- How to Identify which Windows Process is Locking a File or Folder
- Symptoms
- How to Solve the Issue
- Identify what program is using a file
- Identify which handle or DLL is using a file
- Release the lock on the file or folder
- Find what is locking file windows
- How to Identify the Process that has Locked a File in Windows
- Find which process has locked a file using:
- 1. Resource Monitor
- 2. Process Explorer
- 3. Handle from Windows Sysinternals
- Sysinternals Handle: Command-line arguments
- Add Sysinternals Handle to right-click menu
- 4. OpenFiles.exe — a built-in console tool
- Enable “Maintain Objects List” global flag for the First time
- View open files and the corresponding process names
- Disconnect files opened remotely from shared folder.
- 5. OpenedFilesView
- Command-line tool for finding out who is locking a file
- 7 Answers 7
How to Identify which Windows Process is Locking a File or Folder
While attempting to delete, move, or rename a file or folder you get a Windows warning message; the Operating System refuses to complete the operation.
This article helps identifying the process that currently has a handle on the file or folder you are attempting a maintenance operation on.
Symptoms
When trying to delete, move, or rename a file you get a Windows system warning message:
- «Cannot delete file: Access is denied».
- «There has been a sharing violation».
- «The source or destination file may be in use».
- «The file is in use by another program or user».
- «Make sure the disk is not full or write-protected and that the file is not currently in use».
How to Solve the Issue
One of the easiest ways to handle locked files or folders is to use Microsoft Sysinternals Process Explorer.
Identify what program is using a file
Using Process Explorer there is a simple way to find the program:
- Open Process Explorer
- Running as administrator.
- On the toolbar, find the gunsight icon on the right.
- Drag the icon and drop it on the open file or folder that is locked.
- The executable that is using the file will be highlighted in the Process Explorer main display list.
Identify which handle or DLL is using a file
- Open Process Explorer
- Running as administrator.
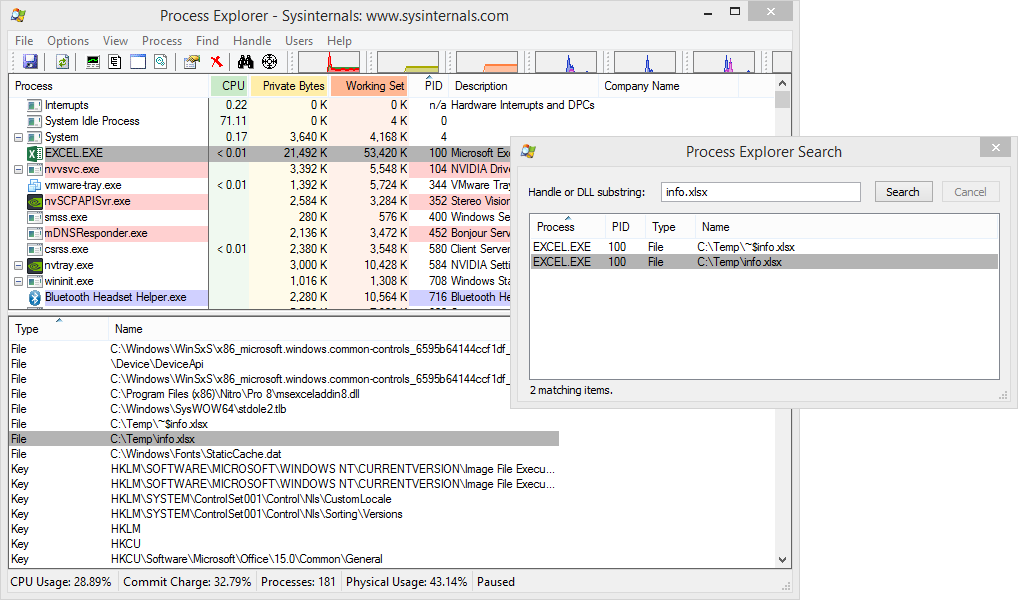
- Enter the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+F.
- Alternatively, click the “Find” menu and select “Find a Handle or DLL”.
- A search dialog box will open.
- Type in the name of the locked file or other file of interest.
- Partial names are usually sufficient.
- Click the button “Search”.
- A list will be generated.
- There may be a number of entries.
Release the lock on the file or folder
To release the lock on the file you are attempting the maintenance operation on, you will need to kill the appropriate process. An individual program or handle in the list provided by Process Explorer can be killed by:
- Selecting the process/handle/program entry.
- Pressing the delete key.
Proceed with care when deleting handles as this may generate erratic behavior and instabilities may occur.
Find what is locking file windows
There are many little utilities (such as Unlocker) that can display which application is locking a particular file and can try to unlock it.
If you like more control or don’t want to install any software on the affected computer, you can use Sysinternals Process Explorer to do the same thing. You can download version 16.04 from here, or check for the latest version on Windows Sysinternals website.
- There is no need to install Process Explorer on your computer. Simply extract the downloaded .zip file and run procexp.exe as administrator. If you don’t run as admin, you will need to click on File >Show Details for All Processes.
If you don’t have administrator right at all, in most cases you can still find what is locking the file, but you won’t be able to force-unlock it. - Now click on Find >Find Handle or DLL, enter file name of the locked file and click Search.
- In a few seconds Process Explorer will display the locking process name and PID. It will also select the locking process in the main application window.
- If you want to force-unlock the file, right click on the file name in the Lower Pane and click on Close Handle.
Windows 7
Windows 8
Sysinternals Process Explorer
How to Identify the Process that has Locked a File in Windows
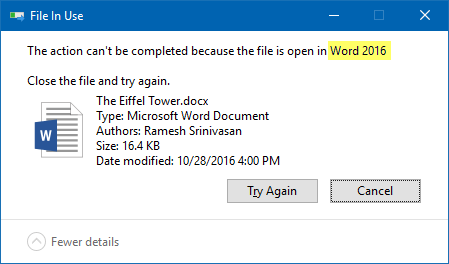
When you attempt to delete a file or folder which is in use by a process, the File In Use dialog appears showing the name of the program that has locked the file.
However, there are cases where the “File In Use” dialog doesn’t show the name of the process that has a lock on the file you’re trying to delete. In some cases, the dialog will show “the action can’t be completed because the file is open in another process“.
For investigating processes and locked files, Windows Sysinternals Process Explorer is probably the first option that comes to mind for most users. However, there are two built-in solutions to display the current open files list along with corresponding process names.
Find which process has locked a file using:
1. Resource Monitor
Resource Monitor (resmon.exe) is a built-in tool that has many useful features. With Resource Monitor, you can track current network and internet usage, view associated handles for locked files, as well as manage processes just as you’d using the Task Manager.
To find the process name that has a file locked, click the CPU tab, type the file name or part of it in the Associated Handles text box.
2. Process Explorer
Process Explorer needs no introduction. In Process Explorer, all you need to do is use the Find feature and type in the file name. This shows the process that’s accessing the file.
From the lower pane view, you can close the file handle if necessary.
You must run Process Explorer as administrator in order to manage processes which are running elevated. To elevate Process Explorer, click the File menu → Show Details for All Processes.
3. Handle from Windows Sysinternals
Handle is a utility from Microsoft Sysinternals that displays information about open handles for any process in the system. You can use it to see the programs that have a file open, or to see the object types and names of all the handles of a program. Handle is like a command-line version of Process Explorer.
Note: Handle v4.21 has a small bug where it always reports “No matching handles found” if the drive-letter is in uppercase. Hope Microsoft fixes it in the next update.
From an admin Command Prompt window, use the command-line syntax to find the process which is having the file open:
If the file name contains spaces, enclose it within double quotes.
Example:
(Mentioning the filename without the path may not necessarily work in every situation. It’s advisable to include the full path always.)
The output shows the process name, the process identifier, user name, the locked (target) file name with path.
Sysinternals Handle: Command-line arguments
| -a | Dump all handle information. |
| -l | Just show pagefile-backed section handles. |
| -c | Closes the specified handle (interpreted as a hexadecimal number). You must specify the process by its PID.WARNING: Closing handles can cause application or system instability. |
| -y | Don’t prompt for close handle confirmation. |
| -s | Print count of each type of handle open. |
| -u | Show the owning user name when searching for handles. |
| -p | Dump handles belonging to process (partial name accepted). |
| name | Search for handles to objects with (fragment accepted). |
| -nobanner | Do not display the startup banner and copyright message. |
No arguments will dump all file references.
Add Sysinternals Handle to right-click menu
You can add Sysinternals Handle to the right-click menu for files to quickly find the program that has locked the file. To add it to the context menu, follow these steps:
- Download Handle from Microsoft Sysinternals site.
- Copy the files handle.exe & handle64.exe to a folder – e.g., d:\tools
- Copy the following lines of code to Notepad, and save the file as find_handle.vbs to a permanent location.
Note: The Sysinternals Handle.exe path is hard-coded as d:\tools\handle.exe in the above script. If the program is located on a different path, modify the path in the script accordingly. For 64-bit Windows, you can use either handle.exe or handle64.exe
To remove the Find Handle context menu entry, start the Registry Editor ( regedit.exe ) and delete the following key:
4. OpenFiles.exe — a built-in console tool
Another built-in tool we’re going to use is Openfiles.exe, a console tool that’s not new to Windows. It was originally introduced in 2000 as part of the Windows Resource Kit 2000/2003 tools. This utility was then included by default in Windows Vista and higher (including Windows 10). Openfiles displays the currently open files list from local or shared folders, along with the Handle ID and Process executable name. This tool also allows you to disconnect one or more files that are opened remotely from a shared folder.
Enable “Maintain Objects List” global flag for the First time
First, to enable tracking of local file handles, you need to turn on ‘maintain objects list’ flag by running the following command from admin Command Prompt.
You’ll see the following message:
INFO: The system global flag ‘maintain objects list’ is currently enabled.
You’ll need to run this command for the first time only. Then restart Windows for the change to take effect.
View open files and the corresponding process names
After restarting Windows, from an admin Command Prompt window, type:
This lists the File/Handle ID, Process Name and the list of files opened locally or opened remotely via local share points, in a table format.
To view the output in List or CSV formats, use the /query parameter.
To copy the output to clipboard, pipe the output to Clip.exe as below. Then paste the output in Notepad or any other editor of your choice.
For more information on copying Command Prompt output to clipboard or save the output to a file, check out the article How to Copy Command Prompt Output Text to Clipboard or Save to File?
To find if a particular file is being in use by a program (and to know which program), you may use the following command-line.
The above command lists all open files that contain the word “eiffel” in the file name. In this example, Word 2016 is currently having the lock over the file “The Eiffel Tower.docx” (ID 4576).
And “File In Use” dialog tells me the same thing.
Disconnect files opened remotely from shared folder.
To disconnect files opened from shared folder so that you can delete, rename the file or modify the contents, use the /disconnect parameter to cut connections to that file. Here are the command-line options.
Openfiles.exe perfectly does the job of listing all open files along with the process names, but it can’t forcibly kill processes. However, this excellent (but overlooked) built-in console tool can come in handy when you want to quickly find a process name that’s using a file, or to disconnect a file that’s being accessed through a shared folder by a network user — without depending on a third-party solution.
5. OpenedFilesView
OpenedFilesView from Nirsoft displays the list of all opened files on your system. For each opened file, additional information is displayed: handle value, read/write/delete access, file position, the process that opened the file, and more… Optionally, you can also close one or more opened files, or close the process that opened these files.
Command-line tool for finding out who is locking a file
I would like to know who is locking a file (win32). I know about WhoLockMe, but I would like a command-line tool which does more or less the same thing.
I also looked at this question, but it seems only applicable for files opened remotely.
7 Answers 7
Handle should do the trick.
Ever wondered which program has a particular file or directory open? Now you can find out. Handle is a utility that displays information about open handles for any process in the system. You can use it to see the programs that have a file open, or to see the object types and names of all the handles of a program.
THis has helped me sooooo many times.
If you want to find what program has a handle on a certain file, run this from the directory that Handle.exe is extracted to. Unless you’ve added Handle.exe to the PATH environment variable. And the file path is C:\path\path\file.txt», run this:
This will tell you what process(es) have the file (or folder) locked.
Handle didn’t find that WhatsApp is holding lock on a file .tmp.node in temp folder. ProcessExplorer — Find works better Look at this answer https://superuser.com/a/399660
Computer Management->Shared Folders->Open Files
In my case Handle.exe did not help. Simple program from official Microsoft called Process Explorer was useful. Just open as administrator and press Ctrl+f , type part of file name it will show process using file.
I have used Unlocker for years and really like it. It not only will identify programs and offer to unlock the folder\file, it will allow you to kill the processing that has the lock as well.
Additionally, it offers actions to do to the locked file in question such as deleting it.
Unlocker helps delete locked files with error messages including «cannot delete file,» and «access is denied.» Video tutorial available.
Some errors you might get that Unlocker can help with include:
- Cannot delete file: Access is denied.
- There has been a sharing violation.
- The source or destination file may be in use.
- The file is in use by another program or user.
- Make sure the disk is not full or write-protected and that the file is not currently in use.