- How to find out if package is installed in Linux
- Debian / Ubuntu Linux
- Red Hat Enterprise / Fedora Linux / Suse Linux / Cent OS
- See also:
- How do I see what packages are installed on Ubuntu Linux?
- How do I see what packages are installed on Ubuntu Linux?
- apt list installed packages
- List all installed packages only
- How to list or find out if a specific package installed or not
- Ubuntu list installed packages
- Listing installed packages sorted by installation date and time
- Conclusion
- How To Find If A Package Is Installed Or Not In Linux And Unix
- Find if a package is installed or not in Linux
- Find if a package is installed or not using «has» utility
- Find if a package is installed or not in Unix
- Conclusion
How to find out if package is installed in Linux
Debian / Ubuntu Linux
Use dpkg command. It is a package manager for Debian/Ubuntu Linux. Suppose you want to find out package apache-perl or sudo is installed or not, type command:
$ dpkg -s apache-perl
Sample outputs:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Another example:
$ dpkg -s sudo
Sample outputs:
Use file /var/lib/dpkg/available to find out all package names available to you. Or you can use following command (list all packages in /var/lib/dpkg/status):
$ dpkg-query -l
You can also try to match package name using wild cards:
$ dpkg-query -l ‘libc6*’
Once you’ve found package name, use the following command to get exact status (whether it is installed or not):
$ dpkg-query -W -f=’$
Sample outputs:
Red Hat Enterprise / Fedora Linux / Suse Linux / Cent OS
Under Red Hat/Fedora/CentOS/Suse Linux use the rpm command:
$ rpm -qa | grep
$ rpm -qa | grep mutt
Output:
If you do not see or get any outputs (package name along with version), it means the package is not installed at all. You can display or list all installed packages with the following command:
$ rpm -qa
$ rpm -qa | less
You can conditionally do something if a rpm command succeeded or failed to find package using bash shell if command:
On a CentOS/RHEL version 6.x/7.x and above use the following yum command to tell whether a package named htop is installed:
$ yum list installed
$ yum list installed htop
Sample outputs:
If you are using Fedora Linux, try the following dnf command:
$ dnf list installed
$ dnf list installed htop
See also:
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
| Category | List of Unix and Linux commands |
|---|---|
| Documentation | help • mandb • man • pinfo |
| Disk space analyzers | df • duf • ncdu • pydf |
| File Management | cat • cp • less • mkdir • more • tree |
| Firewall | Alpine Awall • CentOS 8 • OpenSUSE • RHEL 8 • Ubuntu 16.04 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Linux Desktop Apps | Skype • Spotify • VLC 3 |
| Modern utilities | bat • exa |
| Network Utilities | NetHogs • dig • host • ip • nmap |
| OpenVPN | CentOS 7 • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Debian 8/9 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Package Manager | apk • apt |
| Processes Management | bg • chroot • cron • disown • fg • glances • gtop • jobs • killall • kill • pidof • pstree • pwdx • time • vtop |
| Searching | ag • grep • whereis • which |
| Shell builtins | compgen • echo • printf |
| Text processing | cut • rev |
| User Information | groups • id • lastcomm • last • lid/libuser-lid • logname • members • users • whoami • who • w |
| WireGuard VPN | Alpine • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Firewall • Ubuntu 20.04 |
Comments on this entry are closed.
This is my first massage over here& i hope i will get full support.
How to open usermap.cfg file on NetApp server?- As i have to check whether unix user login is mapped correctly with Windows login.
As the main problem which few of the users are having is as below —
They are NOT able to map from Windows any network
drive (unix accounts) due to they have not access to their share drive.
It ask me for login and password, BUT earliear it never asked me for my windows login and password . It’s been working till the end of the year 2006.
Please suggest solutions—–
Many thanks in Advance
just a small addition –
on Gentoo Linux just do a:
or
cat /var/lib/portage/world
on CentOS or other “yum”-based systems:
yum list installed
how to see the programs and features in redhat linux (e.g– in windows we can check the same through control panel–progrmas)
@john: On RedHat – which is a rpm package management based distribution – you should can use i.e.:
to list all installed packages or
to get out details about the installed package.
how do i verify packages that are installed without using rpm, i mean recently i installed squid using make, make all, configure configure-install
after this, how do I check this package is installed?
…this is not possible as installing “by hand” (make install) has nothing to do with a “package” nor package management.
To find out if i.e. squid was installed just try to locate the squid binary by where, locate or find, even if you build and install software from sources by make.
If you use a port management system from i.e. pkgsrc, getoo portage or even FreeBSD the port management counts each modified and installed file of a port to make it possible to see which file belongs to which port (package) or which are installed etc.
this might be another story.
Thank you very much, I have another issue, I have Installed texlive but I still get an error message in my crm ” pdf latex not installed”, so do you know how check if any software is installed or not ? It’s different from packages, isn’t it ?
If you have a list of packages you want to query, it’s much easier to just list them instead of using grep:
rpm -q automake libtool flex bison pkgconfig gcc-c++ boost-devel libevent-devel
Why such a complicated command for rpm-based systems? On my machine (Fedora 20), I can just run rpm -q $
[blong@blong-desktop tmp]$ rpm -q vala; echo $?
vala-0.22.1-1.fc20.x86_64
0
[blong@blong-desktop tmp]$ rpm -q missing-package; echo $?
package missing-package is not installed
1
Is this a new feature?
In Debian based distros like Ubuntu, you can find out if a package is installed with:
apacheInstalled=$(dpkg -s apache2 | grep ‘Status: install ok installed’| wc -l)
#change apache2 to the package you are checking for. returns 1 if installed, 0 otherwise.
#script does not have to be running as root… but to change installed stuff… it would.
Источник
How do I see what packages are installed on Ubuntu Linux?
I am a new Ubuntu Linux server user. My server hosted at Google cloud VM. How do I see what packages are installed on Ubuntu Linux?
Introduction: Ubuntu Linux is an open source operating system based upon the Linux kernel and GNU command line utilities. Ubuntu Linux is extremely popular among new Linux users as well as developers all around the globe. This page shows how to list all installed packages with apt command or apt-get command on Ubuntu Linux.
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | Debian or Ubuntu Linux |
| Est. reading time | 5 minutes |
You need to use the apt or apt-get or dpkg command to list all installed packages on an Ubuntu Linux server from the bash shell prompt.
How do I see what packages are installed on Ubuntu Linux?
The procedure to list what packages are installed on Ubuntu:
- Open the terminal application or log in to the remote server using ssh (e.g. ssh user @ sever-name )
- Run command apt list —installed to list all installed packages on Ubuntu
- To display a list of packages satisfying certain criteria such as show matching apache2 packages, run apt list apache
Let us see some examples about how to list installed packages on Ubuntu and Debian Linux operating systems.
apt list installed packages
Let us list all software packages on Ubuntu Linux available for us:
$ apt list
You might want to use the grep command/egrep command to filter out:
$ apt list | grep nginx
OR
$ apt list | more
However, you may see message on screen that read as follows:
WARNING: apt does not have a stable CLI interface. Use with caution in scripts.
To avoid this message use the dpkg command as follows:
$ dpkg —list | grep nginx
$ dpkg —list | more
List all installed packages only
The apt command displays both installed and packages available to install. What if you want to list currently installed software only? Fear not, pass the option to the apt command:
$ apt list —installed
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
How to list or find out if a specific package installed or not
Run package policy as follows:
$ apt list -a pkgNameHere
Is sudo package installed?
$ apt list -a sudo
Is sudo package mariadb-server?
$ apt list -a mariadb-server
Ubuntu list installed packages
It is also possible to list installed packages matching given pattern. The syntax is:
dpkg -l pattern
dpkg —list pattern
apt list pattern
apt list —installed pattern
For example:
dpkg —list ‘x*’
Sample outputs:
- ii – Indicates that package named xauth installed.
- un – Indicates that package not installed or in Unknown status.
Listing installed packages sorted by installation date and time
There is no simple command, but we can use the combination of zgrep and other commands as follows. Let us count it:
Total installed packages on nixcraft-wks01 : 6433
List them:
zgrep » installed » /var/log/dpkg.log*
Please note that zgrep will search possibly compressed files for a regular expression as those log files are compressed by system. Hence, we need to use various z commands on Linux. See “How to find out when Debian or Ubuntu package installed or updated” for more info.
Conclusion
You learned how to list both installed and uninstalled packages on an Ubuntu Linux server or desktop using the CLI method. See the following man pages using the man command:
man apt
man apt-get
man dpkg
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
How To Find If A Package Is Installed Or Not In Linux And Unix
A while ago, we learned how to find a package version in Linux. Today, we will see how to find if a package is installed or not in Linux and Unix operating systems. Finding installed packages in GUI mode is easy. All we have to do is to Just open the Menu or Dash, and enter the package name in search box. If the package is installed, you will see the menu entry. It is simple as that. But, it is bit difficult to find it in a system where it doesn’t has GUI mode. So, knowing how to find out a package is installed or not in CLI mode is equally important as we do in GUI mode. Now, let us find out how can we find if a package is installed or not, shall we?
Find if a package is installed or not in Linux
The most common way to find if a package is installed or not is to use «which» command like below:
Example:
If the nano package is installed, it will display the installed path like below.
As you see, nano package is installed in /usr/bin/ path.
Let us check an another package, for example Emacs:
See? Emacs is not installed.
Find if a package is installed or not in Linux Using Which Command
The «which» command is available by default on most Unix-like operating systems.
Also, there are a few other distribution-specific way to find if a package is installed or not. Read on.
On Arch Linux:
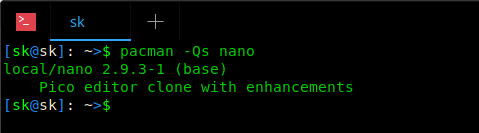
In Arch Linux and its derivatives like Antergos and Manjaro LInux, we can do this using «pacman» command like below:
Sample output:
Find if a package is installed or not in Arch Linux Using Pacman
Did you notice the prefix «local» in-front of the package «nano»? It means that Nano is installed on your system.
If the above command returns nothing, it means that the given package is not installed.
On Fedora / RHEL / CentOS / Scientific Linux:
In RPM based Linux distributions such as Fedora, RHEL and RHEL clones like CentOS, Scientific Linux, we can find out if a package is installed using «rpm» command as shown below.
Sample output:
Also, you can use Yum command like below.
To list all installed packages, run:
As one of our reader «Gregory Pittman» mentioned in the comment section below, we can use dnf command in Fedora to find the installed package.
What you get from these is a list of what is installed and also what is available in repositories. dnf allows a wildcard, and will also be case-insensitive in its search. Sometimes you don’t quite know what you’re looking for or the correct spelling.
On Debian / Ubuntu / Linux Mint:
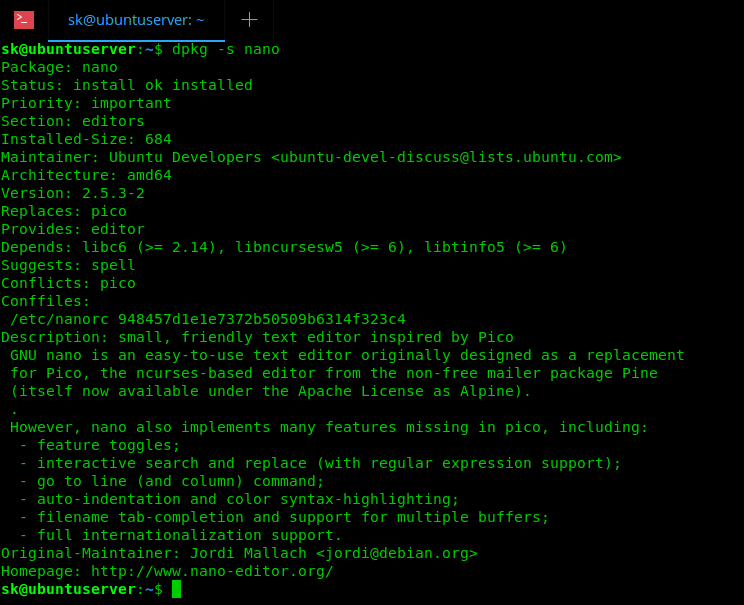
In DEB based system like Debian, Ubuntu and its derivatives like Linux Mint, and Elementary OS, we can do this using «dpkg» command.
Sample output:
Find if a package is installed or not in Debian, Ubuntu Linux Using dpkg command
As you see in the above output, nano package is installed in our Ubuntu system. This command not only shows whether the specified package is installed or not, but also the priority of the package, version number, maintainer name, dependencies, and its description etc.
This is not the only way to find the installed packages. Here are some more commands.
Sample output:
Here is another one.
Sample output:
And one more command.
Sample output:
Or, use this command:
To view list of all installed packages, run:
On SUSE/openSUSE:
To check if a package is installed or not in SUSE and openSUSE, run:
You can also use «rpm» command like below.
Find if a package is installed or not using «has» utility
Trust me, this is super easy! The «has» utility will check the presence of various command line tools on the path and also reports their installed version.
To install it run the following commands:
Now check if a package is available or not like below.
If you see the tick mark (✔), the package is installed. As you see in the above output, nano package is installed and its version is 2.5.3.
You will see the cross mark if the package is not installed. Check the following example.
You can check for multiple packages as well.
If you don’t want to install it, you can directly use it like below. Your system must be connected with Internet though.
To check for multiple packages:
Create an alias if you’re too lazy to type the whole command:
Now, just use this utility like below:
For more details, refer the project’s GitHub page.
Find if a package is installed or not in Unix
The below steps were tested in FreeBSD 10.3. I never tried any other BSD operating systems except FreeBSD. So, there might be different commands to find out if a package installed in other BSD operating systems.
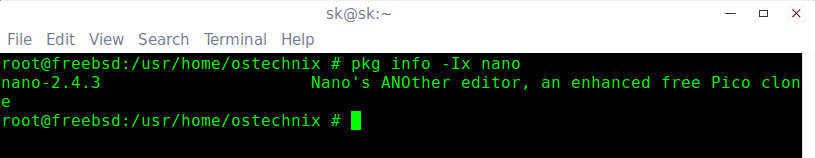
In FreeBSD, we can do this using «pkg» command:
Example:
Sample output:
Find if a package is installed or not in FreeBSD Using pkg command
To view all installed packages, you can use the following command:
This will take a few seconds to minute depending upon the number of packages you have in your FreeBSD system.
Conclusion
You know now how to find if a package is installed or not using the official and non-official way from command line. As you can see, it is not that difficult. It’s just a couple commands which you can easily remember. If you can’t remember these commands, just bookmark them or save them in the Terminal itself to run on demand.
Источник