the # character are comments, do not pay attention to them.
It is important that there is a line:
And this line should be the only uncommented.
The string can be:
It is identical, but HTTP is specified instead of HTTPS. The main thing is to have one of these options, and there are no other uncommented lines.
For more information on updating Kali Linux, any other commands and questions related to updating, see the help article “How to update Kali Linux”.
Error ‘E: Failed to fetch … Cannot initiate the connection’
Part of the output when information update failed because the connection was broken:
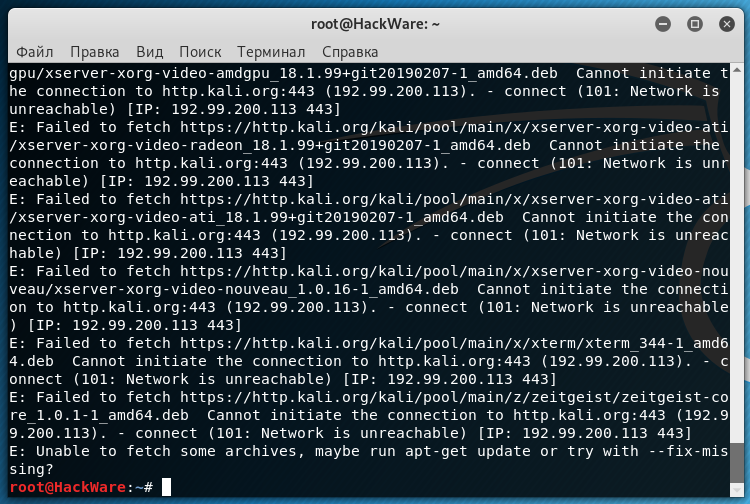
The key information here is:
That is, the system could not download some package files.
- you have an unstable internet connection and some files were not uploaded due to disconnections
- some time passed between updating the application cache and downloading files, during which the packages in the repository managed to be updated — that is, you are trying to download old packages, and are no longer available on the server, as they are replaced by new versions. Such a situation is likely, especially if you need to upgrade many packages, and your Internet connection is slow.
To solve the problem, simply restart the update with the commands:
This should completely correct the error.
During the update, a window or request appears that does not respond to clicks
Sometimes when updating, there are requests to the user, which may look like this:
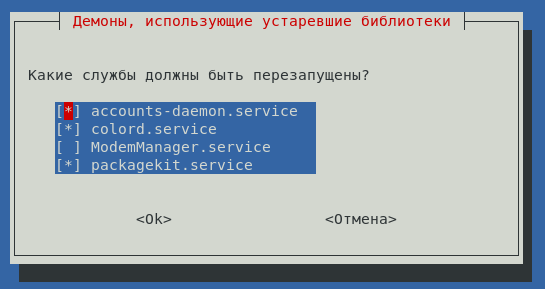
Or look like this:

Since the update takes place in the console, what you see is a pseudo-graphic interface and use special buttons to work with it:
TAB – to navigate through the menu items
SPACE or ENTER – to select or deselect
Use the TAB key to go to the OK button and press ENTER to continue the update.
What to do if the program asks about updating the configuration file
With some updates of some packages, the structure of the configuration file changes. Sometimes the new file contains directives and settings that are necessary for the new version of the program, without which it cannot work.
To set up a program is almost always changing configuration files. The end result can be the result of long work with the configuration and a variety of tests. It may take hours or even days.
Therefore, if necessary, update the configuration, there is a dilemma:
- do not update the config, as a result of which the new version will not work normally
- update config and erase user configuration results
For this reason, the system asks you every time what needs to be done if the configuration file is updated with the program update?
If in reality you did not use this program, or the settings you have made are of no value to you, then always agree to update the configuration file. If the settings you have made are important to you, then:
- refuse to update the configuration file
- make a backup of your config, update the configuration file, and then make the necessary settings in it
For some packages, such as Tor, the configuration file is simply a set of comments in which no settings are active — for such files (if you have not changed them), the update is a mere formality.
Error: 1 404 Not Found [IP:
When updating, the following error may occur:
The key here is the ‘404 Not Found’ — that is, the package file was not found. The most common reason for this is an outdated cache with information about packages and links to download them.
Therefore, before updating packages, update the cache:
Or use such a combined command that will update the cache and immediately start downloading and installing updated versions of packages:
Error “E: Could not access the lock file /var/lib/dpkg/lock”
Perhaps the most common mistake when trying to update or install a new package:
All details on this error, as well as instructions for fixing here: https://miloserdov.org/?p=2016
W: An error occurred during the signature verification. The repository is not updated and the previous index files will be used. GPG error:
The process of updating packages, in addition to downloading and unpacking them, also includes checking their digital signatures. This verification ensures:
- package integrity (that they were not damaged when downloading)
- receiving them from a reliable source (these packages were not modified or created by unauthorized persons
The digital signature is delivered to the system also packaged in a package that is updated along with other packages of the system. If too much time has passed and the digital signature verification files are out of date, then a vicious circle occurs: you cannot update the packages in the system, as they pass the digital signature verification. You cannot update digital signature verification files because they are shipped as a package, and packages cannot be updated because…
In general, the problem is solved by one command that downloads and installs the actual file for checking the digital signature, details here: https://miloserdov.org/?p=893
Kali Linux update is delayed for the whole day
In a virtual machine, I encounter a slowdown in updating packages in Kali Linux. As a result, a big update can literally drag on for the whole day. Moreover, the process of unpacking downloaded updated packages takes the most time. Unpacking the exploitdb or metasploit-framework may take literally hours!
This is not normal – apparently some kind of bug.
Personally, I chose a rather non-standard solution for me – I have Kali Linux installed on a real (and not virtual) external USB drive, which I plug into VirtualBox and boot from it in a virtual machine. That is, without leaving the main system, I boot from an external disk. This is an excellent solution – the process of unpacking packages began to take a few minutes, but this is a little complicated method and it does not suit everyone.
If you want to work exclusively in VirtualBox and not connect an external USB drive, then as an option, you can remove two packages that take the most time to decompress, this is exploitdb and metasploit-framework. Moreover, the metasploit-framework package is a dependency for such tools as: armitage, commix, ghost phisher, jboss-autopwn, maltego-teeth, msfpc, set, u3-pwn, unicorn-magic. If you use any of these packages, then this method will not suit for you. If you do not need these packages, you can remove them with the command:
As a result, the update process will not hang for a whole day if a new version of exploitdb or metasploit-framework has been released.
What to do when the update is broken?
If your computer rebooted (power outages, computer froze, and other causes) when you run Kali Linux updates, an error may occur with the next update.
Start by running the command:
Then try updating again.
If it fails again, then repeat the command
And again try to start the update.
If this does not help, then pay attention to which particular package causes the error? Remove this package. If the system writes that the package being removed is dependencies for other packages, then remove them all.
In this case, I recommend writing out the names of the packages to be deleted somewhere, in order to reinstall them and return the system to its original state.
After removing the problem package, try again a couple of times:
If the error disappears and the system is successfully updated, then return the remote packages.
Failed to fetch InRelease
I did not encounter such an error (apparently due to the fact that I always set the HTTPS protocol in the sources of applications), but this error is described here and shows how to fix it.
This error occurs when updating the program cache with the command:
By default, the /etc/apt/sources.list repository file already mentioned above contains an entry without the HTTPS protocol, but a mirror to which the apt package manager can only use the HTTPS protocol use only HTTP protocol). Due to this incompatibility, the mirror rejects the connection coming from the update manager.
The easiest way to fix this error is to replace HTTP with secure HTTPS. To do this, open the /etc/apt/sources.list file, and replace the line with:
Than again start the cache updating — the problem should now completely disappear:
The system occupies a lot of disk space
If the amount of used space increases and you cannot understand with which files your hard disk is filled, I recommend thinking about the file cache.
By default, all files downloaded for updating are not deleted. To remove them all, run the command:
Packages that are no longer used in the system after the upgrade can also accumulate; to remove them, issue the following command:
Источник
Failed to update Kali «failed to fetch http.kali.org/kali» #1258
Comments
Maur1ch commented Jul 6, 2020 •
Ok my issue seems to be any kind of trouble with the conection between the distro and the android connection
Describe the bug
- Can’t run sudo apt update
Failed to fetch
Steps to reproduce the behavior
$ sudo apt update
Err:1 https://http.kali.org/kali kali-rolling InRelease
Temporary failure resolving ‘http.kali.org’
Reading package lists. Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information. Done
All packages are up to date.
W: Failed to fetch https://http.kali.org/kali/dists/kali-rolling/InRelease Temporary failure resolving ‘http.kali.org’
W: Some index files failed to download. They have been ignored, or old ones used instead.
When I check my sources.list I got
$ cat /etc/apt/sources.list
deb https://http.kali.org/kali kali-rolling main contrib non-free
deb-src https://http.kali.org/kali kali-rolling main contrib non-free
When I run
cat /etc/resolv.conf
$ cat /etc/resolv.conf
nameserver 8.8.8.8
nameserver 8.8.4.4
Device Information
Device: Samsung J400M
Android Version: 9.0
UserLAnd Version: 2.7.2
Whether the device is rooted. No
Whether the device is running LineageOS NO
Seems like there is no connection between the distro and the internet. But as there is no network package install and can’t conect to the kali server I can’t even ping..I’ve looking for all over the network and seems that a lot of people is having this issue and very often even on a regular linux distro but here due to the UserLand might behave different and there is no hint in how to fix it.
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered:
Источник
Ethical hacking and penetration testing
InfoSec, IT, Kali Linux, BlackArch
Errors in Kali Linux ‘W: Failed to fetch’ and ‘W: Some index files failed to download. They have been ignored, or old ones used instead.’ (SOLVED)
1. Cannot update Kali Linux because errors
A couple of people in recent days wrote about errors when updating programs in Kali Linux. An example of one of the errors:
An example of the second error:
The very first thing you need to check if you encounter similar problems, is everything all right with your Internet connection – for example, open some web site.
If your Internet connection is alright, then continue. Let’s consider several examples of solving the problem.
2. Specifying a certain Kali Linux update mirror
When updating Kali Linux, a request is made to the host http.kali.org for a list of mirrors. The system then uses one of these mirrors to update. You can skip the stage of getting the list of mirrors (referring to http.kali.org), and hardcode the desired mirror in the repository sources file /etc/apt/sources.list.
The OFFICIAL Kali Linux repository mirror list is on this page: http://http.kali.org/README.mirrorlist:

On the territory of my country there is one mirror. In other countries, but on the same continent (EU), another 11 mirrors. And another 14 mirrors on other continents.
The mirror line looks like this:
Cut /README from this line and get the mirror address:
Open the /etc/apt/sources.list file:
And enter the mirror address there instead of the ellipsis deb … kali-rolling main non-free contrib, for example:
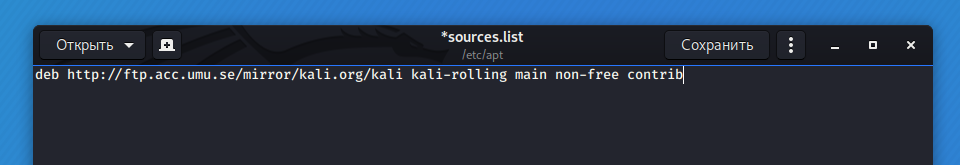
Now a specific mirror will be used for the upgrade.
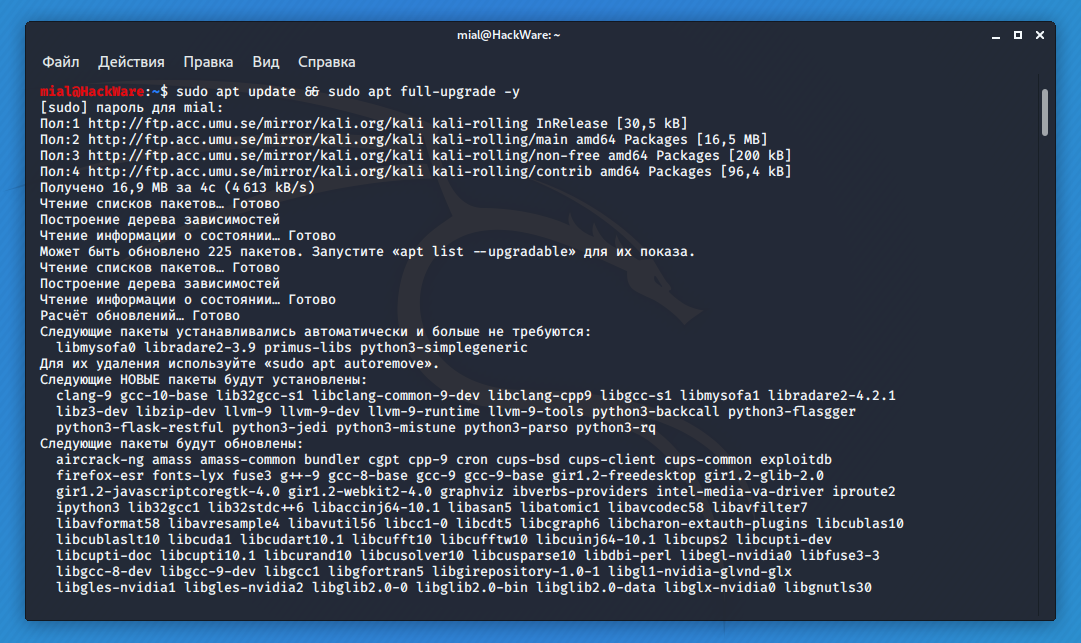
If the mirror is also unavailable, use the following and so on until you find one that works for you.
All other methods are self-sufficient – they do not require to modify the sources.list file.
3. How to bypass ISP censorship to access Kali Linux servers
With TorIptables2 you can enable redirection of all traffic through Tor. Accordingly, all IPs and web-sites blocked by ISP will be available.
Install Tor and TorIptables2
Now, when you want to redirect all traffic through the Tor network (before updating, for example), simply run the command:
To return to the normal settings, do:
Attention : the words “all traffic” means “all HTTP traffic. Some programs send raw packets and/or ignore system-wide proxy settings. TorIptables2 redirects traffic without usage of the proxy settings, but using the Iptables firewall, but with raw packets you still need to be careful and double-check their path.
4. Redirecting traffic through the Tor network using Privoxy
With Privoxy, you can achieve exactly the same effect as with TorIptables2.
5. How to bypass ISP censorship using free VPNs
You can use the autovpn program, which will find a free OpenVPN server for you, download the configuration file and connect to it. You can select the country in which you want a VPN. More details in the article “Free easy way to hide IP in Linux”.
As well the ‘How to redirect all traffic through the Tor network’ will be useful for you if you want to use another tools to redirect traffic though Tor network.
Источник




